3c5da89c2d88d0b0ea71e1df06aa812e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Green IT December 2, 2008 14 th World Electronics Forum India 2008 New Delhi, India
What is Green IT? Green IT entails energy-saving in IT devices and using IT devices to save energy in society. Why Green IT? IT devices will continue to increase. Green IT will be critical in reducing the power consumption of these devices. The rapid worldwide spread of IT devices may lift the current level nine times by 2025 to account for more than 15 percent of world power consumption, and around six percent of total energy consumption. Given this trend, saving energy both in and through IT devices (Green IT) will be critical. 1
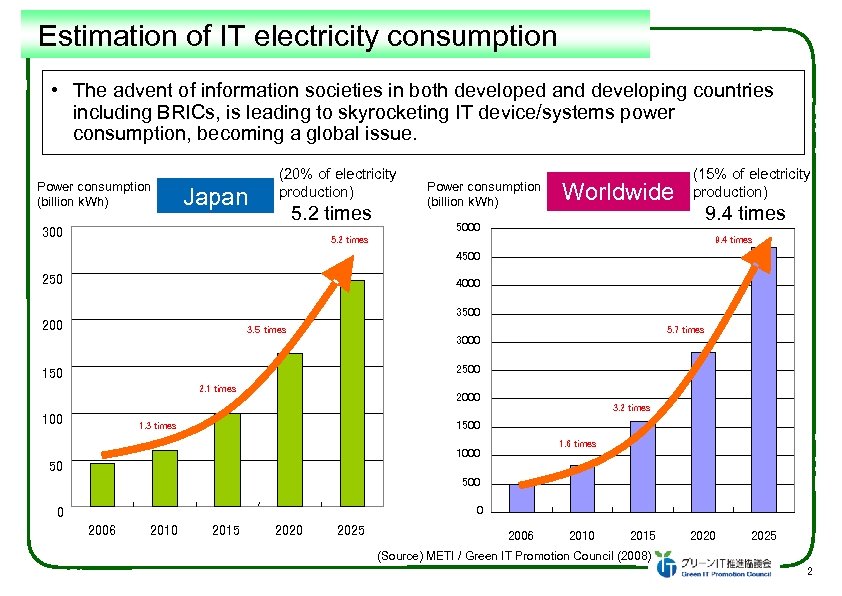
Estimation of IT electricity consumption • The advent of information societies in both developed and developing countries including BRICs, is leading to skyrocketing IT device/systems power consumption, becoming a global issue. Power consumption (billion k. Wh) Japan (20% of electricity production) 5. 2 times 300 Power consumption (billion k. Wh) Worldwide (15% of electricity production) 9. 4 times 5000 5. 2 times 9. 4 times 4500 250 4000 3500 200 3. 5 times 5. 7 times 3000 2500 150 2. 1 times 100 2000 3. 2 times 1500 1. 3 times 1. 6 times 1000 50 500 0 0 2006 2010 2015 2020 2025 (Source) METI / Green IT Promotion Council (2008) 2

I. The Green IT Promotion Council (GIPC) 3

Establishment of the Green IT Promotion Council ○ The industry-led Green IT Promotion Council was launched on 1 February 2008. Members include seven IT-related groups as well as auto, construction and distribution-related groups. Intel, IBM and Microsoft and many other offshore firms also participate, with Japan’s Green IT initiative attracting strong international interest and high hopes. ■Establishment: 1 February 2008 ■Title: Green IT Promotion Council ■ Member companies, institutions and groups: 216 (also includes foreign firms) 【 Initial members: 】 Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA) The Japan Electrical Manufacturers’ Association (JEMA) Japan Electric Measuring Instruments Manufacturers’ Association (JEMIMA) Communications and Information network Association of Japan (CIAJ) Japan Business Machine and Information System Industries Association (JBMIA) Japan Information Technology Services Industry Association (JISA) Japan Users Association of Information Systems (JUAS) Action program * Raising awareness of the environmental contribution made by new technologies and IT technologies and disseminating environmental and IT management * Strengthening international linkages with offshore groups, holding international conferences * Selecting and creating a roadmap for IT energy-saving technologies * Quantitative surveys and analyses on reduction of the environmental burden (possible CO 2 emission reductions, etc. ) 4

Communicating Green IT to the world ◆ The Green IT International Symposium was held in Tokyo on 29 May. Many major offshore firms also participated, sending a ‘Green IT’ message from Japan to the G 8 Hokkaido Toyako Summit. ◆ Following the Summit too, the Council hold a Green IT Forum and an exhibition at CEATEC to boost Japan’s Green IT leadership profile. Fora in the Asian region will also be used. ◆The Council launched a website at the end of April, which will be linked to the Green IT sites of our various member firms to raise the international profile of Green IT. Partnerships will also be developed with the Climate Savers Computing Initiative and The Green Grid. < Outline of the Green IT International Symposium> 1. Date and venue: 29 May 2008, The Prince Park Tower Tokyo 2. Host: Green IT Promotion Council Co-host: New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) 3. Offshore participants: Senior Vice Presidents from Intel, AMD and Sun Microsystems, representatives from IBM, Dell, Cisco Systems, The Green Grid, Climate Savers Computing Initiative, and the World Semiconductor Council, etc. 4. Press conference (21 May) 5. Reception and signing ceremony (28 May) 5
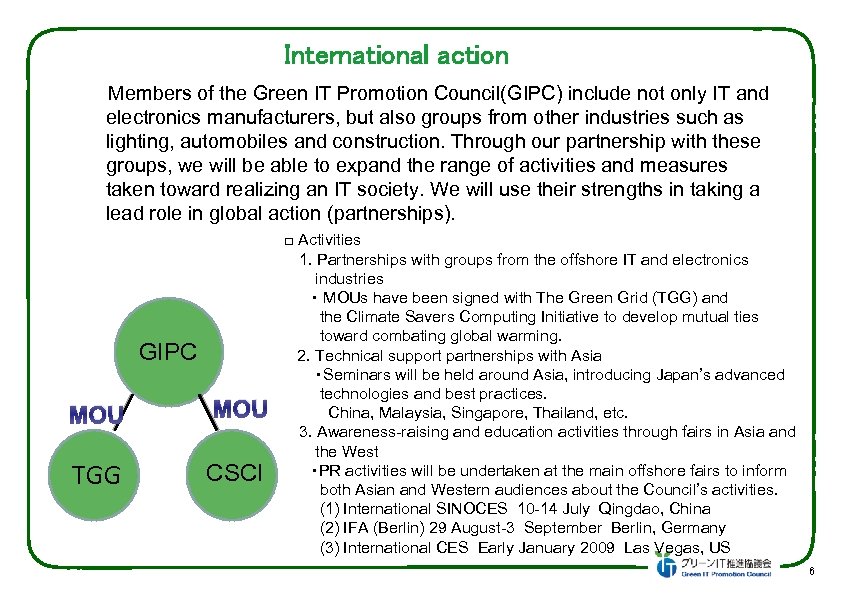
International action Members of the Green IT Promotion Council(GIPC) include not only IT and electronics manufacturers, but also groups from other industries such as lighting, automobiles and construction. Through our partnership with these groups, we will be able to expand the range of activities and measures taken toward realizing an IT society. We will use their strengths in taking a lead role in global action (partnerships). GIPC MOU TGG CSCI □ Activities 1. Partnerships with groups from the offshore IT and electronics industries ・ MOUs have been signed with The Green Grid (TGG) and the Climate Savers Computing Initiative to develop mutual ties toward combating global warming. 2. Technical support partnerships with Asia ・Seminars will be held around Asia, introducing Japan’s advanced technologies and best practices. China, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, etc. 3. Awareness-raising and education activities through fairs in Asia and the West ・PR activities will be undertaken at the main offshore fairs to inform both Asian and Western audiences about the Council’s activities. (1) International SINOCES 10 -14 July Qingdao, China (2) IFA (Berlin) 29 August-3 September Berlin, Germany (3) International CES Early January 2009 Las Vegas, US 6

G 8 Toyako Summit ○ At the July G 8 Toyako Summit, the Green IT Promotion Council set up Green IT exhibits in the Zero Emission House within the International Media Center and in resort hotels and other spots. The aim was to communicate Japan’s Green IT concept to the world via government representatives from the various countries and the domestic and offshore press. Zero Emission House This house of the near future was equipped with a photovoltaic power generation system, fuel cells, advanced robots, and other leading-edge technologies. Source: METI Home page Equipment on display • • • Solar cell panels Home Energy Management System(HEMS) LCD TV, Organic EL TV Energy-saving home appliances, information appliances and systems Portable high-capacity lithium ion battery power supply 7

“Green University Project” • • • Development of totally integrated energy management system for university buildings by deploying many wireless sensors. Development of low-cost, high-performance, and long-lasting sensors, and standardization of output of information of real time power consumption of air conditioners and IT devices Model projects which are expected to be adopted by enterprises e. g. Green University of Tokyo Dr. Komiyama, the president of University of Tokyo, announced “ 15% CO 2 reduction by 2012, 50% CO 2 reduction by 2030” at the entrance ceremony this year. Backgrounds • Large CO 2 emitter • Accumulating cutting-edge sci-tech • Large influence on other universities Objectives • Exercise a pilot program to realize an environment-friendly information society ・Create new information business which realize environmental recognition based on scientific information and knowledge and provide basic information for business innovation 8
Reference: Japan’s Energy Conservation Law and Energy-Saving Home Appliance Popularization Measures Regulations under the Energy Conservation Law (Law Concerning the Rationalization of Energy Use) * This law was formulated in 1979 to secure and ensure the efficient use of fuel resources. Its aim was to develop measures promoting the rational use of energy in (a) factories and workplaces, (b) transportation, (c) housing and buildings, and (d) machinery and equipment. * To constrain household and transportation energy consumption in particular, ‘Top Runner’ standards have been set since 1998 as benchmarks promoting greater energy efficiency by product type. Popularizing energy-saving appliances * To promote energy-saving measures in the household sector, home appliance manufacturers, retailers, consumers and other related parties are working together to popularize energy-saving home appliances (TVs, air conditioners, fridges, lighting, etc. ). ‘Top Runner’ standards under the Energy Conservation Law * This program covers 21 product types, including TVs, DVD recorders, calculators, air-conditioners, fridges, lighting, and cars. * Energy performance standards are set at the same level or higher than the best performance value of those products currently on the market. The year by which the target standard should be achieved is also specified for each product type. * Energy consumption efficiency and other energy information must be indicated in product catalogues and on machinery, etc. Energy-saving home appliance popularization measures Energy-Saving Home Appliance Popularization Forum (est. Oct. 2007) * Works to boost the market penetration of energy-saving home appliances through (a) a unified promotion campaign, (b) provision of information to consumers, and (c) the development of home energy conservation diagnosis tools. Energy-Saving Lighting Forum (est. May 2008) * Aims to replace all general incandescent bulbs by 2012 with, in principle, products with outstanding energy efficiency, such as bulb-type fluorescents (established under the Energy -Saving Home Appliance Popularization Forum). 9

CEATEC 2008 Sep.30 – Oct. 4, 2008 Makuhari Messe ・Green IT Symposium Held as part of CEATEC. * Presentation by the company receiving the METI Minister’s Award * Address by the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry * Introduction to Green IT Promotion Council activities * Introduction to company initiatives, etc. ・Green IT Pavilion Designed to boost the visibility of green IT, the Green IT Pavilion introduced Green IT Promotion Council activities and Japanese companies’ green IT products, services and initiatives. Products and technologies receiving Green IT Awards were also exhibited, providing a showcase for Japan’s energy-saving technologies. 10

CEATEC 2008 Sep.30 – Oct. 4, 2008 Makuhari Messe ・Green IT Handbook ・Green IT Awards Presented for IT devices, software, services, solutions and other products supplied by companies that demonstrate an outstanding energysaving effect. * METI Minister’s Award * Commerce and Information Policy Director- General’s Award * Green IT Promotion Council Chairman’s Award * Green IT Award Judging Committee Special Award Brings together information on the activities of the Green IT Promotion Council and member companies in a convenient handbook form. Energy Saving of IT NEC: "ECO CENTER" Energy-Saving Server METI Minister’s Award Energy Saving by IT Sony and Sony Life: Construction and Operation of cooling and heating system in "Sony City, " Sony headquarters building 11

II. Effects of Green IT Promotion Outline of analysis results 12
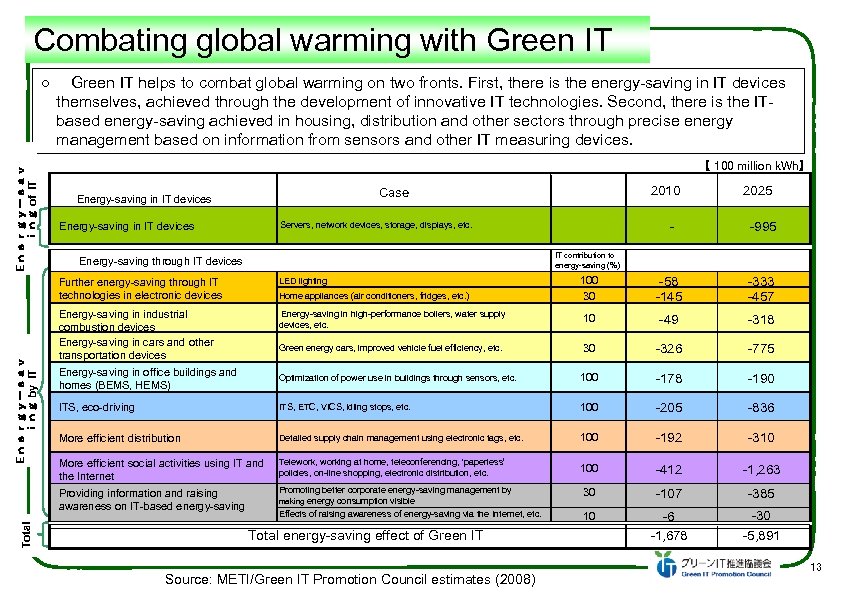
Combating global warming with Green IT Energy-sav ing of IT ○ Green IT helps to combat global warming on two fronts. First, there is the energy-saving in IT devices themselves, achieved through the development of innovative IT technologies. Second, there is the ITbased energy-saving achieved in housing, distribution and other sectors through precise energy management based on information from sensors and other IT measuring devices. 【 100 million k. Wh】 2010 Case Energy-saving in IT devices - -995 100 30 -58 -145 -333 -457 Servers, network devices, storage, displays, etc. Energy-saving in IT devices 2025 IT contribution to energy-saving (%) Energy-saving through IT devices Total LED lighting Energy-saving in industrial combustion devices Energy-saving in cars and other transportation devices Energy-saving in office buildings and homes (BEMS, HEMS) Energy-saving in high-performance boilers, water supply devices, etc. 10 -49 -318 Green energy cars, improved vehicle fuel efficiency, etc. 30 -326 -775 Optimization of power use in buildings through sensors, etc. 100 -178 -190 ITS, eco-driving ITS, ETC, VICS, idling stops, etc. 100 -205 -836 More efficient distribution Detailed supply chain management using electronic tags, etc. 100 -192 -310 More efficient social activities using IT and the Internet Telework, working at home, teleconferencing, ‘paperless’ policies, on-line shopping, electronic distribution, etc. 100 -412 -1, 263 Providing information and raising awareness on IT-based energy-saving Energy-sav ing by IT Further energy-saving through IT technologies in electronic devices Promoting better corporate energy-saving management by making energy consumption visible Effects of raising awareness of energy-saving via the Internet, etc. 30 -107 -385 10 -6 -30 -1, 678 -5, 891 Home appliances (air conditioners, fridges, etc. ) Total energy-saving effect of Green IT Source: METI/Green IT Promotion Council estimates (2008) 13
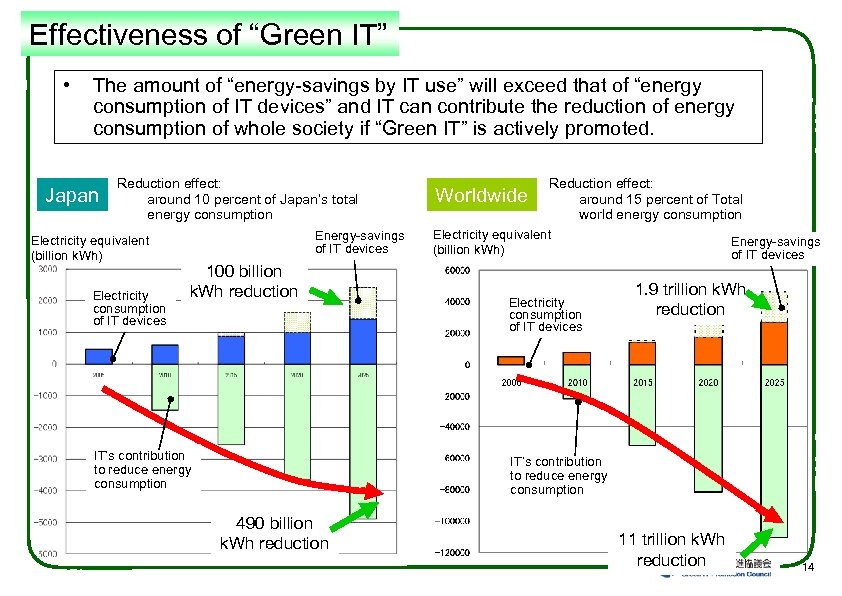
Effectiveness of “Green IT” • The amount of “energy-savings by IT use” will exceed that of “energy consumption of IT devices” and IT can contribute the reduction of energy consumption of whole society if “Green IT” is actively promoted. Japan Reduction effect: around 10 percent of Japan’s total energy consumption Electricity equivalent (billion k. Wh) Electricity consumption of IT devices Energy-savings of IT devices 100 billion k. Wh reduction IT’s contribution to reduce energy consumption Worldwide Reduction effect: around 15 percent of Total world energy consumption Electricity equivalent (billion k. Wh) Electricity consumption of IT devices Energy-savings of IT devices 1. 9 trillion k. Wh reduction IT’s contribution to reduce energy consumption 490 billion k. Wh reduction 11 trillion k. Wh reduction 14

III. Government Initiatives for Green IT 15

Government Initiatives for “Green IT” In May 2007, in his "Invitation to Cool Earth 50" environmental proposal, then Prime Minister Shinzo Abe proposed the "cutting global emissions [of greenhouse gases] by half from the current level by 2050 as a common goal for the entire world. " Innovative new technologies will be needed to achieve such a major reduction in greenhouse gases. In March 2008 METI announced the "Cool Earth Energy Innovative Technology Plan. " -"21" Core Energy Innovative Technologies - Improved efficiency Energy Supply Side Low carbonification ②High-efficiency coal thermal generation Power generation/ delivery ③Carbon capture and storage (CCS) ①High-efficiency natural gas thermal generation ⑥High-efficiency ultraconductor power transmission Logistics Energy Demand Side Industry ⑧Fuel cell vehicles ⑦Advanced road transport systems ⑨Plug-in hybrid/ electric vehicles ⑪Innovative materials/manufacturing/ processing technologies Consumer ⑬Energy-saving housing/ buildings ⑯Ultrahigh-efficiency heat pumps Cross-category ⑭Next-generation highefficiency lighting ⑰Energy-saving information equipment/systems ⑲High-performance electricity storage ⑳Power electronics ⑤Advanced nuclear ④Innovative power generation solar power generation ⑩Biomass alternative fuels ⑫Innovative steel manufacturing technologies ⑮Fixed fuel cells * EMS: Energy Management System HEMS: House Energy Management System BEMS: Building Energy Management System ⑱HEMS/BEMS/Region-level EMS※ 21 Hydrogen mfg/shipping/storage ③CCS (again) 16
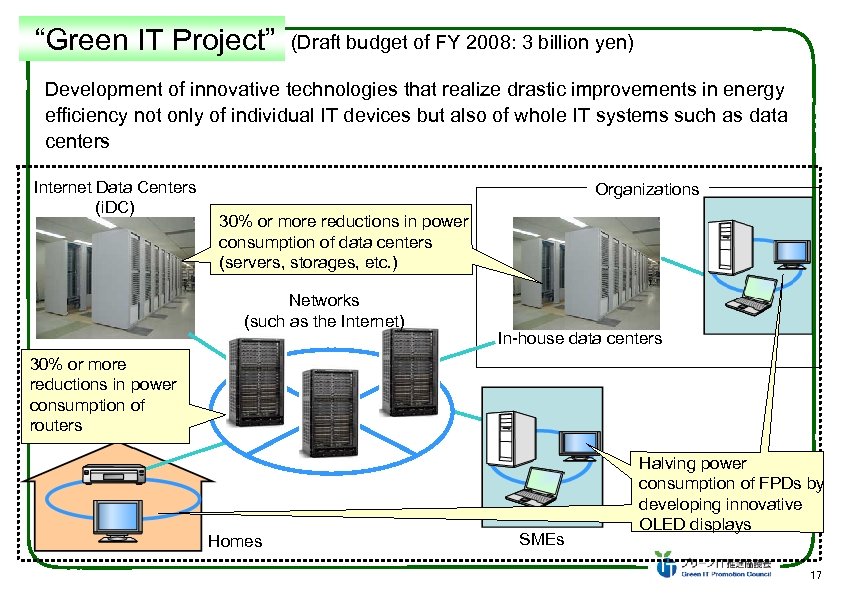
“Green IT Project” (Draft budget of FY 2008: 3 billion yen) Development of innovative technologies that realize drastic improvements in energy efficiency not only of individual IT devices but also of whole IT systems such as data centers Internet Data Centers (i. DC) Organizations 30% or more reductions in power consumption of data centers (servers, storages, etc. ) Networks (such as the Internet) In-house data centers 30% or more reductions in power consumption of routers Homes SMEs Halving power consumption of FPDs by developing innovative OLED displays 17
IV. Examples of Energy-Saving through Green IT 18
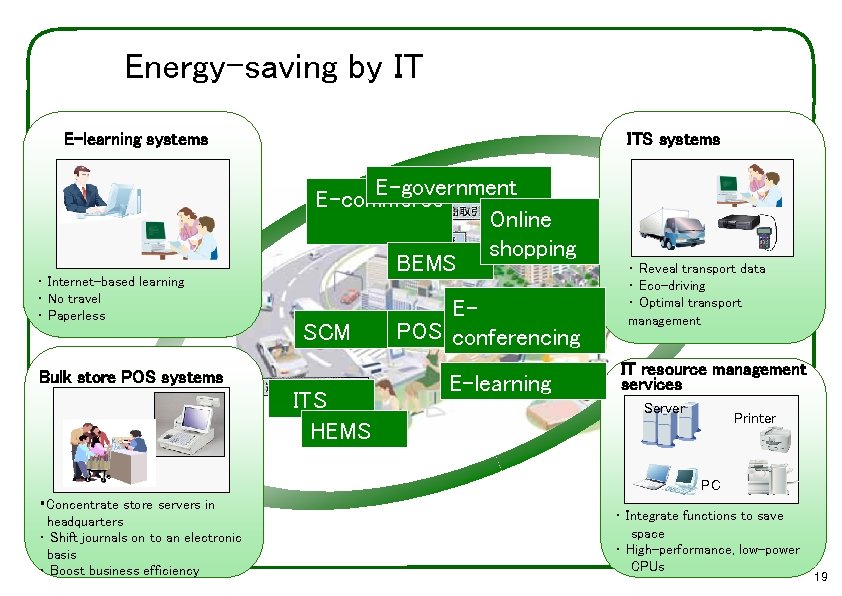
Energy-saving by IT E-learning systems ・ Internet-based learning ・ No travel ・ Paperless Bulk store POS systems ITS systems E-government E-commerce Online shopping BEMS SCM ITS HEMS EPOS conferencing E-learning ・ Reveal transport data ・ Eco-driving ・ Optimal transport management IT resource management services Server Printer PC ・Concentrate store servers in headquarters ・ Shift journals on to an electronic basis ・ Boost business efficiency ・ Integrate functions to save space ・ High-performance, low-power CPUs 19 19
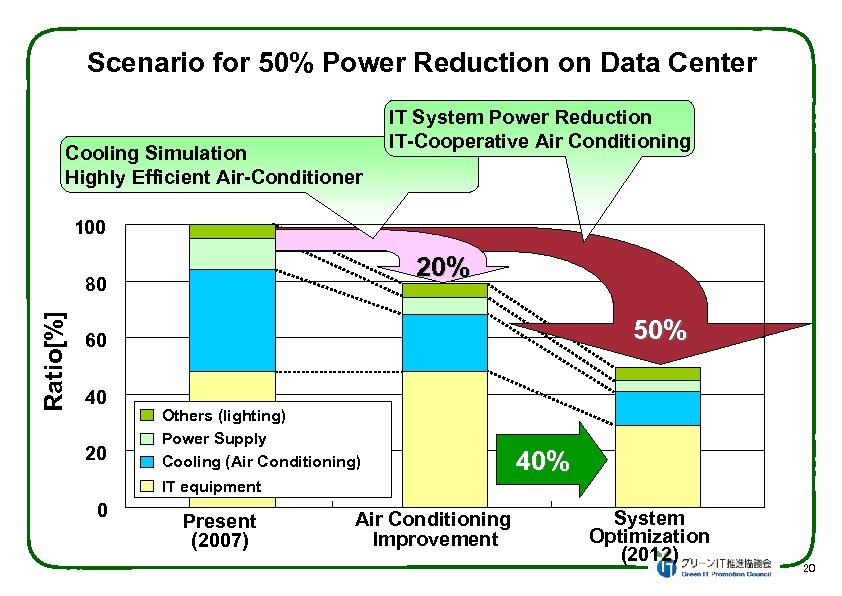
Scenario for 50% Power Reduction on Data Center Cooling Simulation Highly Efficient Air-Conditioner IT System Power Reduction IT-Cooperative Air Conditioning 100 20% Ratio[%] 80 50% 60 40 20 Others (lighting) Power Supply Cooling (Air Conditioning) 40% IT equipment 0 Present (2007) Air Conditioning Improvement System Optimization (2012) 20
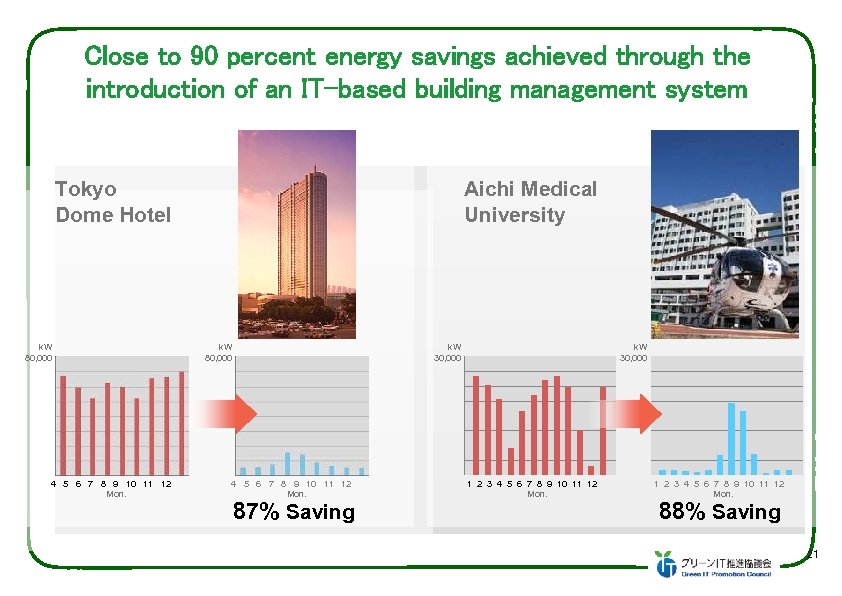
Close to 90 percent energy savings achieved through the introduction of an IT-based building management system Tokyo Dome Hotel k. W 80, 000 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Mon. Aichi Medical University k. W 80, 000 k. W 30, 000 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Mon. 87% Saving k. W 30, 000 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Mon. 88% Saving 21

V. GIPC’s Activity plan in Asia 22

GIPC’s Activity plan in Asia ◆Cooperation in holding seminars or symposium about “Green IT” in Asian countries. (coordinate to send lecturers, etc) ◆Cooperation in “Green IT” exhibit ion in Asian countries (Exhibition in other countries or exhibition from Japan). ◆Technical Cooperation for inducting “Green IT” in Asian countries(coordinate to send engineers, etc. ) ◆Cooperation in establishing “Green IT Association” in each Asian countries(provide information) ◆ Exchange information on various matters on “Green IT” 23

Actual result of GIPC's Activities in Asia July 10 -13, 2008 2009 SINOCES Quingdao International Convention Center, China July 15 -16, 2008 5 th Asia Electronics Forum New World Hotel, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Oct. 17 -20, 2008 China International Energy Saving and Environmental Protection Exhibition Beijing Exhibition Center, China Nov. 12 -15, 2008 JES Shanghai 2008 Shanghai New International Expo Center, China Dec. 1 -5, 2008 14 th World Electronic Forum 2008 New Delhi, India Plans for the future Jan. 13 -14, 2009 International Symposium of Green Business IT Council, Korea Seoul Walkerhill Hotel, Korea Feb. 16 -20, 2009 International Green IT symposium in Asia Singapore, Kuala Lumpur, Bangkok 2009 GIPC is planning to diagnose buildings such as offices and data centers in order to improve energy efficiency in Asia. 24
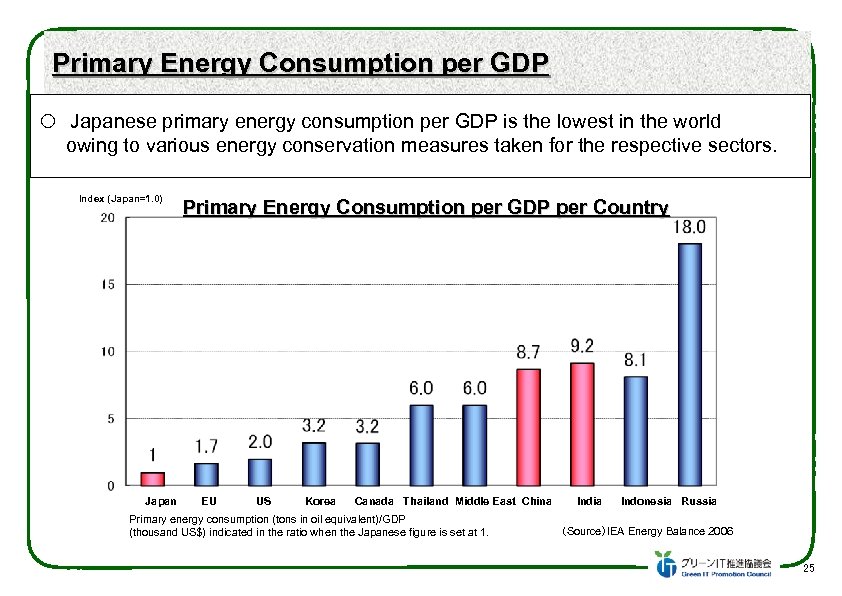
Primary Energy Consumption per GDP Japanese primary energy consumption per GDP is the lowest in the world owing to various energy conservation measures taken for the respective sectors. Index (Japan=1. 0) Japan Primary Energy Consumption per GDP per Country EU US Korea Canada Thailand Middle East China Primary energy consumption (tons in oil equivalent)/GDP (thousand US$) indicated in the ratio when the Japanese figure is set at 1. India Indonesia Russia (Source)IEA Energy Balance 2006 25

END OF PRESENTATION Thank you very much for your kind attention. http: //www. greenit-pc. jp/e/ 26
3c5da89c2d88d0b0ea71e1df06aa812e.ppt