3621e5a0e6600e8769dcd71ae8877f28.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Grant Administration using Technology Kevin Mc. Neal, Program Manager Ryan White Part A, Phoenix EMA Maricopa County, Arizona
Grant Administration using Technology Kevin Mc. Neal, Program Manager Ryan White Part A, Phoenix EMA Maricopa County, Arizona
 Objectives n n Advantages to utilizing technology in Grant Administration Challenges Evolution of a technology-based system of care Results
Objectives n n Advantages to utilizing technology in Grant Administration Challenges Evolution of a technology-based system of care Results
 Advantages n Reporting and Analysis n n n Monitoring/Oversight n n n Real time reporting Aggregate data Provider level Service category level Streamlining the system n n n Reduced manual work Standardized data Consistent across the continuum
Advantages n Reporting and Analysis n n n Monitoring/Oversight n n n Real time reporting Aggregate data Provider level Service category level Streamlining the system n n n Reduced manual work Standardized data Consistent across the continuum
 Challenges n Buy – In n n Implementation n n Not overnight – it’s a process Integrity of Data n n Providers Planning Council Consumers HRSA Critical to maintain data integrity Work Flow n n Adapting to change Process development
Challenges n Buy – In n n Implementation n n Not overnight – it’s a process Integrity of Data n n Providers Planning Council Consumers HRSA Critical to maintain data integrity Work Flow n n Adapting to change Process development
 Evolution n Identify Stakeholders n What do they want/need n n Identify Program Needs n n Planning Council, HRSA, Consumers, etc. What do we want/need to tell them Identify system/technology needs n n n Infrastructure – Grantee and Providers What is utilized What is needed
Evolution n Identify Stakeholders n What do they want/need n n Identify Program Needs n n Planning Council, HRSA, Consumers, etc. What do we want/need to tell them Identify system/technology needs n n n Infrastructure – Grantee and Providers What is utilized What is needed
 Evolution n Plan n Timeline – How long will it take? n n Standardization (across the system – everyone reporting the same way) Expectations n n Conversion n n How to actually implement the changes Protect Data Integrity n n Provider IT AA Infrastructure Testing n Phoenix EMA staggered*** Review/refine n n PDSA Glitches – expect them
Evolution n Plan n Timeline – How long will it take? n n Standardization (across the system – everyone reporting the same way) Expectations n n Conversion n n How to actually implement the changes Protect Data Integrity n n Provider IT AA Infrastructure Testing n Phoenix EMA staggered*** Review/refine n n PDSA Glitches – expect them
 Results n Reporting/Analysis n Data integrityn n Data is from consistent source – The Grantee Providers report in standardized methodology n n n Relational data n n Same expectations across the continuum Multiple providers can be aggregated. Data can be cross referenced across services, providers Standard Reporting n n n Information is standardized and reported across continuum Audience – across all levels n Client level data can report trends and utilization from clients across different service categories. n (Example – graph of PA CM to other services)
Results n Reporting/Analysis n Data integrityn n Data is from consistent source – The Grantee Providers report in standardized methodology n n n Relational data n n Same expectations across the continuum Multiple providers can be aggregated. Data can be cross referenced across services, providers Standard Reporting n n n Information is standardized and reported across continuum Audience – across all levels n Client level data can report trends and utilization from clients across different service categories. n (Example – graph of PA CM to other services)
 BEFORE
BEFORE
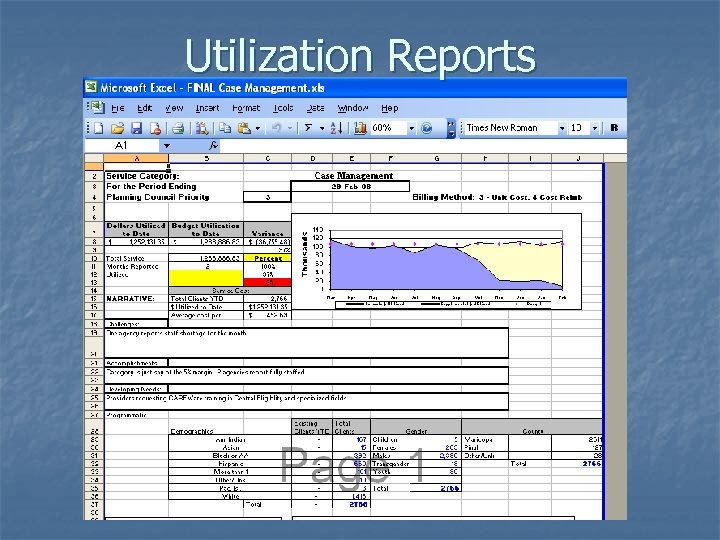 Utilization Reports
Utilization Reports
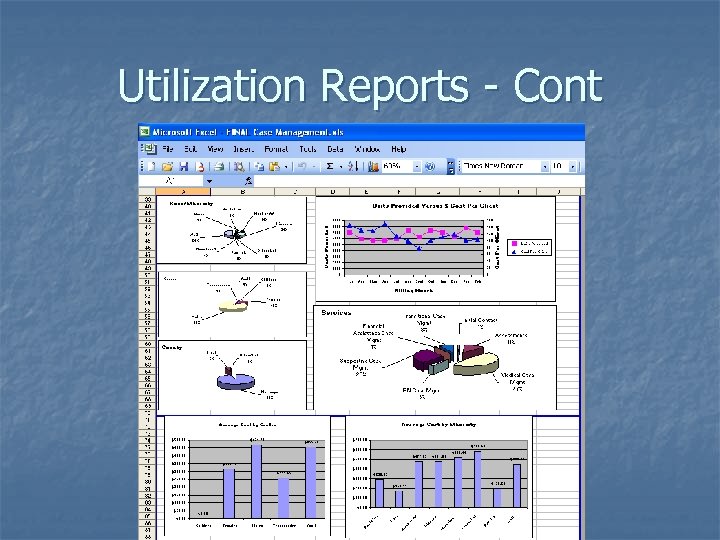 Utilization Reports - Cont
Utilization Reports - Cont
 Data Analysis n Data Analysis/Mining n Central database – Grantee can access the data n n Ad hoc reporting n Query reports as questions arise Relational data n Data is reported across the continuum n Aggregate data reporting
Data Analysis n Data Analysis/Mining n Central database – Grantee can access the data n n Ad hoc reporting n Query reports as questions arise Relational data n Data is reported across the continuum n Aggregate data reporting
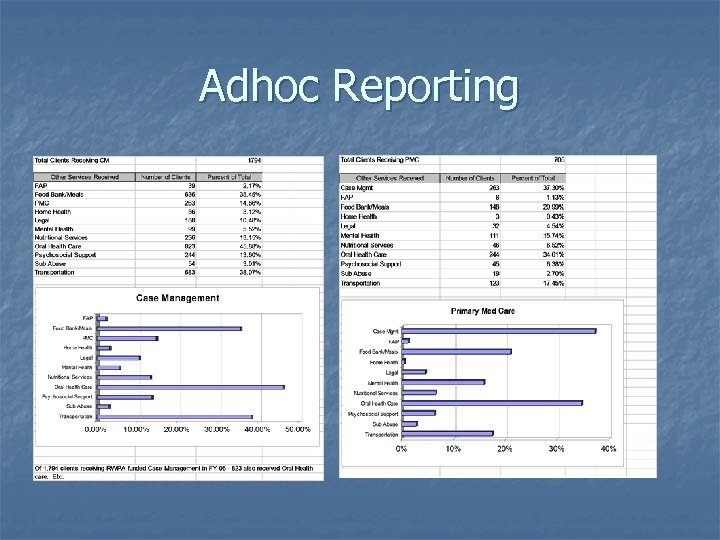 Adhoc Reporting
Adhoc Reporting
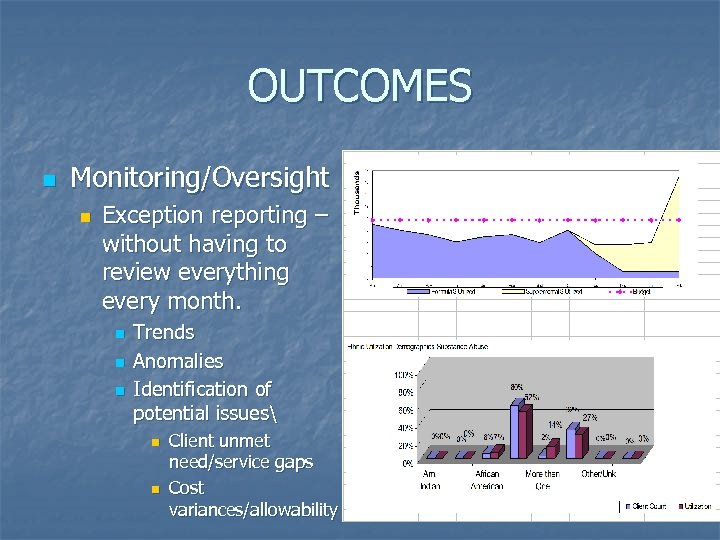 OUTCOMES n Monitoring/Oversight n Exception reporting – without having to review everything every month. n n n Trends Anomalies Identification of potential issues n n Client unmet need/service gaps Cost variances/allowability
OUTCOMES n Monitoring/Oversight n Exception reporting – without having to review everything every month. n n n Trends Anomalies Identification of potential issues n n Client unmet need/service gaps Cost variances/allowability
 Site Visits n Key Factors n n n Grantee has demographic data Reviews conducted at random, not from Providers Real time reporting to Providers Goal to reduce administrative time spent compiling data Process n n Site Visits are performed annually Monitoring tool is automated Data Collection is done on site Reporting can be finalized within 5 days
Site Visits n Key Factors n n n Grantee has demographic data Reviews conducted at random, not from Providers Real time reporting to Providers Goal to reduce administrative time spent compiling data Process n n Site Visits are performed annually Monitoring tool is automated Data Collection is done on site Reporting can be finalized within 5 days
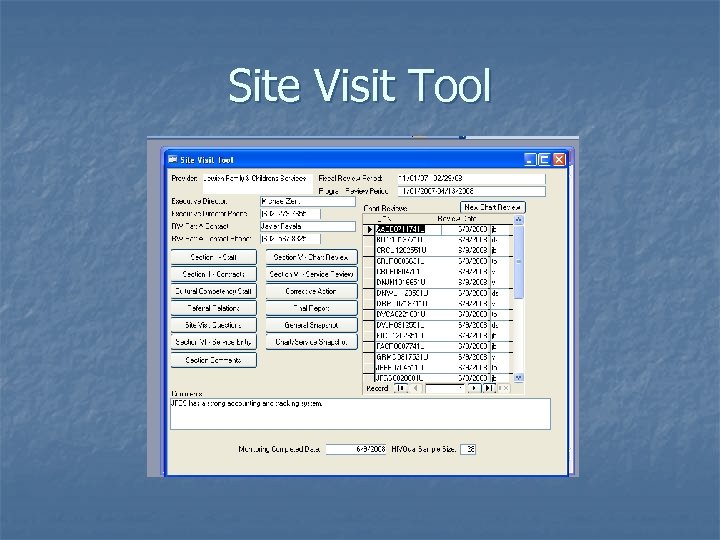 Site Visit Tool
Site Visit Tool
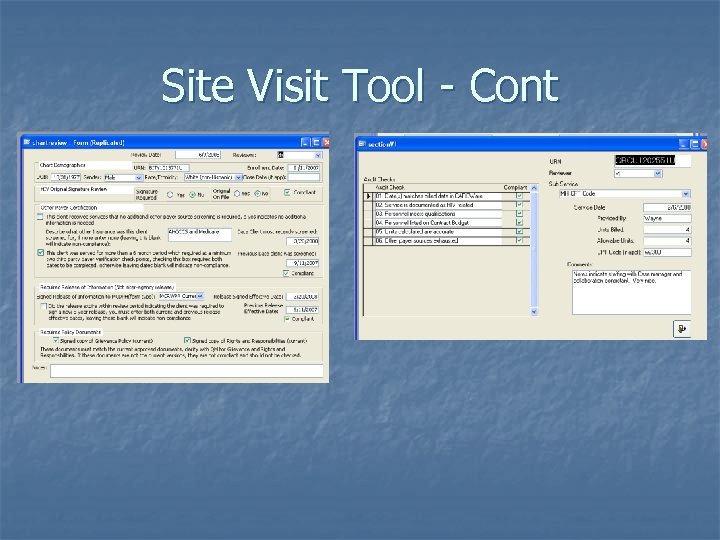 Site Visit Tool - Cont
Site Visit Tool - Cont
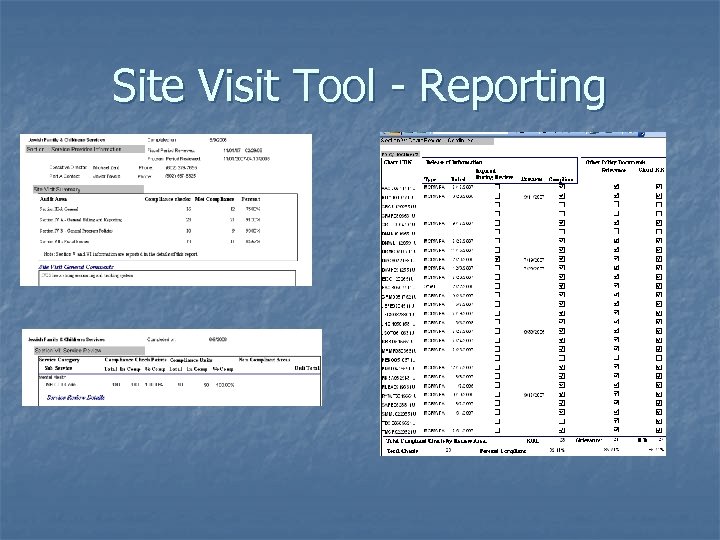 Site Visit Tool - Reporting
Site Visit Tool - Reporting
 Grant Management n Key Factors n n n Core 75% and Supportive 25% Tracking Formula/Supplemental Tracking of Sub Contractors Balancing to Internal Government Finance System Timely Reporting of Grant Performance and Expenditures Goal to Reduce Administrative time to compile data Process n n All data is stored in system Financial and Programmatic monitoring workflow Site Visits and CQM Site Visits data is compiled Grant Performance and Expenditure Reporting can be completed timely
Grant Management n Key Factors n n n Core 75% and Supportive 25% Tracking Formula/Supplemental Tracking of Sub Contractors Balancing to Internal Government Finance System Timely Reporting of Grant Performance and Expenditures Goal to Reduce Administrative time to compile data Process n n All data is stored in system Financial and Programmatic monitoring workflow Site Visits and CQM Site Visits data is compiled Grant Performance and Expenditure Reporting can be completed timely
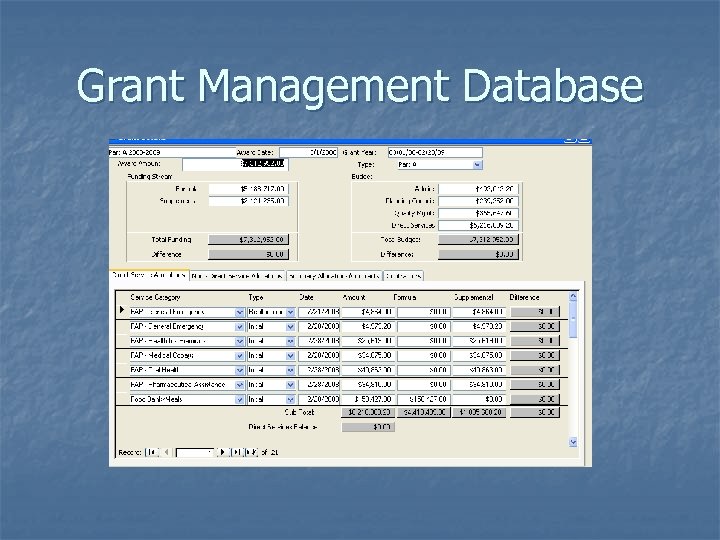 Grant Management Database
Grant Management Database
 OUTCOMES n Streamlining the system n Data Driven decision process n Timely client level reporting n Relational Data n n n Identify unmet need/service gaps Client Level Data - Demographics Service Category Anecdotal information accounted for Technical Assistance n n n Real time TA TA needs can be addressed at Provider and service level Goto meeting n n n Travel Time Can help them directly at their computer Can watch them do data entry – real time
OUTCOMES n Streamlining the system n Data Driven decision process n Timely client level reporting n Relational Data n n n Identify unmet need/service gaps Client Level Data - Demographics Service Category Anecdotal information accounted for Technical Assistance n n n Real time TA TA needs can be addressed at Provider and service level Goto meeting n n n Travel Time Can help them directly at their computer Can watch them do data entry – real time
 Benefits n Reduced Administrative Costs n Grantee n n n Integrated tools reduce manual data entry and compilation of data n Site visit/ Grant Management database Adhoc and custom reporting n Queries can be run quickly without having to collect data from multiple providers n Standardized data can compile and aggregate data easily and quickly Providers n n Data connectors (reduce double data entry) n Importer transactions – 6500 transactions / month = 55 hours Adhoc reporting n Less administrative burden by compiling and reporting data manually to the AA Variance check points Providers can quickly check grant compliance/monitor their own activity
Benefits n Reduced Administrative Costs n Grantee n n n Integrated tools reduce manual data entry and compilation of data n Site visit/ Grant Management database Adhoc and custom reporting n Queries can be run quickly without having to collect data from multiple providers n Standardized data can compile and aggregate data easily and quickly Providers n n Data connectors (reduce double data entry) n Importer transactions – 6500 transactions / month = 55 hours Adhoc reporting n Less administrative burden by compiling and reporting data manually to the AA Variance check points Providers can quickly check grant compliance/monitor their own activity
 Requirements n n n Understanding what is needed Developing processes and standards Technology should be used to reduce time on mundane tasks n n n Data Entry Data Compilation – Standard Requirements Adhoc tools available to answer questions Validation tests to ensure data is accurate Technical Assistance for staff and providers
Requirements n n n Understanding what is needed Developing processes and standards Technology should be used to reduce time on mundane tasks n n n Data Entry Data Compilation – Standard Requirements Adhoc tools available to answer questions Validation tests to ensure data is accurate Technical Assistance for staff and providers
 Lessons Learned n n n Without Buy-In systems will fail Implementation timelines must be realistic Include a PDSA cycle Develop a plan with flexibility Technical Assistance is critical
Lessons Learned n n n Without Buy-In systems will fail Implementation timelines must be realistic Include a PDSA cycle Develop a plan with flexibility Technical Assistance is critical
 Contact Information n Kevin Mc. Neal Maricopa County 301 W Jefferson, Suite 3200 Phoenix, Arizona 85003 602 -506 -6181 kevinmcneal@mail. maricopa. gov n Julie Young Tri. Young Business Solutions, Inc 8024 N 24 th Ave, Suite 302 Phoenix, Az 85021 602 -424 -1700 jyoung@azbizsolutions. com
Contact Information n Kevin Mc. Neal Maricopa County 301 W Jefferson, Suite 3200 Phoenix, Arizona 85003 602 -506 -6181 kevinmcneal@mail. maricopa. gov n Julie Young Tri. Young Business Solutions, Inc 8024 N 24 th Ave, Suite 302 Phoenix, Az 85021 602 -424 -1700 jyoung@azbizsolutions. com


