f47fb1c0557cb3c5a18f3297bc926673.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Greenhouse Structures and Systems ERT 352
Greenhouse Structures and Systems ERT 352
 What is a greenhouse? • A greenhouse is an area designed to grow plants. • It is a controlled environment which allow optimum growth. • When several of these buildings are joined together they are often referred to as a greenhouse range. • A greenhouse at home is usually attached to the house or the garage.
What is a greenhouse? • A greenhouse is an area designed to grow plants. • It is a controlled environment which allow optimum growth. • When several of these buildings are joined together they are often referred to as a greenhouse range. • A greenhouse at home is usually attached to the house or the garage.
 Location • There are several factors to be considered in establishing a greenhouse range. • A. Room for expansion – 1. Land larger then immediate needs should be acquired. – 2. Area should be added to this figure to accommodate service buildings, storage, and access drivers.
Location • There are several factors to be considered in establishing a greenhouse range. • A. Room for expansion – 1. Land larger then immediate needs should be acquired. – 2. Area should be added to this figure to accommodate service buildings, storage, and access drivers.
 • B. Topography – 1. The building site should be as level as possible to reduce the cost of grading. – 2. The site should be also well drained. Due to the vast amount of water in the green house it is always advisable to provide a drainage system. Try to select a site with deep, well drained loam, or sandy loam soil.
• B. Topography – 1. The building site should be as level as possible to reduce the cost of grading. – 2. The site should be also well drained. Due to the vast amount of water in the green house it is always advisable to provide a drainage system. Try to select a site with deep, well drained loam, or sandy loam soil.
 – 3. You should select a site with a natural wind break such as a tree line or a hill. • C. Land use Prediction – 1. Local zoning and tax laws are subject to change brought on by development pressures. Such changes have brought about the termination of many greenhouse business.
– 3. You should select a site with a natural wind break such as a tree line or a hill. • C. Land use Prediction – 1. Local zoning and tax laws are subject to change brought on by development pressures. Such changes have brought about the termination of many greenhouse business.
 • D. Climate – 1. The greenhouse site should be selected with specific crops in mind. • E. Accessibility – 1. A site should be selected which has easily accessible shipping routes. – 2. Select a site that isn’t long distance. – 3. Site location is often the deciding factor in the type of fuel used.
• D. Climate – 1. The greenhouse site should be selected with specific crops in mind. • E. Accessibility – 1. A site should be selected which has easily accessible shipping routes. – 2. Select a site that isn’t long distance. – 3. Site location is often the deciding factor in the type of fuel used.
 Types of Greenhouses Even Span Uneven Span Lean-to Quonset Gothic Arch Curvilinear Dome Shaped
Types of Greenhouses Even Span Uneven Span Lean-to Quonset Gothic Arch Curvilinear Dome Shaped
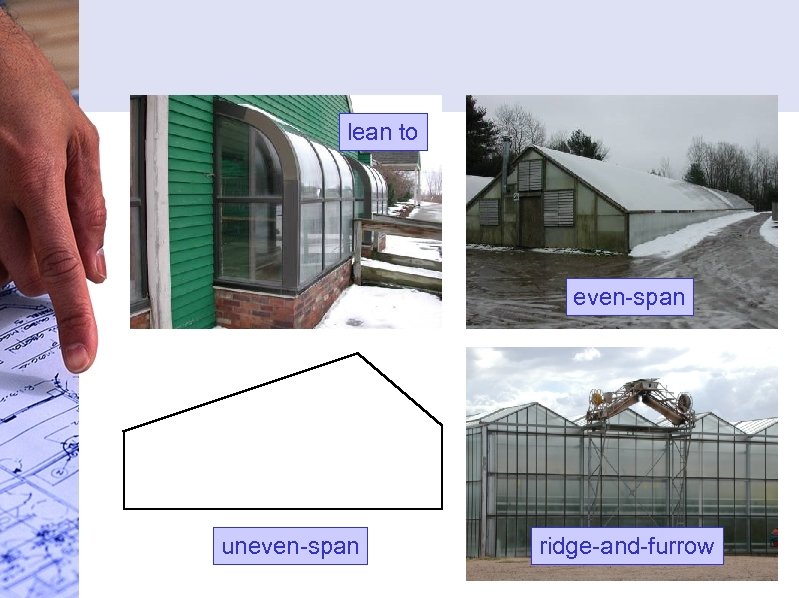 lean to even-span uneven-span ridge-and-furrow
lean to even-span uneven-span ridge-and-furrow
 Single Span Greenhouse
Single Span Greenhouse
 1. EVEN SPAN • Greenhouse with two roof slopes of equal pitch and width • Benefits: • Excellent light, ventilation, and temp control • Disadvantages: • Wasted heat air in the gables
1. EVEN SPAN • Greenhouse with two roof slopes of equal pitch and width • Benefits: • Excellent light, ventilation, and temp control • Disadvantages: • Wasted heat air in the gables
 EVEN SPAN
EVEN SPAN
 Even span gutter connected house.
Even span gutter connected house.
 2. GOTHIC ARCH • • POINTED ARCH ROOF TRUSSES HAVE BEEN ELIMINATED Not as popular today Can have sidewalls • Side walls are a short base wall of a solid material – often cinderblocks
2. GOTHIC ARCH • • POINTED ARCH ROOF TRUSSES HAVE BEEN ELIMINATED Not as popular today Can have sidewalls • Side walls are a short base wall of a solid material – often cinderblocks
 GOTHIC ARCH
GOTHIC ARCH
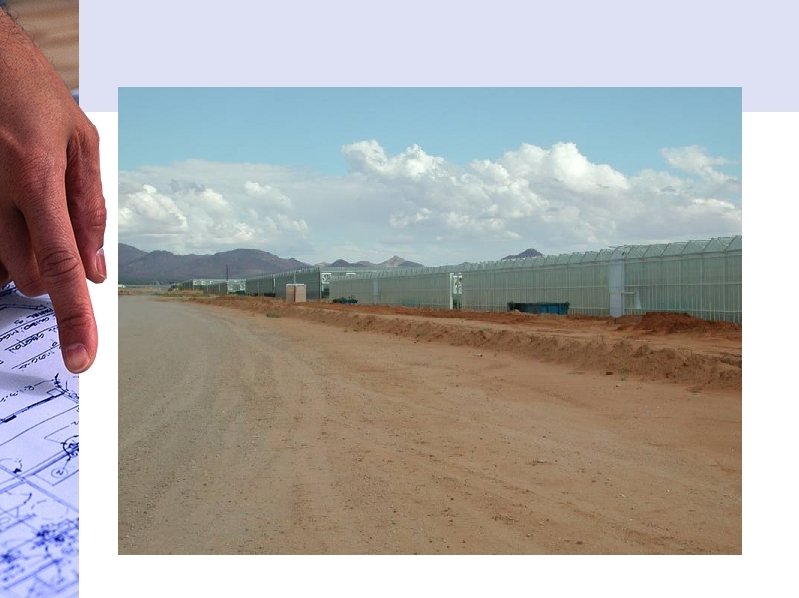
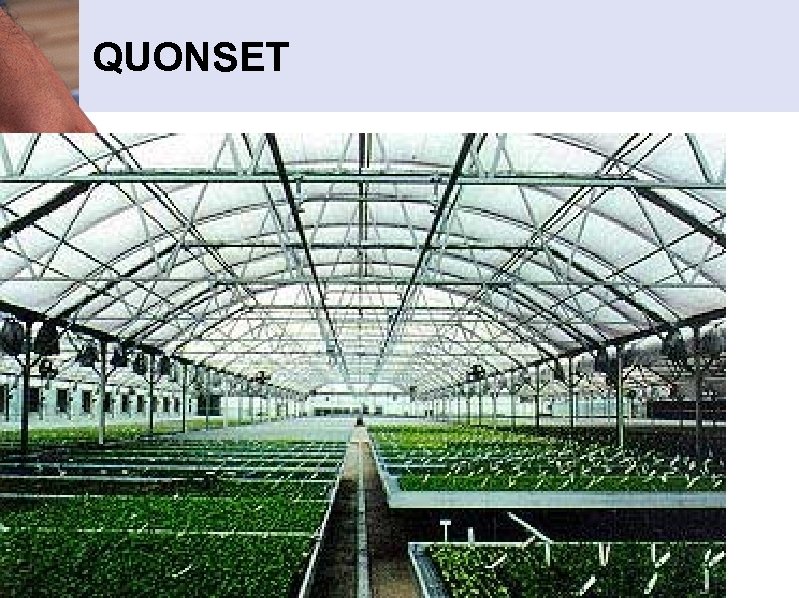
 3. QUONSET • A greenhouse with a semicircular arch that starts at ground level or on top of a sidewall – (Half moon shape) • Benefits: – Less Expensive to construct – Few shadows • Disadvantage: – Cannot handle as much wind and snow
3. QUONSET • A greenhouse with a semicircular arch that starts at ground level or on top of a sidewall – (Half moon shape) • Benefits: – Less Expensive to construct – Few shadows • Disadvantage: – Cannot handle as much wind and snow
 3. QUONSET
3. QUONSET
 QUONSET
QUONSET
 QUONSET WITH TOP VENT
QUONSET WITH TOP VENT
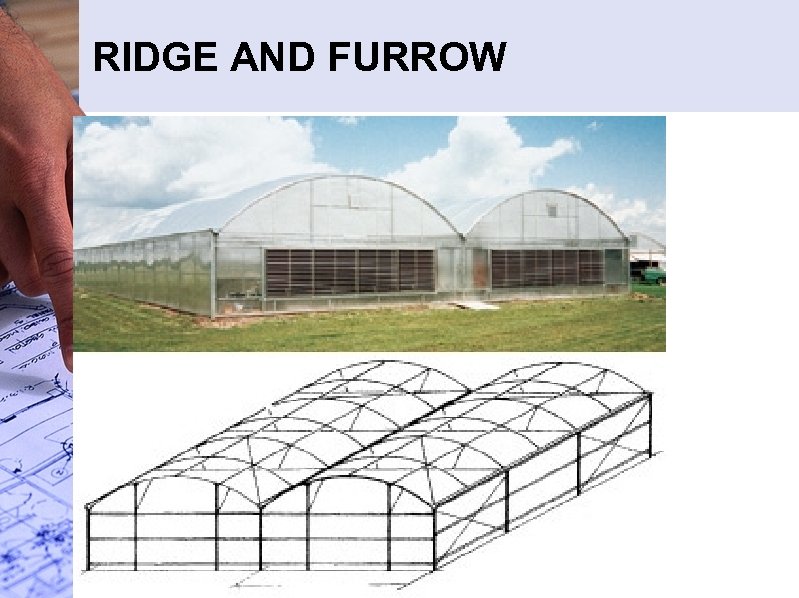
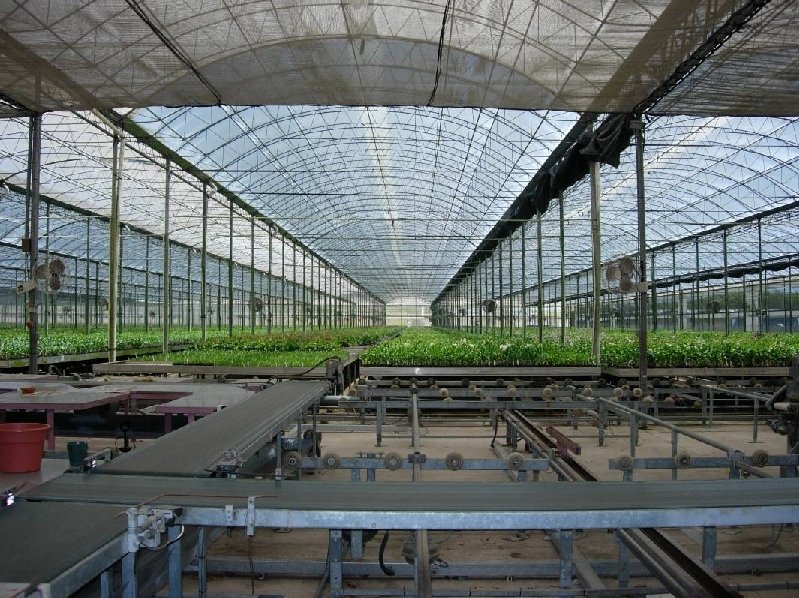
 4. RIDGE AND FURROW • Several greenhouses connected along the length of the eaves • Benefits: – Large interior areas – Reduced heat loss – Less expensive construction • Disadvantages: – More difficult to control pest and temperature – Difficult snow removal
4. RIDGE AND FURROW • Several greenhouses connected along the length of the eaves • Benefits: – Large interior areas – Reduced heat loss – Less expensive construction • Disadvantages: – More difficult to control pest and temperature – Difficult snow removal
 RIDGE AND FURROW
RIDGE AND FURROW
 RIDGE AND FURROW
RIDGE AND FURROW
 RIDGE AND FURROW
RIDGE AND FURROW
 RIDGE AND FURROW
RIDGE AND FURROW
 RIDGE AND FURROW
RIDGE AND FURROW

 1. GLASS • ADVANTAGES: – Excellent Light Transmission – Available • DISADVANTAGES: – Breakable – High heat loss – Most Expensive
1. GLASS • ADVANTAGES: – Excellent Light Transmission – Available • DISADVANTAGES: – Breakable – High heat loss – Most Expensive
 2. FLEXIBLE PLASTIC FILMS • EXAMPLES: – PVC- POLYVINYL CHLORIDE – PVF- POLYVINYL FLOURIDE FILM – POLYETHYLENE- Most Common • ADVANTAGES: – Inexpensive – Easy to Install • DISADVANTAGES: – Not as durable
2. FLEXIBLE PLASTIC FILMS • EXAMPLES: – PVC- POLYVINYL CHLORIDE – PVF- POLYVINYL FLOURIDE FILM – POLYETHYLENE- Most Common • ADVANTAGES: – Inexpensive – Easy to Install • DISADVANTAGES: – Not as durable
 3. RIGID PLASTIC SHEETS • EXAMPLES: – FIBERGLASS – ACRYLIC- PLEXIGLASS – POLYCARBONATE- LEXAN • ADVANTAGES: – Light weight – Most Durable • DISADVANTAGES: – More expensive than flexible plastic
3. RIGID PLASTIC SHEETS • EXAMPLES: – FIBERGLASS – ACRYLIC- PLEXIGLASS – POLYCARBONATE- LEXAN • ADVANTAGES: – Light weight – Most Durable • DISADVANTAGES: – More expensive than flexible plastic
 Cooling and Ventilation Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. No Cooling NATURAL VENTILATION FAN & SHUTTER COOLING with SHADE CLOTH 5. Evaporative Cooling 6. Fan & Pad (Evaporative Cooling)
Cooling and Ventilation Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. No Cooling NATURAL VENTILATION FAN & SHUTTER COOLING with SHADE CLOTH 5. Evaporative Cooling 6. Fan & Pad (Evaporative Cooling)
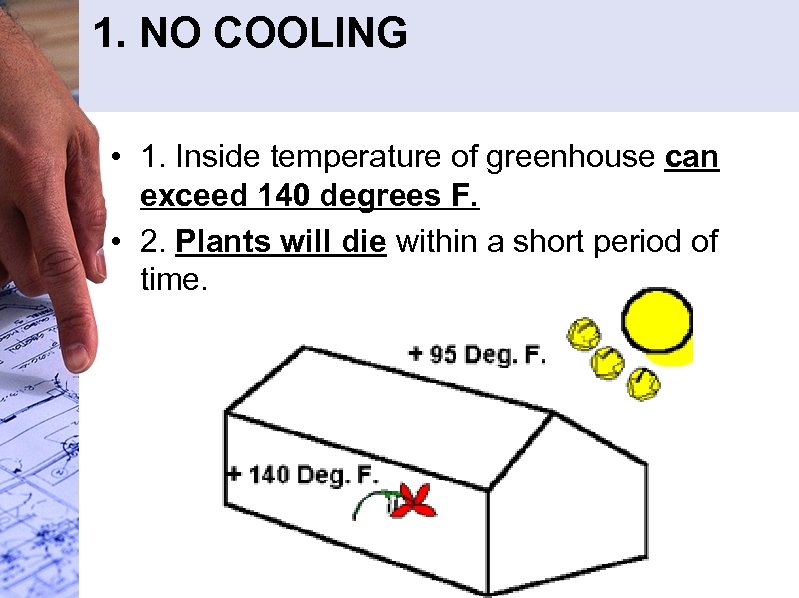 1. NO COOLING • 1. Inside temperature of greenhouse can exceed 140 degrees F. • 2. Plants will die within a short period of time.
1. NO COOLING • 1. Inside temperature of greenhouse can exceed 140 degrees F. • 2. Plants will die within a short period of time.
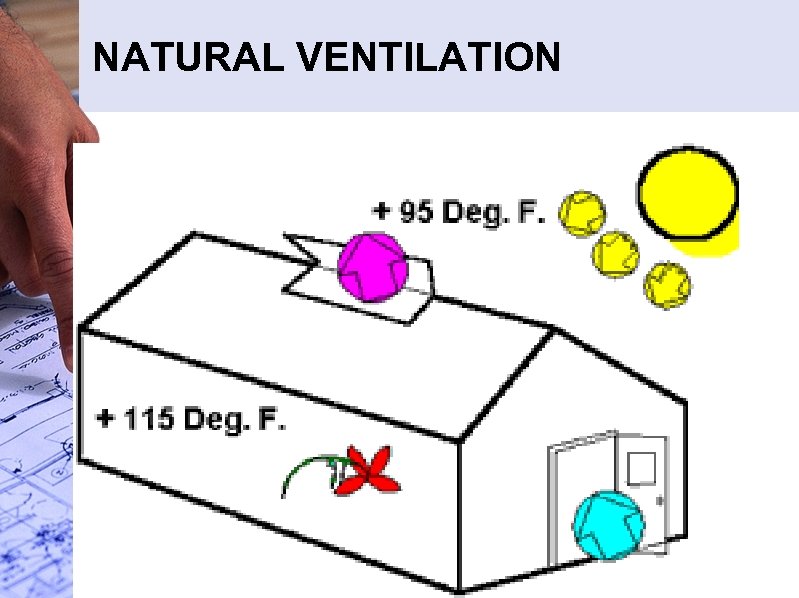 NATURAL VENTILATION
NATURAL VENTILATION
 NATURAL VENTILATION
NATURAL VENTILATION
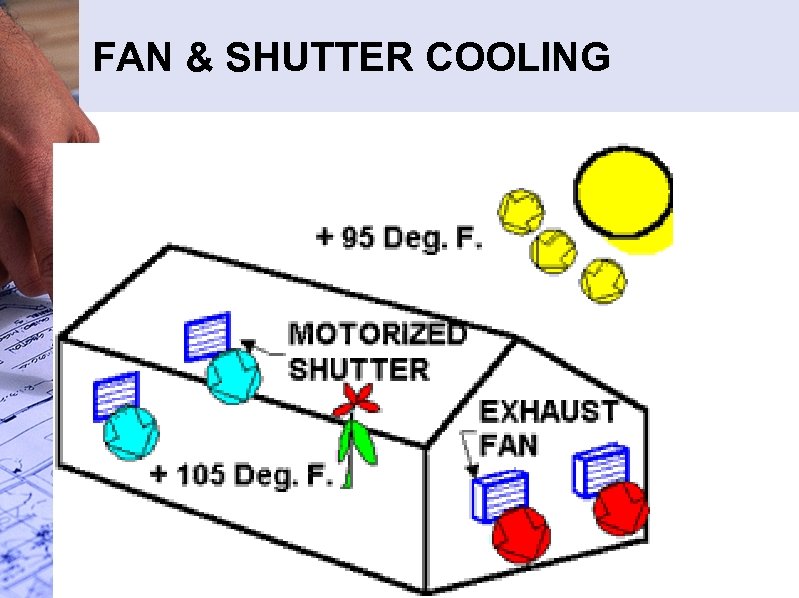 FAN & SHUTTER COOLING
FAN & SHUTTER COOLING
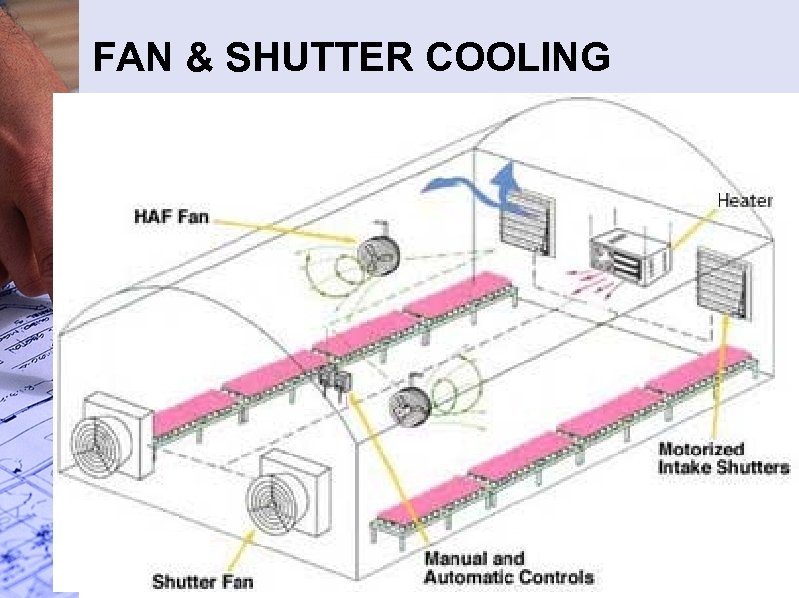 FAN & SHUTTER COOLING
FAN & SHUTTER COOLING
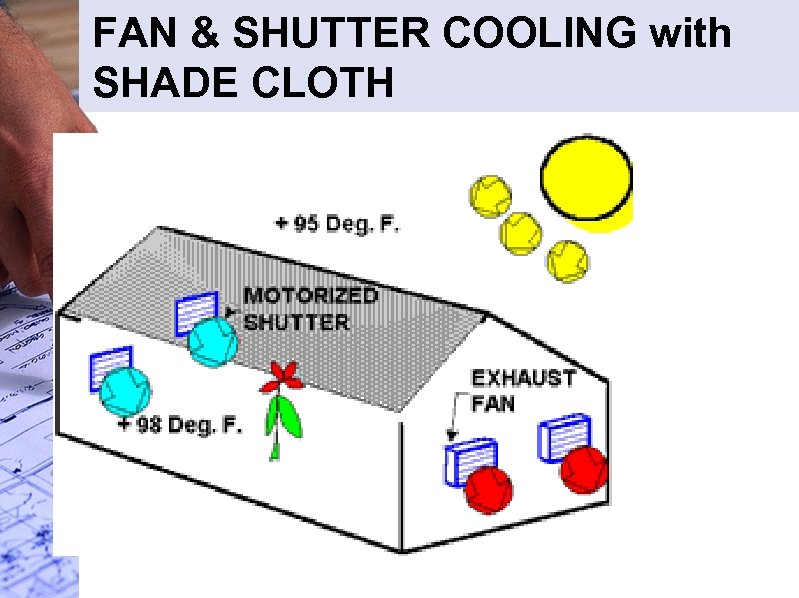 FAN & SHUTTER COOLING with SHADE CLOTH
FAN & SHUTTER COOLING with SHADE CLOTH
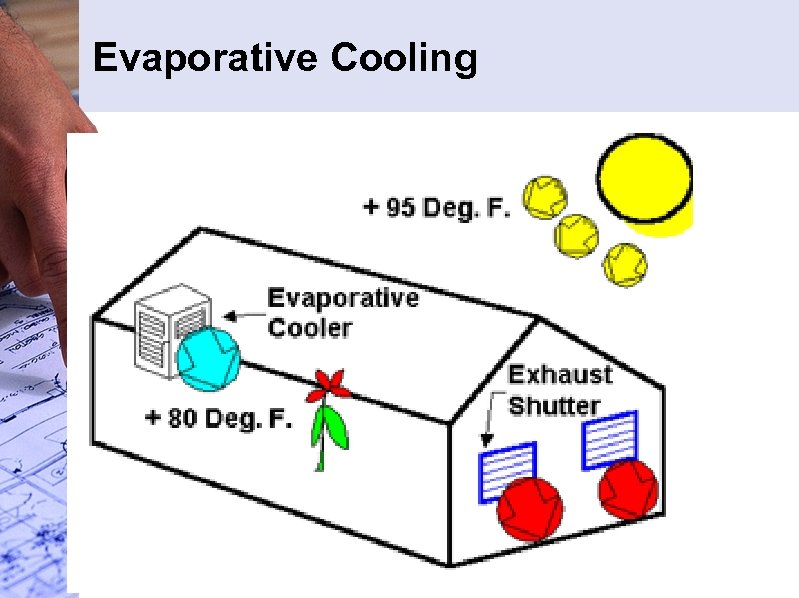 Evaporative Cooling
Evaporative Cooling
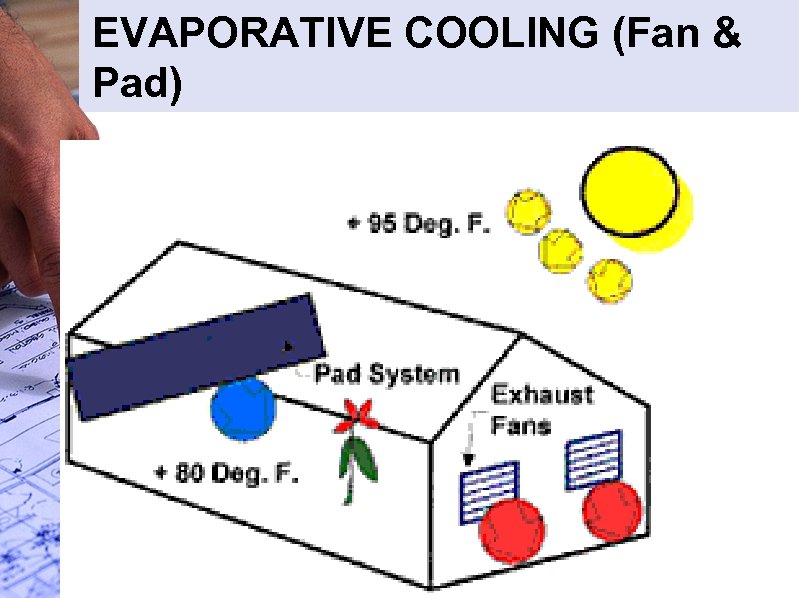 EVAPORATIVE COOLING (Fan & Pad)
EVAPORATIVE COOLING (Fan & Pad)
 EVAPORATIVE COOLING (Fan & Pad) • Pad • Water Tank With pump
EVAPORATIVE COOLING (Fan & Pad) • Pad • Water Tank With pump
 D. IRRIGATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Drip irrigation Mist nozzles Fertilizer injectors Automatic Controls Solenoid valves
D. IRRIGATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Drip irrigation Mist nozzles Fertilizer injectors Automatic Controls Solenoid valves
 DRIP IRRIGATION (tubes)
DRIP IRRIGATION (tubes)
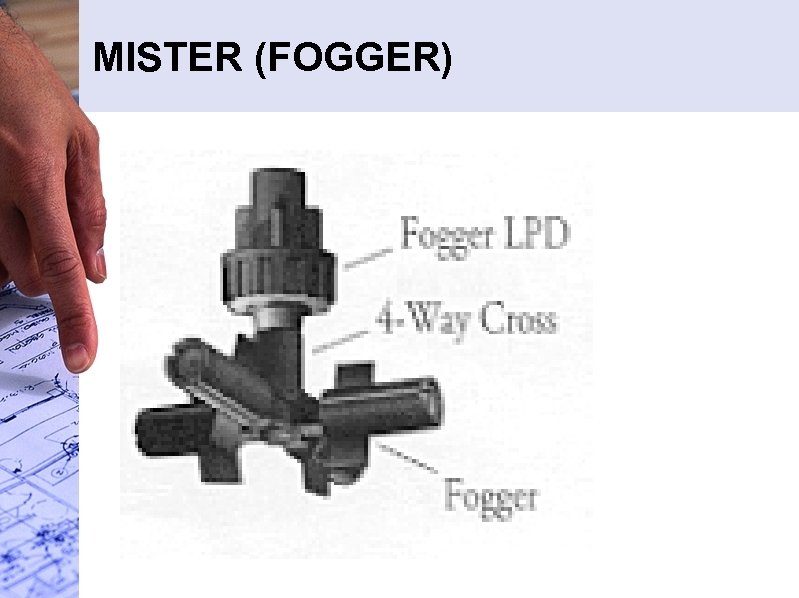 MISTER (FOGGER)
MISTER (FOGGER)
 FERTILIZER INJECTORS • SLOWLY ADD FERTILIZERS TO IRRIGATION WATER, AT A SET RATE
FERTILIZER INJECTORS • SLOWLY ADD FERTILIZERS TO IRRIGATION WATER, AT A SET RATE
 IRRIGATION CONTROLS • Solenoid Valves – Help control flow rate
IRRIGATION CONTROLS • Solenoid Valves – Help control flow rate
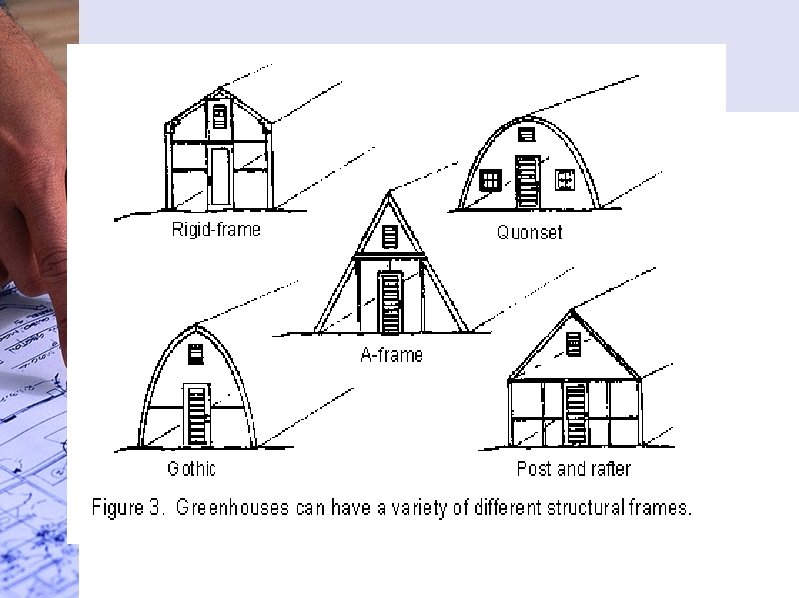
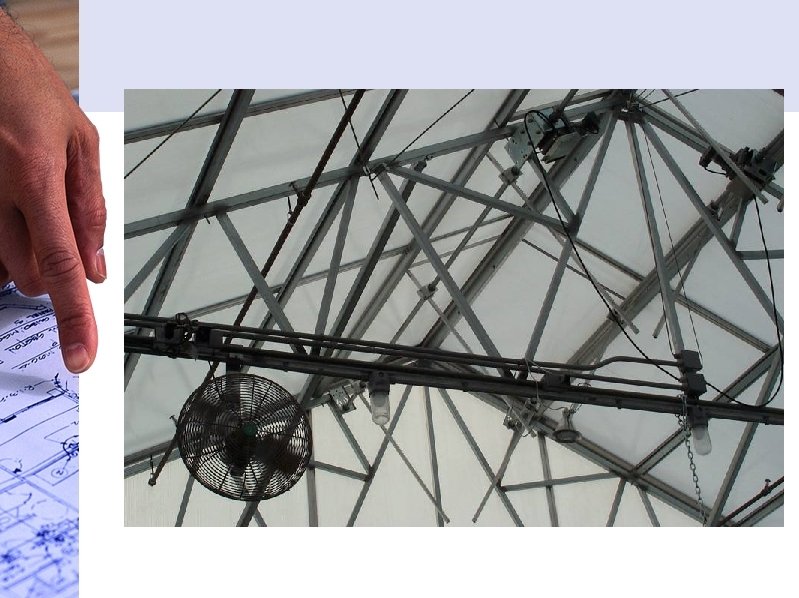
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Greenhouse Structural Components
Greenhouse Structural Components
 Ridge-and-Furrow Greenhouses
Ridge-and-Furrow Greenhouses
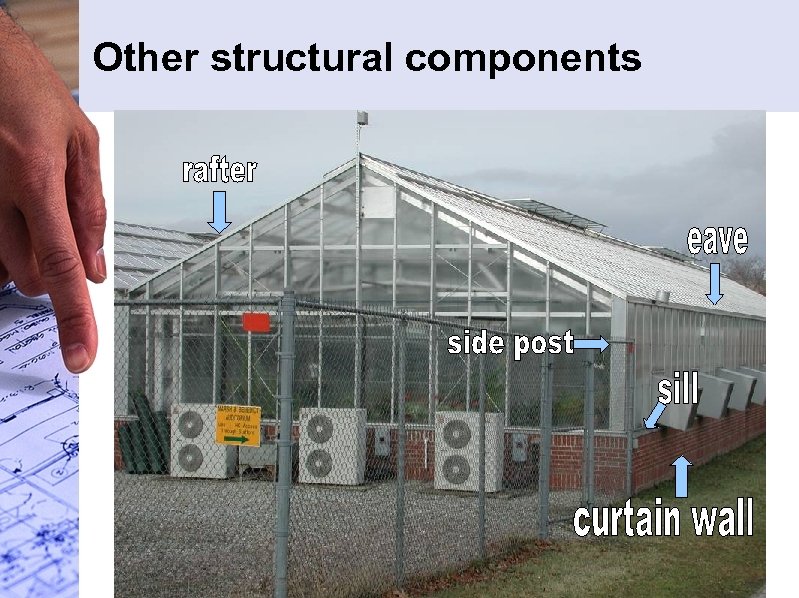 Other structural components
Other structural components
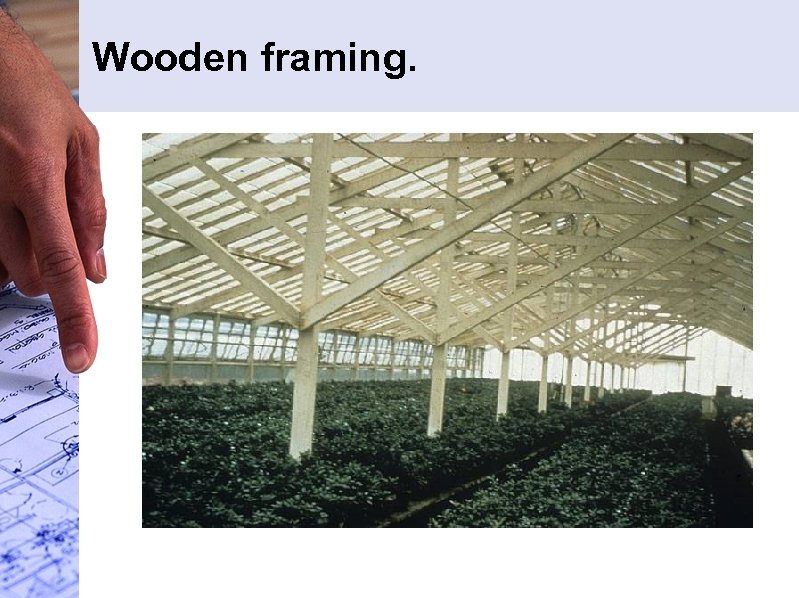
 Wooden framing.
Wooden framing.
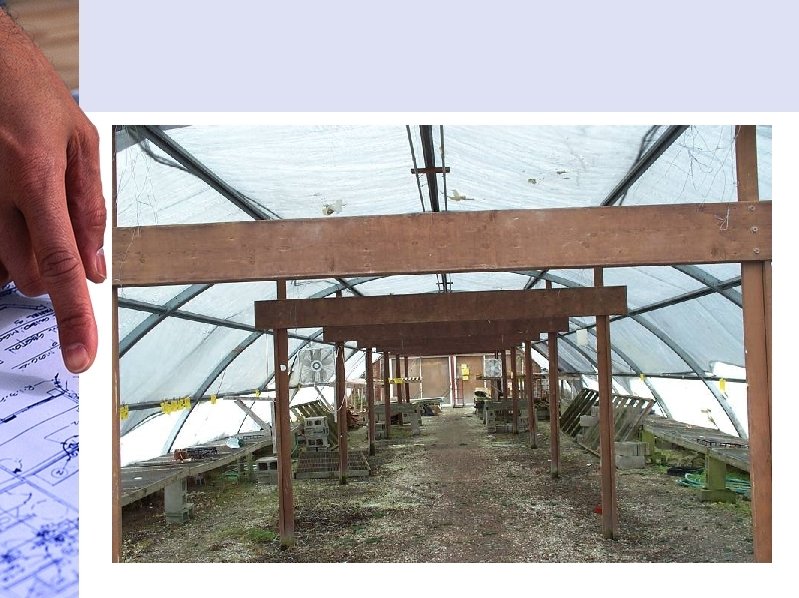
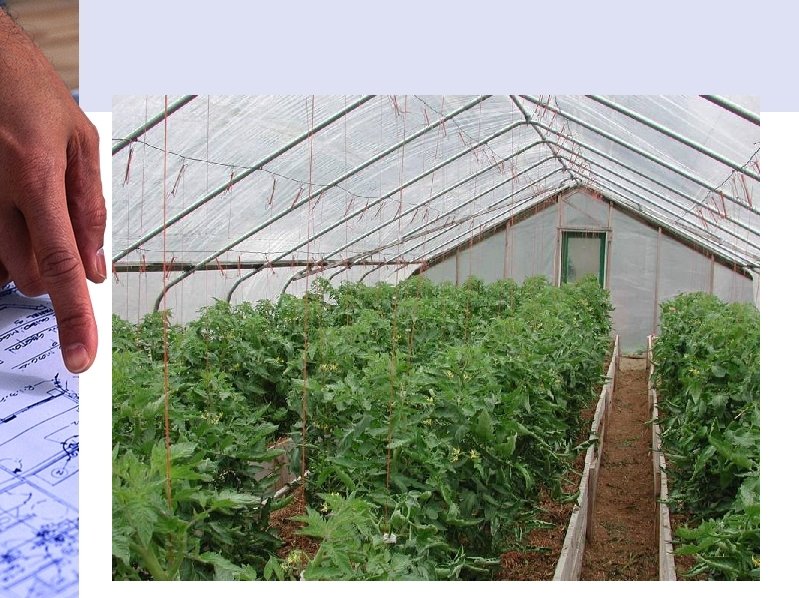



 Sawtooth Construction
Sawtooth Construction



