a3ff28e2479d3b99d4d6f37426047c97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Green House Lighting Shannon Lawrence HORT 6050
Green House Lighting Shannon Lawrence HORT 6050
 What is Light? -Light is electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength between 4, 000 (violet) to about 7, 700 (red) angstroms -Utilized by plants during photosynthesis - Measured in Lumens and Foot Candles (for our purposes)
What is Light? -Light is electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength between 4, 000 (violet) to about 7, 700 (red) angstroms -Utilized by plants during photosynthesis - Measured in Lumens and Foot Candles (for our purposes)
 Lumens l It is the basic unit of light l Describes the total amount of light present
Lumens l It is the basic unit of light l Describes the total amount of light present
 Foot Candle l Basic unit of light intensity l Measured in Square Feet l One lumen per sq. ft. = 1 foot candle (500 lumens per sq. ft. = 500 fc)
Foot Candle l Basic unit of light intensity l Measured in Square Feet l One lumen per sq. ft. = 1 foot candle (500 lumens per sq. ft. = 500 fc)
 How Much Light to Expect l Average lit room is about 7 foot candles l Summer days can be close to 12, 000 Foot Candles l Cloudy days can vary from around 1, 000 to below 300 Foot Candles l Full Moon Light-. 02 Foot Candles l Starlight-. 000011
How Much Light to Expect l Average lit room is about 7 foot candles l Summer days can be close to 12, 000 Foot Candles l Cloudy days can vary from around 1, 000 to below 300 Foot Candles l Full Moon Light-. 02 Foot Candles l Starlight-. 000011
 Why Light is important? When light is absorbed by a plant leaf, it is used as the main energy source to start extremely important processes such as photosynthesis (Light, CO 2, and Water) l It also aids in the maintaining of homeostasis. l l http: //www. bbc. co. uk/gardening/htbg/videos/the_i mportance_of_light. shtml
Why Light is important? When light is absorbed by a plant leaf, it is used as the main energy source to start extremely important processes such as photosynthesis (Light, CO 2, and Water) l It also aids in the maintaining of homeostasis. l l http: //www. bbc. co. uk/gardening/htbg/videos/the_i mportance_of_light. shtml
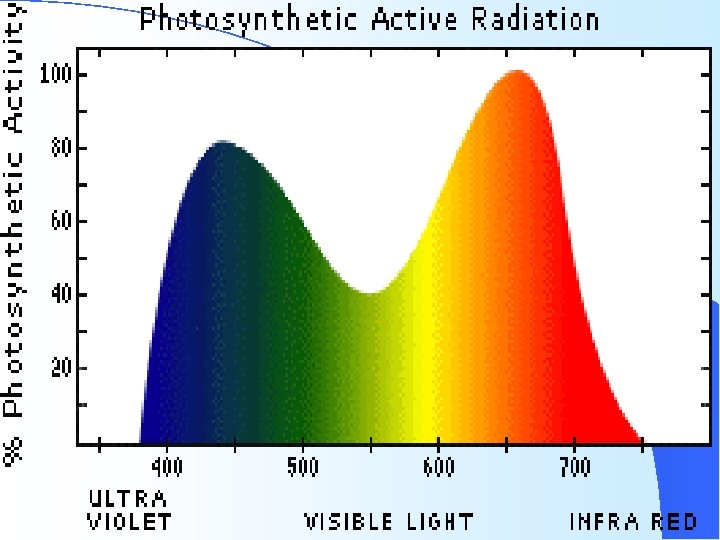
 200 - 280 nm 280 - 315 nm 315 - 380 nm 380 - 400 nm UVC ultraviolet range which is extremely harmful to plants because it is highly toxic. Includes harmful UVB ultraviolet light which causes plants colors to fade. Range of UVA ultraviolet light which is neither harmful nor beneficial to plant growth. Start of visible light spectrum. Process of chlorophyll absorption begins. 400 - 520 nm 520 - 610 nm 610 - 720 nm Peak absorption by chlorophyll occurs, and a strong influence on photosynthesis. (promotes vegetative growth) green, yellow, and orange bands - less absorption by pigments. red band. Large absorption by chlorophyll occurs, most significant influence on photosynthesis. (promotes flowering and budding) 720 - 1000 There is little absorption by chlorophyll here. Flowering and nm germination is influenced. Totally infrared range. All energy absorbed at this point is 1000+ nm converted to heat.
200 - 280 nm 280 - 315 nm 315 - 380 nm 380 - 400 nm UVC ultraviolet range which is extremely harmful to plants because it is highly toxic. Includes harmful UVB ultraviolet light which causes plants colors to fade. Range of UVA ultraviolet light which is neither harmful nor beneficial to plant growth. Start of visible light spectrum. Process of chlorophyll absorption begins. 400 - 520 nm 520 - 610 nm 610 - 720 nm Peak absorption by chlorophyll occurs, and a strong influence on photosynthesis. (promotes vegetative growth) green, yellow, and orange bands - less absorption by pigments. red band. Large absorption by chlorophyll occurs, most significant influence on photosynthesis. (promotes flowering and budding) 720 - 1000 There is little absorption by chlorophyll here. Flowering and nm germination is influenced. Totally infrared range. All energy absorbed at this point is 1000+ nm converted to heat.
 Determine Your Lighting Needs! l Know what the requirements are for your Know crop l Know the type of weather you have Know l If beginning in a new area, look at old look weather data to determine the number of cloudy days for years past.
Determine Your Lighting Needs! l Know what the requirements are for your Know crop l Know the type of weather you have Know l If beginning in a new area, look at old look weather data to determine the number of cloudy days for years past.
 What are the options? l Natural… you get it whether you like it or not! l Artificial…like a Loan Shark… you may need one, but its gonna cost you. l Shading… A good dark side? ? ?
What are the options? l Natural… you get it whether you like it or not! l Artificial…like a Loan Shark… you may need one, but its gonna cost you. l Shading… A good dark side? ? ?
 Natural Lighting l Cheap source of lighting and is the first choice for most growers l In the South, sunlight is usually not a problem… usually! l Intensity Can Be Controlled (with labor and or investment) l Helps warm a greenhouse during winter. l It is what most plants are accustomed to.
Natural Lighting l Cheap source of lighting and is the first choice for most growers l In the South, sunlight is usually not a problem… usually! l Intensity Can Be Controlled (with labor and or investment) l Helps warm a greenhouse during winter. l It is what most plants are accustomed to.
 Negative Aspects of Natural Lighting l Uncontrollable- We must accept what nature gives us. (Cloudy, dark) l Not all plants are sun lovers and can tolerate full sun- African Violets (only about 1000 fc)
Negative Aspects of Natural Lighting l Uncontrollable- We must accept what nature gives us. (Cloudy, dark) l Not all plants are sun lovers and can tolerate full sun- African Violets (only about 1000 fc)
 Artificial Lighting
Artificial Lighting
 Artificial Light l Enables a grower to extend the growing day l Can be used for night breaks on plants(shortens day length) l Can be utilized on cloudy days, so plants can perform better l Can provide red light or blue light l Red for flowering/Blue for Vegatative
Artificial Light l Enables a grower to extend the growing day l Can be used for night breaks on plants(shortens day length) l Can be utilized on cloudy days, so plants can perform better l Can provide red light or blue light l Red for flowering/Blue for Vegatative
 Not So Good Things About Artificial Light l l l Initial Cost is sometimes extreme Your greenhouse may need upgrades (electrical, support for lights, rearrangement, etc) Use electricity Electricity may not always be available (Thunderstorms in the South) All add up to $$$$
Not So Good Things About Artificial Light l l l Initial Cost is sometimes extreme Your greenhouse may need upgrades (electrical, support for lights, rearrangement, etc) Use electricity Electricity may not always be available (Thunderstorms in the South) All add up to $$$$
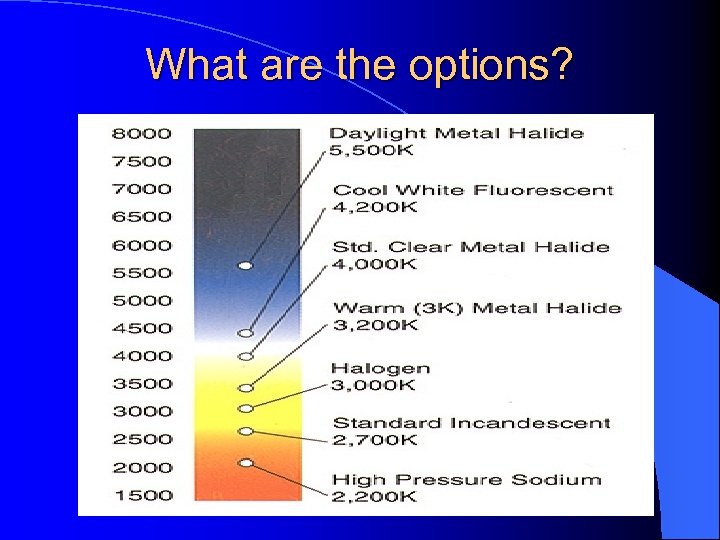 What are the options?
What are the options?
 What are the Options?
What are the Options?
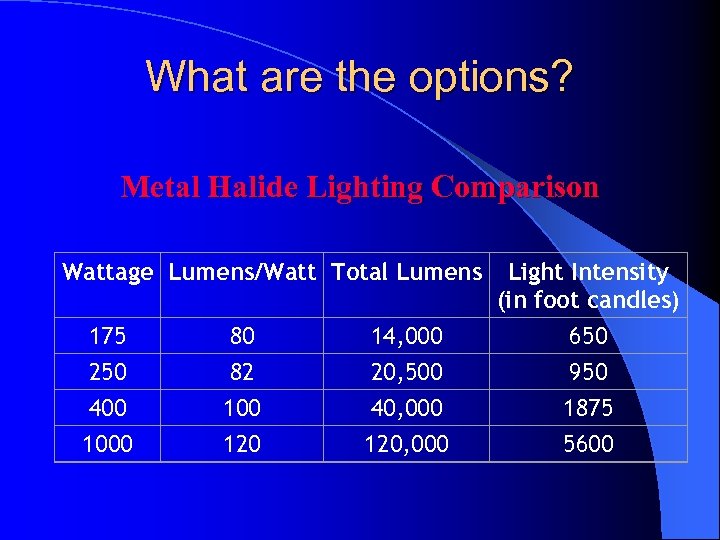 What are the options? Metal Halide Lighting Comparison Wattage Lumens/Watt Total Lumens 175 250 400 1000 80 82 100 120 14, 000 20, 500 40, 000 120, 000 Light Intensity (in foot candles) 650 950 1875 5600
What are the options? Metal Halide Lighting Comparison Wattage Lumens/Watt Total Lumens 175 250 400 1000 80 82 100 120 14, 000 20, 500 40, 000 120, 000 Light Intensity (in foot candles) 650 950 1875 5600
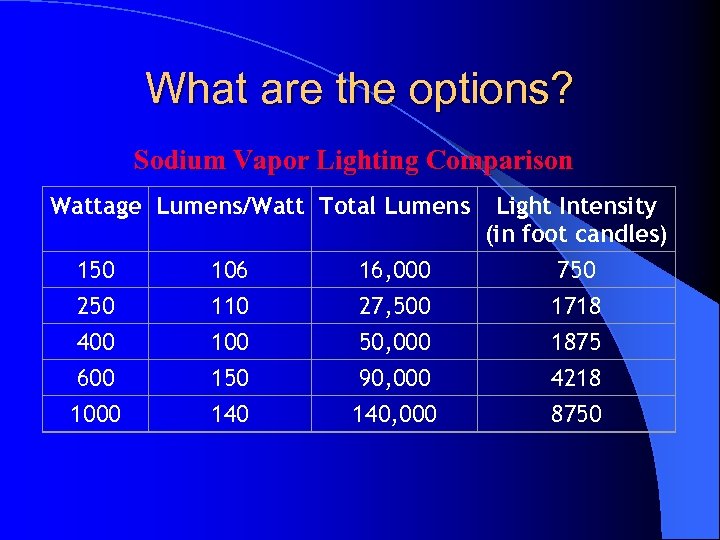 What are the options? Sodium Vapor Lighting Comparison Wattage Lumens/Watt Total Lumens 150 250 400 600 106 110 100 150 140 16, 000 27, 500 50, 000 90, 000 140, 000 Light Intensity (in foot candles) 750 1718 1875 4218 8750
What are the options? Sodium Vapor Lighting Comparison Wattage Lumens/Watt Total Lumens 150 250 400 600 106 110 100 150 140 16, 000 27, 500 50, 000 90, 000 140, 000 Light Intensity (in foot candles) 750 1718 1875 4218 8750
 COST l Around $2. 65 ft² for High Intensity Discharge l (light wattage / 1000) x electricity cost per kilowatt hour = Operating cost per hr l operating cost per hour x hours used per month = Operating cost per month
COST l Around $2. 65 ft² for High Intensity Discharge l (light wattage / 1000) x electricity cost per kilowatt hour = Operating cost per hr l operating cost per hour x hours used per month = Operating cost per month
 HID Light Output Primary Growing Area 100 watts 2' x 2' 250 watts 3' x 3' 400 watts 5' x 5' 600 watts 6' x 6' 1000 watts 8' x 8' Supplemental Growing Area 3' x 3' 5' x 5' 8' x 8' 10' x 10' 12' x 12'
HID Light Output Primary Growing Area 100 watts 2' x 2' 250 watts 3' x 3' 400 watts 5' x 5' 600 watts 6' x 6' 1000 watts 8' x 8' Supplemental Growing Area 3' x 3' 5' x 5' 8' x 8' 10' x 10' 12' x 12'
 l. Unifier 400 MH (36, 000 lumens) l. Price: $215 l. Unifier 1000 MH (110, 000 lumens) l. Price: $255 l. Unifier 400 HPS (50, 000 lumens) l. Price: $229 l. Unifier 1000 HPS (140, 000 lumens) l. Price: $319 l 30 x 75 GH=2250 ft²: 2250/ 144= 15. 625 or 16 1000 w HPS lights 16 l 16 x $319= $5104/2250= $2. 27 ft² for a good supplemental light $5104 $2. 27 system (Initial Cost)
l. Unifier 400 MH (36, 000 lumens) l. Price: $215 l. Unifier 1000 MH (110, 000 lumens) l. Price: $255 l. Unifier 400 HPS (50, 000 lumens) l. Price: $229 l. Unifier 1000 HPS (140, 000 lumens) l. Price: $319 l 30 x 75 GH=2250 ft²: 2250/ 144= 15. 625 or 16 1000 w HPS lights 16 l 16 x $319= $5104/2250= $2. 27 ft² for a good supplemental light $5104 $2. 27 system (Initial Cost)
 Shade
Shade
 Benefits and Drawbacks l l l Can be used to keep plants from burning up Can be used to lower the temperature of greenhouse Can grow certain plants outside in a shade house (Low overhead) Pulling shade can be labor intensive $$$$ Can be automated Sometimes it is unwanted (Too much Superstructure)
Benefits and Drawbacks l l l Can be used to keep plants from burning up Can be used to lower the temperature of greenhouse Can grow certain plants outside in a shade house (Low overhead) Pulling shade can be labor intensive $$$$ Can be automated Sometimes it is unwanted (Too much Superstructure)
 A Few Recommendations By A Supplier -30% Chrysanthemums, Asters, Snapdragons, Geraniums l -47% Various Vegetables & Herbs, Iris, Lilies, Gloxinias, Misc. Bedding Plants l -55% Bromeliads, Ficus, Orchids l -63% Orchids – l 73% Ferns, Philodendron, Orchids l -78% Ginseng (Special lath weave fabric for ginseng growers) l -80% Similar to 73% l -92% Aglaonema (Chinese Evergreen) l
A Few Recommendations By A Supplier -30% Chrysanthemums, Asters, Snapdragons, Geraniums l -47% Various Vegetables & Herbs, Iris, Lilies, Gloxinias, Misc. Bedding Plants l -55% Bromeliads, Ficus, Orchids l -63% Orchids – l 73% Ferns, Philodendron, Orchids l -78% Ginseng (Special lath weave fabric for ginseng growers) l -80% Similar to 73% l -92% Aglaonema (Chinese Evergreen) l
 $. 13 sq/ft $. 15 sq/ft $. 16 sq/ft $. 18 sq/ft $. 20 sq/ft $. 24 sq/ft $. 25 sq/ft 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% Cost of Shade
$. 13 sq/ft $. 15 sq/ft $. 16 sq/ft $. 18 sq/ft $. 20 sq/ft $. 24 sq/ft $. 25 sq/ft 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% Cost of Shade
 What is right for you? Evaluate your crop lighting needs l Determine if you are in a low/medium/high light intensity grower l Weigh the costs- can extra expenses be justified? l
What is right for you? Evaluate your crop lighting needs l Determine if you are in a low/medium/high light intensity grower l Weigh the costs- can extra expenses be justified? l


