c669571157b3001d76cb4ced665b3afe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Grid Computing Middleware Presenter: Xon Xay Nguyen Tuan Viet Tram The Phien 1
Grid Computing Middleware Presenter: Xon Xay Nguyen Tuan Viet Tram The Phien 1
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 2
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 2
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 3
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 3
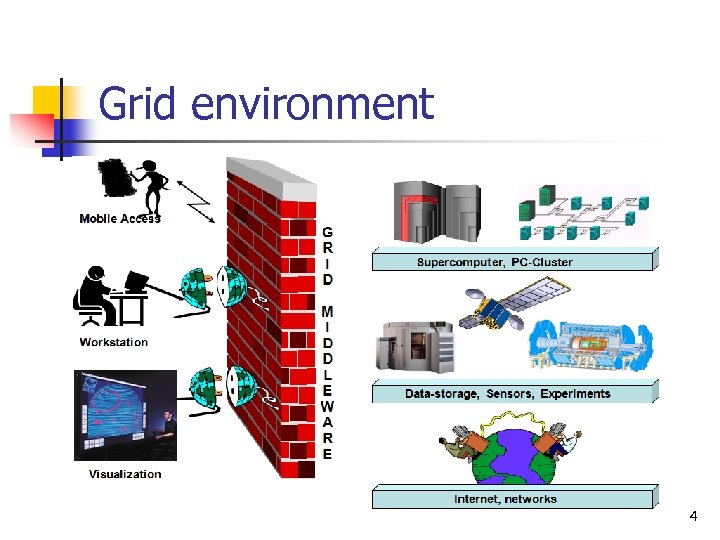 Grid environment 4
Grid environment 4
 Introduction n Three main issues to confont in Grid environment: n n n Heterogeneity – multiplicity of resources Scalability Adaptability - Resource managers or applications dynamic to extract the maximum performance from the available resources and services. 5
Introduction n Three main issues to confont in Grid environment: n n n Heterogeneity – multiplicity of resources Scalability Adaptability - Resource managers or applications dynamic to extract the maximum performance from the available resources and services. 5
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 6
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 6
 Grid Middleware n System software between applications and operating system n Provide services to application n Discovery, storage, execution, information, service integration, resource monitoring, failure detection and recovery, … Hide heterogeneous of the Grid environment Provide standardised interfaces to services. 7
Grid Middleware n System software between applications and operating system n Provide services to application n Discovery, storage, execution, information, service integration, resource monitoring, failure detection and recovery, … Hide heterogeneous of the Grid environment Provide standardised interfaces to services. 7
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 8
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 8
 Purposes of Middleware n n Open, general-purpose and standard Standard protocols n n n Defines the contents and sequence of message exchanges used to request remote operation Important and essential to achieve the interoperability that Grid depends on Standard APIs n n Interfaces to code libraries Facilitate construction of Grid components by allowing code components to be reused 9
Purposes of Middleware n n Open, general-purpose and standard Standard protocols n n n Defines the contents and sequence of message exchanges used to request remote operation Important and essential to achieve the interoperability that Grid depends on Standard APIs n n Interfaces to code libraries Facilitate construction of Grid components by allowing code components to be reused 9
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 10
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 10
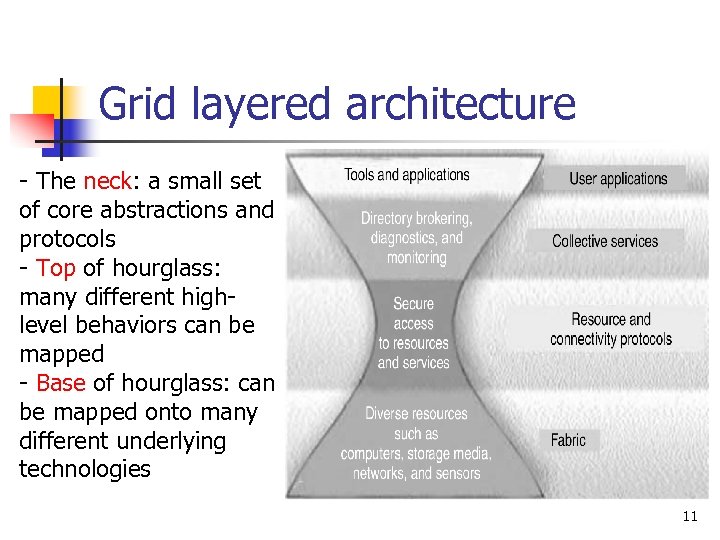 Grid layered architecture - The neck: a small set of core abstractions and protocols - Top of hourglass: many different highlevel behaviors can be mapped - Base of hourglass: can be mapped onto many different underlying technologies 11
Grid layered architecture - The neck: a small set of core abstractions and protocols - Top of hourglass: many different highlevel behaviors can be mapped - Base of hourglass: can be mapped onto many different underlying technologies 11
 Component of Middleware n n n Connectivity layer Resource layer Collective layer 12
Component of Middleware n n n Connectivity layer Resource layer Collective layer 12
 Connectivity layer n n n Communicating easily and securely Communication protocol: exchange data Authentication protocol: cryptographically secure mechanism for verifying the identity of users and resources. n n Single sign-on Delegation Integration with various local security solutions User-based trust relationships 13
Connectivity layer n n n Communicating easily and securely Communication protocol: exchange data Authentication protocol: cryptographically secure mechanism for verifying the identity of users and resources. n n Single sign-on Delegation Integration with various local security solutions User-based trust relationships 13
 Resource layer n n Sharing single resources Define protocols (and APIs and SDKs) for the secure negotiation, initiation, monitoring, control, accounting, and payment of sharing operations on individual resources Information protocols - obtain information about the structure and state of a resource Management protocols - negotiate access to a shared resource 14
Resource layer n n Sharing single resources Define protocols (and APIs and SDKs) for the secure negotiation, initiation, monitoring, control, accounting, and payment of sharing operations on individual resources Information protocols - obtain information about the structure and state of a resource Management protocols - negotiate access to a shared resource 14
 Collective layer n n n Coordinating multiple resources Implement a wide variety of sharing behaviors without placing new requirements on the resources being shared Example – Directory services, co-allocation, scheduling, brokering services, Monitoring and diagnostics services, Data replication services, Gridenabled programming systems, … 15
Collective layer n n n Coordinating multiple resources Implement a wide variety of sharing behaviors without placing new requirements on the resources being shared Example – Directory services, co-allocation, scheduling, brokering services, Monitoring and diagnostics services, Data replication services, Gridenabled programming systems, … 15
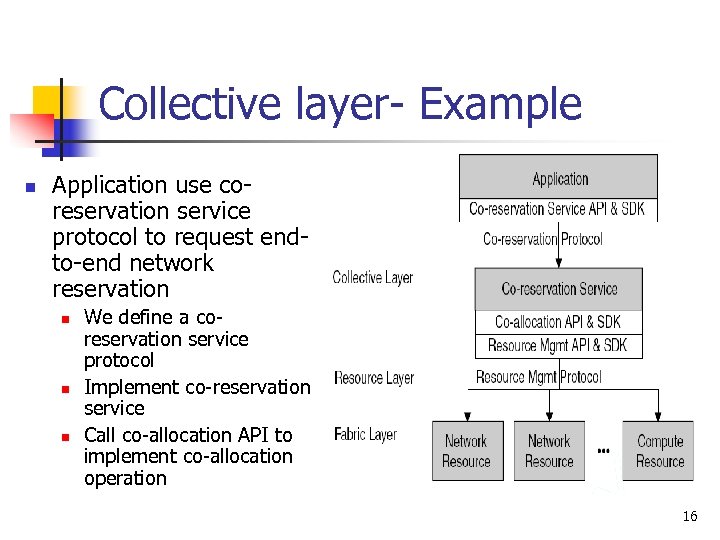 Collective layer- Example n Application use coreservation service protocol to request endto-end network reservation n We define a coreservation service protocol Implement co-reservation service Call co-allocation API to implement co-allocation operation 16
Collective layer- Example n Application use coreservation service protocol to request endto-end network reservation n We define a coreservation service protocol Implement co-reservation service Call co-allocation API to implement co-allocation operation 16
 Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 17
Outline n n n Introduction Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 17
 Globus Toolkit n n Evolution Globus Toolkit version 2 Globus Toolkit version 3 Globus Toolkit version 4 18
Globus Toolkit n n Evolution Globus Toolkit version 2 Globus Toolkit version 3 Globus Toolkit version 4 18
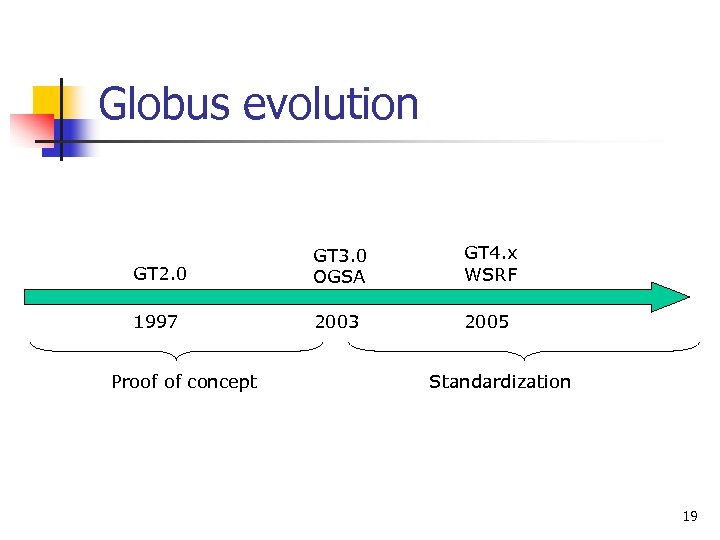 Globus evolution GT 2. 0 GT 3. 0 OGSA GT 4. x WSRF 1997 2003 2005 Proof of concept Standardization 19
Globus evolution GT 2. 0 GT 3. 0 OGSA GT 4. x WSRF 1997 2003 2005 Proof of concept Standardization 19
 Globus Toolkit version 2 n n Community-based, open-architecture, open source set of services and software libraries that support Grids and Grid applications. De facto standard for Grid computing Focus on usability and interoperability Middleware n n n GT 2 – Connectivity layer GT 2 - Resource layer GT 2 - Collective layer 20
Globus Toolkit version 2 n n Community-based, open-architecture, open source set of services and software libraries that support Grids and Grid applications. De facto standard for Grid computing Focus on usability and interoperability Middleware n n n GT 2 – Connectivity layer GT 2 - Resource layer GT 2 - Collective layer 20
 GT 2 – Connectivity Authentication protocol n Public-key based GSI protocols n n n GSI - Grid Security Infrastructure authentication, communication protection, authorization GSI builds on and extends the TLS protocols n n TLS - Transport Layer Security TLS - defines a protocol to provide privacy and data integrity between two communicating applications. 21
GT 2 – Connectivity Authentication protocol n Public-key based GSI protocols n n n GSI - Grid Security Infrastructure authentication, communication protection, authorization GSI builds on and extends the TLS protocols n n TLS - Transport Layer Security TLS - defines a protocol to provide privacy and data integrity between two communicating applications. 21
 GT 2 – Connectivity layer Communication protocol n Internet layered protocol architecture n n n Internet layer - IP and ICMP Transport - TCP, UDP Application layer - DNS, OSPF, RSVP, … 22
GT 2 – Connectivity layer Communication protocol n Internet layered protocol architecture n n n Internet layer - IP and ICMP Transport - TCP, UDP Application layer - DNS, OSPF, RSVP, … 22
 GT 2 - Resource layer n n A Grid Resource Information Protocol – base on Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) HTTP-based GRAM protocol n n GRAM - Grid Resource Access and Management allocation of computational resources monitoring and control of computation on resources Grid. FTP - a management protocol for data access n An extended version of the File Transfer Protocol 23
GT 2 - Resource layer n n A Grid Resource Information Protocol – base on Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) HTTP-based GRAM protocol n n GRAM - Grid Resource Access and Management allocation of computational resources monitoring and control of computation on resources Grid. FTP - a management protocol for data access n An extended version of the File Transfer Protocol 23
 GT 2 - Collective layer n n build on Globus Connectivity and Resource protocols Meta Directory Service n n introduces Grid Information Index Servers (GIISs) LDAP information protocol n n n Access resource-specific GRISs to obtain resource state GRRP used for resource registration. DUROC resource co-allocation library provides an SDK and API for resource co-allocation 24
GT 2 - Collective layer n n build on Globus Connectivity and Resource protocols Meta Directory Service n n introduces Grid Information Index Servers (GIISs) LDAP information protocol n n n Access resource-specific GRISs to obtain resource state GRRP used for resource registration. DUROC resource co-allocation library provides an SDK and API for resource co-allocation 24
 Globus Toolkit version 3 n n Build on and significantly extend GT 2 concepts and technologies Base on Open Grid Services Architecture n n n Factoring of component behaviors – identify essential Grid functions and express Service orientation – enable a uniform treatment of all network entities Align with Web services – WSDL (Web Services Definition Language) 25
Globus Toolkit version 3 n n Build on and significantly extend GT 2 concepts and technologies Base on Open Grid Services Architecture n n n Factoring of component behaviors – identify essential Grid functions and express Service orientation – enable a uniform treatment of all network entities Align with Web services – WSDL (Web Services Definition Language) 25
 Globus Toolkit version 4 n n n developed by The Globus Alliance OGSA requires “stateful services” WSRF – Web Service Resources Framework n n developed by OASIS (http: //www. oasis-open. org) WSRF provides the stateful services that OGSA needs 26
Globus Toolkit version 4 n n n developed by The Globus Alliance OGSA requires “stateful services” WSRF – Web Service Resources Framework n n developed by OASIS (http: //www. oasis-open. org) WSRF provides the stateful services that OGSA needs 26
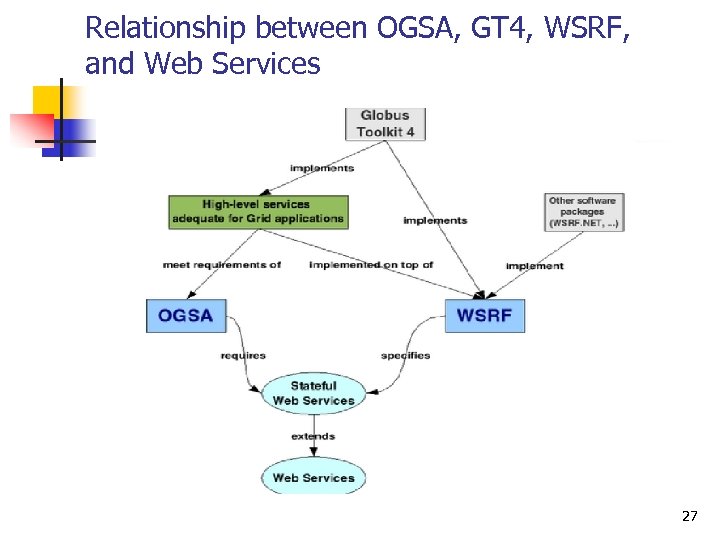 Relationship between OGSA, GT 4, WSRF, and Web Services 27
Relationship between OGSA, GT 4, WSRF, and Web Services 27
 g. Lite Toolkit n n The Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E project (EGEE) Middleware stack that combines components developed in various related projects. 28
g. Lite Toolkit n n The Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E project (EGEE) Middleware stack that combines components developed in various related projects. 28
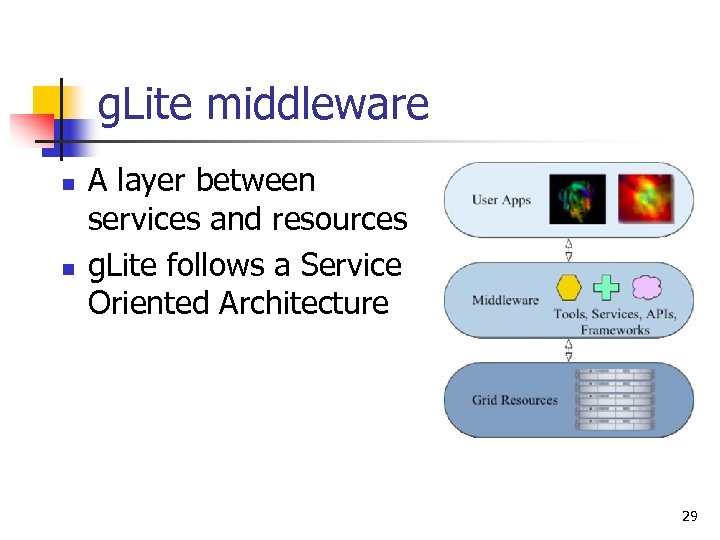 g. Lite middleware n n A layer between services and resources g. Lite follows a Service Oriented Architecture 29
g. Lite middleware n n A layer between services and resources g. Lite follows a Service Oriented Architecture 29
 g. Lite - guiding principles n Service oriented approach n n Allow for multiple interoperable implementations Lightweight (existing) services n n Easily and quickly deployable Use existing services where possible n n Portable n n Condor, EDG, Globus, LCG, … Being built on Scientific Linux and Windows Security n Sites and Applications 30
g. Lite - guiding principles n Service oriented approach n n Allow for multiple interoperable implementations Lightweight (existing) services n n Easily and quickly deployable Use existing services where possible n n Portable n n Condor, EDG, Globus, LCG, … Being built on Scientific Linux and Windows Security n Sites and Applications 30
 g. Lite - guiding principles n Performance/Scalability & Resilience/Fault Tolerance n n Co-existence with deployed infrastructure n n Co-existence with LCG-2 and OSG (US) are essential for the EGEE Grid services Site autonomy n n Comparable to deployed infrastructure Reduce dependence on ‘global, central’ services Open source license 31
g. Lite - guiding principles n Performance/Scalability & Resilience/Fault Tolerance n n Co-existence with deployed infrastructure n n Co-existence with LCG-2 and OSG (US) are essential for the EGEE Grid services Site autonomy n n Comparable to deployed infrastructure Reduce dependence on ‘global, central’ services Open source license 31
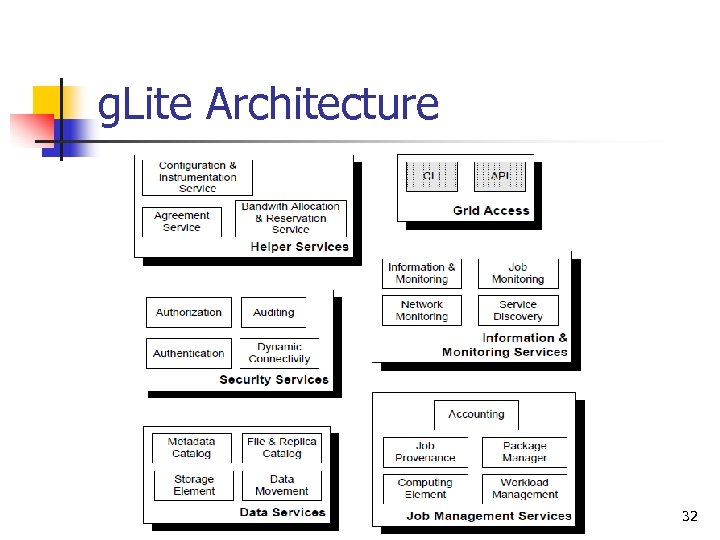 g. Lite Architecture 32
g. Lite Architecture 32
 g. Lite - Access All of the g. Lite services are accessible via APIs and CLIs. n n n API - Application Programming Interface CLI - Command Line Interface 33
g. Lite - Access All of the g. Lite services are accessible via APIs and CLIs. n n n API - Application Programming Interface CLI - Command Line Interface 33
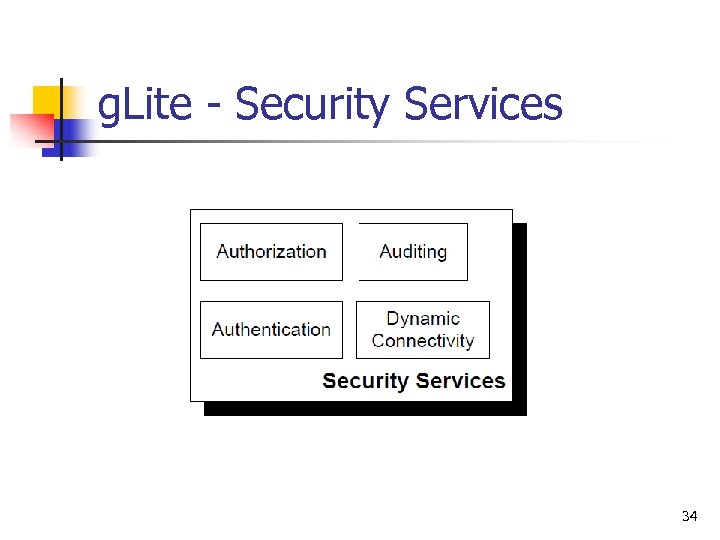 g. Lite - Security Services 34
g. Lite - Security Services 34
 g. Lite - Security Services n Authentication n Authorization n allows or denies access to specific services three basic authorization models, classified as agent, push and pull. Dynamic Connectivity Service n n identify entities PKI (X. 509) infrastructure with CA third party for signature tackle the problems that arise when connectivity is restricted by the resource owner. Auditing n monitoring and providing for post-mortem analysis of security related events. 35
g. Lite - Security Services n Authentication n Authorization n allows or denies access to specific services three basic authorization models, classified as agent, push and pull. Dynamic Connectivity Service n n identify entities PKI (X. 509) infrastructure with CA third party for signature tackle the problems that arise when connectivity is restricted by the resource owner. Auditing n monitoring and providing for post-mortem analysis of security related events. 35
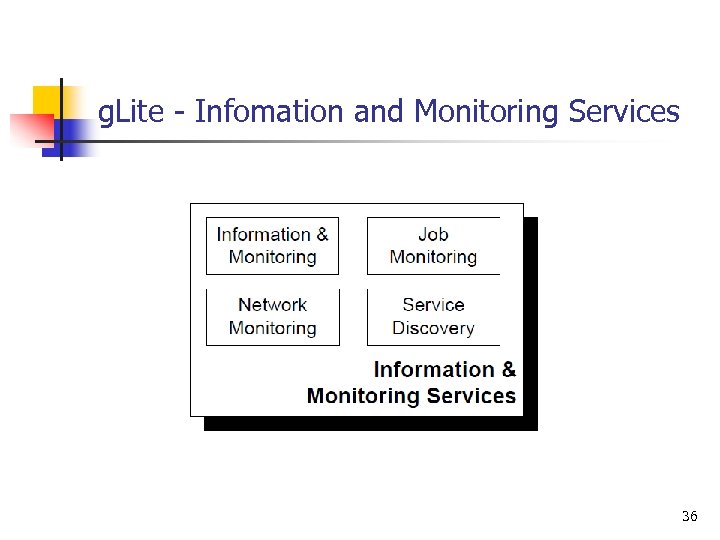 g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services 36
g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services 36
 g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services n Infomation and Monitoring Services a vital low -level component of any grid 37
g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services n Infomation and Monitoring Services a vital low -level component of any grid 37
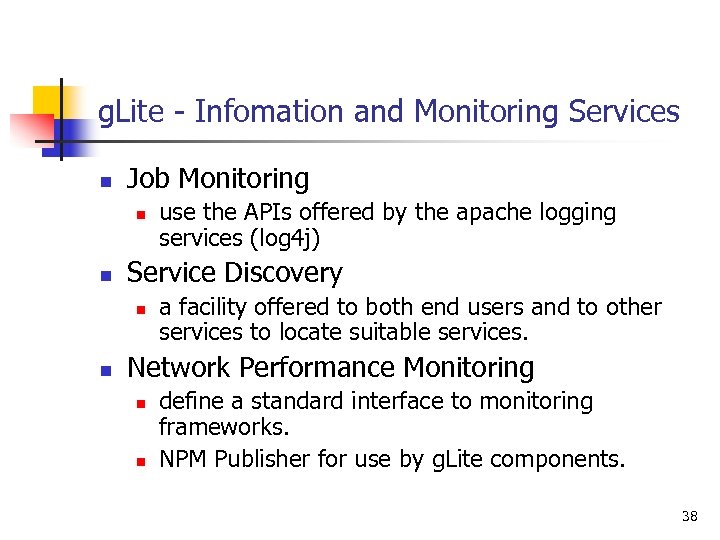 g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services n Job Monitoring n n Service Discovery n n use the APIs offered by the apache logging services (log 4 j) a facility offered to both end users and to other services to locate suitable services. Network Performance Monitoring n n define a standard interface to monitoring frameworks. NPM Publisher for use by g. Lite components. 38
g. Lite - Infomation and Monitoring Services n Job Monitoring n n Service Discovery n n use the APIs offered by the apache logging services (log 4 j) a facility offered to both end users and to other services to locate suitable services. Network Performance Monitoring n n define a standard interface to monitoring frameworks. NPM Publisher for use by g. Lite components. 38
 g. Lite - Helper Services 39
g. Lite - Helper Services 39
 g. Lite - Helper Services n Configuration and Instrumentation Service n n Bandwidth Allocation and Reservation Service n n common, standard-based configuration and instrumentation functionality to the g. Lite services. control and balance the usage of the network and categorise and prioritise traffic flows. Agreement Service n implements the communication protocol used to exchange information about Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and defines the SLA structure. 40
g. Lite - Helper Services n Configuration and Instrumentation Service n n Bandwidth Allocation and Reservation Service n n common, standard-based configuration and instrumentation functionality to the g. Lite services. control and balance the usage of the network and categorise and prioritise traffic flows. Agreement Service n implements the communication protocol used to exchange information about Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and defines the SLA structure. 40
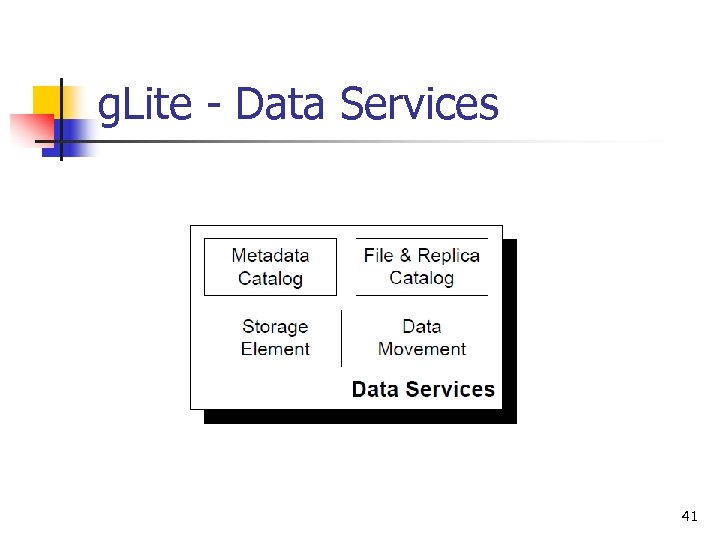 g. Lite - Data Services 41
g. Lite - Data Services 41
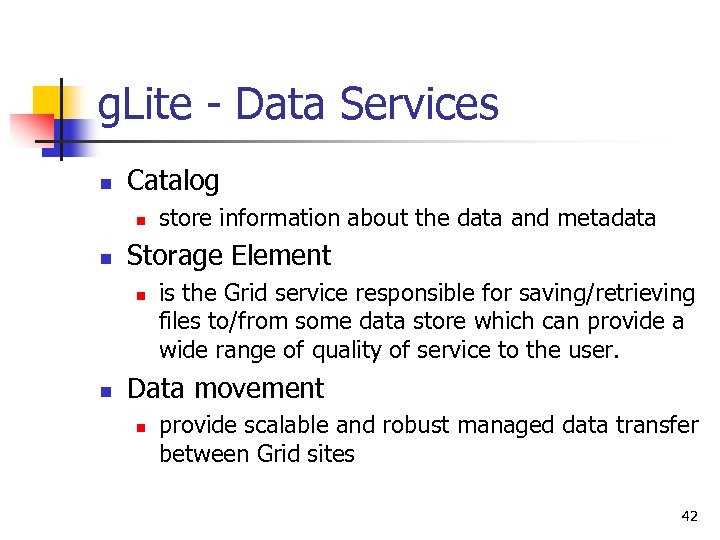 g. Lite - Data Services n Catalog n n Storage Element n n store information about the data and metadata is the Grid service responsible for saving/retrieving files to/from some data store which can provide a wide range of quality of service to the user. Data movement n provide scalable and robust managed data transfer between Grid sites 42
g. Lite - Data Services n Catalog n n Storage Element n n store information about the data and metadata is the Grid service responsible for saving/retrieving files to/from some data store which can provide a wide range of quality of service to the user. Data movement n provide scalable and robust managed data transfer between Grid sites 42
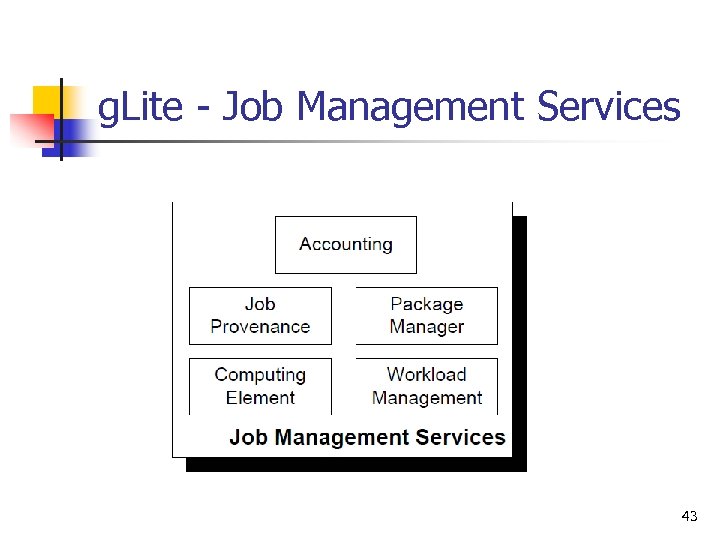 g. Lite - Job Management Services 43
g. Lite - Job Management Services 43
 g. Lite - Job Management Services n Accounting n n Computing element n n n accumulates information about the usage of Grid resources representing a computing resource job management and other capabilities Workload Management n comprises a set of Grid middleware components responsible for the distribution and management of tasks across Grid resources 44
g. Lite - Job Management Services n Accounting n n Computing element n n n accumulates information about the usage of Grid resources representing a computing resource job management and other capabilities Workload Management n comprises a set of Grid middleware components responsible for the distribution and management of tasks across Grid resources 44
 g. Lite - Job Management Services n Job Provenance n n keep track of the definition of submitted jobs, execution conditions and environment. Package Manager n is a helper service that automates the process of installing, upgrading configuring, and removing software packages from a shared area 45
g. Lite - Job Management Services n Job Provenance n n keep track of the definition of submitted jobs, execution conditions and environment. Package Manager n is a helper service that automates the process of installing, upgrading configuring, and removing software packages from a shared area 45
 Comparison n Globus Toolkit - faster and more efficient g. Lite - sophisticated and developer friendly Document n n Globus documents - sketchy and missing g. Lite documents - sufficient, available 46
Comparison n Globus Toolkit - faster and more efficient g. Lite - sophisticated and developer friendly Document n n Globus documents - sketchy and missing g. Lite documents - sufficient, available 46
 Summary n n Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 47
Summary n n Definition of Grid Middleware Purpose of Middleware Grid layered architecture Technology n n Globus GLite 47
 Reference n n n n I. Foster and C. Kesselman, The Grid: Blueprint for a New Computing Infrastructure. Morgab Kaufmann Publishers, 1999. Fran Berman, Anthony J. G. Hey and Geoffrey C. Fox, Grid computing: Making the Global Infrastructure a Reality. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2003. Globus project: http: //www. globus. org/alliance/ Grid Computing Slides – Nguyen Tuan Anh Grid Computing Slides – Pham Tran Vu von. Laszewski--grid-middleware 03 -grid-concepts-architecture-middleware-adler-vortrag Websites of g. Lite (http: //www. eu-egee. org) 48
Reference n n n n I. Foster and C. Kesselman, The Grid: Blueprint for a New Computing Infrastructure. Morgab Kaufmann Publishers, 1999. Fran Berman, Anthony J. G. Hey and Geoffrey C. Fox, Grid computing: Making the Global Infrastructure a Reality. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2003. Globus project: http: //www. globus. org/alliance/ Grid Computing Slides – Nguyen Tuan Anh Grid Computing Slides – Pham Tran Vu von. Laszewski--grid-middleware 03 -grid-concepts-architecture-middleware-adler-vortrag Websites of g. Lite (http: //www. eu-egee. org) 48
 Q&A 49
Q&A 49


