61ac909267223e7c582fbefd85c7feef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Greenman-Pedersen, Inc. Coatings Group Review of Maintenance Prioritization Schemes from Three Transportation Authorities Christopher L. Farschon, P. E. , PCS Greenman – Pedersen, Inc. Coatings Group October 7, 2009 NACE Eastern Area Conference
Greenman-Pedersen, Inc. Coatings Group Review of Maintenance Prioritization Schemes from Three Transportation Authorities Christopher L. Farschon, P. E. , PCS Greenman – Pedersen, Inc. Coatings Group October 7, 2009 NACE Eastern Area Conference
 Why Prioritize Bridge Painting?
Why Prioritize Bridge Painting?
 Why Prioritize? PLANNING t Money t Define an acceptable state of existence u How coating conditions affect a bridge throughout its lifetime t Identify what funding is needed to meet that need u Justify painting budgets
Why Prioritize? PLANNING t Money t Define an acceptable state of existence u How coating conditions affect a bridge throughout its lifetime t Identify what funding is needed to meet that need u Justify painting budgets
 Where to Start Planning? t Bridge type t Size t Proximity t Location t Traffic Conditions t Deck t Substructure t Future Rehabilitation – Coating and Corrosion Condition
Where to Start Planning? t Bridge type t Size t Proximity t Location t Traffic Conditions t Deck t Substructure t Future Rehabilitation – Coating and Corrosion Condition
 Goals of a Prioritization Program t Vary by Agency u Lowest overall cost (today, life cycle, year 20? ) u Define needed funding u Meet constraints • Integrate with other work • Improvements Design • Traffic • Aesthetics u Monitor Be adaptable Learn
Goals of a Prioritization Program t Vary by Agency u Lowest overall cost (today, life cycle, year 20? ) u Define needed funding u Meet constraints • Integrate with other work • Improvements Design • Traffic • Aesthetics u Monitor Be adaptable Learn
 Three Authorities t A - Toll Authority 1 u Major structures only (9 facilities – 26 M square feet) u Metropolitan area u 100% self funded t B - Toll Authority 2 u Major highway (hundreds of bridges – focus on 16) u Urban / Metropolitan / Rural u Combination funding t C - State DOT District u Over 1, 000 bridges (focus on overpasses) u Metropolitan and Suburban area u Federal / state funding
Three Authorities t A - Toll Authority 1 u Major structures only (9 facilities – 26 M square feet) u Metropolitan area u 100% self funded t B - Toll Authority 2 u Major highway (hundreds of bridges – focus on 16) u Urban / Metropolitan / Rural u Combination funding t C - State DOT District u Over 1, 000 bridges (focus on overpasses) u Metropolitan and Suburban area u Federal / state funding
 Historical - Toll Authority A t Years of “as-required” maintenance painting t Increasing environmental concerns t Increasing steel repair frequency t Painting Program was planned around 1990, implemented 1993 -1995 t Unofficial Program Goals Reduce lead paint liabilities u Reduce as-needed steel repairs u Improve bridge appearance u Define needed funding u
Historical - Toll Authority A t Years of “as-required” maintenance painting t Increasing environmental concerns t Increasing steel repair frequency t Painting Program was planned around 1990, implemented 1993 -1995 t Unofficial Program Goals Reduce lead paint liabilities u Reduce as-needed steel repairs u Improve bridge appearance u Define needed funding u
 Program Description – Toll Authority A t Based on a facility wide survey conducted in 1993 t Categorizes bridge areas based on paint conditions and “local” environments t Appropriate painting is performed in each area to minimize costs Access costs very high = minimal contracts u One contract – multiple Items – multiple methods u
Program Description – Toll Authority A t Based on a facility wide survey conducted in 1993 t Categorizes bridge areas based on paint conditions and “local” environments t Appropriate painting is performed in each area to minimize costs Access costs very high = minimal contracts u One contract – multiple Items – multiple methods u
 Program Goals – Toll Authority A t Maintain an acceptable paint condition while maintaining budget goals t Coordinate with Capital improvement projects and biennial inspections t Address highest priorities within 12 years
Program Goals – Toll Authority A t Maintain an acceptable paint condition while maintaining budget goals t Coordinate with Capital improvement projects and biennial inspections t Address highest priorities within 12 years
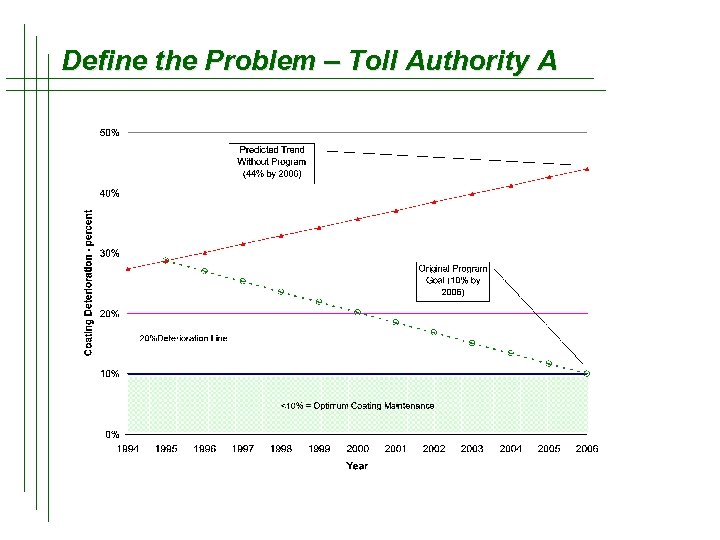 Define the Problem – Toll Authority A
Define the Problem – Toll Authority A
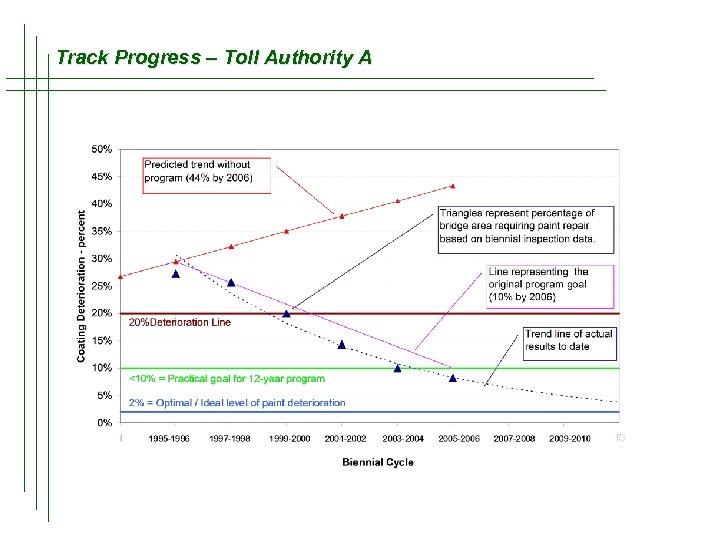 Track Progress – Toll Authority A
Track Progress – Toll Authority A
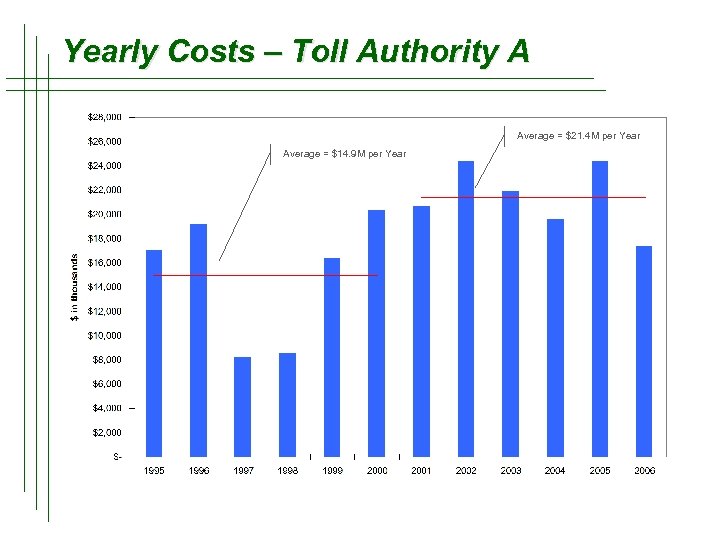 Yearly Costs – Toll Authority A Average = $21. 4 M per Year Average = $14. 9 M per Year
Yearly Costs – Toll Authority A Average = $21. 4 M per Year Average = $14. 9 M per Year
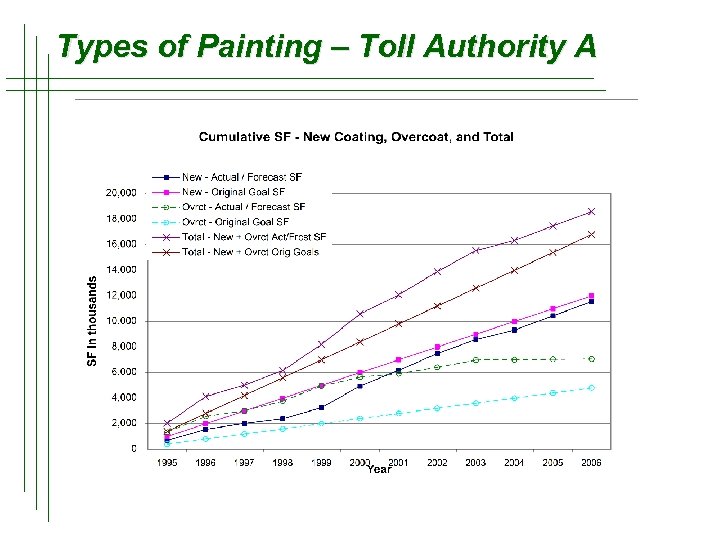 Types of Painting – Toll Authority A
Types of Painting – Toll Authority A
 Unit Cost Trends – Toll Authority A t Low early – High middle – Lower recently t Worst corrosion addressed first u Large projects (economies of scale were good) t Concurrent with some maintenance u Aesthetic areas u Hold until re-paint t Combination / Rehabilitation Projects u Difficult projects? u Some shared costs u Some additional costs u Maximize shop painting
Unit Cost Trends – Toll Authority A t Low early – High middle – Lower recently t Worst corrosion addressed first u Large projects (economies of scale were good) t Concurrent with some maintenance u Aesthetic areas u Hold until re-paint t Combination / Rehabilitation Projects u Difficult projects? u Some shared costs u Some additional costs u Maximize shop painting
 Cost/Specification Factors- Authority A t Size of the project t Mobilization and staging areas t Access to work- placement of equipment u Lane closures, water - barge etc. t Environmental controls t Inspection requirements - warranty t Configuration or type of structure t Labor, equipment, and material costs t Bidding climate (other work, available bidders)
Cost/Specification Factors- Authority A t Size of the project t Mobilization and staging areas t Access to work- placement of equipment u Lane closures, water - barge etc. t Environmental controls t Inspection requirements - warranty t Configuration or type of structure t Labor, equipment, and material costs t Bidding climate (other work, available bidders)
 Program Summary – Toll Authority A t Budgets were justified t Funding allocated t Projects designed t Conditions were monitored with database population u Influenced priorities on a biennial basis t Program is in place that relates painting needs to available time to needed funding u Needs not always driven by conditions
Program Summary – Toll Authority A t Budgets were justified t Funding allocated t Projects designed t Conditions were monitored with database population u Influenced priorities on a biennial basis t Program is in place that relates painting needs to available time to needed funding u Needs not always driven by conditions
 Toll Authority - B t Program recently enacted to prioritize painting t t of major structures Not an authority-wide plan (16 of several hundred structures, but the most significant 16) Works around/with major capital programs Coordination with other maintenance work Constructability a key factor
Toll Authority - B t Program recently enacted to prioritize painting t t of major structures Not an authority-wide plan (16 of several hundred structures, but the most significant 16) Works around/with major capital programs Coordination with other maintenance work Constructability a key factor
 Project Background – Toll Authority B t Program has 2 objectives: u Part 1 - The investigation and assessment of the existing coating system on 16 major bridges, development of a prioritized list of bridges requiring repainting, and recommendations related to bridge painting as part of a Ten Year Capital Program u Part 2 - The design and development of documents for two (2) Major Bridge Repainting contracts
Project Background – Toll Authority B t Program has 2 objectives: u Part 1 - The investigation and assessment of the existing coating system on 16 major bridges, development of a prioritized list of bridges requiring repainting, and recommendations related to bridge painting as part of a Ten Year Capital Program u Part 2 - The design and development of documents for two (2) Major Bridge Repainting contracts
 Budget / Financial – Toll Authority B t Predetermined budget and timeframe u anticipated value of $250 M u 10 year effort t Prioritize the needs based on constraints, coordination, conditions t Generate project specific engineer’s estimates for near-term painting costs
Budget / Financial – Toll Authority B t Predetermined budget and timeframe u anticipated value of $250 M u 10 year effort t Prioritize the needs based on constraints, coordination, conditions t Generate project specific engineer’s estimates for near-term painting costs
 Bridge Surveys – Toll Authority B t Technical Paint Condition Data – Adhesion, thickness, lab tests, visual survey data for paint (peeling and corrosion) t Development of square footage quantities t Other considerations - Deck and Joint condition, planned rehabilitations and prior painting work
Bridge Surveys – Toll Authority B t Technical Paint Condition Data – Adhesion, thickness, lab tests, visual survey data for paint (peeling and corrosion) t Development of square footage quantities t Other considerations - Deck and Joint condition, planned rehabilitations and prior painting work
 Painting Options – Toll Authority B t Total Coating Removal and Replacement t Zone Coating Repair (Beam Ends, Bearings, Weathering Steel) t Maintenance Spot Painting and Full Overcoating
Painting Options – Toll Authority B t Total Coating Removal and Replacement t Zone Coating Repair (Beam Ends, Bearings, Weathering Steel) t Maintenance Spot Painting and Full Overcoating
 Prioritization – Toll Authority B t Rough Budget Estimates – Key to project designs and evening out the workload across the program duration t Coordination with other work – Use of the deck condition study data, coordination with completed deck/rehabilitation projects and the capital improvement projects t Prioritization factors u u u u Condition of the existing coatings and extent of corrosion Condition of the existing deck Availability of construction staging areas Complexity of maintenance and protection of traffic Complexity of containment Environmental impacts Outside agency coordination
Prioritization – Toll Authority B t Rough Budget Estimates – Key to project designs and evening out the workload across the program duration t Coordination with other work – Use of the deck condition study data, coordination with completed deck/rehabilitation projects and the capital improvement projects t Prioritization factors u u u u Condition of the existing coatings and extent of corrosion Condition of the existing deck Availability of construction staging areas Complexity of maintenance and protection of traffic Complexity of containment Environmental impacts Outside agency coordination
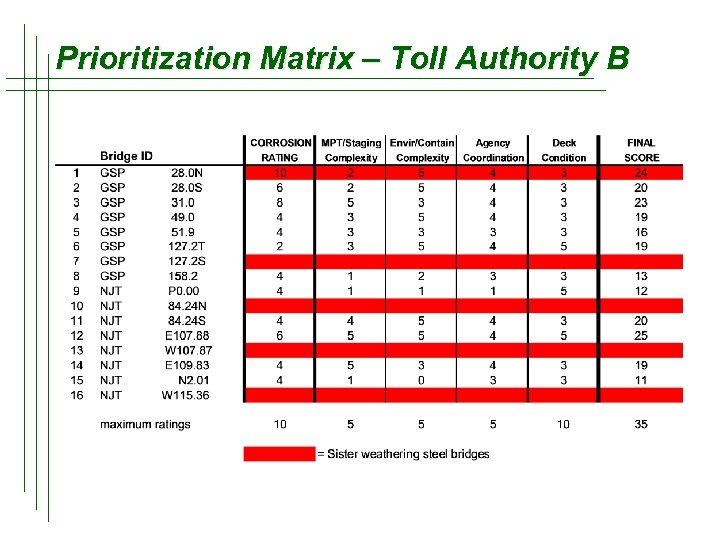 Prioritization Matrix – Toll Authority B
Prioritization Matrix – Toll Authority B
 Project Sequencing – Toll Authority B t Projects of constructible size and duration were appropriately prioritized / sequenced t Highest 2 priorities under design /construction t Update survey needed Project was a snapshot of conditions combined with other available data to make the most appropriate prioritization today u Future survey will justify extending durations before painting or accelerating certain projects u
Project Sequencing – Toll Authority B t Projects of constructible size and duration were appropriately prioritized / sequenced t Highest 2 priorities under design /construction t Update survey needed Project was a snapshot of conditions combined with other available data to make the most appropriate prioritization today u Future survey will justify extending durations before painting or accelerating certain projects u
 Program Summary – Toll Authority B t Select group of bridges t Projects designed and estimated to fit available budget t Technical data / conditions were not always the priority driver t Program is based on a snapshot survey of facilities t Follow-up survey will be needed
Program Summary – Toll Authority B t Select group of bridges t Projects designed and estimated to fit available budget t Technical data / conditions were not always the priority driver t Program is based on a snapshot survey of facilities t Follow-up survey will be needed
 Authority C t State Department of Transportation District t 1998 project t Over 1, 000 bridges u Majority are highway overpasses and smaller structures t Semi “Automated” database system t Used condition data, constraints, project- specific factors t Prioritization was based on Return on Investment
Authority C t State Department of Transportation District t 1998 project t Over 1, 000 bridges u Majority are highway overpasses and smaller structures t Semi “Automated” database system t Used condition data, constraints, project- specific factors t Prioritization was based on Return on Investment
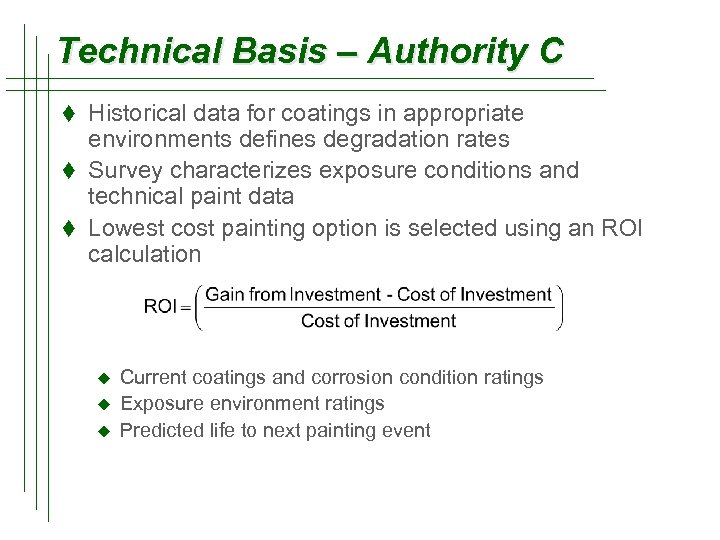 Technical Basis – Authority C t Historical data for coatings in appropriate environments defines degradation rates t Survey characterizes exposure conditions and technical paint data t Lowest cost painting option is selected using an ROI calculation u u u Current coatings and corrosion condition ratings Exposure environment ratings Predicted life to next painting event
Technical Basis – Authority C t Historical data for coatings in appropriate environments defines degradation rates t Survey characterizes exposure conditions and technical paint data t Lowest cost painting option is selected using an ROI calculation u u u Current coatings and corrosion condition ratings Exposure environment ratings Predicted life to next painting event
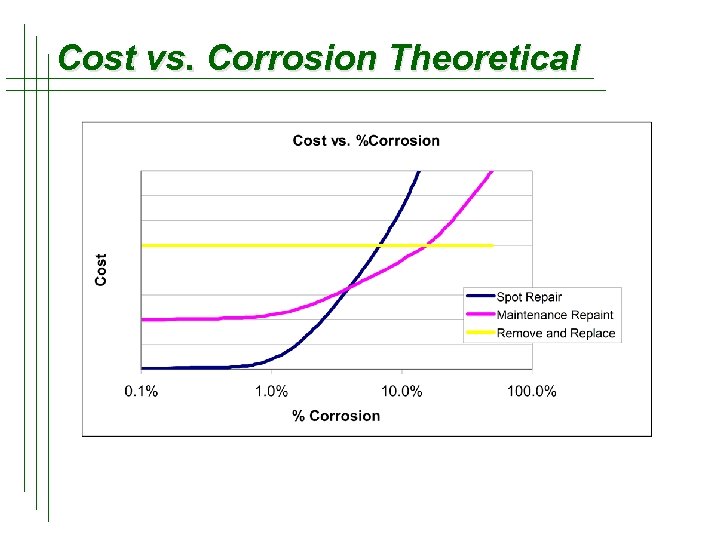 Cost vs. Corrosion Theoretical
Cost vs. Corrosion Theoretical
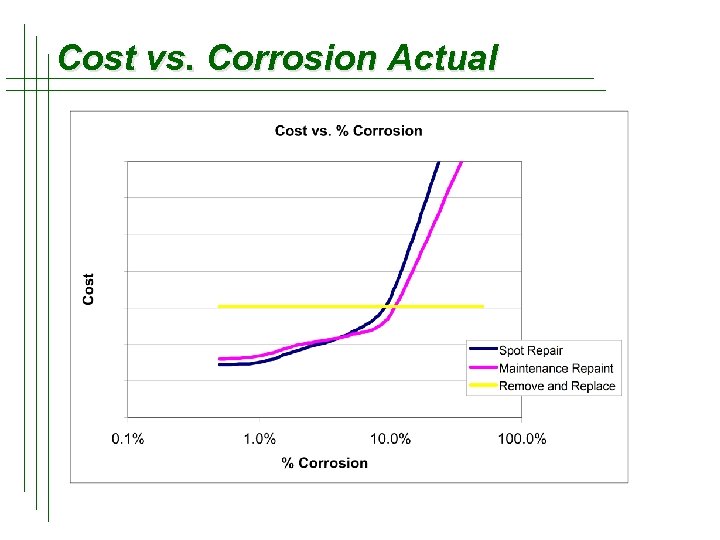 Cost vs. Corrosion Actual
Cost vs. Corrosion Actual
 Program Summary – Authority C t Database program generates a list of structures t t t sorted by ROI DOT organizes projects to address priorities (human factor is required) Condition data easily attained Degradation models and cost factors were fixed Constraints were variable Does not estimate budgets
Program Summary – Authority C t Database program generates a list of structures t t t sorted by ROI DOT organizes projects to address priorities (human factor is required) Condition data easily attained Degradation models and cost factors were fixed Constraints were variable Does not estimate budgets
 Common Threads t All prioritization programs were custom t Authority constraints were custom t All used existing data sources with enhancements t All need maintenance to remain accurate t All provide a starting point for defendable analysis
Common Threads t All prioritization programs were custom t Authority constraints were custom t All used existing data sources with enhancements t All need maintenance to remain accurate t All provide a starting point for defendable analysis
 Feedback is Needed t Programs are tools – use for designated purpose and within limitations Design Monitor Learn
Feedback is Needed t Programs are tools – use for designated purpose and within limitations Design Monitor Learn
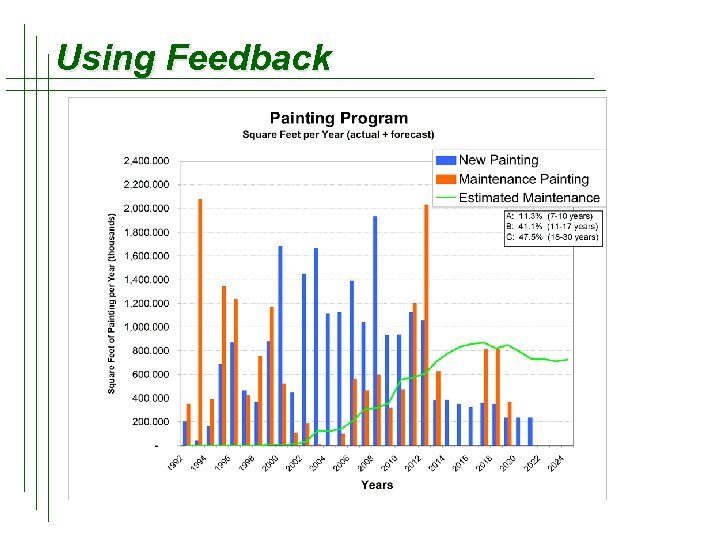 Using Feedback
Using Feedback
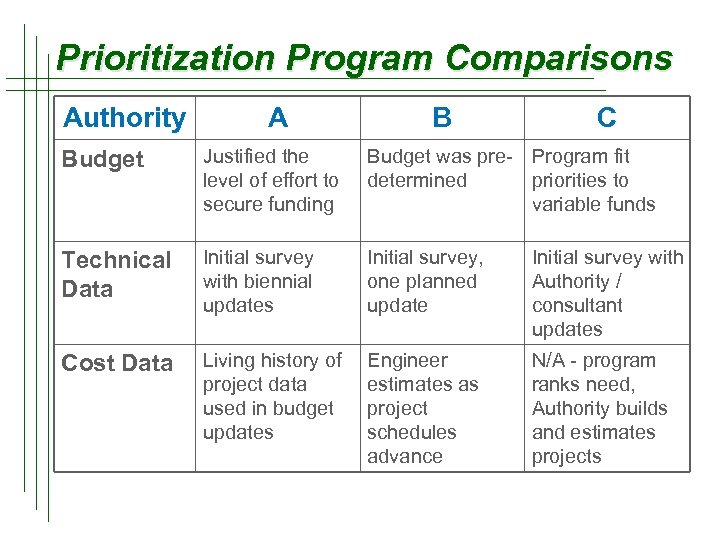 Prioritization Program Comparisons Authority A B C Budget Justified the level of effort to secure funding Budget was pre- Program fit determined priorities to variable funds Technical Data Initial survey with biennial updates Initial survey, one planned update Initial survey with Authority / consultant updates Cost Data Living history of project data used in budget updates Engineer estimates as project schedules advance N/A - program ranks need, Authority builds and estimates projects
Prioritization Program Comparisons Authority A B C Budget Justified the level of effort to secure funding Budget was pre- Program fit determined priorities to variable funds Technical Data Initial survey with biennial updates Initial survey, one planned update Initial survey with Authority / consultant updates Cost Data Living history of project data used in budget updates Engineer estimates as project schedules advance N/A - program ranks need, Authority builds and estimates projects
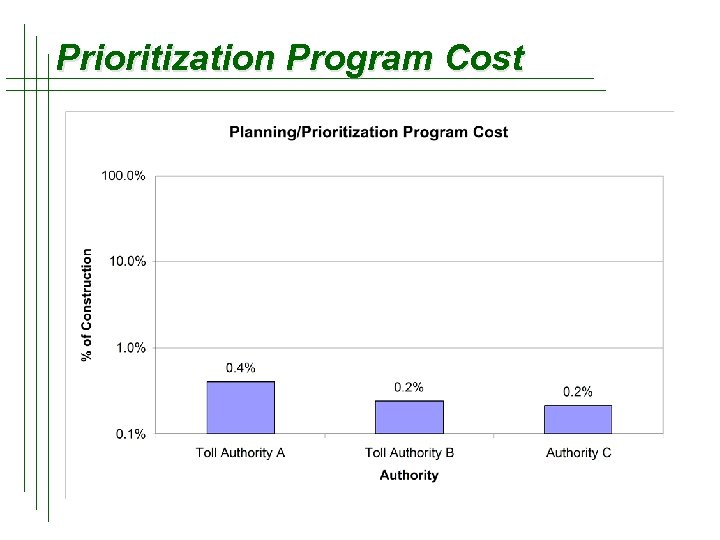 Prioritization Program Cost
Prioritization Program Cost
 Inspection vs. Expectation
Inspection vs. Expectation
 Planning a Project
Planning a Project
 Conclusions t Maintenance painting is needed t All painting can be scheduled with the most benefit (least cost) by evaluating structures and implementing a maintenance painting program t Numerous “constraints” affect a program Other work u Cost trends u Priorities / Goals u t Program must be adaptable t Use existing data or existing inspection activities
Conclusions t Maintenance painting is needed t All painting can be scheduled with the most benefit (least cost) by evaluating structures and implementing a maintenance painting program t Numerous “constraints” affect a program Other work u Cost trends u Priorities / Goals u t Program must be adaptable t Use existing data or existing inspection activities


