a43bf5343d1c19396801795ddca4ee10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Gravity from quantum entanglement Jae-Weon Lee (Jungwon univ. )
Gravity from quantum entanglement Jae-Weon Lee (Jungwon univ. )
 Outline u Gravity is emergent • Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) • Entropy gravity (Verlinde , 2010) • Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2010) u Spacetime is emergent • Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters) • Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk) u QM is emergent • Information loss QM (Lee, 2011)
Outline u Gravity is emergent • Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) • Entropy gravity (Verlinde , 2010) • Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2010) u Spacetime is emergent • Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters) • Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk) u QM is emergent • Information loss QM (Lee, 2011)
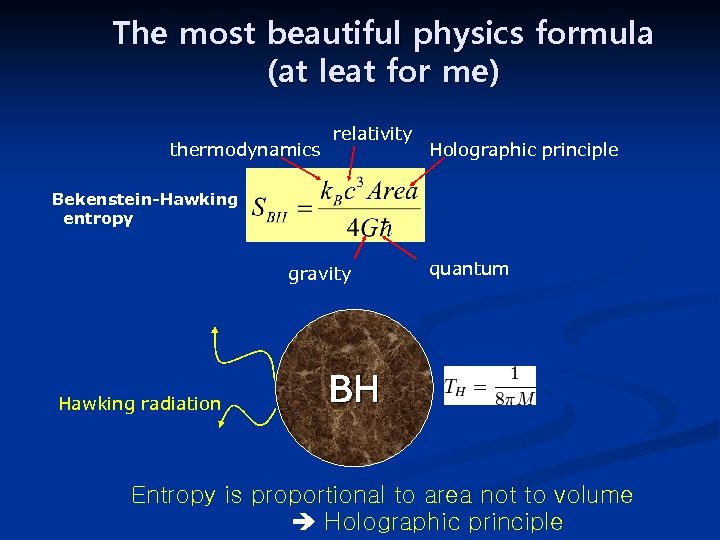 The most beautiful physics formula (at leat for me) thermodynamics relativity Holographic principle Bekenstein-Hawking entropy gravity Hawking radiation quantum BH Entropy is proportional to area not to volume Holographic principle
The most beautiful physics formula (at leat for me) thermodynamics relativity Holographic principle Bekenstein-Hawking entropy gravity Hawking radiation quantum BH Entropy is proportional to area not to volume Holographic principle
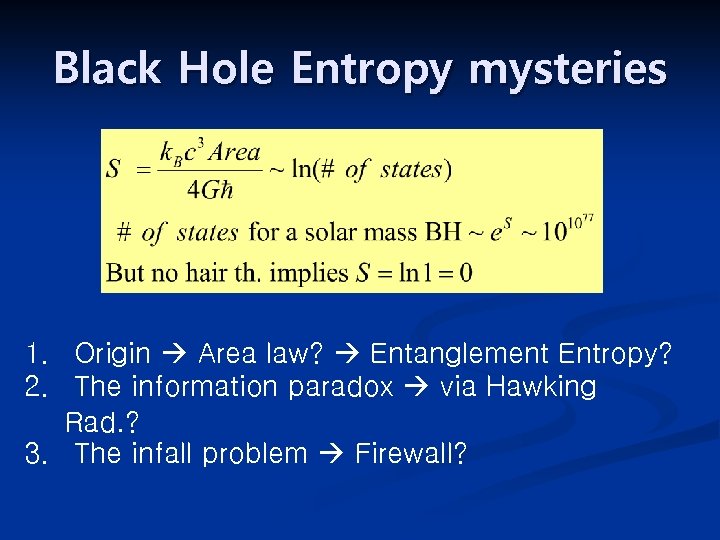 Black Hole Entropy mysteries 1. Origin Area law? Entanglement Entropy? 2. The information paradox via Hawking Rad. ? 3. The infall problem Firewall?
Black Hole Entropy mysteries 1. Origin Area law? Entanglement Entropy? 2. The information paradox via Hawking Rad. ? 3. The infall problem Firewall?
 History • • • • • BH thermodynamics (Bekenstein & Hawking 1972) d. E=Td. S Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters 1983 ) Entanglement BH entropy (Bombelli et al 1986) BH war (Hawking vs Susskind) Entanglement Arrow of time (Llyod, 1988) Holographic principle (t’Hooft & Susskind) Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) Entanglement Dark energy (Lee, Kim, 2007) Entropy Gravity (Verlinde , 2010) Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2010 ) Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk 2010 ) Holography Entanglement (Takayhanagi, 2012) BH Firewall paradox Entanglement=Wormhole (ER=EPR, Maldacena) Experimental realization of Pa. W ( Moreva et al, 2013) Entanglement Gravity in Ad. S/CFT ( Raamsdonk 2014) Entanglement Gravity (Jacobson 2015)
History • • • • • BH thermodynamics (Bekenstein & Hawking 1972) d. E=Td. S Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters 1983 ) Entanglement BH entropy (Bombelli et al 1986) BH war (Hawking vs Susskind) Entanglement Arrow of time (Llyod, 1988) Holographic principle (t’Hooft & Susskind) Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) Entanglement Dark energy (Lee, Kim, 2007) Entropy Gravity (Verlinde , 2010) Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2010 ) Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk 2010 ) Holography Entanglement (Takayhanagi, 2012) BH Firewall paradox Entanglement=Wormhole (ER=EPR, Maldacena) Experimental realization of Pa. W ( Moreva et al, 2013) Entanglement Gravity in Ad. S/CFT ( Raamsdonk 2014) Entanglement Gravity (Jacobson 2015)
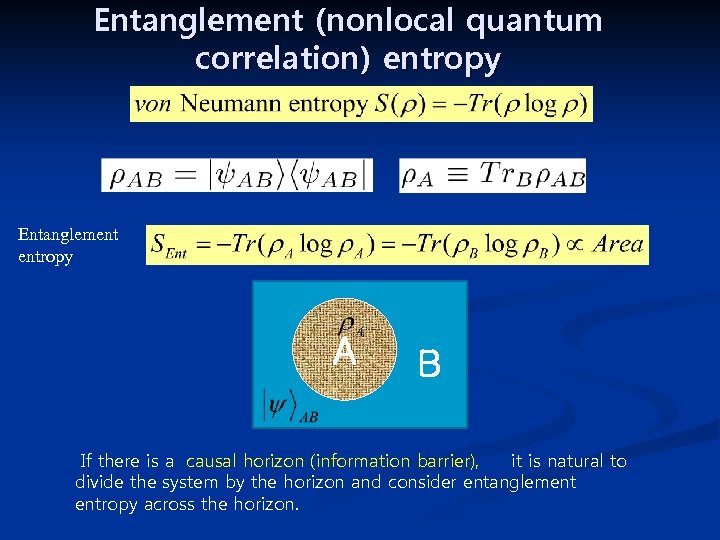 Entanglement (nonlocal quantum correlation) entropy , Entanglement entropy A B If there is a causal horizon (information barrier), it is natural to divide the system by the horizon and consider entanglement entropy across the horizon.
Entanglement (nonlocal quantum correlation) entropy , Entanglement entropy A B If there is a causal horizon (information barrier), it is natural to divide the system by the horizon and consider entanglement entropy across the horizon.
 Holography and Entanglement has 1. Area Law (in general) 2. Nonlocality 3. Relation to causality 4. Something fundamental 5. Observer dependency It reminds us of the Holographic principle! * Entanglement is faster than light! ( v > O(103)c ) Entanglement is more fundamental than anything with v <= c
Holography and Entanglement has 1. Area Law (in general) 2. Nonlocality 3. Relation to causality 4. Something fundamental 5. Observer dependency It reminds us of the Holographic principle! * Entanglement is faster than light! ( v > O(103)c ) Entanglement is more fundamental than anything with v <= c
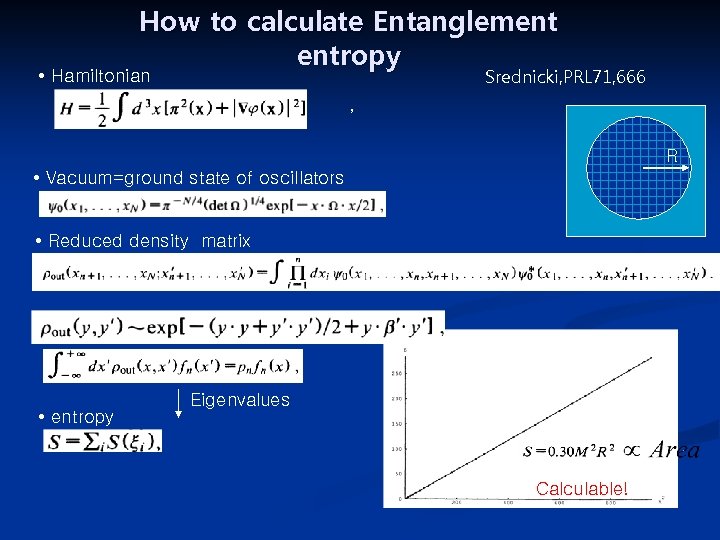 How to calculate Entanglement entropy Srednicki, PRL 71, 666 • Hamiltonian , R • Vacuum=ground state of oscillators • Reduced density matrix • entropy Eigenvalues Calculable!
How to calculate Entanglement entropy Srednicki, PRL 71, 666 • Hamiltonian , R • Vacuum=ground state of oscillators • Reduced density matrix • entropy Eigenvalues Calculable!
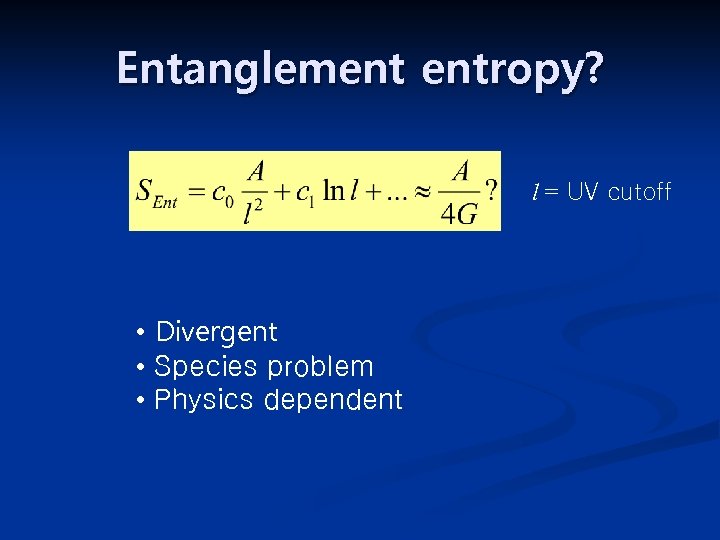 Entanglement entropy? l = UV cutoff • Divergent • Species problem • Physics dependent
Entanglement entropy? l = UV cutoff • Divergent • Species problem • Physics dependent
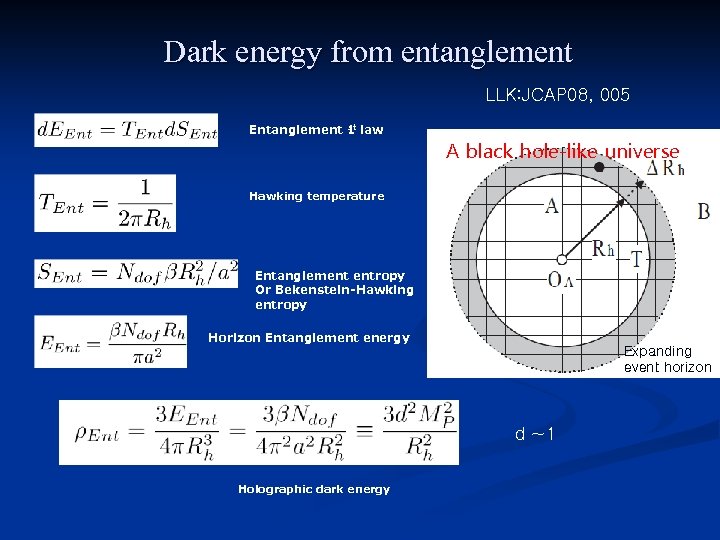 Dark energy from entanglement LLK: JCAP 08, 005 st Entanglement 1 law A black hole-like universe Hawking temperature Entanglement entropy Or Bekenstein-Hawking entropy Horizon Entanglement energy Expanding event horizonn d ~1 Holographic dark energy
Dark energy from entanglement LLK: JCAP 08, 005 st Entanglement 1 law A black hole-like universe Hawking temperature Entanglement entropy Or Bekenstein-Hawking entropy Horizon Entanglement energy Expanding event horizonn d ~1 Holographic dark energy
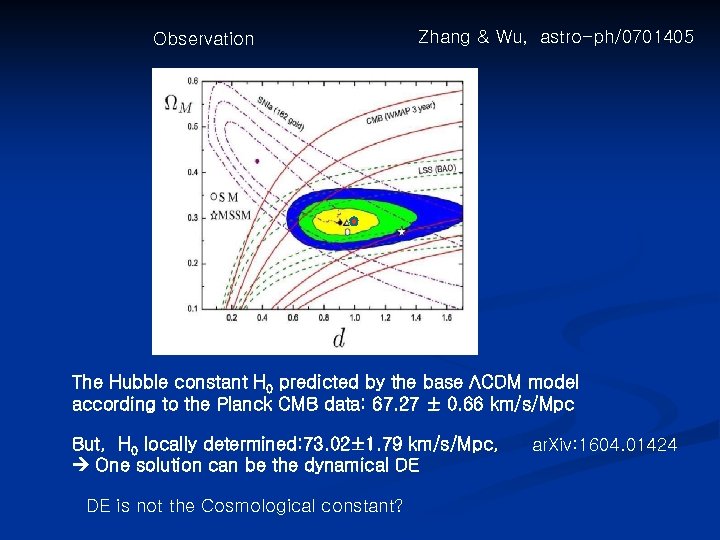 Observation Zhang & Wu, astro-ph/0701405 The Hubble constant H 0 predicted by the base ΛCDM model according to the Planck CMB data: 67. 27 ± 0. 66 km/s/Mpc But, H 0 locally determined: 73. 02± 1. 79 km/s/Mpc, One solution can be the dynamical DE DE is not the Cosmological constant? ar. Xiv: 1604. 01424
Observation Zhang & Wu, astro-ph/0701405 The Hubble constant H 0 predicted by the base ΛCDM model according to the Planck CMB data: 67. 27 ± 0. 66 km/s/Mpc But, H 0 locally determined: 73. 02± 1. 79 km/s/Mpc, One solution can be the dynamical DE DE is not the Cosmological constant? ar. Xiv: 1604. 01424
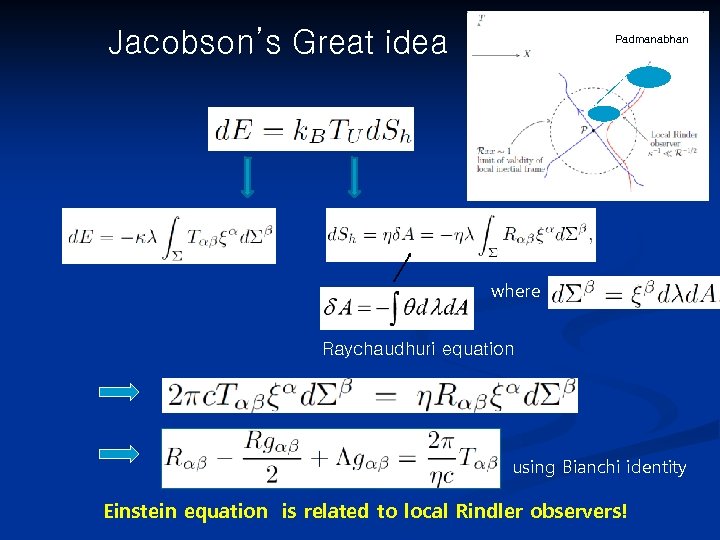 Jacobson’s Great idea Padmanabhan R x where Raychaudhuri equation using Bianchi identity Einstein equation is related to local Rindler observers!
Jacobson’s Great idea Padmanabhan R x where Raychaudhuri equation using Bianchi identity Einstein equation is related to local Rindler observers!
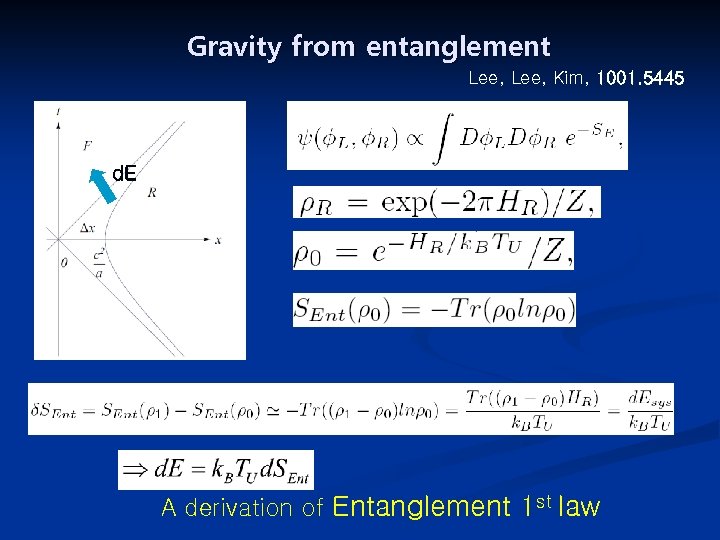 Gravity from entanglement Lee, Kim, 1001. 5445 d. E A derivation of Entanglement 1 st law
Gravity from entanglement Lee, Kim, 1001. 5445 d. E A derivation of Entanglement 1 st law
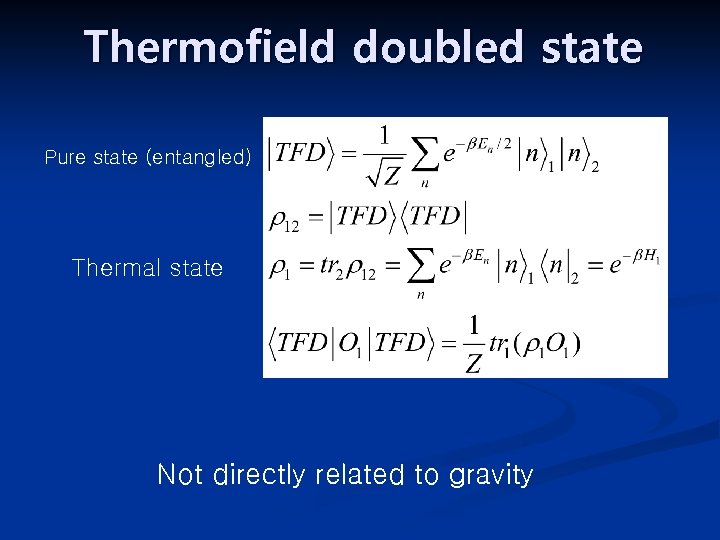 Thermofield doubled state Pure state (entangled) Thermal state Not directly related to gravity
Thermofield doubled state Pure state (entangled) Thermal state Not directly related to gravity
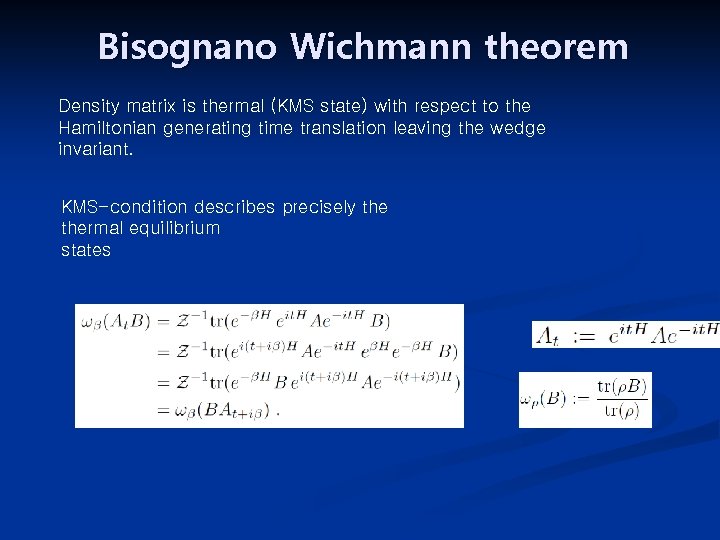 Bisognano Wichmann theorem Density matrix is thermal (KMS state) with respect to the Hamiltonian generating time translation leaving the wedge invariant. KMS-condition describes precisely thermal equilibrium states
Bisognano Wichmann theorem Density matrix is thermal (KMS state) with respect to the Hamiltonian generating time translation leaving the wedge invariant. KMS-condition describes precisely thermal equilibrium states
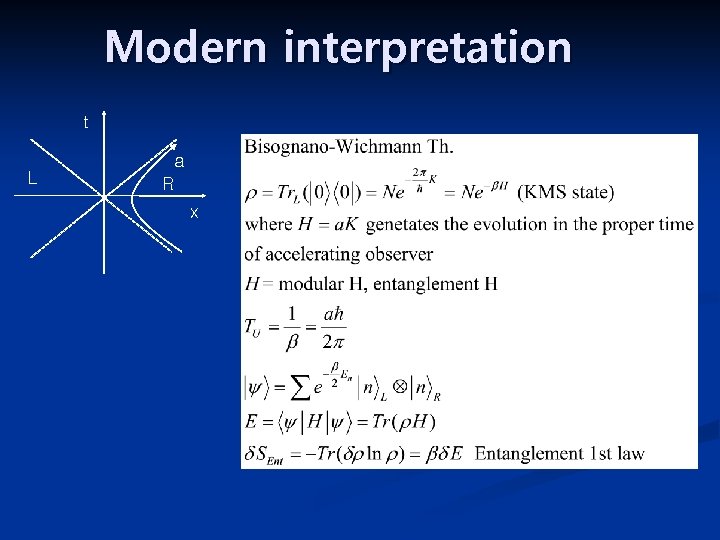 Modern interpretation t L a R x
Modern interpretation t L a R x
 Perturbative QG Einstein Eq. + low energy QG EE is SBH Perturbative quantum gravity EOM Bianchi 1211. 0522
Perturbative QG Einstein Eq. + low energy QG EE is SBH Perturbative quantum gravity EOM Bianchi 1211. 0522
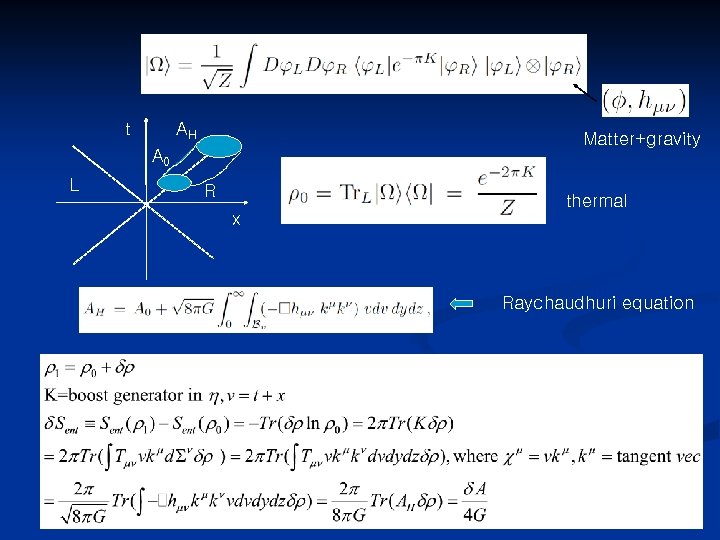 t AH Matter+gravity A 0 L R x thermal Raychaudhuri equation
t AH Matter+gravity A 0 L R x thermal Raychaudhuri equation
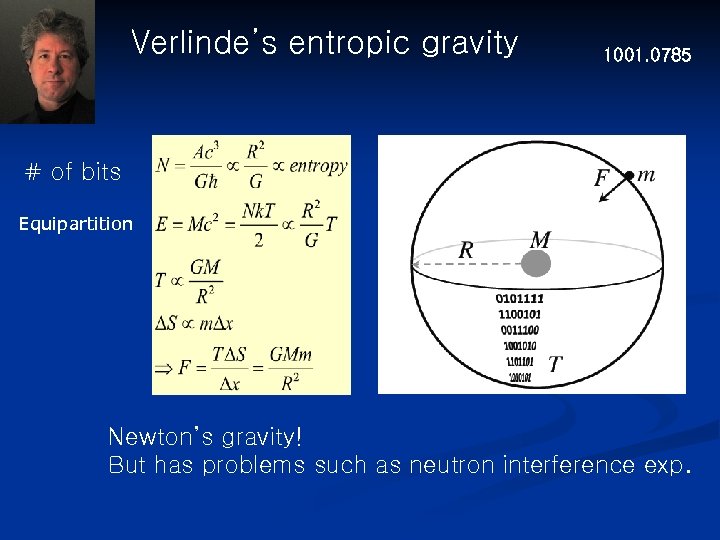 Verlinde’s entropic gravity 1001. 0785 # of bits Equipartition Newton’s gravity! But has problems such as neutron interference exp.
Verlinde’s entropic gravity 1001. 0785 # of bits Equipartition Newton’s gravity! But has problems such as neutron interference exp.
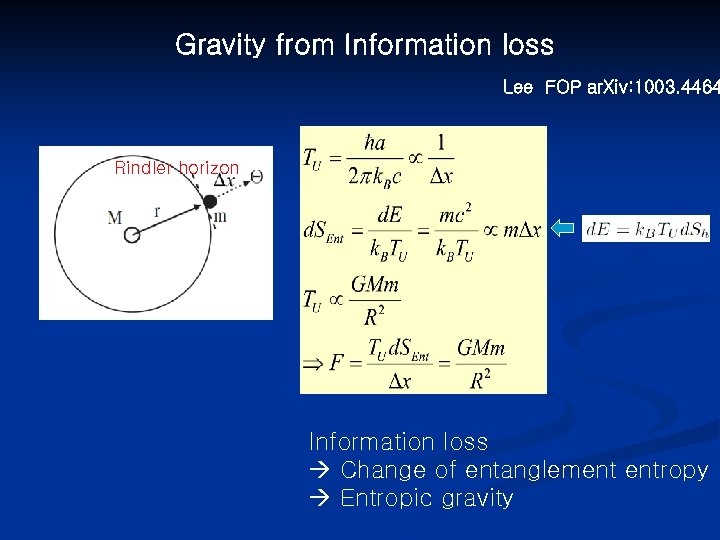 Gravity from Information loss Lee FOP ar. Xiv: 1003. 4464 Rindler horizon Information loss Change of entanglement entropy Entropic gravity
Gravity from Information loss Lee FOP ar. Xiv: 1003. 4464 Rindler horizon Information loss Change of entanglement entropy Entropic gravity

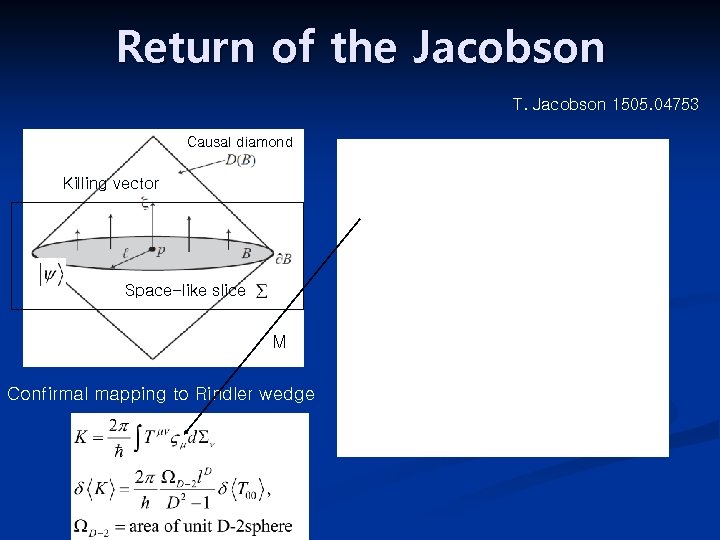 Return of the Jacobson T. Jacobson 1505. 04753 Causal diamond Killing vector Space-like slice M Confirmal mapping to Rindler wedge
Return of the Jacobson T. Jacobson 1505. 04753 Causal diamond Killing vector Space-like slice M Confirmal mapping to Rindler wedge
 continued T. Jacobson 1505. 04753 The area variation at constant V for a maximally symmetric spacetime C. C.
continued T. Jacobson 1505. 04753 The area variation at constant V for a maximally symmetric spacetime C. C.
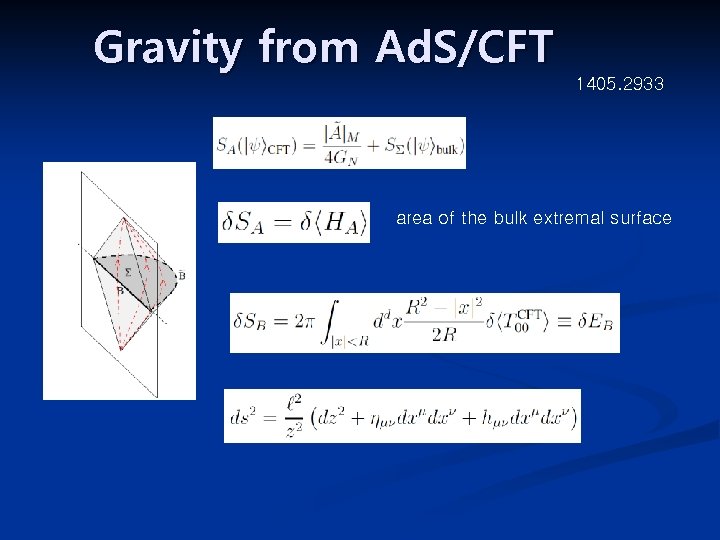 Gravity from Ad. S/CFT 1405. 2933 area of the bulk extremal surface
Gravity from Ad. S/CFT 1405. 2933 area of the bulk extremal surface
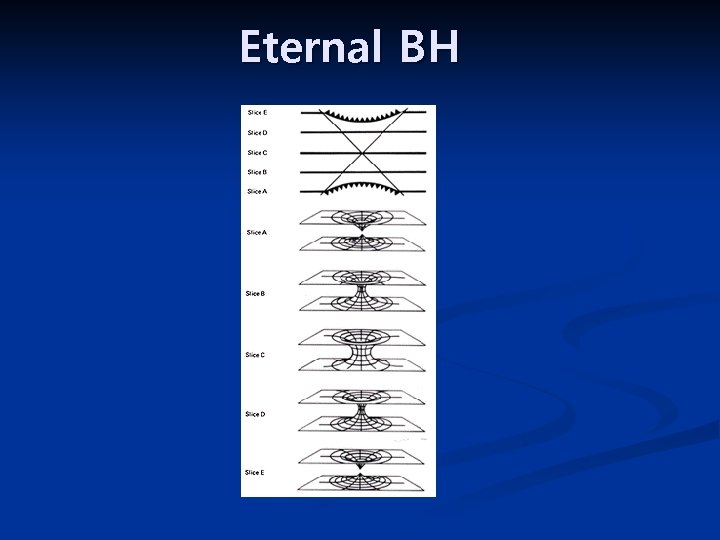 Eternal BH
Eternal BH
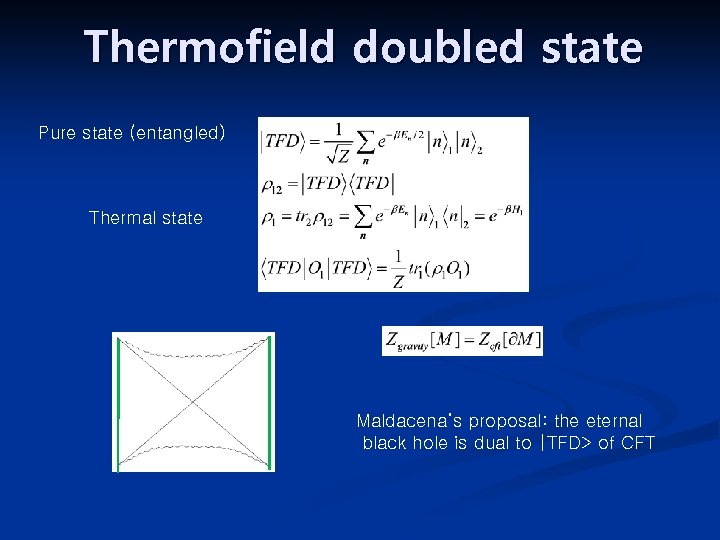 Thermofield doubled state Pure state (entangled) Thermal state Maldacena’s proposal: the eternal black hole is dual to |TFD> of CFT
Thermofield doubled state Pure state (entangled) Thermal state Maldacena’s proposal: the eternal black hole is dual to |TFD> of CFT
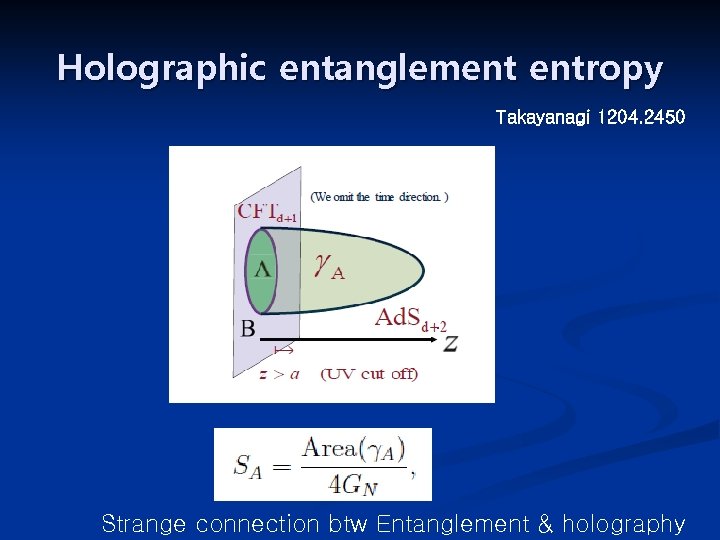 Holographic entanglement entropy Takayanagi 1204. 2450 Strange connection btw Entanglement & holography
Holographic entanglement entropy Takayanagi 1204. 2450 Strange connection btw Entanglement & holography
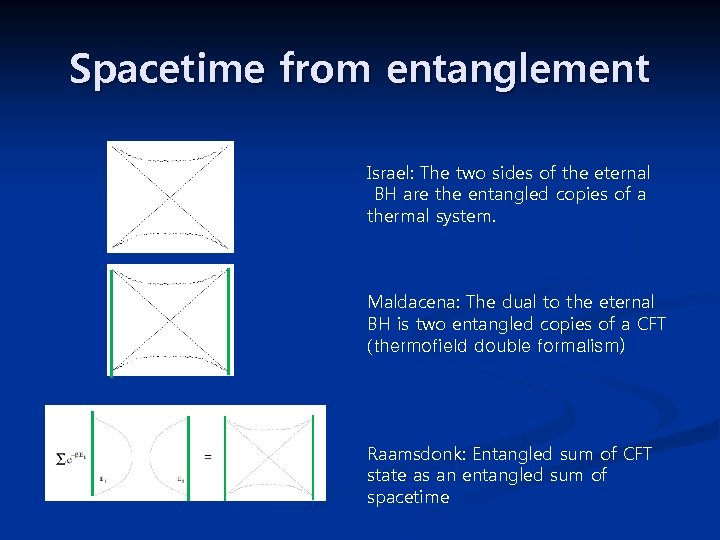 Spacetime from entanglement Israel: The two sides of the eternal BH are the entangled copies of a thermal system. Maldacena: The dual to the eternal BH is two entangled copies of a CFT (thermofield double formalism) Raamsdonk: Entangled sum of CFT state as an entangled sum of spacetime
Spacetime from entanglement Israel: The two sides of the eternal BH are the entangled copies of a thermal system. Maldacena: The dual to the eternal BH is two entangled copies of a CFT (thermofield double formalism) Raamsdonk: Entangled sum of CFT state as an entangled sum of spacetime
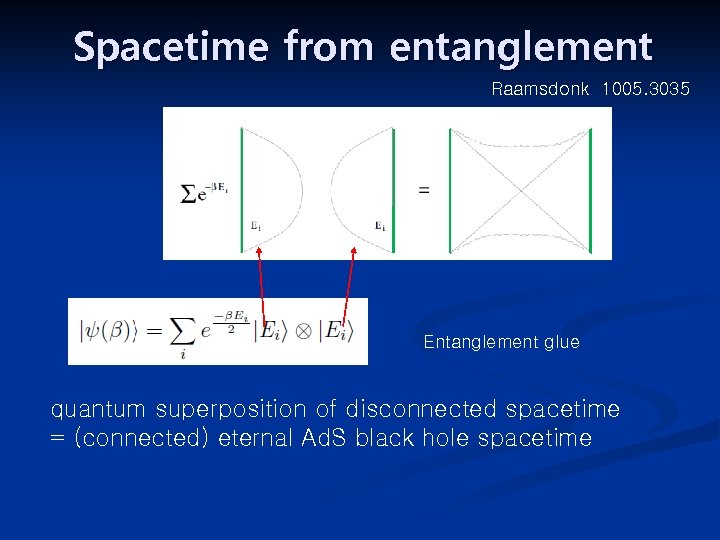 Spacetime from entanglement Raamsdonk 1005. 3035 Entanglement glue quantum superposition of disconnected spacetime = (connected) eternal Ad. S black hole spacetime
Spacetime from entanglement Raamsdonk 1005. 3035 Entanglement glue quantum superposition of disconnected spacetime = (connected) eternal Ad. S black hole spacetime
 The Time problem • In QM time labels the dynamics but does not participate as a degree of freedom. • In GR, time is just an arbitrary label theory is invariant under time reparameterizations. Wave function of WDE is static. There is no time in canonical Q. Gravity
The Time problem • In QM time labels the dynamics but does not participate as a degree of freedom. • In GR, time is just an arbitrary label theory is invariant under time reparameterizations. Wave function of WDE is static. There is no time in canonical Q. Gravity
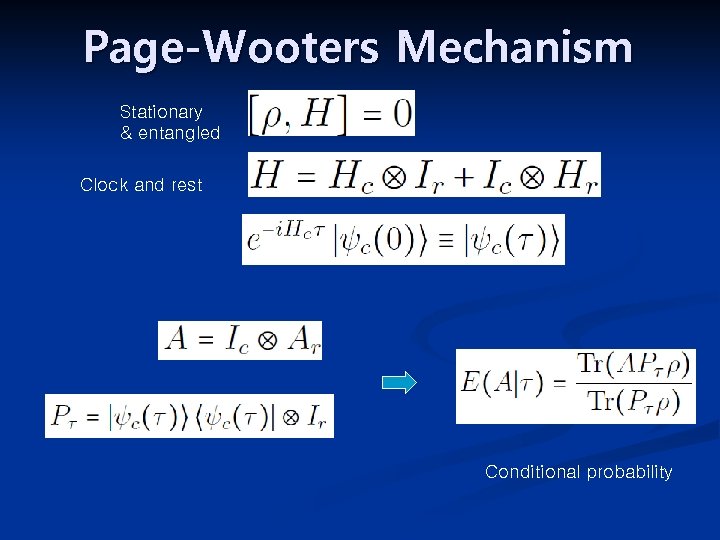 Page-Wooters Mechanism Stationary & entangled Clock and rest Conditional probability
Page-Wooters Mechanism Stationary & entangled Clock and rest Conditional probability
 where
where
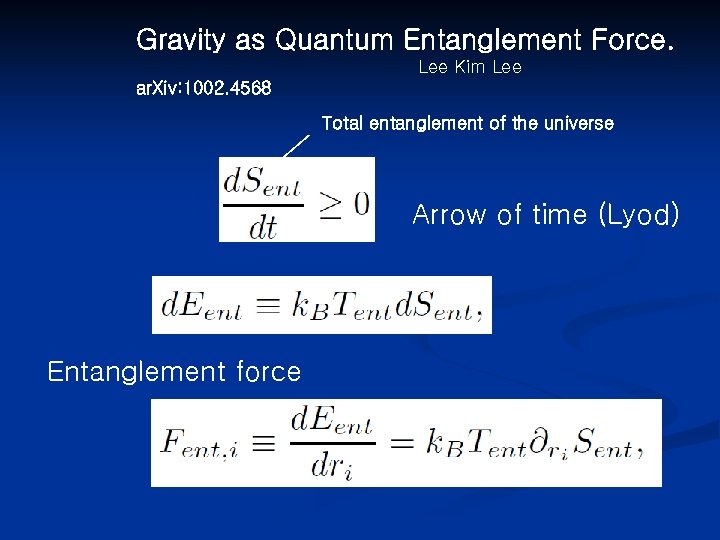 Gravity as Quantum Entanglement Force. Lee Kim Lee ar. Xiv: 1002. 4568 Total entanglement of the universe Arrow of time (Lyod) Entanglement force
Gravity as Quantum Entanglement Force. Lee Kim Lee ar. Xiv: 1002. 4568 Total entanglement of the universe Arrow of time (Lyod) Entanglement force
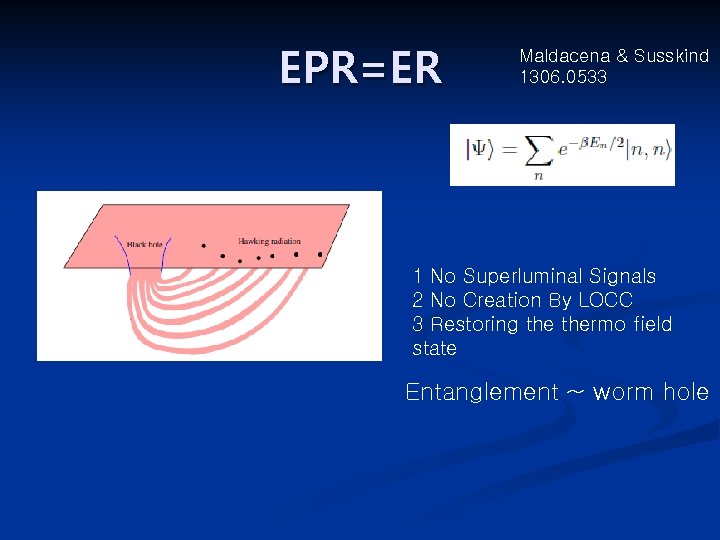 EPR=ER Maldacena & Susskind 1306. 0533 1 No Superluminal Signals 2 No Creation By LOCC 3 Restoring thermo field state Entanglement ~ worm hole
EPR=ER Maldacena & Susskind 1306. 0533 1 No Superluminal Signals 2 No Creation By LOCC 3 Restoring thermo field state Entanglement ~ worm hole
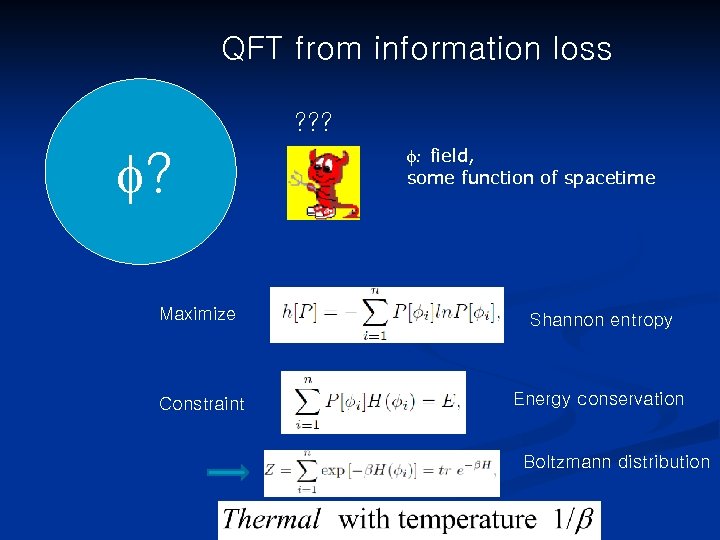 QFT from information loss ? ? ? f: field, some function of spacetime Maximize Shannon entropy Constraint Energy conservation Boltzmann distribution
QFT from information loss ? ? ? f: field, some function of spacetime Maximize Shannon entropy Constraint Energy conservation Boltzmann distribution
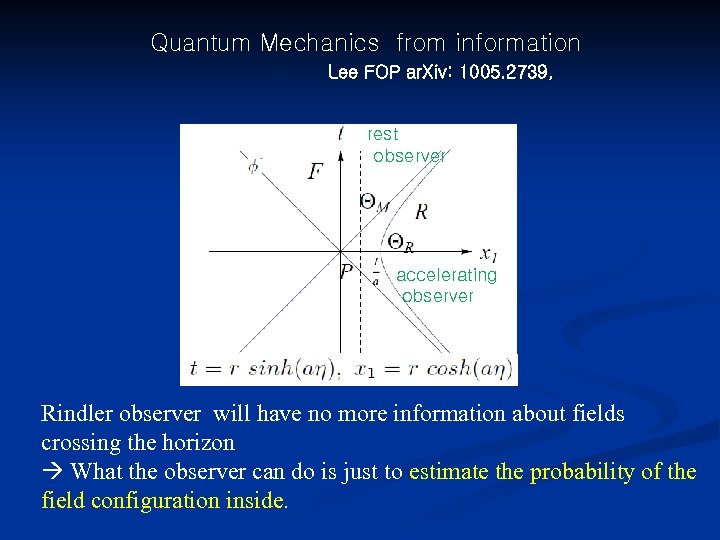 Quantum Mechanics from information Lee FOP ar. Xiv: 1005. 2739, rest observer accelerating observer Rindler observer will have no more information about fields crossing the horizon What the observer can do is just to estimate the probability of the field configuration inside.
Quantum Mechanics from information Lee FOP ar. Xiv: 1005. 2739, rest observer accelerating observer Rindler observer will have no more information about fields crossing the horizon What the observer can do is just to estimate the probability of the field configuration inside.
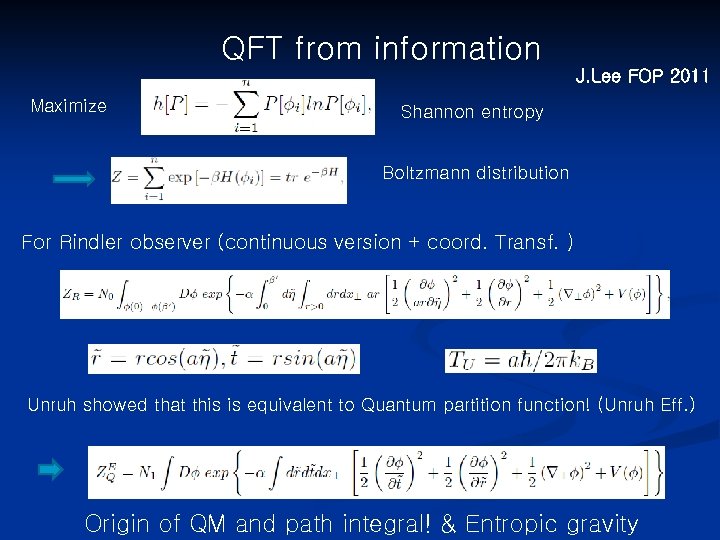 QFT from information J. Lee FOP 2011 Maximize Shannon entropy Boltzmann distribution For Rindler observer (continuous version + coord. Transf. ) Unruh showed that this is equivalent to Quantum partition function! (Unruh Eff. ) Origin of QM and path integral! & Entropic gravity
QFT from information J. Lee FOP 2011 Maximize Shannon entropy Boltzmann distribution For Rindler observer (continuous version + coord. Transf. ) Unruh showed that this is equivalent to Quantum partition function! (Unruh Eff. ) Origin of QM and path integral! & Entropic gravity
 Conclusion: Emergent universe? u Gravity is emergent • Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) • Entropy gravity (Verlinde , 2011) • Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2011) u Spacetime is emergent • Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters) • Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk) u QM is emergent • Information loss QM (Lee, 2011) Universe is emergent! from what ? ? ? Information! Information of what? ? ?
Conclusion: Emergent universe? u Gravity is emergent • Thermodynamics Gravity (Jacobson, Padmanabhan) • Entropy gravity (Verlinde , 2011) • Entanglement Gravity (Lee, Kim, 2011) u Spacetime is emergent • Entanglement Time (Page & Wooters) • Entanglement Spacetime (Raamsdonk) u QM is emergent • Information loss QM (Lee, 2011) Universe is emergent! from what ? ? ? Information! Information of what? ? ?

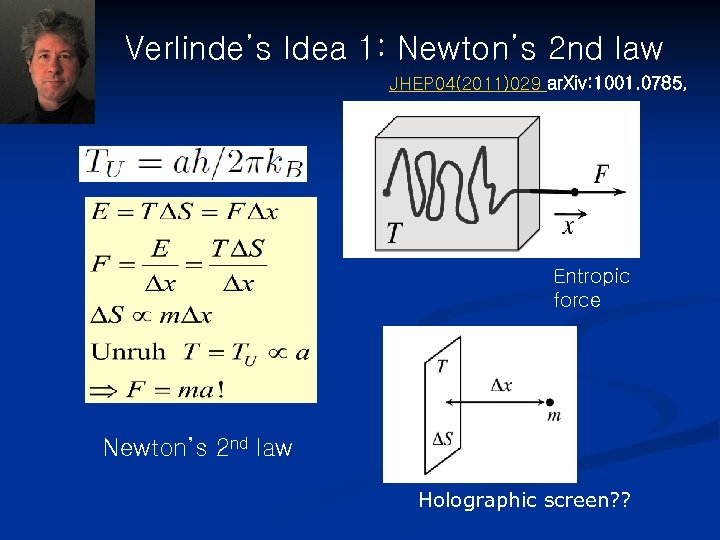 Verlinde’s Idea 1: Newton’s 2 nd law JHEP 04(2011)029 ar. Xiv: 1001. 0785, Entropic force Newton’s 2 nd law Holographic screen? ?
Verlinde’s Idea 1: Newton’s 2 nd law JHEP 04(2011)029 ar. Xiv: 1001. 0785, Entropic force Newton’s 2 nd law Holographic screen? ?

 Lovelock Theorem in a 3+1 D differentiable manifold, the Einstein tensor is the only tensorial and divergence-free function of the and at most their first and second partial derivatives.
Lovelock Theorem in a 3+1 D differentiable manifold, the Einstein tensor is the only tensorial and divergence-free function of the and at most their first and second partial derivatives.
 Our works so far 1) Dark energy from vacuum entanglement. JCAP 0708: 005, 2007. dark energy from information 2) Does information rule the quantum black hole? ar. Xiv: 0709. 3573 (MPLA) Black hole mass from information 3) Is dark energy from cosmic Hawking radiation? Mod. Phys. Lett. A 25: 257 -267, 2010 Dark energy is cosmic Hawking radiation Verlinde’s paper: Gravity and mechanics from entropic force ar. Xiv: 1001. 0785 1) Gravity from Quantum Information. 1001. 5445 [hep-th] gravity is related to quantum entanglement or information loss 2) Gravity as Quantum Entanglement Force. ar. Xiv: 1002. 4568 [hep-th] 3) Zero Cosmological Constant and Nonzero Dark Energy from Holographic Principle. ar. Xiv: 1003. 1878 (Lee) 4) On the Origin of Entropic Gravity and Inertia. ar. Xiv: 1003. 4464 [hep-th] (Lee) Verlinde’s theory from quantum information model 5) Quantum mechanics emerges from information theory applied to causal horizons ar. Xiv: 0041329 (Lee)
Our works so far 1) Dark energy from vacuum entanglement. JCAP 0708: 005, 2007. dark energy from information 2) Does information rule the quantum black hole? ar. Xiv: 0709. 3573 (MPLA) Black hole mass from information 3) Is dark energy from cosmic Hawking radiation? Mod. Phys. Lett. A 25: 257 -267, 2010 Dark energy is cosmic Hawking radiation Verlinde’s paper: Gravity and mechanics from entropic force ar. Xiv: 1001. 0785 1) Gravity from Quantum Information. 1001. 5445 [hep-th] gravity is related to quantum entanglement or information loss 2) Gravity as Quantum Entanglement Force. ar. Xiv: 1002. 4568 [hep-th] 3) Zero Cosmological Constant and Nonzero Dark Energy from Holographic Principle. ar. Xiv: 1003. 1878 (Lee) 4) On the Origin of Entropic Gravity and Inertia. ar. Xiv: 1003. 4464 [hep-th] (Lee) Verlinde’s theory from quantum information model 5) Quantum mechanics emerges from information theory applied to causal horizons ar. Xiv: 0041329 (Lee)
 Black hole thermodynamics Bekenstein & Hawking 1) The First Law 2) The Second Law d. E=THd. S BH area always increases =entropy always increases Nobody knows the physical origin of these laws!
Black hole thermodynamics Bekenstein & Hawking 1) The First Law 2) The Second Law d. E=THd. S BH area always increases =entropy always increases Nobody knows the physical origin of these laws!
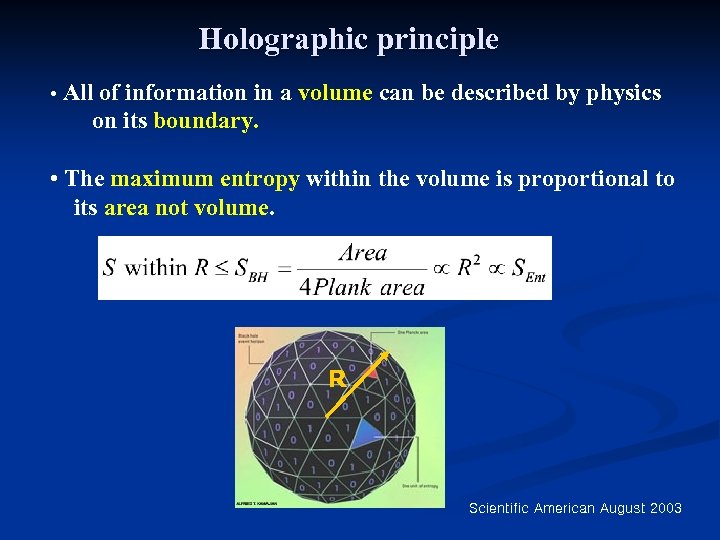 Holographic principle • All of information in a volume can be described by physics on its boundary. • The maximum entropy within the volume is proportional to its area not volume. R Scientific American August 2003
Holographic principle • All of information in a volume can be described by physics on its boundary. • The maximum entropy within the volume is proportional to its area not volume. R Scientific American August 2003


