2dd6dbb50b78cb456df2a3f27ed130dd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 GREAT DEPRESSION A severe economic decline that lasted 1929 -WWII, causing millions of Americans to lose jobs, farms and homes
GREAT DEPRESSION A severe economic decline that lasted 1929 -WWII, causing millions of Americans to lose jobs, farms and homes
 EOC STANDARDS • e. Identify and explain the economic factors that contributed to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression • f. Explain the economic, environmental, and social impact of the Great Depression on American society • g. Evaluate the impact of the New Deal on various elements of American society (e. g. , social, political) • CORE CONTENT • SS-HS-5. 1. 1 Students will use a variety of tools (e. g. , primary and secondary sources, data, artifacts) to analyze perceptions and perspectives (e. g. , gender, race, region, ethnic group, nationality, age, economic status, religion, politics, geographic factors) of people and historical events in the modern world (1500 A. D. to present) and United States History (Reconstruction to present). DOK 3 • SS-HS-5. 1. 2 Students will analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present. DOK 3 • SS-HS-5. 2. 5 Students will evaluate how the Great Depression, New Deal policies and World War II transformed America socially and politically at home (e. g. , stock market crash, relief, recovery, reform initiatives, increased role of government in business, influx of women into workforce, rationing) and reshaped its role in world affairs (e. g. , emergence of the U. S. as economic and political superpower). DOK 3
EOC STANDARDS • e. Identify and explain the economic factors that contributed to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression • f. Explain the economic, environmental, and social impact of the Great Depression on American society • g. Evaluate the impact of the New Deal on various elements of American society (e. g. , social, political) • CORE CONTENT • SS-HS-5. 1. 1 Students will use a variety of tools (e. g. , primary and secondary sources, data, artifacts) to analyze perceptions and perspectives (e. g. , gender, race, region, ethnic group, nationality, age, economic status, religion, politics, geographic factors) of people and historical events in the modern world (1500 A. D. to present) and United States History (Reconstruction to present). DOK 3 • SS-HS-5. 1. 2 Students will analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present. DOK 3 • SS-HS-5. 2. 5 Students will evaluate how the Great Depression, New Deal policies and World War II transformed America socially and politically at home (e. g. , stock market crash, relief, recovery, reform initiatives, increased role of government in business, influx of women into workforce, rationing) and reshaped its role in world affairs (e. g. , emergence of the U. S. as economic and political superpower). DOK 3
 Causes of the Great Depression
Causes of the Great Depression
 Myths and Misconceptions • Many people believe that the crash of the stock market was the cause of the Depression. Not so, it was only a symptom. • Many people also believe that Herbert Hoover’s laissez-fair economic philosophy prevented the federal government from taking steps to prevent the crisis. Hoover was proactive in trying to ease the impact of the depression, it was too little, too late. • Many people think that the Great Depression was the only major economic crisis in U. S. history. Nope, but it was the worst. • Many people do not realize that the Depression was global and affected almost every capitalist economy on earth • Some believe that FDR and the New Deal ended the Depression. Wrong again, WWII ended he Depression
Myths and Misconceptions • Many people believe that the crash of the stock market was the cause of the Depression. Not so, it was only a symptom. • Many people also believe that Herbert Hoover’s laissez-fair economic philosophy prevented the federal government from taking steps to prevent the crisis. Hoover was proactive in trying to ease the impact of the depression, it was too little, too late. • Many people think that the Great Depression was the only major economic crisis in U. S. history. Nope, but it was the worst. • Many people do not realize that the Depression was global and affected almost every capitalist economy on earth • Some believe that FDR and the New Deal ended the Depression. Wrong again, WWII ended he Depression
 ECONOMY of late 1920’s OPTIMISTIC ATTITUDE • President Hoover – 1928 • Economy great • “Everybody ought to be Rich” mentality • Increase income by investments Stock market high
ECONOMY of late 1920’s OPTIMISTIC ATTITUDE • President Hoover – 1928 • Economy great • “Everybody ought to be Rich” mentality • Increase income by investments Stock market high
 DEPRESSION FORESHADOWED • • • Rising unemployment Declining of the Farming industry Stock prices dropping Buying on Credit (did not have money) Too many goods, Too little demand Unequal distribution of wealth – • 71% families earned less $2500
DEPRESSION FORESHADOWED • • • Rising unemployment Declining of the Farming industry Stock prices dropping Buying on Credit (did not have money) Too many goods, Too little demand Unequal distribution of wealth – • 71% families earned less $2500
 STOCKMARKET 101 STOCK is partial ownership in a company • If others want to buy stock it increases. If others do not it decreases • BUY LOW SELL HIGH • Once you sell you receive money- until then just a sheet of paper
STOCKMARKET 101 STOCK is partial ownership in a company • If others want to buy stock it increases. If others do not it decreases • BUY LOW SELL HIGH • Once you sell you receive money- until then just a sheet of paper
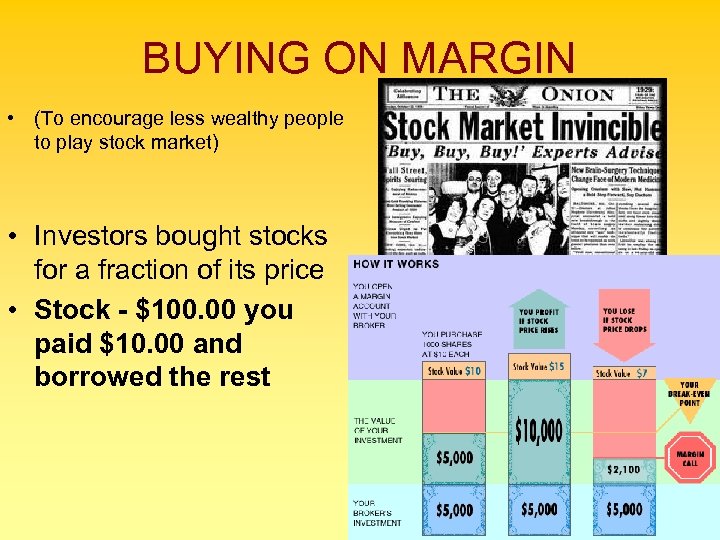 BUYING ON MARGIN • (To encourage less wealthy people to play stock market) • Investors bought stocks for a fraction of its price • Stock - $100. 00 you paid $10. 00 and borrowed the rest
BUYING ON MARGIN • (To encourage less wealthy people to play stock market) • Investors bought stocks for a fraction of its price • Stock - $100. 00 you paid $10. 00 and borrowed the rest
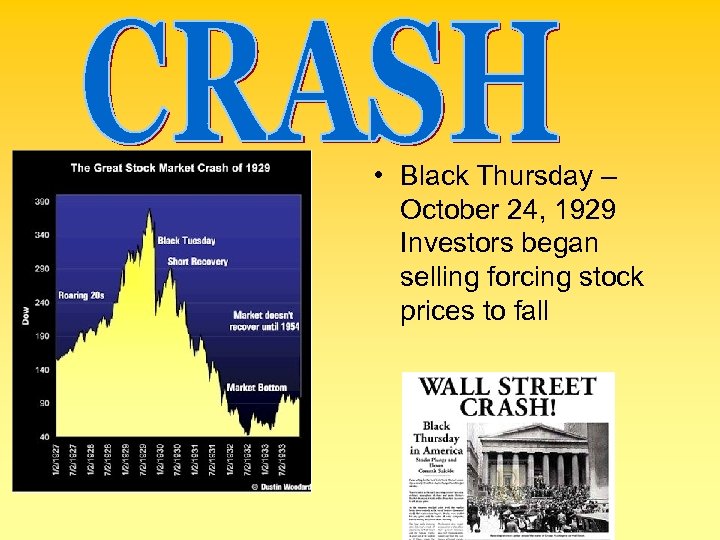 • Black Thursday – October 24, 1929 Investors began selling forcing stock prices to fall
• Black Thursday – October 24, 1929 Investors began selling forcing stock prices to fall
 SELL !!! • BLACK TUESDAY – 10/29/29 – 16. 4 million shares were sold – GREAT CRASH – Losses over 30 billion dollars – This is the beginning of the Great Depression!
SELL !!! • BLACK TUESDAY – 10/29/29 – 16. 4 million shares were sold – GREAT CRASH – Losses over 30 billion dollars – This is the beginning of the Great Depression!
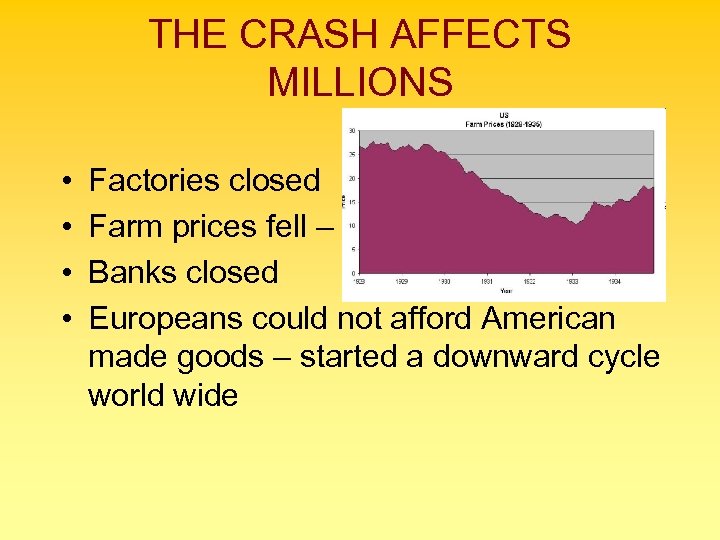 THE CRASH AFFECTS MILLIONS • • Factories closed Farm prices fell – Banks closed Europeans could not afford American made goods – started a downward cycle world wide
THE CRASH AFFECTS MILLIONS • • Factories closed Farm prices fell – Banks closed Europeans could not afford American made goods – started a downward cycle world wide
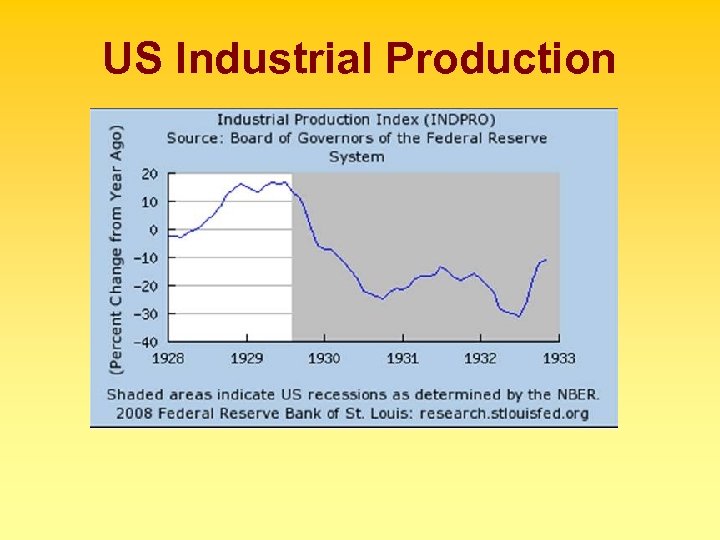 US Industrial Production
US Industrial Production
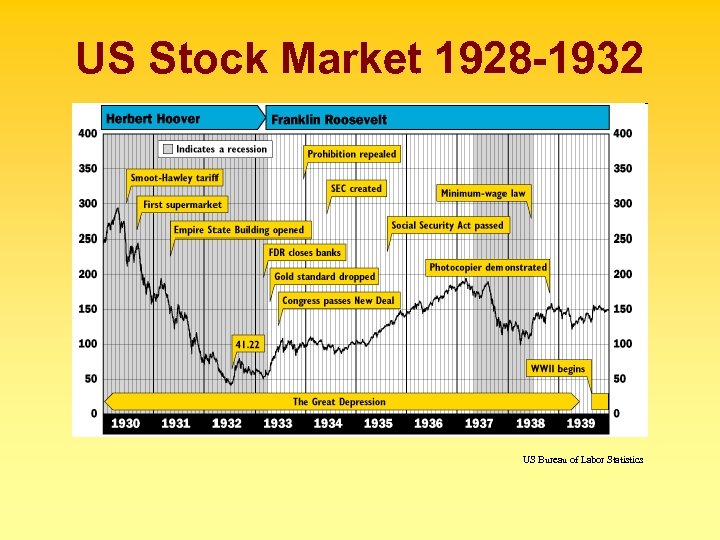 US Stock Market 1928 -1932 US Bureau of Labor Statistics
US Stock Market 1928 -1932 US Bureau of Labor Statistics
 CAUSES FOR THE GREAT DEPRESSION • • • 1. Overproduction of goods 2. Widening of Wealth Gap 3. Stock and Real estate speculation 4. unregulated banking practices 5. Declining of farming industry 6. High Tariffs – – Hawley Smoot Tariff Act 1930
CAUSES FOR THE GREAT DEPRESSION • • • 1. Overproduction of goods 2. Widening of Wealth Gap 3. Stock and Real estate speculation 4. unregulated banking practices 5. Declining of farming industry 6. High Tariffs – – Hawley Smoot Tariff Act 1930
 Many did not realize how severe the downturn was until 1932, when the economy had technically “hit bottom. ”
Many did not realize how severe the downturn was until 1932, when the economy had technically “hit bottom. ”
 Brother Can You Spare a Dime? Once I built a railroad, I made it run I made it race against time Once I built a railroad, now it's done Brother, can you spare a dime? Once I built a tower, up to the sun Bricks and mortar and lime Once I built a tower, now it's done Brother, can you spare a dime?
Brother Can You Spare a Dime? Once I built a railroad, I made it run I made it race against time Once I built a railroad, now it's done Brother, can you spare a dime? Once I built a tower, up to the sun Bricks and mortar and lime Once I built a tower, now it's done Brother, can you spare a dime?
 RESPONSE TO ECONOMIC COLLASPE • Hoover’s response – Cautious approach – limited govt intervention – Unemployment increased – Hoovervilles sprung up(shantytowns made up of scraps in cities for the homeless)
RESPONSE TO ECONOMIC COLLASPE • Hoover’s response – Cautious approach – limited govt intervention – Unemployment increased – Hoovervilles sprung up(shantytowns made up of scraps in cities for the homeless)
 Hoover’s Political Decisions • Hoover promoted volunteerism. Cooperation between government and business instead of coercive policies.
Hoover’s Political Decisions • Hoover promoted volunteerism. Cooperation between government and business instead of coercive policies.

 • 1932 - Hoover created RFC (reconstruction Finance Corporation) • Agency issued govt loans to banks, rr’s, businesses, etc. • Believed TRICKLE DOWN theory-
• 1932 - Hoover created RFC (reconstruction Finance Corporation) • Agency issued govt loans to banks, rr’s, businesses, etc. • Believed TRICKLE DOWN theory-
 “The sole function of the government is to bring about a condition of affairs favorable to the beneficial development of private enterprise. ” ~Herbert Hoover (1930) “The Fed will stand by as the market works itself out: Liquidate labor, liquidate stocks, liquidate real estate… values will be adjusted, and enterprising people will pick up the wreck from lesscompetent people. " ~ Andrew Mellon (1930)
“The sole function of the government is to bring about a condition of affairs favorable to the beneficial development of private enterprise. ” ~Herbert Hoover (1930) “The Fed will stand by as the market works itself out: Liquidate labor, liquidate stocks, liquidate real estate… values will be adjusted, and enterprising people will pick up the wreck from lesscompetent people. " ~ Andrew Mellon (1930)
 The Dust Bowl • Between 1929 and 1932, about 400, 000 farms were lost to foreclosure • Not only economic damages, but environmental ▫ Land was overworked • Drought and dust storms in the Midwest for much of the 1930 s ▫ “Black Sunday” – worst dust storm – April 14, 1935 ▫ Dust would get into everything…kitchens, bedrooms, hair, nails, mouths ▫ Wrapped faces in damp rags to filter out the grit ▫ Nostrils with Vaseline to keep noses from clogging and bleeding ▫ “dust pneumonia” ▫ Many packed up families and headed west to California along Route 66
The Dust Bowl • Between 1929 and 1932, about 400, 000 farms were lost to foreclosure • Not only economic damages, but environmental ▫ Land was overworked • Drought and dust storms in the Midwest for much of the 1930 s ▫ “Black Sunday” – worst dust storm – April 14, 1935 ▫ Dust would get into everything…kitchens, bedrooms, hair, nails, mouths ▫ Wrapped faces in damp rags to filter out the grit ▫ Nostrils with Vaseline to keep noses from clogging and bleeding ▫ “dust pneumonia” ▫ Many packed up families and headed west to California along Route 66
 Click below for a video!
Click below for a video!
 Bonus Army of 1932 • Veterans marched on Washington DC to demand their bonus from services during WWI • Hoover sent Douglas Mac. Arthur in to remove the veterans who would not leave using tear gas and bayonets
Bonus Army of 1932 • Veterans marched on Washington DC to demand their bonus from services during WWI • Hoover sent Douglas Mac. Arthur in to remove the veterans who would not leave using tear gas and bayonets
 African Americans • Higher unemployment rates and they received the lowest pay • Faced increased racial violence from whites competing for jobs • 1933: 24 African Americans died by lynching
African Americans • Higher unemployment rates and they received the lowest pay • Faced increased racial violence from whites competing for jobs • 1933: 24 African Americans died by lynching
 Next. The FDR Mystique
Next. The FDR Mystique
 ELECTION OF 1932 FDR (DEM) • Promised jobs • He used his “Brain Trust” of trusted aides to help write speeches, etc. • Used the radio HOOVER (REP) • “Prosperity is Just Around the Corner” • Seen as a “do nothing” president
ELECTION OF 1932 FDR (DEM) • Promised jobs • He used his “Brain Trust” of trusted aides to help write speeches, etc. • Used the radio HOOVER (REP) • “Prosperity is Just Around the Corner” • Seen as a “do nothing” president
 NEW DEAL • His first Hundred Days were filled with legislation, over 15 pieces of major legislation • Expanded the role of the federal government • 1 st job was to restore public confidence in banks • March 6 -10 Nationwide Bank Holiday – Closed all banks to prevent withdrawals – Passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to inspect the country’s banks – Banks that couldn’t pay debts remained closed, restored confidence
NEW DEAL • His first Hundred Days were filled with legislation, over 15 pieces of major legislation • Expanded the role of the federal government • 1 st job was to restore public confidence in banks • March 6 -10 Nationwide Bank Holiday – Closed all banks to prevent withdrawals – Passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to inspect the country’s banks – Banks that couldn’t pay debts remained closed, restored confidence
 FDIC • FEDERAL DEPOSIT INSURANCE CORPORTATION • To insure individuals savings and deposits.
FDIC • FEDERAL DEPOSIT INSURANCE CORPORTATION • To insure individuals savings and deposits.
 3 Rs – Relief, Recovery, and Reform • Relief – short range goals • Recovery – long range goals • Reform – deal with current abuses
3 Rs – Relief, Recovery, and Reform • Relief – short range goals • Recovery – long range goals • Reform – deal with current abuses
 Emergency Banking Relief Act of 1933 • Power to regulate the banking system • Close and reopen banks • Safer to keep money in a reopened bank than in the back yard!
Emergency Banking Relief Act of 1933 • Power to regulate the banking system • Close and reopen banks • Safer to keep money in a reopened bank than in the back yard!
 Fireside Chats • Roosevelt used the radio to talk to Americans • Focused on Priming the Pump • Click picture for his first fireside chat during the bank holiday
Fireside Chats • Roosevelt used the radio to talk to Americans • Focused on Priming the Pump • Click picture for his first fireside chat during the bank holiday
 Federal Emergency Relief Administration (May 1933) • $500 million for states agencies for the poor
Federal Emergency Relief Administration (May 1933) • $500 million for states agencies for the poor
 Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) • Most popular of all the New Deal alphabet agencies… • Employment in fresh air government camps for about 3 million uniformed young men • Reforestation, firefighting, flood control, swamp drainage • Paid $30 a month, sent $25 home to their families
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) • Most popular of all the New Deal alphabet agencies… • Employment in fresh air government camps for about 3 million uniformed young men • Reforestation, firefighting, flood control, swamp drainage • Paid $30 a month, sent $25 home to their families
 • Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA)– help farmers meet mortgages, raised farm prices & paid farmers to grow less • Home Owners’ Loan Corporation (HOLC) – to refinance mortgages on non-farm homes
• Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA)– help farmers meet mortgages, raised farm prices & paid farmers to grow less • Home Owners’ Loan Corporation (HOLC) – to refinance mortgages on non-farm homes
 Civil Works Administration (CWA) • Provided 4 million temporary jobs during cruel winter months • Built 40, 000 schools and half a million roads
Civil Works Administration (CWA) • Provided 4 million temporary jobs during cruel winter months • Built 40, 000 schools and half a million roads
 Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA)— • renovated five dams and constructed 20 new ones. • Created jobs, provided flood control, hydroelectric power
Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA)— • renovated five dams and constructed 20 new ones. • Created jobs, provided flood control, hydroelectric power
 SEC – Securities Exchange Commission • Watchdog over stock market and protect investors.
SEC – Securities Exchange Commission • Watchdog over stock market and protect investors.
 The Supreme Court • Struck down two New Deal acts because federal government overstepped their roles (NIRA and AAA) • FDR tried to pass a court-reform bill in 1937 reorganizing the federal judiciary and appoint new justices • Criticized it upset judicial independence and checks and balances • Over next four years, FDR appointed 7 new justices from resignations
The Supreme Court • Struck down two New Deal acts because federal government overstepped their roles (NIRA and AAA) • FDR tried to pass a court-reform bill in 1937 reorganizing the federal judiciary and appoint new justices • Criticized it upset judicial independence and checks and balances • Over next four years, FDR appointed 7 new justices from resignations
 Some people hated the New Deal • Didn’t go far enough to help the poor and reform the economic system • FDR spent too much on direct relief and used New Deal to control business and socialize economy • Huey Long—Share-Our-Wealth promised “Every Man a King” – Had 7. 5 million members until he was assassinated • Father Charles Coughlin – Catholic priest who became anti Semitic – Broadcasted on radio economic, political, and religious ideas
Some people hated the New Deal • Didn’t go far enough to help the poor and reform the economic system • FDR spent too much on direct relief and used New Deal to control business and socialize economy • Huey Long—Share-Our-Wealth promised “Every Man a King” – Had 7. 5 million members until he was assassinated • Father Charles Coughlin – Catholic priest who became anti Semitic – Broadcasted on radio economic, political, and religious ideas
 Second Hundred Days (or Second New Deal) • Spring 1935 • More relief for farmers and workers • Eleanor Roosevelt travelled the country to remind her husband of the suffering • 1936 election FDR wins overwhelmingly – 1 st time African Americans voted solidly Democratic and labor unions supported a candidate
Second Hundred Days (or Second New Deal) • Spring 1935 • More relief for farmers and workers • Eleanor Roosevelt travelled the country to remind her husband of the suffering • 1936 election FDR wins overwhelmingly – 1 st time African Americans voted solidly Democratic and labor unions supported a candidate
 Works Progress Administration (WPA) • 1935 • Employment on useful projects • $11 billion spent to give jobs to over 8 million workers • WKU’s Cherry Hall was a recipient of the WPA money and workers • Federal Art Project was also started
Works Progress Administration (WPA) • 1935 • Employment on useful projects • $11 billion spent to give jobs to over 8 million workers • WKU’s Cherry Hall was a recipient of the WPA money and workers • Federal Art Project was also started
 Wagner Act • 1935 (National labor relations board) • Protected right of workers to join unions and collective bargain • Prohibited unfair labor practices like threatening workers, firing union members, and interfering with union organizing • 1938 Fair Labor Standards Act • Set maximum hours at 44 and minimum wage at $0. 25 • Set rules for 16 and under, and banned dangerous work for under 18
Wagner Act • 1935 (National labor relations board) • Protected right of workers to join unions and collective bargain • Prohibited unfair labor practices like threatening workers, firing union members, and interfering with union organizing • 1938 Fair Labor Standards Act • Set maximum hours at 44 and minimum wage at $0. 25 • Set rules for 16 and under, and banned dangerous work for under 18
 Social Securities Act • 1935 • “Aged” insurance for retirees 65 or older and their spouses • Unemployment compensation system – $15 -$18 a week • Aid to families with dependent children and the disabled
Social Securities Act • 1935 • “Aged” insurance for retirees 65 or older and their spouses • Unemployment compensation system – $15 -$18 a week • Aid to families with dependent children and the disabled
 Rural Electrification Administration • 1935 • Brought electricity to isolated areas • In 1935, only 12. 6% of American farms had electricity • 48% in 1945, 90% in 1949
Rural Electrification Administration • 1935 • Brought electricity to isolated areas • In 1935, only 12. 6% of American farms had electricity • 48% in 1945, 90% in 1949
 New Roles for Women • More women working outside of home • Frances Perkins – Secretary of labor– First woman to head an executive department – Helped create the Social Security system • Mary Mc. Leod Bethune – Leader of the Black Cabinet and director of Negro Affairs in the National Youth Administration – Advised FDR on racial issues and made provided job training and benefits to minority students
New Roles for Women • More women working outside of home • Frances Perkins – Secretary of labor– First woman to head an executive department – Helped create the Social Security system • Mary Mc. Leod Bethune – Leader of the Black Cabinet and director of Negro Affairs in the National Youth Administration – Advised FDR on racial issues and made provided job training and benefits to minority students
 1937 A Troubled Year • Moving Forward – Supreme court upheld many New Deal programs • March 1937 upheld a Washington law that granted Minimum Wage • Ruled both, a key part of the Wagner Act and Social Security constitutional. – Farm Tenancy Act - 1937 • Gave tenant farmers and Sharecroppers a chance to buy land of their own • Recovery in Doubt – FDR scaled back federal deficit spending – 1937 - A bad year for recovery. Massive drop in stocks and by the end of the year another 2 million American unemployed.
1937 A Troubled Year • Moving Forward – Supreme court upheld many New Deal programs • March 1937 upheld a Washington law that granted Minimum Wage • Ruled both, a key part of the Wagner Act and Social Security constitutional. – Farm Tenancy Act - 1937 • Gave tenant farmers and Sharecroppers a chance to buy land of their own • Recovery in Doubt – FDR scaled back federal deficit spending – 1937 - A bad year for recovery. Massive drop in stocks and by the end of the year another 2 million American unemployed.
 Impact of the New Deal • Relief, Recovery, Reform – Which area was the New Deal most successful? • Changing relationships – Changed the link between the American people and the Government – New Role for Government meant a much larger Government. • As a result many more people now looked to the Government for help
Impact of the New Deal • Relief, Recovery, Reform – Which area was the New Deal most successful? • Changing relationships – Changed the link between the American people and the Government – New Role for Government meant a much larger Government. • As a result many more people now looked to the Government for help
 End of the New Deal • Weakened support – 1937 – What happened in 1937 to cause loss of support? • The 1938 Election – Republicans and Southern Democrats gained seats in the House and the Senate – Why did this happen? • After the New Deal – After 1938 FDR lacked the support to pass New Deal Styled programs. – Problems in Europe now held the attention of the American Public. – In 1939 and 1940 international conflict will ultimately do what FDR’s programs could not.
End of the New Deal • Weakened support – 1937 – What happened in 1937 to cause loss of support? • The 1938 Election – Republicans and Southern Democrats gained seats in the House and the Senate – Why did this happen? • After the New Deal – After 1938 FDR lacked the support to pass New Deal Styled programs. – Problems in Europe now held the attention of the American Public. – In 1939 and 1940 international conflict will ultimately do what FDR’s programs could not.


