be887b70e4c37a974b2abb9ddb7f1477.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Greenhouse Structures, Climate Control, and Automation How are greenhouse structures, climate control, and automation used in the floriculture industry?
Greenhouse Structures, Climate Control, and Automation How are greenhouse structures, climate control, and automation used in the floriculture industry?
 Key Questions What are the different types of greenhouse designs? What are the different types of greenhouse covering materials? What are environmental controls? How are greenhouses heated and cooled? What types of plant bench materials are used and how are plants spaced? What are automated systems? What safety hazards exist in a greenhouse?
Key Questions What are the different types of greenhouse designs? What are the different types of greenhouse covering materials? What are environmental controls? How are greenhouses heated and cooled? What types of plant bench materials are used and how are plants spaced? What are automated systems? What safety hazards exist in a greenhouse?
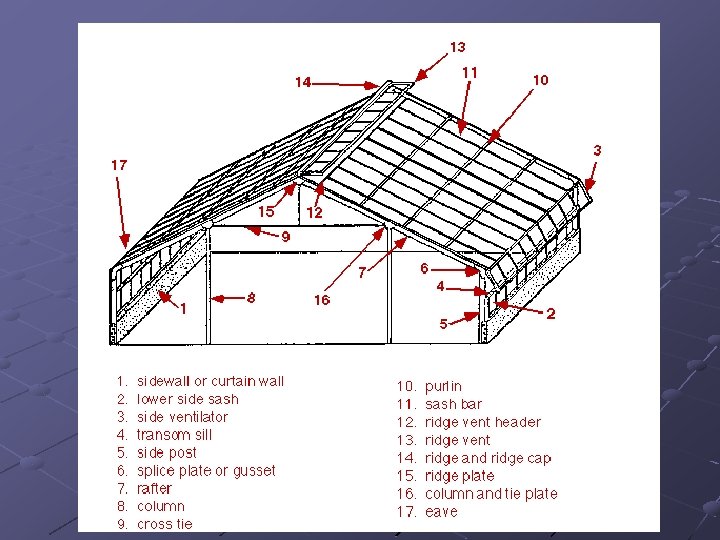
 What are the different types of greenhouse designs? Greenhouse- structure enclosed by a translucent material in which plants are grown n n Allow light in but serve as barrier between inside and outside environments Give grower control on environmental factors inside structure
What are the different types of greenhouse designs? Greenhouse- structure enclosed by a translucent material in which plants are grown n n Allow light in but serve as barrier between inside and outside environments Give grower control on environmental factors inside structure
 Lean-to greenhouse Attached to a building Building provides support for the roof Should be placed on the south side of building
Lean-to greenhouse Attached to a building Building provides support for the roof Should be placed on the south side of building
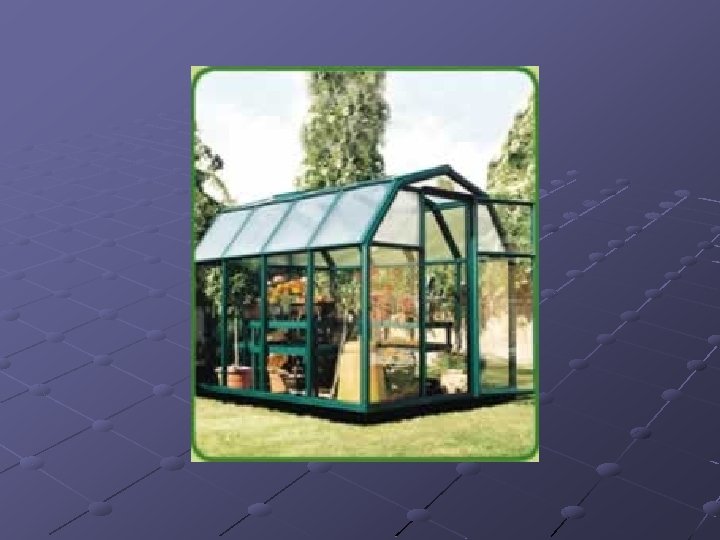
 Even-span greenhouse Have roofs with an even pitch and an even width Single houses
Even-span greenhouse Have roofs with an even pitch and an even width Single houses
 Hoop houses Arching pipes used in framework Low-cost, even-span greenhouse
Hoop houses Arching pipes used in framework Low-cost, even-span greenhouse
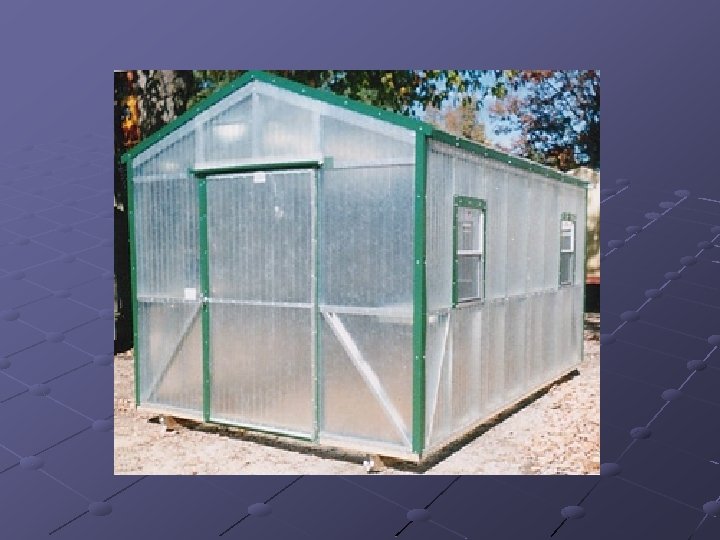
 Un-even span greenhouse Have roofs with unequal pitch and width Use is limited to hillsides Few are built today, because don’t support automation
Un-even span greenhouse Have roofs with unequal pitch and width Use is limited to hillsides Few are built today, because don’t support automation
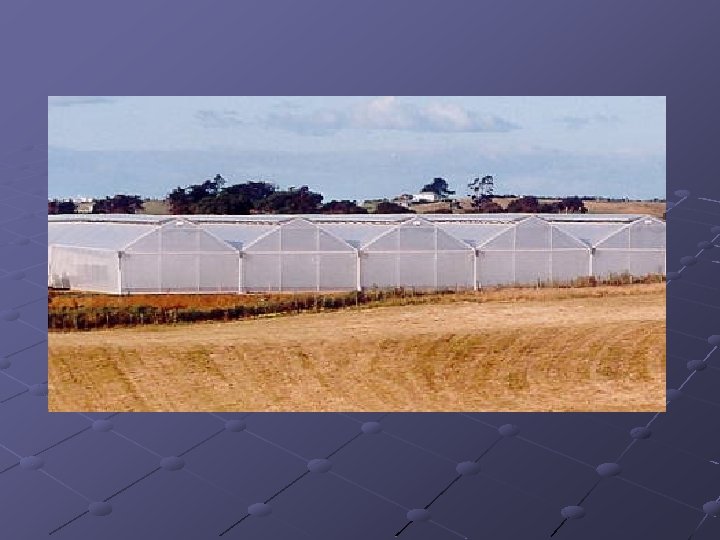
 Ridge-and-furrow greenhouse Consist of a number of structures joined together along the length of the houses Shared side walls are eliminated to create a large interior space Lower heating costs Gutters installed at connection points to remove water Best oriented N to S Eliminates permanent shadows at gutters Widely used in automated operations Higher gutters create better air circulation, cooler summer temps at bench level
Ridge-and-furrow greenhouse Consist of a number of structures joined together along the length of the houses Shared side walls are eliminated to create a large interior space Lower heating costs Gutters installed at connection points to remove water Best oriented N to S Eliminates permanent shadows at gutters Widely used in automated operations Higher gutters create better air circulation, cooler summer temps at bench level

 Headhouse Attached to greenhouse Storage area for media, containers, fertilizers, etc. Work area for potting and packaging
Headhouse Attached to greenhouse Storage area for media, containers, fertilizers, etc. Work area for potting and packaging
 Framework Supports covering material Should be strong without creating shade n Aluminum and aluminum/steel combos used
Framework Supports covering material Should be strong without creating shade n Aluminum and aluminum/steel combos used
 What are the different types of greenhouse “glazing” materials? Glazing- covering of a greenhouse n n Must be durable Light transmission Cost Heat loss
What are the different types of greenhouse “glazing” materials? Glazing- covering of a greenhouse n n Must be durable Light transmission Cost Heat loss
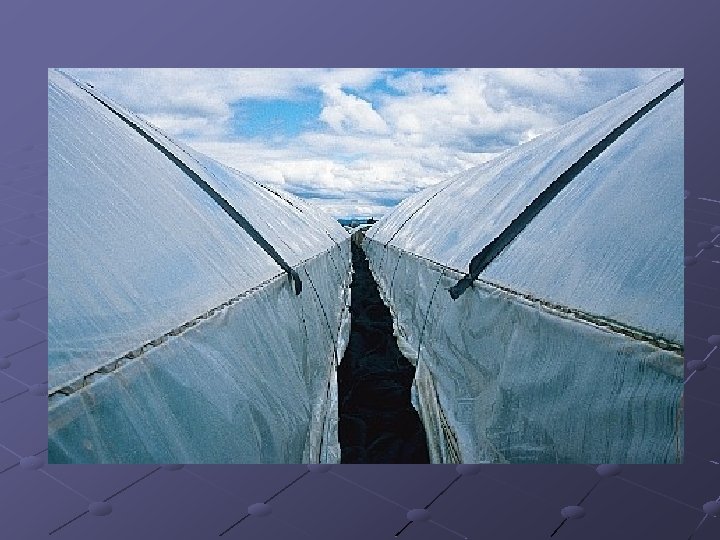
 Polyethylene Advantages n n n Most widely used and inexpensive Flexible sheets are stretched over framework Used in double layers with air blown between layers to produce 3 -9” bubble-like covering that insulates house Heating costs 1/3 of glass-covered house
Polyethylene Advantages n n n Most widely used and inexpensive Flexible sheets are stretched over framework Used in double layers with air blown between layers to produce 3 -9” bubble-like covering that insulates house Heating costs 1/3 of glass-covered house
 Polyethylene Disadvantages n Not durable b/c light breaksdown plastic Poly sheets with ultraviolet light inhibitors last 3 -4 years n One layer cuts light 85 -90% and 2 layers reduce light 70 -75% Limits the type of crop that can be produced, esp. in the North Have tight growing env. and can cause high humidity levels Fungus disease, Botrytis, can be problem in high humidity
Polyethylene Disadvantages n Not durable b/c light breaksdown plastic Poly sheets with ultraviolet light inhibitors last 3 -4 years n One layer cuts light 85 -90% and 2 layers reduce light 70 -75% Limits the type of crop that can be produced, esp. in the North Have tight growing env. and can cause high humidity levels Fungus disease, Botrytis, can be problem in high humidity

 Polycarbonate structured sheets Most widely used sheets Manufactured with a “twin wall” held together by ribs n n Appearance is hollow tubes, side by side, running the length of the sheet Tubing effect provides insulation and cuts heating costs Treated with ultraviolet light inhibitors and are guaranteed for 10 years
Polycarbonate structured sheets Most widely used sheets Manufactured with a “twin wall” held together by ribs n n Appearance is hollow tubes, side by side, running the length of the sheet Tubing effect provides insulation and cuts heating costs Treated with ultraviolet light inhibitors and are guaranteed for 10 years
 PSS 80% light transmission Resist hail damage Used widely in hail belt stretching from Colorado to Texas Easy to work with and flexible Can be bent around hoop greenhouses Fire resistant Expensive
PSS 80% light transmission Resist hail damage Used widely in hail belt stretching from Colorado to Texas Easy to work with and flexible Can be bent around hoop greenhouses Fire resistant Expensive


 Acrylic structured sheets Made with twin walls in like Polycarb Provide good insulation High light transmission (86%) Last 8 -10 years Cost more that Polycarb Less flexible that Polycarb and more prone to hail damage
Acrylic structured sheets Made with twin walls in like Polycarb Provide good insulation High light transmission (86%) Last 8 -10 years Cost more that Polycarb Less flexible that Polycarb and more prone to hail damage

 Fiberglass Widely use in 1960 -70 s Use has dropped since intro of polycarb and acrylics Light transmission is good but discolors after 7 -10 years Hail causes damage Highly flammable and has poor insulation
Fiberglass Widely use in 1960 -70 s Use has dropped since intro of polycarb and acrylics Light transmission is good but discolors after 7 -10 years Hail causes damage Highly flammable and has poor insulation

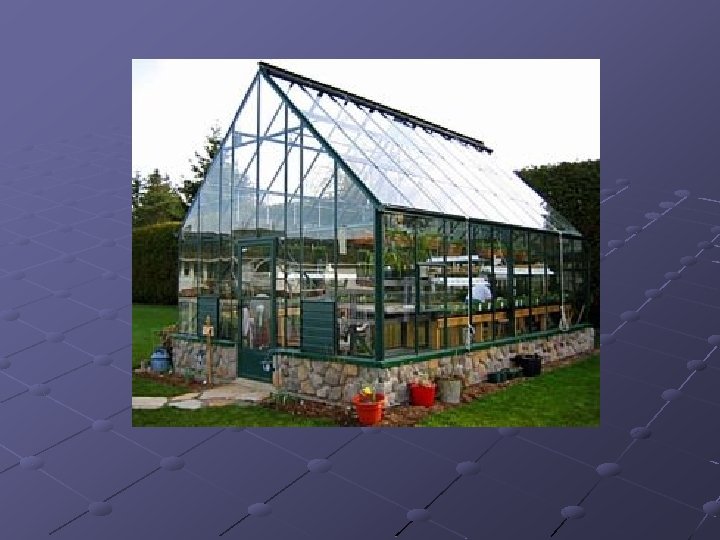
 Glass Considered best for plant production Provides high light transmission (88 -89%) Panes of glass overlap producing openings that allow air exchange Initial cost is expensive Can be long lasting if not broken Over long term it can be less costly than other coverings
Glass Considered best for plant production Provides high light transmission (88 -89%) Panes of glass overlap producing openings that allow air exchange Initial cost is expensive Can be long lasting if not broken Over long term it can be less costly than other coverings
 Disadvantages of glass BREAKABLE Must purchase hail and crop insurance Can use tempered glass which is stronger n n Withstands hail better but is more expensive Strength allows for use of larger panes Light transmission is increased b/c supports further apart Lowers heat loss Very poor insulation qualities
Disadvantages of glass BREAKABLE Must purchase hail and crop insurance Can use tempered glass which is stronger n n Withstands hail better but is more expensive Strength allows for use of larger panes Light transmission is increased b/c supports further apart Lowers heat loss Very poor insulation qualities
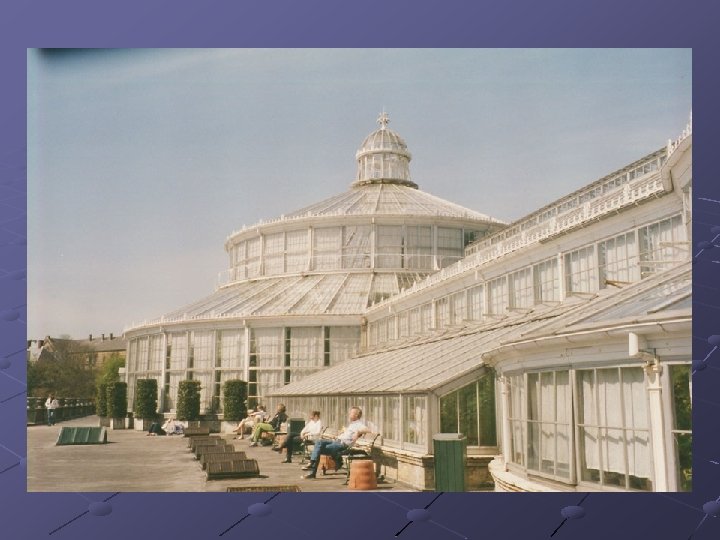


 Retractable-roof greenhouses Roofs can be opened and closed Open when weather is favorable and close when crops need protection Low-cost was to provide extra growing space Excellent for bedding plants, perennials, and field-grown cut flowers Help plants become acclimated to outdoors Better ventilation, reduced irrigation, more effective temp control
Retractable-roof greenhouses Roofs can be opened and closed Open when weather is favorable and close when crops need protection Low-cost was to provide extra growing space Excellent for bedding plants, perennials, and field-grown cut flowers Help plants become acclimated to outdoors Better ventilation, reduced irrigation, more effective temp control
 Three main styles of RR Flat roof houses- shade and frost protection Peaked roofs- designed for snow loads and keeping out rain Sawtooth- allow venting when other parts are closed Poly- sections are withdrawn and folded up by electric motors, can be open & closed in minutes
Three main styles of RR Flat roof houses- shade and frost protection Peaked roofs- designed for snow loads and keeping out rain Sawtooth- allow venting when other parts are closed Poly- sections are withdrawn and folded up by electric motors, can be open & closed in minutes

 What are the different types of plant bench materials and how are they spaced?
What are the different types of plant bench materials and how are they spaced?
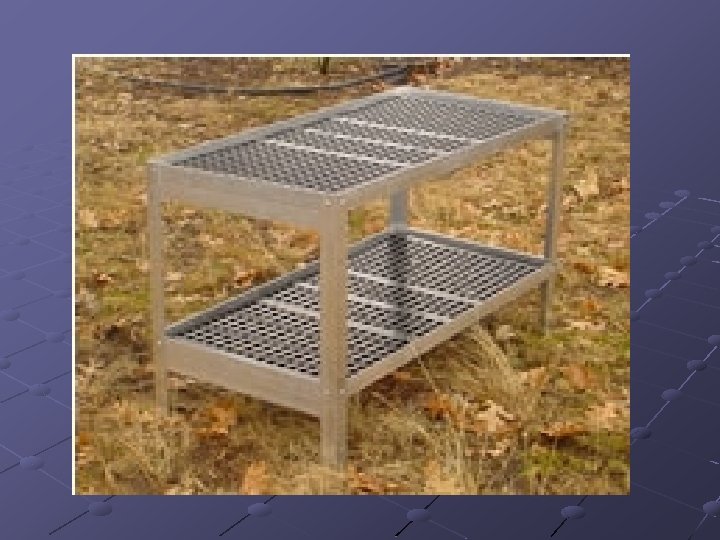
 Greenhouse Benches Levels at which crops are grown in a greenhouse depends on the crop Conservatory plants grown in beds on the floorlarger greenhouses Production greenhouses utilize benches, floor, beds n n Bedding plants- benches 2 -3 ft off ground Cut flowers- in beds Must withstand wet climate, be strong Usually 13 -gauge expanded galvanized steel, aluminum and plastic Can use rot-resistant wood
Greenhouse Benches Levels at which crops are grown in a greenhouse depends on the crop Conservatory plants grown in beds on the floorlarger greenhouses Production greenhouses utilize benches, floor, beds n n Bedding plants- benches 2 -3 ft off ground Cut flowers- in beds Must withstand wet climate, be strong Usually 13 -gauge expanded galvanized steel, aluminum and plastic Can use rot-resistant wood
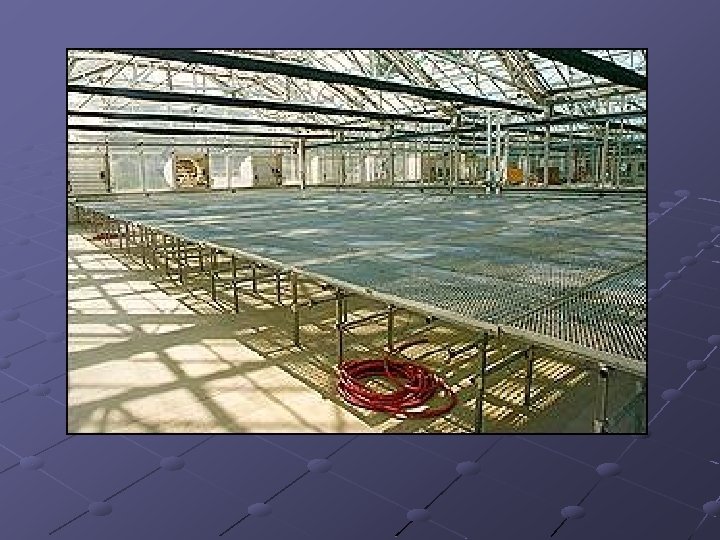
 Bench Spacing Recommended width n n 3 feet if working from one aisle 6 feet in working from two aisles Conservatory- wide aisles, stationary Production- 18” aisles n n Rolling benches- maximize growing space, rest on pipes and rolled from side to side Use only one aisle
Bench Spacing Recommended width n n 3 feet if working from one aisle 6 feet in working from two aisles Conservatory- wide aisles, stationary Production- 18” aisles n n Rolling benches- maximize growing space, rest on pipes and rolled from side to side Use only one aisle



 What are methods of heating and cooling the greenhouse?
What are methods of heating and cooling the greenhouse?
 Provide growers with power to control temp, water, humidity, and light Environmental controls- devices used to automatically turn greenhouse systems on and off
Provide growers with power to control temp, water, humidity, and light Environmental controls- devices used to automatically turn greenhouse systems on and off
 Thermostats Low cost and easy to install On-off thermostat n Control fans, heaters, and vents with change in temp Proportioning thermostats n Provide continuous control of systems with changes in temp
Thermostats Low cost and easy to install On-off thermostat n Control fans, heaters, and vents with change in temp Proportioning thermostats n Provide continuous control of systems with changes in temp
 Analog controls Use proportioning thermostats or electronic sensors to run amplifiers and electronic circuitry Integrate operations of heating and cooling equipment Better performance than thermostats alone
Analog controls Use proportioning thermostats or electronic sensors to run amplifiers and electronic circuitry Integrate operations of heating and cooling equipment Better performance than thermostats alone
 Computer controls Use microprocessors n Make complex judgements based on info from a number of sensors that gather info on temp, relative humidity, and sunlight
Computer controls Use microprocessors n Make complex judgements based on info from a number of sensors that gather info on temp, relative humidity, and sunlight
 Computerized environmental management systems Expensive but accurate Offer greatest range of uses All pieces of equipment can be controlled at same time Can be programmed to provide different zones in the greenhouse with different climate conditions
Computerized environmental management systems Expensive but accurate Offer greatest range of uses All pieces of equipment can be controlled at same time Can be programmed to provide different zones in the greenhouse with different climate conditions
 Heating Systems Hot water n n n Water is heated in boilers and pumped thru pipes in the greenhouse Pipes often placed under benches or in floor Relatively low maintenance and heat delivered evenly
Heating Systems Hot water n n n Water is heated in boilers and pumped thru pipes in the greenhouse Pipes often placed under benches or in floor Relatively low maintenance and heat delivered evenly
 Steam heat n n Standard method for heating cut flower operations Large boilers bring water to a boil to produce steam that flows thru pipes in greenhouse Not as uniform as hot water heat and not easy to adjust temp Steam can be used to sterilize growing media Unit heaters or hot air heaters n n Air is heated in unit then blown thru house Less expensive to install than hot water sys. Long term fuel costs are higher Heat delivered above crops May use poly tubes to evenly distribute warm air for uniform temps and fewer foliar diseases
Steam heat n n Standard method for heating cut flower operations Large boilers bring water to a boil to produce steam that flows thru pipes in greenhouse Not as uniform as hot water heat and not easy to adjust temp Steam can be used to sterilize growing media Unit heaters or hot air heaters n n Air is heated in unit then blown thru house Less expensive to install than hot water sys. Long term fuel costs are higher Heat delivered above crops May use poly tubes to evenly distribute warm air for uniform temps and fewer foliar diseases
 Infrared heat systems n n n Produce heat energy that is absorbed by plants, media, and benches Heat transfers to air space around plants High fuel efficiency results in low operating costs Less problems with foliar diseases Placed in peak of greenhouse and function best in high structures
Infrared heat systems n n n Produce heat energy that is absorbed by plants, media, and benches Heat transfers to air space around plants High fuel efficiency results in low operating costs Less problems with foliar diseases Placed in peak of greenhouse and function best in high structures
 Energy curtains Automated systems utilizing fabrics that insulate greenhouse at night and shade crops during day Installed from gutter to gutter and are 8 -12 feet above ground Computerized systems open and close curtains based on preset light levels or temps
Energy curtains Automated systems utilizing fabrics that insulate greenhouse at night and shade crops during day Installed from gutter to gutter and are 8 -12 feet above ground Computerized systems open and close curtains based on preset light levels or temps
 Curtains can lowers daytime temps 8 -10 degrees than full sun n Reduce stress on plants and lower water/fertilizer needs At night, closed curtains trap heat energy and saves 25 -35% in heating fuel costs Short-day curtains n n Block light from reaching crops Closed for 12 -13 hours to produce short-day effect Used in timing poinsettia, chrysanthemum and kalanchoe crops Black poly or aluminum and poly combo
Curtains can lowers daytime temps 8 -10 degrees than full sun n Reduce stress on plants and lower water/fertilizer needs At night, closed curtains trap heat energy and saves 25 -35% in heating fuel costs Short-day curtains n n Block light from reaching crops Closed for 12 -13 hours to produce short-day effect Used in timing poinsettia, chrysanthemum and kalanchoe crops Black poly or aluminum and poly combo
 Cooling and Ventilation Systems Fan and pad system n n Based on evaporation of water Wall of cellulose or aspen pads on one end of greenhouse that are kept wet by systems of pumps and gutters that recirculate water Other end of greenhouse has fans that pull air thru the pads and across greenhouse As water evaporates, air is cooled
Cooling and Ventilation Systems Fan and pad system n n Based on evaporation of water Wall of cellulose or aspen pads on one end of greenhouse that are kept wet by systems of pumps and gutters that recirculate water Other end of greenhouse has fans that pull air thru the pads and across greenhouse As water evaporates, air is cooled
 Fog system or mist system n n Involve an atomizer that produces water vapor Water vapor cools house by flash evaporation Increase humidity while they cool Lower temp throughout house and used in southern states Vents n n n Panels that open to allow air exchange with outside Roof vents allow hot air to rise out of house Less expensive than fan and pad systems
Fog system or mist system n n Involve an atomizer that produces water vapor Water vapor cools house by flash evaporation Increase humidity while they cool Lower temp throughout house and used in southern states Vents n n n Panels that open to allow air exchange with outside Roof vents allow hot air to rise out of house Less expensive than fan and pad systems


