0eee0783de1315deec57a4be372cdf10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Grid on Blades Basil Smith 7/2/2005 © 2003 IBM Corporation

What is the problem? § Inefficient utilization of resources (MIPS, Memory, Storage, Bandwidth) § Fundamentally resources are being wasted due to wide and unpredictable dynamic range in workload burdens – static or pseudo static resource allocation schemes do not work. § Underutilized resources in: § In server farms § At client endpoints § Constraints § Security: need to run most apps with glass house class security § Licenses: need to get as much bang for buck for each license (this puts very real constraints on utilization of highly fragmented resources) § Software conflicts – hosting of grid application on a shared OS raises serious problems with conflicts and compatibility – frequently does not work at all and testing for obscure interaction is prohibitive § Software compatibility - applications cannot be extensively rewritten, they tend to run in context of a specific OS, middleware, and cluster environment § Dependability: particularly with respect to data integrity Slide 1 © 2003 IBM Corporation

Some observations and context: § Except for some very niche applications, trying to better utilize client endpoint resources is unproductive – why? § Security: no real solution exists, physical remains security essential part of picture. § Licenses: inefficient license utlitization wastes more than the value of the HW resources being retrieved. § Software conflicts: no efficient solution exists to assuring grid application will not conflict with client applications in shared host environments. § Software compatibility: OS/middleware/application stacks are mostly deployed using “clone” model, this would dictate reboot of client to grid clone image (or virtualization equivalent) – mostly this is an issue of switching from Windows client to Linux grid application. § Server hosting of clients (with thin display head) is likely a more effective means of addressing client resource waste. § Dependability: Dependability burden of using client HW on glass house core may be greater than payback – need for secure storage in anycase, and client storage is more inefficient than data center storage. § Practicality dictates grid on/among scale out server farms Slide 2 © 2003 IBM Corporation

At the very bottom, what is the deployment model § An application on a single node is deployed using “clone model” § Clone == boot disk image of OS/middleware/application instance, normally created from golden image, plus some customization § Virgin image – never been run no state beyond T 0 image §Easily recreated from golden image § Dirty image – includes state changes from running image §May include extensive application state Golden Image Repository Slide 3 Provisioned Server Diskless (Stateless) Server © 2003 IBM Corporation

Why Cloning – what’s the application stack look like? System Management Services Grid Services OGSI – Open Grid. OGSA Infrastructure Services OGSA Enabled OGSA Enabled Security Workflow Database File Systems Directory Messaging OGSA Enabled IBM Global Services Autonomic Capabilities It looks like a bill board of stuff you need, and we will sell you ; -) OGSA Enabled Build is tedious and release to “gold” is a lot of testing, somewhere in all of this you also might actually have to write some lines of code. Slide 4 © 2003 IBM Corporation

At the very bottom, retasking a server § To retask: § “Hibernate” an active server (force all state to disk – a dirty clone) § Turn server off § Disconnect dirty clone of that image from server § Connect new clone to server § Boot new image Clone Image Repository Slide 5 Provisioned Server © 2003 IBM Corporation

Grid Logical View Internet Grid Presentation Grid Resources Grid Services HTTP/HTTPS/SOAP TCP/IP/IIOP Grid Security HTTP/HTTPS TCP/IP Compute Cluster Certificate Authority Compute Resource Job Scheduling and Provisioning Storage HTTP/HTTPS/SOAP TCP/IP/IIOP Grid Portal Virtual Storage, Naming, and Replica Management User Administration Each box represents logical functionality that may be implemented by combining onto a single server or separating onto one or more servers. Measuring, Accounting and Reporting Monitoring Archive Instruments, Sensors, and Test Devices Collaborating Grids Firewall Slide 6 © 2003 IBM Corporation

Portal submits Manager The License Manager The Provisioningjobs The grid resources is Provisioning Manager CSCI and to the Grid Manager constantly monitoring provisions the determines. I/O using perform users ENG that which distributes work to thereavailablefor the is the licenses work resources a submit jobs file system. to theresources that are in use meet the do free available todemand Grid Demo AIX Resource Pool A CSCI A A Platinum A A >=1 L CSCI Linux Resource Pool L Web Portal ! L L L Provisioning Manager ENG Grid Manager Gold ENG L >=1 L, >=1 A Information Virtualization Data Virtualization A File Virtualization Storage Virtualization Slide 7 L License Monitor Administration © 2003 IBM Corporation

The Provisioning Manager As Again, servers become CSCI samecancan Administrators. License Administrators The the shared Again, The resources The ENG job removesthe Provisioning Manager idle CSCI job idle, storage License Manager the Manager query Provisioning used querythe resources the Grid is is from CSCI monitoring the load constantly and the user completes looksresource utilization Manager running the jobs for for license constantly monitoring while other applications on the provisions themresults may view environment in used to usage utilization reports results are need of resources license view reports to do ENG work Grid Demo AIX Resource Pool Platinum CSCI A >=1 L A A CSCI L L Provisioning Linux Resource Pool Web Portal Scheduling ! Provisioning Manager ENG Grid Mgr Gold ENG >=1 L, >=1 A Information Virtualization Data Storage Virtualization A A A File Virtualization Slide 8 L L Resource Management License Monitor Administration © 2003 IBM Corporation

Again back to the bottom – what are these resources Slide 9 © 2003 IBM Corporation

Again back to the bottom – what are these resources Slide 10 © 2003 IBM Corporation

Again back to the bottom – what are these resources Processor Blade (Dual Xeon) Slide 11 © 2003 IBM Corporation
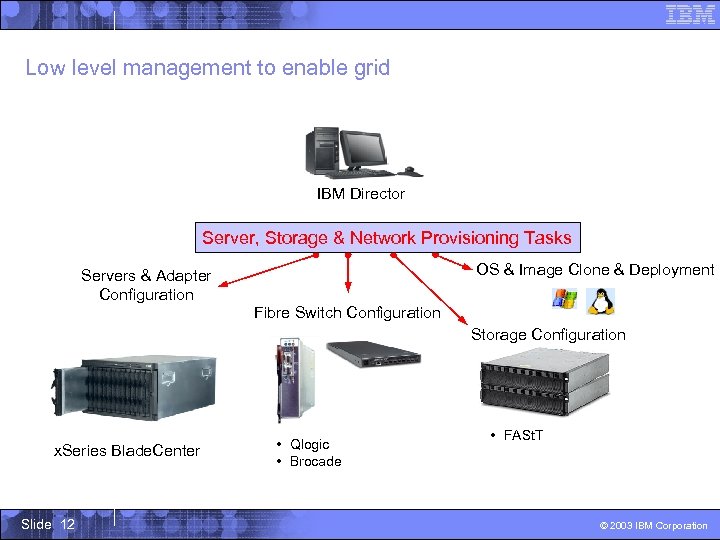
Low level management to enable grid IBM Director Server, Storage & Network Provisioning Tasks OS & Image Clone & Deployment Servers & Adapter Configuration Fibre Switch Configuration Storage Configuration x. Series Blade. Center Slide 12 • Qlogic • Brocade • FASt. T © 2003 IBM Corporation

Finally, the dependability challenge § Break the problem down to known solutions § Classic cluster recovery for failed node in application § Reprovisioning of spare node to replace capacity § Is this with a virgin copy, checkpointed copy, or by just attaching failed image to another server and restarting § File and disk dependability and integrity management is critical, ultimately protecting against loss of state § RAID storage subsystems § Replicas and checkpoints (point in time copies) § Geographic replication (for disaster recovery) Slide 13 © 2003 IBM Corporation
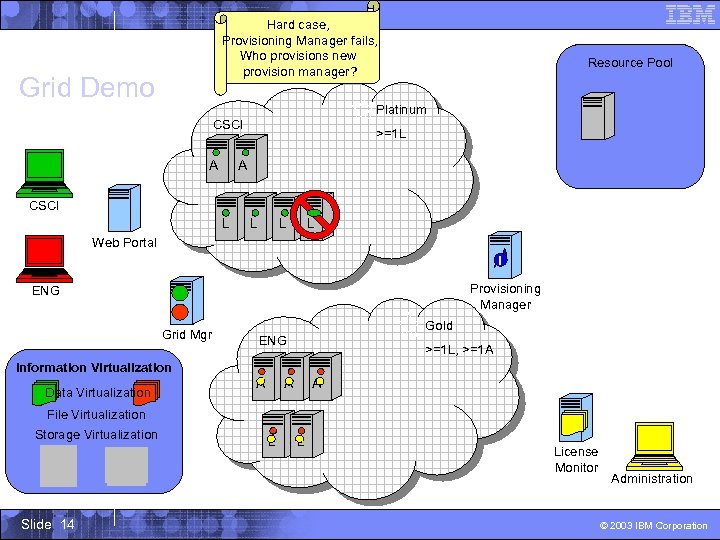
Hard case, Simple case, Provisioning Manager fails, Who fixes problems? CSCI server fails Who provisions new provision manager? Grid Demo Resource Pool Platinum CSCI A >=1 L A CSCI L L Web Portal ! Provisioning Manager ENG Grid Mgr Gold ENG >=1 L, >=1 A Information Virtualization Data Virtualization A A A File Virtualization Storage Virtualization Slide 14 L L License Monitor Administration © 2003 IBM Corporation

The dependability challenge § Options / candidates for availability manager § What grid services need to be availability aware § Lots of problems § Who recovers lost licenses § Strategy for recoverying basic grid services. § Break the problem down to known solutions § Who keeps compatibility matrix § Role of virtualization § Whats disaster recovery procedure for storage subsystem failure Slide 15 © 2003 IBM Corporation

Grid Computing Institute Aligning IBM Research with the Grid Strategy, Product Development, and Customer Needs Resource Scheduling And Deployment Networking Systems Management IBM Research Grid Computing Institute Valuation and Economic Models Product Development (SWG, IS&TG, IGS) Slide 16 Application Development Security Customers Information Grids Design Centers for e-business on demand © 2003 IBM Corporation

Discussion: Slide 17 © 2003 IBM Corporation
0eee0783de1315deec57a4be372cdf10.ppt