19777a00ad0846282bc0c62dac45f008.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Greek Achievements • • • Key Terms Socrates Plato Aristotle reason Socrates Euclid Hippocrates The Big Idea : Ancient Greeks made lasting contributions in the Arts, philosophy, and science. Plato Aristotle
Greek Achievements • • • Key Terms Socrates Plato Aristotle reason Socrates Euclid Hippocrates The Big Idea : Ancient Greeks made lasting contributions in the Arts, philosophy, and science. Plato Aristotle
 Greek sculpture is admired for its realism and details. The Arts : Statues were made of stone or marble. • Greeks were master artists. • They were so good because they paid attention to fine detail. • They also studied the human body. • Many of their sculptures looked like they could come to life.
Greek sculpture is admired for its realism and details. The Arts : Statues were made of stone or marble. • Greeks were master artists. • They were so good because they paid attention to fine detail. • They also studied the human body. • Many of their sculptures looked like they could come to life.
 The Arts : Paintings • Greek paintings are also admired for their detail. • Many of the painted scenes show athletics, their gods or scenes from myths. • Scenes were usually done in red and black.
The Arts : Paintings • Greek paintings are also admired for their detail. • Many of the painted scenes show athletics, their gods or scenes from myths. • Scenes were usually done in red and black.
 The Arts : Architecture • The Greeks took great care in designing their buildings inspired by proportions of the human body. • They wanted their buildings to be a The pillars of the Greek temples appear perfectly straight. Greeks understood that in order reflection of their city. for pillars to appear to be straight, they needed to actually be wider in the middle.
The Arts : Architecture • The Greeks took great care in designing their buildings inspired by proportions of the human body. • They wanted their buildings to be a The pillars of the Greek temples appear perfectly straight. Greeks understood that in order reflection of their city. for pillars to appear to be straight, they needed to actually be wider in the middle.
 Inside the Parthenon stood a statue of Athena. The Parthenon was built by Pericles for Athena, the protector of Athens. The Parthenon has 46 columns. Once a year, the people of Athens held a festival in honor of Athena.
Inside the Parthenon stood a statue of Athena. The Parthenon was built by Pericles for Athena, the protector of Athens. The Parthenon has 46 columns. Once a year, the people of Athens held a festival in honor of Athena.
 Socrates Philosophy Plato • People began to question gods as the reason for life being the way it was. • These people who questioned life were called philosophers. • Philosophers believed in the power of the human mind the think and explain. Aristotle
Socrates Philosophy Plato • People began to question gods as the reason for life being the way it was. • These people who questioned life were called philosophers. • Philosophers believed in the power of the human mind the think and explain. Aristotle
 “What is love? ” “What is courage? ” Socrates • Socrates believed people should never stop looking for knowledge. • He was a teacher who taught people to ask questions of life. • He frustrated many and was accused of questioning the gods and corrupting youth. • For questioning the gods, he was condemned to death. At his death, his students watched him calmly take the poison and die.
“What is love? ” “What is courage? ” Socrates • Socrates believed people should never stop looking for knowledge. • He was a teacher who taught people to ask questions of life. • He frustrated many and was accused of questioning the gods and corrupting youth. • For questioning the gods, he was condemned to death. At his death, his students watched him calmly take the poison and die.
 The Republic discussed the ideal society based on justice and fairness. Plato I believed philosophers should rule because only we understand what was best. • Plato was Socrates’ student. • Plato also taught along with being a philosopher. • Plato had a famous school for philosophers and scientist to come and discuss ideas. • Plato wrote a famous philosophy work, The Republic.
The Republic discussed the ideal society based on justice and fairness. Plato I believed philosophers should rule because only we understand what was best. • Plato was Socrates’ student. • Plato also taught along with being a philosopher. • Plato had a famous school for philosophers and scientist to come and discuss ideas. • Plato wrote a famous philosophy work, The Republic.
 Aristotle, Plato’s student, was the greatest thinker in Greece. Aristotle was against greed but felt like you shouldn’t give away everything you own. • He believed in moderation, or finding a balance in life. • He believed moderation was based on reason, or clear and ordered thinking. • He believed people should think about the actions before doing them and predict how they will Aristotle was a master at logic, the process of making inferences. For example, if you know Socrates lived affect others. in Athens, and Athens is in Greece, Socrates must live in Greece and possibly be Athenian.
Aristotle, Plato’s student, was the greatest thinker in Greece. Aristotle was against greed but felt like you shouldn’t give away everything you own. • He believed in moderation, or finding a balance in life. • He believed moderation was based on reason, or clear and ordered thinking. • He believed people should think about the actions before doing them and predict how they will Aristotle was a master at logic, the process of making inferences. For example, if you know Socrates lived affect others. in Athens, and Athens is in Greece, Socrates must live in Greece and possibly be Athenian.
 Greeks also began recording history by writing about it. They tried to write neutral accounts of what happened in Greece. The Arts : Writing • Greeks created drama and historical writing. • Their writing was a large source of entertainment. • They performed tragedies and comedies, writing about wars and bringing light to them. Aeschylus and Sophocles were among the best tragedy writers. Aristophanes was a famous comedy writer.
Greeks also began recording history by writing about it. They tried to write neutral accounts of what happened in Greece. The Arts : Writing • Greeks created drama and historical writing. • Their writing was a large source of entertainment. • They performed tragedies and comedies, writing about wars and bringing light to them. Aeschylus and Sophocles were among the best tragedy writers. Aristophanes was a famous comedy writer.
 Homer • famous epic poet, who wrote The Iliad and Odyssey
Homer • famous epic poet, who wrote The Iliad and Odyssey
 The study of flat shapes and lines is called Euclidean geometry. Math in Ancient Greece With math, the Greeks led by Eratosthenes, were able to measure the size of Earth. • Some Greeks spent their lives studying math. • Euclid (YOO-kluhd) was one of these people, and many geometry rules we study today come from his studies. Hypatia (hy-PAY-shuh) was another famous, Greek Mathematician. She devoted her life to teaching her findings to others.
The study of flat shapes and lines is called Euclidean geometry. Math in Ancient Greece With math, the Greeks led by Eratosthenes, were able to measure the size of Earth. • Some Greeks spent their lives studying math. • Euclid (YOO-kluhd) was one of these people, and many geometry rules we study today come from his studies. Hypatia (hy-PAY-shuh) was another famous, Greek Mathematician. She devoted her life to teaching her findings to others.
 Pythagoras 582 -500 B. C. • The universe could only be understood thru numbers. • Sun, moon, and earth revolved around a central fire. • Each planet produces a tone! • Famous for the Pythagorean Theorem: a 2 + b 2 = c 2
Pythagoras 582 -500 B. C. • The universe could only be understood thru numbers. • Sun, moon, and earth revolved around a central fire. • Each planet produces a tone! • Famous for the Pythagorean Theorem: a 2 + b 2 = c 2
 Medicine in Ancient Greece • Greeks also studied medicine. • They studied the human body and how it worked. • They tried to cure diseases and keep people healthy. • Hippocrates (hip-AHK-ruh -teez) was a great Greek doctor who studied what caused disease. Today, Hippocrates is known for his ideas about how doctors should behave. When doctors graduate medical school, the recite the Hippocratic oath.
Medicine in Ancient Greece • Greeks also studied medicine. • They studied the human body and how it worked. • They tried to cure diseases and keep people healthy. • Hippocrates (hip-AHK-ruh -teez) was a great Greek doctor who studied what caused disease. Today, Hippocrates is known for his ideas about how doctors should behave. When doctors graduate medical school, the recite the Hippocratic oath.
 Hippocrates 460 -377 B. C. • Founded a school of medicine • Rejected that sickness comes from the gods, rather natural causes • Careful observations of symptoms • Acute • Chronic • “Holistic” healing • Hygiene • Diet • Curative powers of nature • The Hippocratic Oath • FIRST DO NO HARM
Hippocrates 460 -377 B. C. • Founded a school of medicine • Rejected that sickness comes from the gods, rather natural causes • Careful observations of symptoms • Acute • Chronic • “Holistic” healing • Hygiene • Diet • Curative powers of nature • The Hippocratic Oath • FIRST DO NO HARM
 Hippocratic Oath Historically Sworn (by Apollo) by Doctors “I will prescribe treatment for the good of my patients according to my ability. . . And never do harm to anyone. O please no one will I prescribe a deadly drug nor give advice which may cause death. . . In every house where I come I will enter only for the good of my patients. . . All I learn from my patients. . . I will keep secret. If I keep this oath faithfully, may I enjoy my life and practice my art, respected by all men and in all times.
Hippocratic Oath Historically Sworn (by Apollo) by Doctors “I will prescribe treatment for the good of my patients according to my ability. . . And never do harm to anyone. O please no one will I prescribe a deadly drug nor give advice which may cause death. . . In every house where I come I will enter only for the good of my patients. . . All I learn from my patients. . . I will keep secret. If I keep this oath faithfully, may I enjoy my life and practice my art, respected by all men and in all times.
 Herodotus 484 - 425 B. C. • “Father of History” • Wanted not only to learn what had happened but WHY it had happened
Herodotus 484 - 425 B. C. • “Father of History” • Wanted not only to learn what had happened but WHY it had happened
 Science The Greeks used hypotheses! Early Greek scientists’ hypotheses were not always correct. One of their most famous scientists, Thales of Miletus, believed all things were made of water. He also believed the Earth was a disk that floated in water.
Science The Greeks used hypotheses! Early Greek scientists’ hypotheses were not always correct. One of their most famous scientists, Thales of Miletus, believed all things were made of water. He also believed the Earth was a disk that floated in water.
 Thales of Miletus 636 -546 B. C. • Earliest known philosopher • Studied Egyptian and Babylonian astronomy and mathematics • Believed that the universe was controlled by fixed laws • Basic element – water. • Got rich with olive presses!
Thales of Miletus 636 -546 B. C. • Earliest known philosopher • Studied Egyptian and Babylonian astronomy and mathematics • Believed that the universe was controlled by fixed laws • Basic element – water. • Got rich with olive presses!
 Athletics Spartans and other Greeks believed in healthy, strong bodies. Some religious festivals included athletic contests and athletes competed in boxing, wrestling, and running, and throwing the javelin and discus to display their skill and strength to honor their gods.
Athletics Spartans and other Greeks believed in healthy, strong bodies. Some religious festivals included athletic contests and athletes competed in boxing, wrestling, and running, and throwing the javelin and discus to display their skill and strength to honor their gods.
 The Olympics The most famous Greek athletic completion in honor of their god, Zeus. The Olympic Games took place every four years in Athens. All conflicts between citystates ceased, even wars, to allow athlets and spectators to travel and watch the games in safety.
The Olympics The most famous Greek athletic completion in honor of their god, Zeus. The Olympic Games took place every four years in Athens. All conflicts between citystates ceased, even wars, to allow athlets and spectators to travel and watch the games in safety.
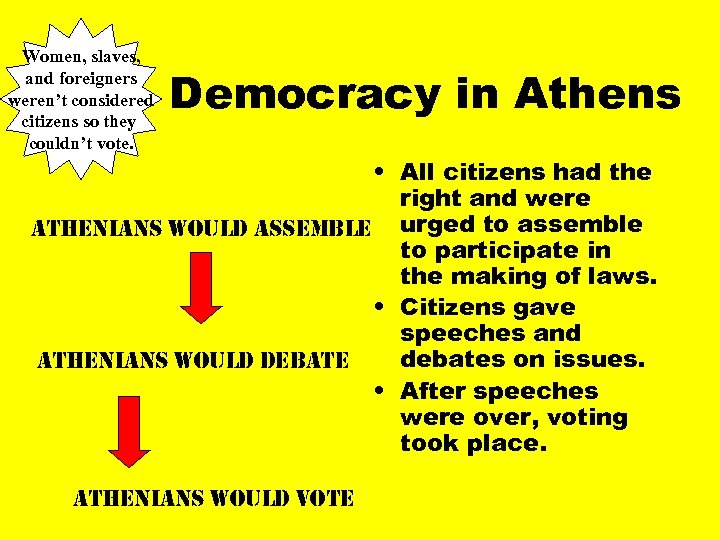 Women, slaves, and foreigners weren’t considered citizens so they couldn’t vote. Democracy in Athens • All citizens had the right and were athenians would assemble urged to assemble to participate in the making of laws. • Citizens gave speeches and debates on issues. athenians would debate • After speeches were over, voting took place. athenians would vote
Women, slaves, and foreigners weren’t considered citizens so they couldn’t vote. Democracy in Athens • All citizens had the right and were athenians would assemble urged to assemble to participate in the making of laws. • Citizens gave speeches and debates on issues. athenians would debate • After speeches were over, voting took place. athenians would vote
 Warfare In the ancient Greek world, warfare was seen as a necessary evil of the human condition. Whether it be small frontier skirmishes between neighboring city-states, lengthy city-sieges, civil wars, or large-scale battles between multialliance blocks (leagues) on land sea, the vast rewards of war could outweigh the costs in material and lives, or did it?
Warfare In the ancient Greek world, warfare was seen as a necessary evil of the human condition. Whether it be small frontier skirmishes between neighboring city-states, lengthy city-sieges, civil wars, or large-scale battles between multialliance blocks (leagues) on land sea, the vast rewards of war could outweigh the costs in material and lives, or did it?
 The mainstay of any Greek army was the hoplite and circular bronze shield The peltast warrior, armed with short javelins and more lightlyarmored than the hoplite became a mobile and dangerous threat to the slower moving hoplites. The first strategy was actually employed before any fighting took place at all. Religion and ritual were important features of Greek life, and before embarking on campaign, the will of the gods had to be determined. Some states such as Athens, Aegina, Corinth, and Rhodes amassed fleets of warships, most commonly the trireme, which could allow these states to forge lucrative trading partnerships and deposit troops on foreign territory and so establish and protect colonies. They could even block enemy harbors and launch amphibious landings.
The mainstay of any Greek army was the hoplite and circular bronze shield The peltast warrior, armed with short javelins and more lightlyarmored than the hoplite became a mobile and dangerous threat to the slower moving hoplites. The first strategy was actually employed before any fighting took place at all. Religion and ritual were important features of Greek life, and before embarking on campaign, the will of the gods had to be determined. Some states such as Athens, Aegina, Corinth, and Rhodes amassed fleets of warships, most commonly the trireme, which could allow these states to forge lucrative trading partnerships and deposit troops on foreign territory and so establish and protect colonies. They could even block enemy harbors and launch amphibious landings.
 Greek Phalanx Greek armies changed the way they were organized. Earlier wars mainly consisted and man-to-man combat and battle outcomes depended on fights between aristocratic warrior. Around 700 BV. C. , Greeks began to use the phalanx, a formation of heavily armed foot soldiers, who moved as a unit. Each soldier’s shield help protect his neighbor. Since horses were not needed in a phalanx, more men could afford to join up as foot soldiers with just the necessary weapons and armor. This gave more men a place in the military and government.
Greek Phalanx Greek armies changed the way they were organized. Earlier wars mainly consisted and man-to-man combat and battle outcomes depended on fights between aristocratic warrior. Around 700 BV. C. , Greeks began to use the phalanx, a formation of heavily armed foot soldiers, who moved as a unit. Each soldier’s shield help protect his neighbor. Since horses were not needed in a phalanx, more men could afford to join up as foot soldiers with just the necessary weapons and armor. This gave more men a place in the military and government.
 Citizenship Civic Responsibility Citizenship gives a person both rights AND responsibilities. Rights Responsibilities
Citizenship Civic Responsibility Citizenship gives a person both rights AND responsibilities. Rights Responsibilities


