6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

Greatest invention since sliced bread There were more claims to gold than there were ounces of gold. “Wow, you mean we can create money out of thin air. ? ” The fractional banking system began when someone issued claims for gold that already belonged to someone else. Once upon a time there was a gold-smithy who offered to store people’s gold in his vault. He issued paper receipts for the gold, and it was not long gold before the townsfolk used the paper to purchase eggs and beer. The smithy’s beer paper receipts [first checks] became as “good as gold. ” checks Our Smithy was not stupid. He said to himself. “I have 2000 ounces of gold stupid stored in my vault, but in the last year I was never called upon to pay out more than 100 ounces in a single day. What harm could it do if I lent out say, half day the gold I now have? I’ll still have more than enough to pay off any depositors that come in for a withdrawal. No one will know the difference. I could earn 30 additional ounces of gold each week. I think I’ll do it. ” “The smithy has invented the Fractional Reserve Banking System. ” Advantages of Lending [One disadvantage was the possibility of “bank runs”] runs” 1. Depositors haven’t lost money [Goldsmiths paid them instead of other way] 2. With the interest you earned you could give some to depositors 3. The loans benefited the community thru loans.

Give me a loan so there will be more DD in the system. How Banks Create Money [MS] MS MS = Currency + DD of Public Banks [thru loans] Create More DD loans

1. Fractional Reserve Banking System – a fraction of DD are kept in reserve (say, 10%) at either the bank’s vault or at the Fed. 2. Vault cash – cash held by a bank (banks rarely keep more than 2% of their RR in cash). 3. Required Reserve(RR) – specified % of DD that banks must keep as RR. 4. Excess Reserves(ER) – amount of money over the RR, which can be loaned out. 5. Total(Actual) Reserves(TR) – RR + ER. 6. Money(Deposit) Multiplier – reciprocal of the RR; or 1/RR = MM. RR 10% 25% 40% 50% = = = 1/RR 10 5 4 2. 5 2 You could also use these! RR = 1/RR 5% = 20 12. 5% = 8 16. 67% = 6 33. 33% = 3 7. Balance Sheet – statement of assets & liabilities [assets = liabilities] liabilities 8. Discount Rate – when banks borrow from the Fed. [symbolic] (for emergencies) symbolic “wholesale price of money” 9. Federal Funds Target Rate – banks borrow from other banks for overnight loans 10. Prime Rate – when a bank’s prime customers [good credit] get loans. “Retail price of money” 11. Buying Bonds – “buying” bonds means “bigger” MS & “lower interest rates” 12. Selling Bonds – “selling” bonds means “smaller” MS & “higher interest rates”

Money Creation with Fractional-Reserve Banking • When a bank makes a loan from its reserves, the money supply increases. (not literally) • The money supply is affected by the amount deposited in banks and the amount that banks loan. • Deposits into a bank are recorded as both assets and liabilities. • The fraction of total deposits that a bank has to keep as reserves is called the reserve ratio. • Loans become an asset to the bank. © 2007 Thomson South-Western

How does a loan create money? • Remember it doesn’t literally create money. There are the same amount of dollars in the economy. So how does this work. When I say they create money they really create transactions. Let me show you what I mean. © 2007 Thomson South-Western

Money Creation • So lets say that you put $100 dollars in a Wellsfargo bank account. The bank when then lend out most of that money. Lets say the reserve requirement is 10%. So the bank can lend out $90 dollars. Someone comes in and wants a loan for $90 dollars to buy an ipod. The bank lends them the money. They then buy the ipod and the person who sold the ipod takes the 90 dollars they just made and puts it in their bank at Bank of America must keep 9 dollars in their vault but they lend out the other 81 dollars. So you can see your $100 dollars creates transactions. This is said to be creating money. © 2007 Thomson South-Western

Money Creation with Fractional-Reserve Banking • When one bank loans money, that money is generally deposited into another bank. • This creates more deposits and more reserves to be lent out. • When a bank makes a loan from its reserves, the money supply increases. (not literally) © 2007 Thomson South-Western

How Banks and Thrifts Create Money

Rodman’s . 10 90 cents RR Excess Reserves Total (Actual) Reserves One Dollar One bank’s loan becomes another bank’s DD. PMC = M x ER, so 10 x 90¢ = $9 TMS = PMC[$9] + DD[$1] = $10 [MS = Currency + DD of Public]

Eva Longoria Deposits $1 with a 20% RR Eva Longoria’s . 20 80 cents RR Excess Reserves Total(Actual) Reserves One Dollar PMC = M x ER, so 5 x 80¢ =$4 TMS = PMC[$4] + DD[$1] = $5 [MS = Currency + DD of Public]

BANKS AND THE MONEY SUPPLY • Reserves are deposits that banks have received but have not loaned out. • In a fractional-reserve banking system, banks hold a fraction of the money deposited as reserves and lend out the rest. © 2007 Thomson South-Western

BANKS AND THE MONEY SUPPLY • The reserve ratio is the fraction of deposits that banks hold as reserves. © 2007 Thomson South-Western

Banking Money Creation with Fractional. Reserve • This T-Account shows First National Bank a bank that… • accepts deposits, • keeps a portion as reserves, • and lends out the rest. • It assumes a reserve ratio of 10%. Assets Reserves $10. 00 Liabilities Deposits $100. 00 Loans $90. 00 Total Assets $100. 00 Total Liabilities $100. 00 © 2007 Thomson South-Western

Money Creation with Fractional-Reserve Banking • When one bank loans money, that money is generally deposited into another bank. • This creates more deposits and more reserves to be lent out. • When a bank makes a loan from its reserves, the money supply increases. (not literally) © 2007 Thomson South-Western

The Money Multiplier • How much money is eventually created by the new deposit in this economy? © 2007 Thomson South-Western

The Money Multiplier • The money multiplier is the amount of money the banking system generates with each dollar of reserves. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
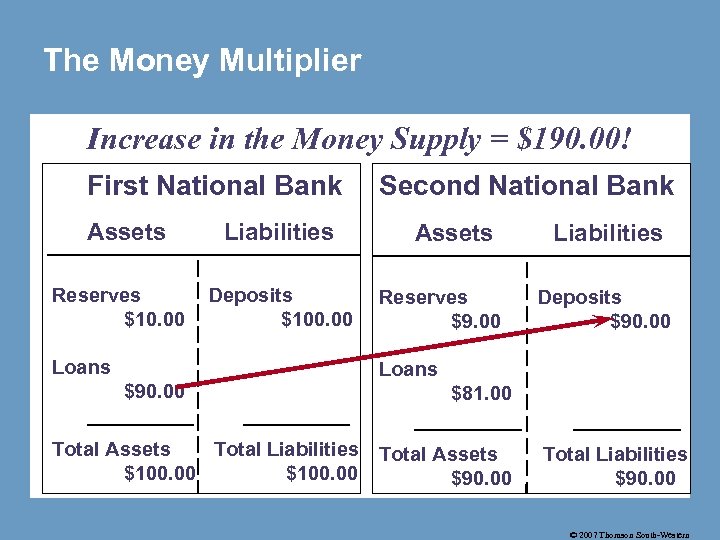
The Money Multiplier Increase in the Money Supply = $190. 00! First National Bank Assets Reserves $10. 00 Liabilities Deposits $100. 00 Loans $90. 00 Total Assets Total Liabilities $100. 00 Second National Bank Assets Reserves $9. 00 Liabilities Deposits $90. 00 Loans $81. 00 Total Assets $90. 00 Total Liabilities $90. 00 © 2007 Thomson South-Western

The Money Multiplier Original deposit = $100. 00 • 1 st Natl. Lending = 90. 00 (=. 9 x $100. 00) • 2 nd Natl. Lending = 81. 00 (=. 9 x $ 90. 00) • 3 rd Natl. Lending = 72. 90 (=. 9 x $ 81. 00) • … and on until there are just pennies left to lend! • Total money created by this $100. 00 deposit is $1000. (= 1/. 1 x $100. 00) © 2007 Thomson South-Western
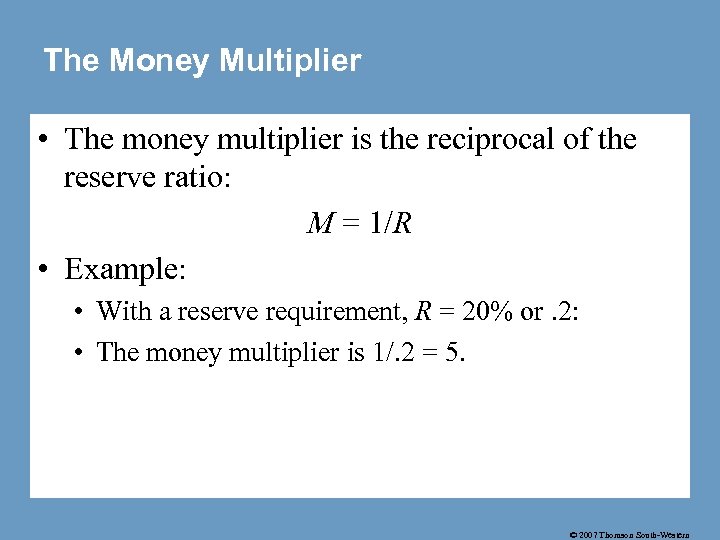
The Money Multiplier • The money multiplier is the reciprocal of the reserve ratio: M = 1/R • Example: • With a reserve requirement, R = 20% or. 2: • The money multiplier is 1/. 2 = 5. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
![THE Money [Deposit] MULTIPLIER MM = 1 RR The MM is the reciprocal of THE Money [Deposit] MULTIPLIER MM = 1 RR The MM is the reciprocal of](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-21.jpg)
THE Money [Deposit] MULTIPLIER MM = 1 RR The MM is the reciprocal of the RR. Maximum Potential money checkable. Creation in the Bankingdeposit System expansion [PMC] = ER x MM
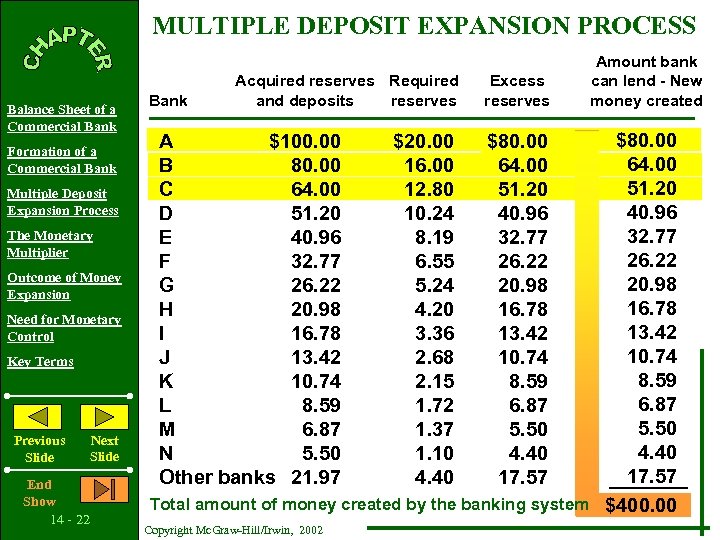
MULTIPLE DEPOSIT EXPANSION PROCESS Balance Sheet of a Commercial Bank Formation of a Commercial Bank Multiple Deposit Expansion Process The Monetary Multiplier Outcome of Money Expansion Need for Monetary Control Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 14 - 22 Next Slide Bank Acquired reserves Required and deposits reserves Excess reserves Amount bank can lend - New money created $80. 00 64. 00 51. 20 40. 96 32. 77 26. 22 20. 98 16. 78 13. 42 10. 74 8. 59 6. 87 5. 50 4. 40 17. 57 Total amount of money created by the banking system $400. 00 A $100. 00 B 80. 00 C 64. 00 D 51. 20 E 40. 96 F 32. 77 G 26. 22 H 20. 98 I 16. 78 J 13. 42 K 10. 74 L 8. 59 M 6. 87 N 5. 50 Other banks 21. 97 Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 $20. 00 16. 00 12. 80 10. 24 8. 19 6. 55 5. 24 4. 20 3. 36 2. 68 2. 15 1. 72 1. 37 1. 10 4. 40 $80. 00 64. 00 51. 20 40. 96 32. 77 26. 22 20. 98 16. 78 13. 42 10. 74 8. 59 6. 87 5. 50 4. 40 17. 57
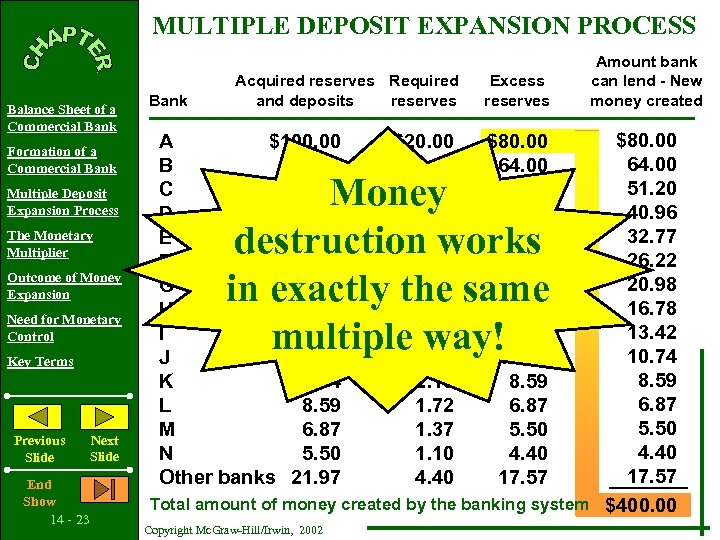
MULTIPLE DEPOSIT EXPANSION PROCESS Balance Sheet of a Commercial Bank Formation of a Commercial Bank Multiple Deposit Expansion Process The Monetary Multiplier Outcome of Money Expansion Need for Monetary Control Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 14 - 23 Next Slide Bank Acquired reserves Required and deposits reserves Excess reserves Amount bank can lend - New money created $80. 00 64. 00 51. 20 40. 96 32. 77 26. 22 20. 98 16. 78 13. 42 10. 74 8. 59 6. 87 5. 50 4. 40 17. 57 Total amount of money created by the banking system $400. 00 A $100. 00 B 80. 00 C 64. 00 D 51. 20 E 40. 96 F 32. 77 G 26. 22 H 20. 98 I 16. 78 J 13. 42 K 10. 74 L 8. 59 M 6. 87 N 5. 50 Other banks 21. 97 $20. 00 16. 00 12. 80 10. 24 8. 19 6. 55 5. 24 4. 20 3. 36 2. 68 2. 15 1. 72 1. 37 1. 10 4. 40 $80. 00 64. 00 51. 20 40. 96 32. 77 26. 22 20. 98 16. 78 13. 42 10. 74 8. 59 6. 87 5. 50 4. 40 17. 57 Money destruction works in exactly the same multiple way! Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002
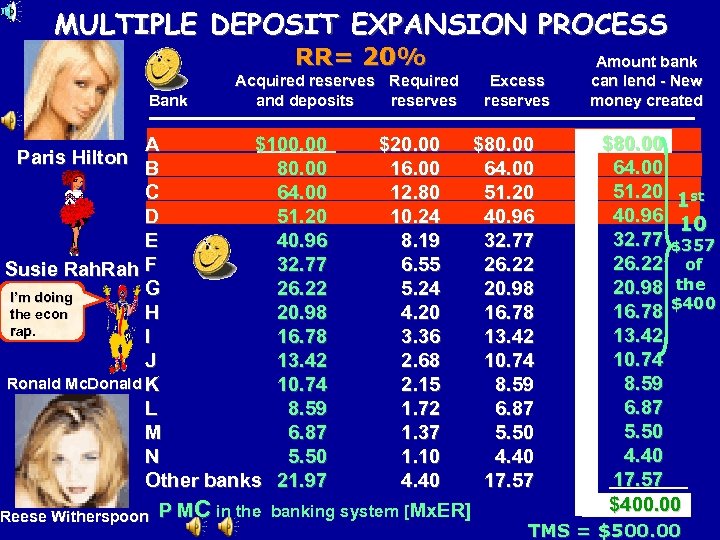
MULTIPLE DEPOSIT EXPANSION PROCESS RR= 20% Bank Acquired reserves Required and deposits reserves Excess reserves A $100. 00 $20. 00 $80. 00 B 80. 00 16. 00 64. 00 C 64. 00 12. 80 51. 20 D 51. 20 10. 24 40. 96 E 40. 96 8. 19 32. 77 6. 55 26. 22 Susie Rah F G 26. 22 5. 24 20. 98 I’m doing H 20. 98 4. 20 16. 78 the econ rap. I 16. 78 3. 36 13. 42 J 13. 42 2. 68 10. 74 Ronald Mc. Donald K 10. 74 2. 15 8. 59 L 8. 59 1. 72 6. 87 M 6. 87 1. 37 5. 50 N 5. 50 1. 10 4. 40 Other banks 21. 97 4. 40 17. 57 Reese Witherspoon P MC in the banking system [Mx. ER] Paris Hilton Amount bank can lend - New money created $80. 00 64. 00 51. 20 1 st 40. 96 10 32. 77 $357 26. 22 of 20. 98 the 16. 78 $400 13. 42 10. 74 8. 59 6. 87 5. 50 4. 40 17. 57 $400. 00 TMS = $500. 00
![$1, 000 DD by Morgan[MS=Currency+DD of Public] Currency Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank $1, 000 DD by Morgan[MS=Currency+DD of Public] Currency Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-25.jpg)
$1, 000 DD by Morgan[MS=Currency+DD of Public] Currency Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank DD A $1, 000. 00 DD Created By New Loans [equal to new ER] New Required Reserves RR=10% $100. 00 900. 00 B 900. 00 $90. 00 810. 00 C 810. 00 $81. 00 729. 00 D 729. 00 $72. 90 656. 10 PMC = ER[$900] x M[10] Morgan’s DD + PMC $1, 000. 00 + $9, 000. 00 One year “all u can eat” hot wings at Hooters $729. 00 for a “cat bodyguard” PMC = $9, 000. 00 = = Dog that can Yo. Yo TMS Smoking cat $10, 000. 00 MS grows by multiple of 10
![$1, 000 DD by Rachel [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank $1, 000 DD by Rachel [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-26.jpg)
$1, 000 DD by Rachel [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank DD Created By New Loans [equal to new ER] New Required Reserves RR=20% A $1, 000. 00 $200. 00 800. 00 B 800. 00 $160. 00 640. 00 $128. 00 512. 00 D 512. 00 $102. 40 Purchase of a donkey 640. 00 C Hair care for 1 year 409. 60 PMC = ER[$800 x M[5] Rachel’s DD + PMC $1, 000. 00 + $4, 000. 00 = = Two Monkeys PMC = $4, 000. 00 TMS $5, 000. 00 A chauffeur dog MS grows by multiple of 5
![$1, 000 DD by Jordan [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank $1, 000 DD by Jordan [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-27.jpg)
$1, 000 DD by Jordan [MS=Currency+DD of Public] Public New Deposits [New Reserves] Bank DD Created By New Loans [equal to new ER] New Required Reserves RR=25% A $1, 000. 00 $250. 00 750. 00 B 750. 00 $188. 00 562. 00 C 562. 00 $140. 00 422. 00 D 422. 00 $105. 00 317. 00 E 317. 00 $80. 00 Shark to keep in bathtub Prom date w. Linda Blair Frog with teeth 237. 00 PMC = ER[$750] x M[4] Jordan’s DD + PMC $1, 000. 00 + $3, 000. 00 PMC = $ = = Teach Stuart Little how to brush his teeth Cat with human teeth TMS $4, 000. 00 MS grows by multiple of 4
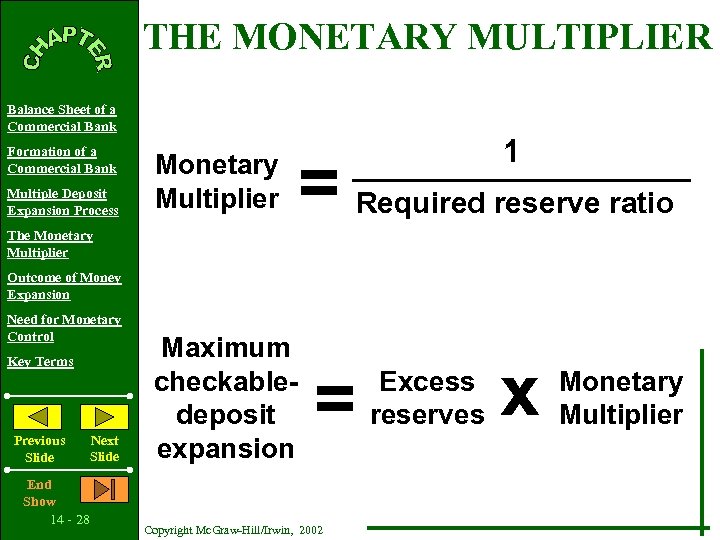
THE MONETARY MULTIPLIER Balance Sheet of a Commercial Bank Formation of a Commercial Bank Multiple Deposit Expansion Process Monetary Multiplier 1 = Required reserve ratio The Monetary Multiplier Outcome of Money Expansion Need for Monetary Control Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 14 - 28 Next Slide Maximum checkabledeposit expansion = Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Excess reserves x Monetary Multiplier
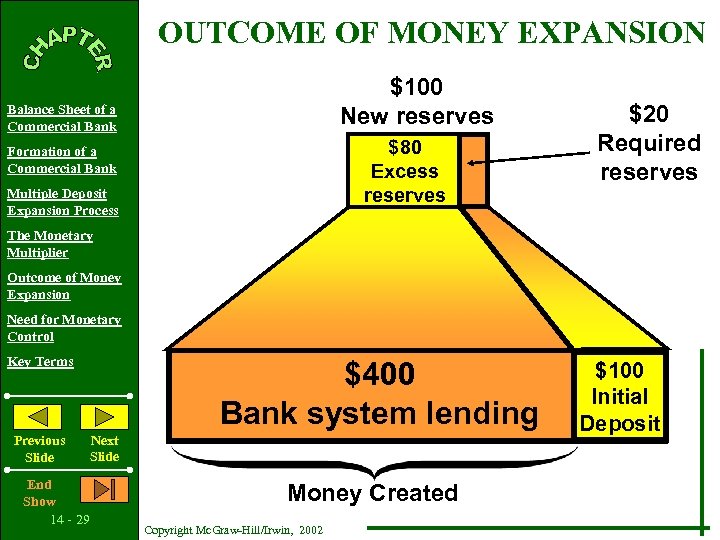
OUTCOME OF MONEY EXPANSION $100 New reserves Balance Sheet of a Commercial Bank $80 Excess reserves Formation of a Commercial Bank Multiple Deposit Expansion Process $20 Required reserves The Monetary Multiplier Outcome of Money Expansion Need for Monetary Control Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 14 - 29 $400 Bank system lending Next Slide Money Created Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 $100 Initial Deposit

OUTCOME OF MONEY EXPANSION $100 New reserves Balance Sheet of a Commercial Bank Formation of a Commercial Bank Multiple Deposit Expansion Process The Monetary Multiplier Outcome of Money Expansion Need for Monetary Control Key Terms $80 Excess reserves Leakages exist. . . Currency Drains Excess Reserves $100 $400 Bank system lending Previous Slide End Show 14 - 30 $20 Required reserves Next Slide Money Created Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Initial Deposit
![Kristen Stewart Deposits $1, 000 In Her Bank [RR is 20%] New reserves $800 Kristen Stewart Deposits $1, 000 In Her Bank [RR is 20%] New reserves $800](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-31.jpg)
Kristen Stewart Deposits $1, 000 In Her Bank [RR is 20%] New reserves $800 $200 Excess Reserves Kristen’s RR Kristen [member of the public] $4, 000 PMC thru Bank Lending TMS is $5, 000 $1, 000 Initial Deposit

Ashley Olsen Deposits $1, 000 in her bank RR = 25% Ashley Olsen’s $1, 000 New reserves $750 $250 Excess reserves RR Ashley Olsen deposits $1, 000 $3, 000 PMC thru bank lending TMS = $4, 000 $1, 000 Initial Deposit

Fed buys a $1, 000 Bond from Kristen’s Bank New reserves 20% RR Fed Kristen’s $1, 000 Excess Reserves $5, 000 PMC thru Bank System Lending TMS is $5000

Fed Buys A $1, 000 Bond From Ashley’s Bank Ashley Olsen’s New reserves $1, 000 Excess Reserves 25% RR $4, 000 PMC thru Bank Lending TMS is $4, 000 TMS
![Eva’s Bank Borrows $1 From The Fed [20% RR] Fed Eva Longoria’s One Dollar Eva’s Bank Borrows $1 From The Fed [20% RR] Fed Eva Longoria’s One Dollar](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-35.jpg)
Eva’s Bank Borrows $1 From The Fed [20% RR] Fed Eva Longoria’s One Dollar 0 RR Excess Reserves Total(Actual) Reserves One Dollar PMC = M x ER, so 5 x $1 = $5 TMS [$5] = PMC [$5] [MS = currency + DD of Public]

Fed Rodman’s Bank 0 One Dollar RR Excess Reserves Total(Actual) Reserves One Dollar PMC = M x ER, so 10 x $1 = $10 TMS [$10] = PMC[$10] [MS = Currency + DD of Public]

q. Type 1: Calculate the initial change in Excess Reserves once a bank obtains money. qa. k. a. the amount a single Bank can loan from the initial deposit is the ER [DD-RR(Public)] or [All if from Fed] Fed q. Type 2: Calculate the Potential change in loans [Money Creation] in the banking system [PMC][ERx. MM] system q. Type 3: Calculate the potential Total change in the Money Supply [TMS] [DD or loan x MM] DD upply q. Type 2 [PMC] and type 3 [TMS] will have the same result if a Bank gets their money from the Bank Fed and not the Public. Fed
![Money Supply = DD + Currency of the Public ER “PMC” Loans $100[10% RR] Money Supply = DD + Currency of the Public ER “PMC” Loans $100[10% RR]](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-38.jpg)
Money Supply = DD + Currency of the Public ER “PMC” Loans $100[10% RR] [1 st Bank] Banks/Public DD [$100] $90 Fed /Public/Banks DD[$100] $90 “PMC” Crea. In “TMS” “Potential” System Total MS $900 $1, 000 [*Fed buys bonds from public who put the money in their DD] Banks/Fed Loan[$100] $100 [or sells bonds to Fed] ER $100 $1, 000 “PMC” Loans “PMC” Crea. In $100 [20% RR] [1 st Bank] System Banks/Public DD [$100] $80 $400 Fed/Public/Banks DD [$100] $80 $400 $1, 000 “TMS” “Potential” Total MS $500 [*Fed buys bonds from public who put the money in their DD] Banks/Fed Loan[$100] $100 [or sells bonds to Fed] $100 $500
![[No Cash Leakages And Zero Excess Reserves] v. Assumptions: v. All monies are deposited [No Cash Leakages And Zero Excess Reserves] v. Assumptions: v. All monies are deposited](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-39.jpg)
[No Cash Leakages And Zero Excess Reserves] v. Assumptions: v. All monies are deposited in bank checking accounts and become demand deposits [DD]. v. Every bank lent all its excess reserves, leaving reserves every bank with zero excess reserves v. Because we assumed no cash leakages and zero excess reserves, the change in checkable reserves deposits is the maximum possible change.

2 Big Exceptions I have seen on AP Test If The FED Buys or Sells bonds it literally affect money supply. The banks don’t have to keep a reserve like if it was a deposit from someone else. So if the fed does it the whole thing gets multiplied out. Also if they ask about demand deposits. You do the whole thing. Because a demand deposit is part of what is put in reserve so you add that to the potential money creation.

![3. [6 pts] Assume that the reserve requirement is 20% & banks hold no 3. [6 pts] Assume that the reserve requirement is 20% & banks hold no](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-42.jpg)
3. [6 pts] Assume that the reserve requirement is 20% & banks hold no excess reserves. pts (a) [3 pts] Assume that Kim deposits $100 of cash from her pocket into her checking account. pts Calculate each of the following. (i) The maximum dollar amount the commercial bank can initially lend (ii) The maximum total change in demand deposits in the banking system (iii) The maximum change in the money supply. Answer to 3. (a) [1 pt each for (i) $80, (ii) $500, and (iii) $400] (i) The $100 in DD will result in $80 new ER that the banks can initially lend. (ii) Maximum total DD could be as high as $500. This includes $100 DD in the first bank and a PMC of $400. MM [5] x ER [$80] = PMC of $400. Total DD of $500. (iii) The MS was already $100 as the $100 in cash was part of MS, so this results in an increase in money supply of $400. (b) [1 pts] With the 20% RR, assume that the Fed buys $5 million in government bonds on pts the open market from the public. As a result of the open market purchase, calculate the maximum increase in the money supply in the banking system. Answer to 3. (b) Once this $5 million is deposited by the public, $1 million has to be kept in RR and $4 million becomes ER. MM [5] x ER [$4 M] = $20 million increase in the MS in the banking system. The Total MS is now $25 million [DD of $5 & PMC of $20] (c) [2 pts] Given the increase in the money supply in part b, what happens to real wages in the pts short run? Explain. Answer to 3. (c) The increase in MS results in a decrease in the nominal interest rate, resulting in an increase in QID, and an increase in AD, which pushes prices up [1 pt], therefore a decrease in real wages [1 pt].
![NS 31 -35 AP Econ [MS = Currrency + DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; NS 31 -35 AP Econ [MS = Currrency + DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER;](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-43.jpg)
NS 31 -35 AP Econ [MS = Currrency + DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS Excess Reserves prior to new currency deposit (DD) = $0 Britney Spears deposits in the banking system = $40 million Legal Reserve Requirement [RR] = 20% 31. The $40 million deposit of Currency into DD would result in MS staying at ($8/$40/$160) million. [MS composition changed from currency to DD] 32. The $40 million deposit of currency into checking accounts will create ER of ($20/$32/$40) million. 33. The Potential Money Creation of the banking system through loans is ($40/$160/$$200) mil. The Potential TMS [all DD of the public] could be as much as ($40/$160/$200) mil. 34. The RR applies to checkable deposits at (banks/S&Ls/ credit unions/ all depository institutions). 35. If the Duck National Bank has ER of $6, 000 & DD of $100, 000 what is the size of the bank’s TR if the RR is 25%? 25% 25, 000 6, 000 31, 000 ($25, 000/$75, 000/$31, 000) [RR($____)+ER($___)=TR($____)
![NS 36 -45 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS NS 36 -45 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-44.jpg)
NS 36 -45 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS 36. A stranger deposits $1, 000 in a bank that has a RR of 10%. The $1, 000 maximum possible change in the dollar value of the local bank’s loans would 900 9, 000 be $______. PMC[M X ER] in the banking system is $_____. Potential TMS PMC ER 10, 000 could become as high as $_______. 37. Suppose a commercial bank has DD of $100, 000 and the RR is 10%. $100, 000 10% If the bank’s RR & ER are equal, then its TR are ($10, 000/$20, 000/$30, 000). equal TR 38. Total Reserves (minus/plus) RR = ER. ER 39. Suppose the Thunderduck Bank has DD of $500, 000 & the RR is 10%. $500, 000 10% If the institution has ER of $4, 000 then its TR are ($46, 000/$54, 000/$4, 000). $4, 000 TR 40. If ER in a bank are $4, 000, DD are $40, 000, & the RR is 10%, then ER $4, 000 $40, 000 10% TR are ($4, 000/$8, 000). TR 41. The main purpose of the RR is to (have funds for emergency withdrawals/ RR influence the lending ability of commercial banks). 42. If I write you a check for $1 & we both have our checking accts at the $1 Poorman Bank, the bank’s balance sheet will (increase/decrease/be unchanged). 43. Banks (create/destroy) money when they make loans and repaying bank loans (create/destroy) money. loans 44. When a bank loan is repaid the MS is (increased/decreased). repaid MS 45. The Fed Funds rate is a loan by one bank (to another bank/from the Fed). rate
![NS 46 -47 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS NS 46 -47 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS](https://present5.com/presentation/6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802/image-45.jpg)
NS 46 -47 [MS = Currrency+DD of Public] RR+ER=TR; TR-RR=ER; TR-ER=RR; MXER=PMC; PMC(Public)+DD=TMS; PMC(Fed)=TMS 46. If the RR was lowered [say, from 50% to 10%], the size of the monetary multiplier [MM] would (increase/decrease). Leakages (limitations) of the Money Creating Process 1. Cash leakages [taking part of loan in cash] 2. ER (banks don’t loan it or we don’t borrow] 47. If borrowers take a portion of their loans as cash, the maximum amount by cash which the banking system increases the MS by lending will (increase/decrease). MS
6f2574f6da5262a28897cf53b6ac5802.ppt