01bfee0924623602073e7cf0e204b6ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 GRACE Science Data System Status Michael Watkins, Gerard Kruizinga, Da Kuang, Willy Bertiger, Dah-Ning Yuan Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Frank Flechtner, Roland Schmidt, Uli Meyer, Christoph Dahle Geo. Forschungs. Zentrum Potsdam Srinivas Bettadpur, Furun Wang Center for Space Research, University of Texas at Austin GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 1
GRACE Science Data System Status Michael Watkins, Gerard Kruizinga, Da Kuang, Willy Bertiger, Dah-Ning Yuan Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Frank Flechtner, Roland Schmidt, Uli Meyer, Christoph Dahle Geo. Forschungs. Zentrum Potsdam Srinivas Bettadpur, Furun Wang Center for Space Research, University of Texas at Austin GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 1
 Overview • Level-0/Level-1 processing and alignments status • Onboard detection of KBR Missed Interrupts • Advisory for ACC 1 B data affected by “Disconnect Supplementary Heater Lines” (DSHL) events • AOD status • Level-2 Status and Product Availability • Usage Notes GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 2
Overview • Level-0/Level-1 processing and alignments status • Onboard detection of KBR Missed Interrupts • Advisory for ACC 1 B data affected by “Disconnect Supplementary Heater Lines” (DSHL) events • AOD status • Level-2 Status and Product Availability • Usage Notes GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 2
 Level-0/Level-1 Processing Status • Standard automatic Level-0/Level-1 processing is fully operational at PO. DAAC (JPL) since 2004 -01 -01. – Occasional manual interventions during off-nominal operations of the GRACE spacecraft. – Latency ~12 days to L-2 processing centers • Quick look Level-0/Level-1 processing is fully operational at JPL since 2003 -09 -01 to monitor for non-nominal states of the science payload (latency ~24 hours) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 3
Level-0/Level-1 Processing Status • Standard automatic Level-0/Level-1 processing is fully operational at PO. DAAC (JPL) since 2004 -01 -01. – Occasional manual interventions during off-nominal operations of the GRACE spacecraft. – Latency ~12 days to L-2 processing centers • Quick look Level-0/Level-1 processing is fully operational at JPL since 2003 -09 -01 to monitor for non-nominal states of the science payload (latency ~24 hours) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 3
 Data Flow Statistics as of 27 September 2007 • > 99. 9 % of raw data has been retrieved successfully and reformatted by the Science Data System (data latency < 1. 0 hour) • 2005 days of Level-1 B data have been distributed to the level-2 centers (CSR, GFZ , JPL) ( data latency < 12 days) – 1952 days pass KBR quality check, which serves as proxy for overall data quality (24 days in 2007 affected by DSHL included) – 1845 days all instruments available, required for nominal level 2 processing GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 4
Data Flow Statistics as of 27 September 2007 • > 99. 9 % of raw data has been retrieved successfully and reformatted by the Science Data System (data latency < 1. 0 hour) • 2005 days of Level-1 B data have been distributed to the level-2 centers (CSR, GFZ , JPL) ( data latency < 12 days) – 1952 days pass KBR quality check, which serves as proxy for overall data quality (24 days in 2007 affected by DSHL included) – 1845 days all instruments available, required for nominal level 2 processing GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 4
 GRACE Alignment Status • Eight simultaneous COM calibration maneuvers performed since July 2004 – Center of Mass for both GRACE S/C are located within the required 100 microns of the ACC proof mass COM. – COM calibration analysis continues to be limited by ACC “twangs” except last COM calibration maneuver (31 May 2007) – Trim performed 12 April 2007 (x, y, z components) • Work on improving SCA alignment with respect to ACC is suspended GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 5
GRACE Alignment Status • Eight simultaneous COM calibration maneuvers performed since July 2004 – Center of Mass for both GRACE S/C are located within the required 100 microns of the ACC proof mass COM. – COM calibration analysis continues to be limited by ACC “twangs” except last COM calibration maneuver (31 May 2007) – Trim performed 12 April 2007 (x, y, z components) • Work on improving SCA alignment with respect to ACC is suspended GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 5
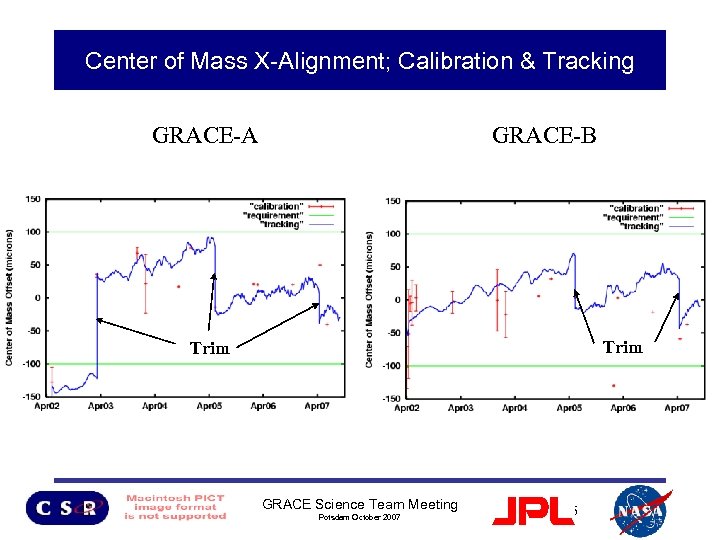 Center of Mass X-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 6
Center of Mass X-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 6
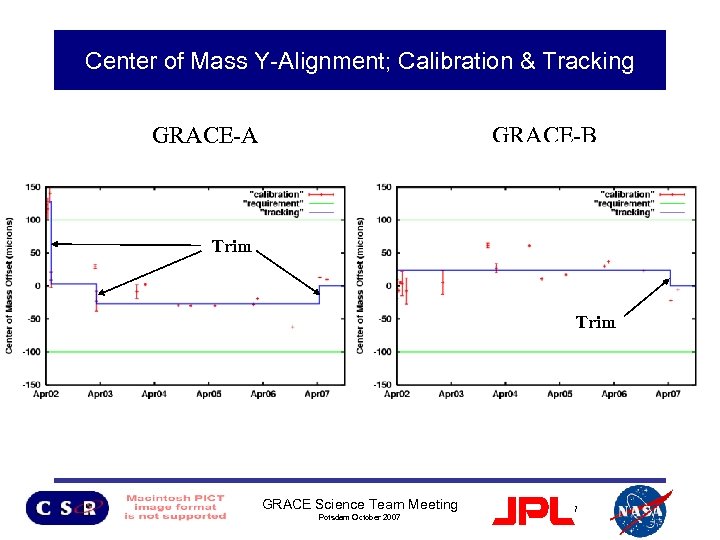 Center of Mass Y-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 7
Center of Mass Y-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 7
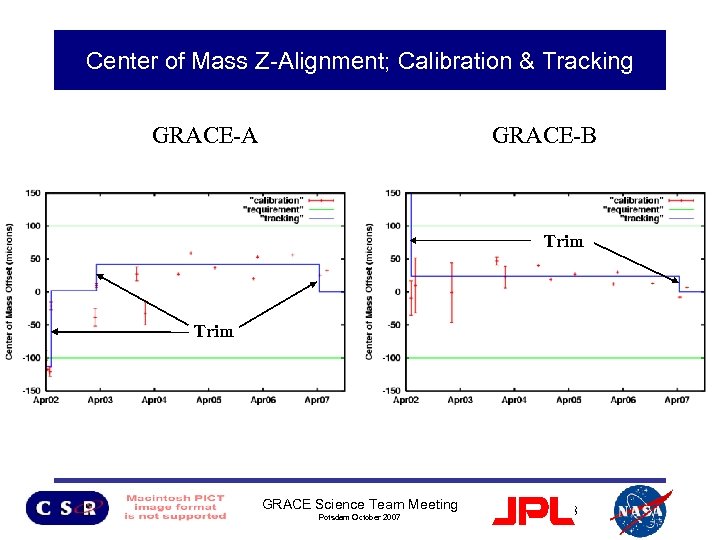 Center of Mass Z-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 8
Center of Mass Z-Alignment; Calibration & Tracking GRACE-A GRACE-B Trim GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 8
 Onboard Detection of KBR Missed Interrupts (MI) • Ground detection uses Level-1 software/algorithms to detect MI after data dumps. GSOC is automatically notified when a MI has occurred. Upon notification GSOC sends restart tracker to spacecraft at next commanding opportunity (Latency up to 24 hours) • Onboard detection uses Level-1 software/algorithms to detect MI within 10 seconds of occurrence. Restart tracker command sent by onboard IPU autonomously upon detection – – – Expected MI detection rate 95 % Ground detection still needed for 5 % Very few false positives expected (e. g. Solar Activity) KBR data loss minimal (< 40 seconds) Significant risk reduction of data corruption due to anomalous MIs GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 9
Onboard Detection of KBR Missed Interrupts (MI) • Ground detection uses Level-1 software/algorithms to detect MI after data dumps. GSOC is automatically notified when a MI has occurred. Upon notification GSOC sends restart tracker to spacecraft at next commanding opportunity (Latency up to 24 hours) • Onboard detection uses Level-1 software/algorithms to detect MI within 10 seconds of occurrence. Restart tracker command sent by onboard IPU autonomously upon detection – – – Expected MI detection rate 95 % Ground detection still needed for 5 % Very few false positives expected (e. g. Solar Activity) KBR data loss minimal (< 40 seconds) Significant risk reduction of data corruption due to anomalous MIs GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 9
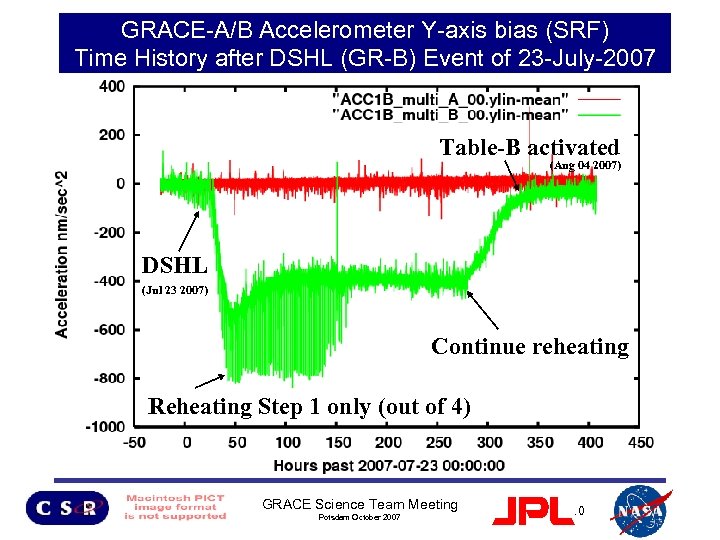 GRACE-A/B Accelerometer Y-axis bias (SRF) Time History after DSHL (GR-B) Event of 23 -July-2007 Table-B activated (Aug 04 2007) DSHL (Jul 23 2007) Continue reheating Reheating Step 1 only (out of 4) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 10
GRACE-A/B Accelerometer Y-axis bias (SRF) Time History after DSHL (GR-B) Event of 23 -July-2007 Table-B activated (Aug 04 2007) DSHL (Jul 23 2007) Continue reheating Reheating Step 1 only (out of 4) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 10
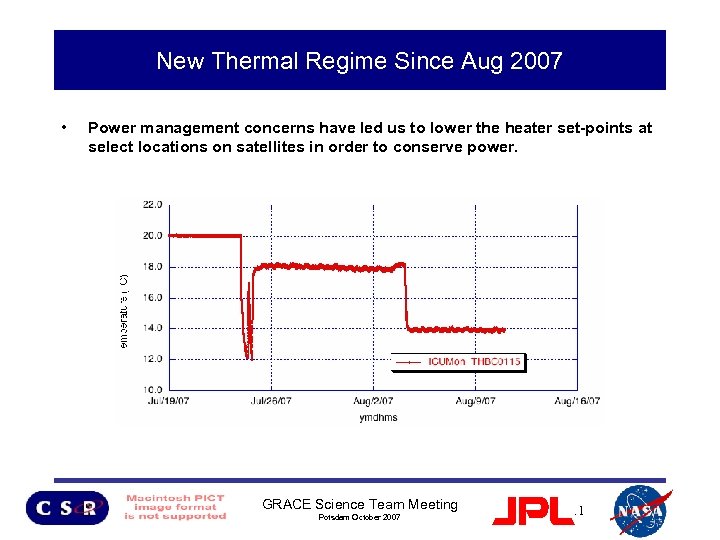 New Thermal Regime Since Aug 2007 • Power management concerns have led us to lower the heater set-points at select locations on satellites in order to conserve power. GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 11
New Thermal Regime Since Aug 2007 • Power management concerns have led us to lower the heater set-points at select locations on satellites in order to conserve power. GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 11
 ACC 1 B Data Advisory affected by DSHL events • ACC biases (all three axis) show exponential decay signature after a DSHL event (4 -5 days before stabilization occurs) • Nominal Level-2 processing is not possible during these intervals • Modeling of ACC biases as a function of time during these events may be possible but requires an in depth study of it’s effect on the gravity field solutions which is beyond the scope of the L 1 processing. • No ACC bias model is applied in the ACC 1 B data • ACC 1 B data affect by DSHL events are identified in SDS news letter GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 12
ACC 1 B Data Advisory affected by DSHL events • ACC biases (all three axis) show exponential decay signature after a DSHL event (4 -5 days before stabilization occurs) • Nominal Level-2 processing is not possible during these intervals • Modeling of ACC biases as a function of time during these events may be possible but requires an in depth study of it’s effect on the gravity field solutions which is beyond the scope of the L 1 processing. • No ACC bias model is applied in the ACC 1 B data • ACC 1 B data affect by DSHL events are identified in SDS news letter GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 12
 Dealiasing Product Status • Atmosphere and Ocean De-aliasing Level 1 B (AOD 1 B) Release 04 (RL 04) based on ECMWF 6 h meteorological data and output from (mass conserving) baroclinic ocean model OMCT routinely generated at GFZ. Available since January 1, 2001 until today. • RL 01 and RL 03 generation stopped with June 30, 2007 and January 31, 2007 products, respectively (formerly used in CSR RL 01 and GFZ RL 03 GSMs). • AOD 1 B RL 04 has been extended backwards to 1991 (back to 1976 planned) based on ERA 40 (ECMWF Re-Analysis) data for improved Lageos data processing (see talk by König et al. , Session B, Tuesday). 13
Dealiasing Product Status • Atmosphere and Ocean De-aliasing Level 1 B (AOD 1 B) Release 04 (RL 04) based on ECMWF 6 h meteorological data and output from (mass conserving) baroclinic ocean model OMCT routinely generated at GFZ. Available since January 1, 2001 until today. • RL 01 and RL 03 generation stopped with June 30, 2007 and January 31, 2007 products, respectively (formerly used in CSR RL 01 and GFZ RL 03 GSMs). • AOD 1 B RL 04 has been extended backwards to 1991 (back to 1976 planned) based on ERA 40 (ECMWF Re-Analysis) data for improved Lageos data processing (see talk by König et al. , Session B, Tuesday). 13
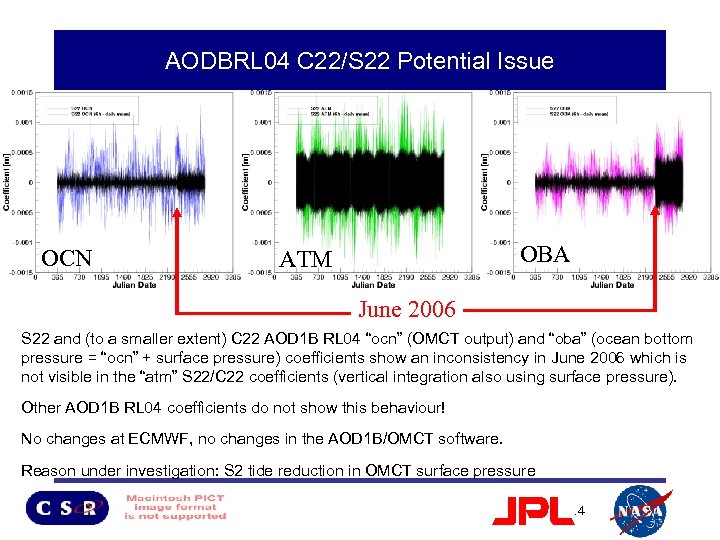 AODBRL 04 C 22/S 22 Potential Issue 2001 -2007 S 22 minus daily mean OCN OBA ATM June 2006 • S 22 and (to a smaller extent) C 22 AOD 1 B RL 04 “ocn” (OMCT output) and “oba” (ocean bottom pressure = “ocn” + surface pressure) coefficients show an inconsistency in June 2006 which is not visible in the “atm” S 22/C 22 coefficients (vertical integration also using surface pressure). • Other AOD 1 B RL 04 coefficients do not show this behaviour! • No changes at ECMWF, no changes in the AOD 1 B/OMCT software. • Reason under investigation: S 2 tide reduction in OMCT surface pressure? 14
AODBRL 04 C 22/S 22 Potential Issue 2001 -2007 S 22 minus daily mean OCN OBA ATM June 2006 • S 22 and (to a smaller extent) C 22 AOD 1 B RL 04 “ocn” (OMCT output) and “oba” (ocean bottom pressure = “ocn” + surface pressure) coefficients show an inconsistency in June 2006 which is not visible in the “atm” S 22/C 22 coefficients (vertical integration also using surface pressure). • Other AOD 1 B RL 04 coefficients do not show this behaviour! • No changes at ECMWF, no changes in the AOD 1 B/OMCT software. • Reason under investigation: S 2 tide reduction in OMCT surface pressure? 14
 General Level-2 (gravity fields) Product Status • CSR, GFZ, and JPL have all developed new Release 4 (RL 04) solutions in Fall 2006 (first discussed at last year’s GSTM) • Centers have extended and improved these series from 2002 -2007 (minus few degraded months - typically 55 -60 months total) • These solutions are significantly better than past generation solutions • Improved background static field, tides, etc • Generally consistent models and quality but • Pay attention to differences in individual models and standards • JPL and several other organizations (GSFC, OSU…) also produce alternative basis function (non spherical harmonics) solutions • Mascons, grids, wavelets, etc 15
General Level-2 (gravity fields) Product Status • CSR, GFZ, and JPL have all developed new Release 4 (RL 04) solutions in Fall 2006 (first discussed at last year’s GSTM) • Centers have extended and improved these series from 2002 -2007 (minus few degraded months - typically 55 -60 months total) • These solutions are significantly better than past generation solutions • Improved background static field, tides, etc • Generally consistent models and quality but • Pay attention to differences in individual models and standards • JPL and several other organizations (GSFC, OSU…) also produce alternative basis function (non spherical harmonics) solutions • Mascons, grids, wavelets, etc 15
 CSR Level-2 (gravity fields) Product Status • CSR RL 04: From April 2002 through June 2007 – Except: May-June 2002 and June 2003 – Solved and delivered to degree/order 60 • No constraints applied • • Starting with Sep 2007 solution, CSR RL 04 solutions will use ITRF 2005. – Earlier solutions used ITRF 2000 – Changes: Station coordinates, velocities, and EOPDAT • EOPDAT changes are an effective change in the background gravity model, as it changes modeled (2, 1) harmonics through pole tide. Tests for past two months (May & June 2007) show no sensible difference between using ITRF 2000 and ITRF 2005. • Long running standard series CSRRL 01 is now terminated • RL 04 Products Delivered: – GSM-2: Monthly gravity field estimate – GAC-2/GAD-2: Average of the non-tidal atmosphere+ocean dealiasing model – Calibrated (provisional) error estimates (sigma-only) – Additional Info: SLR-based estimates of C 20 (TN-05) 16
CSR Level-2 (gravity fields) Product Status • CSR RL 04: From April 2002 through June 2007 – Except: May-June 2002 and June 2003 – Solved and delivered to degree/order 60 • No constraints applied • • Starting with Sep 2007 solution, CSR RL 04 solutions will use ITRF 2005. – Earlier solutions used ITRF 2000 – Changes: Station coordinates, velocities, and EOPDAT • EOPDAT changes are an effective change in the background gravity model, as it changes modeled (2, 1) harmonics through pole tide. Tests for past two months (May & June 2007) show no sensible difference between using ITRF 2000 and ITRF 2005. • Long running standard series CSRRL 01 is now terminated • RL 04 Products Delivered: – GSM-2: Monthly gravity field estimate – GAC-2/GAD-2: Average of the non-tidal atmosphere+ocean dealiasing model – Calibrated (provisional) error estimates (sigma-only) – Additional Info: SLR-based estimates of C 20 (TN-05) 16
 GFZ Level-2 Product Status Monthly RL 04 Level-2 products (EIGEN-GRACE 05 S) routinely generated based on improved background models and processing standards (nearly identical within SDS), • Background gravity model EIGEN-GL 04 C (n=150) • Drift rates for C 21, S 21, C 20, C 30 and C 40 in background gravity field; epoch now 1. 1. 2000 (instead of 1. 1. 1997) • Updated K 2 (FES 2002 values, see Lyard et al. , 2006 (difference w. r. t CSR)) and included M 4 tide in FES 2004 ocean tides • AOD 1 B RL 04 de-aliasing • IERS 2003 nutation and precession model • JPL provided GPS antenna masks for GRACE-A/B • For details see “GFZ L 2 Processing Standards Doc. for RL 04” 17
GFZ Level-2 Product Status Monthly RL 04 Level-2 products (EIGEN-GRACE 05 S) routinely generated based on improved background models and processing standards (nearly identical within SDS), • Background gravity model EIGEN-GL 04 C (n=150) • Drift rates for C 21, S 21, C 20, C 30 and C 40 in background gravity field; epoch now 1. 1. 2000 (instead of 1. 1. 1997) • Updated K 2 (FES 2002 values, see Lyard et al. , 2006 (difference w. r. t CSR)) and included M 4 tide in FES 2004 ocean tides • AOD 1 B RL 04 de-aliasing • IERS 2003 nutation and precession model • JPL provided GPS antenna masks for GRACE-A/B • For details see “GFZ L 2 Processing Standards Doc. for RL 04” 17
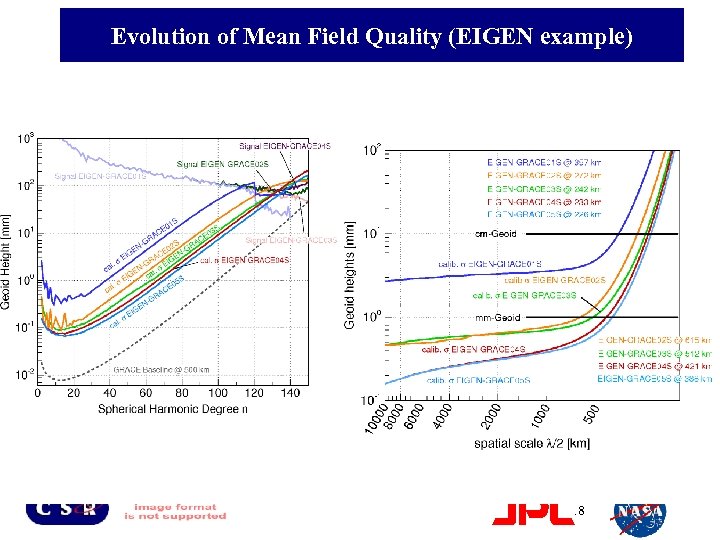 Evolution of Mean Field Quality (EIGEN example) 18
Evolution of Mean Field Quality (EIGEN example) 18
 JPL GRACE Gravity Validation Solution • Spherical Harmonic solution series JPLRL 04 - Uses standards similar to CSR/GFZ but deliberately different processing algorithms - available from 2002 -2007 - now replaced with JPLRL 04. 1 - only change is improved GPS pseudorange/carrier relative weighting, only minor changes in gravity field - JPLRL 04. 1 extends from 2002 -August 2007 (minus usual bad months) • Mascon solutions JPLRL 04. 1 M - Global 4 degree mascons from L 1 B range rate • Research solution JPLRL 04. 1 MRA - Global 4 degree mascons from handfiltered range acceleration GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 19
JPL GRACE Gravity Validation Solution • Spherical Harmonic solution series JPLRL 04 - Uses standards similar to CSR/GFZ but deliberately different processing algorithms - available from 2002 -2007 - now replaced with JPLRL 04. 1 - only change is improved GPS pseudorange/carrier relative weighting, only minor changes in gravity field - JPLRL 04. 1 extends from 2002 -August 2007 (minus usual bad months) • Mascon solutions JPLRL 04. 1 M - Global 4 degree mascons from L 1 B range rate • Research solution JPLRL 04. 1 MRA - Global 4 degree mascons from handfiltered range acceleration GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 19
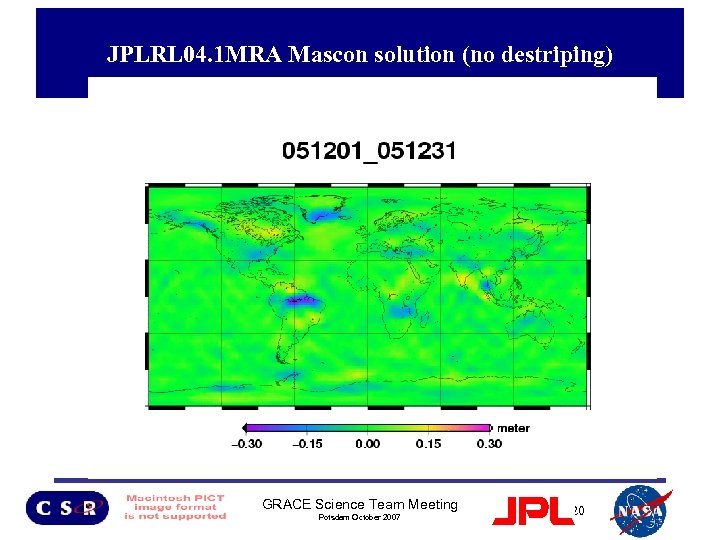 JPLRL 04. 1 MRA Mascon solution (no destriping) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 20
JPLRL 04. 1 MRA Mascon solution (no destriping) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 20
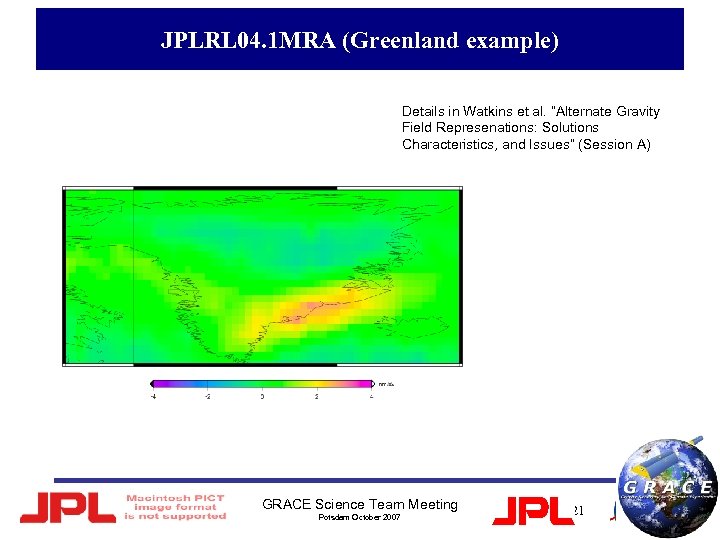 JPLRL 04. 1 MRA (Greenland example) Details in Watkins et al. ”Alternate Gravity Field Represenations: Solutions Characteristics, and Issues” (Session A) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 21
JPLRL 04. 1 MRA (Greenland example) Details in Watkins et al. ”Alternate Gravity Field Represenations: Solutions Characteristics, and Issues” (Session A) GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 21
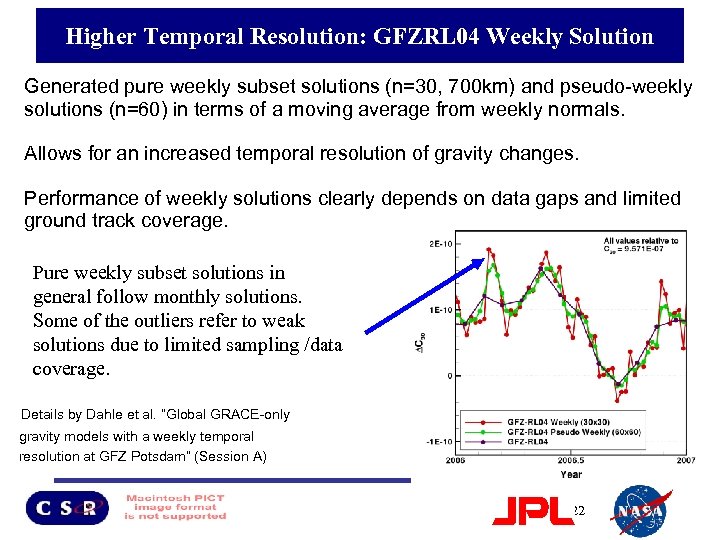 GFZ L 2 RL 04 Weekly Solutions Higher Temporal Resolution: GFZRL 04 Weekly Solution • Generated pure weekly subset solutions (n=30, 700 km) and pseudo-weekly solutions (n=60) in terms of a moving average from weekly normals. • Allows for an increased temporal resolution of gravity changes. • Performance of weekly solutions clearly depends on data gaps and limited ground track coverage. Pure weekly subset solutions in general follow monthly solutions. Some of the outliers refer to weak solutions due to limited sampling /data coverage. • Details by Dahle et al. ”Global GRACE-only gravity models with a weekly temporal resolution at GFZ Potsdam” (Session A) 22
GFZ L 2 RL 04 Weekly Solutions Higher Temporal Resolution: GFZRL 04 Weekly Solution • Generated pure weekly subset solutions (n=30, 700 km) and pseudo-weekly solutions (n=60) in terms of a moving average from weekly normals. • Allows for an increased temporal resolution of gravity changes. • Performance of weekly solutions clearly depends on data gaps and limited ground track coverage. Pure weekly subset solutions in general follow monthly solutions. Some of the outliers refer to weak solutions due to limited sampling /data coverage. • Details by Dahle et al. ”Global GRACE-only gravity models with a weekly temporal resolution at GFZ Potsdam” (Session A) 22
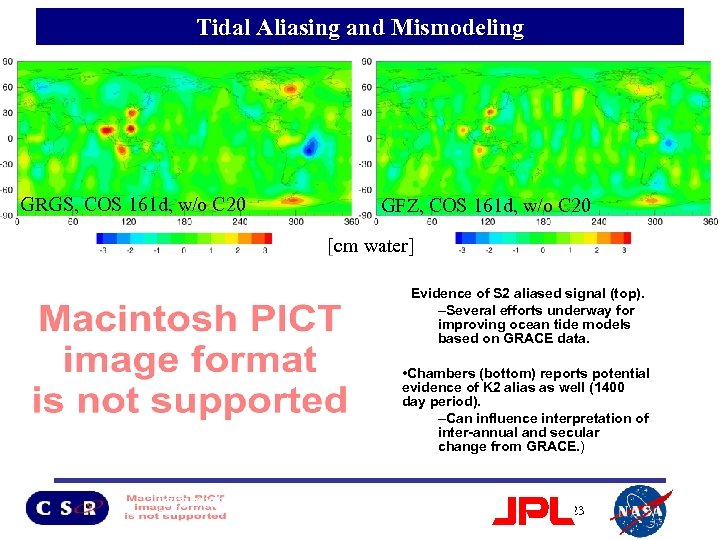 Tidal Aliasing and Mismodeling GRGS, COS 161 d, w/o C 20 GFZ, COS 161 d, w/o C 20 [cm water] • Evidence of S 2 aliased signal (top). –Several efforts underway for improving ocean tide models based on GRACE data. • Chambers (bottom) reports potential evidence of K 2 alias as well (1400 day period). –Can influence interpretation of inter-annual and secular change from GRACE. ) [cm water] 23
Tidal Aliasing and Mismodeling GRGS, COS 161 d, w/o C 20 GFZ, COS 161 d, w/o C 20 [cm water] • Evidence of S 2 aliased signal (top). –Several efforts underway for improving ocean tide models based on GRACE data. • Chambers (bottom) reports potential evidence of K 2 alias as well (1400 day period). –Can influence interpretation of inter-annual and secular change from GRACE. ) [cm water] 23
 Overall GRACE SDS Status Summary • GRACE L 1 B data flowing well in automated system • AODRL 04 has become primary dealiasing product • L 2 Gravity Field releases RL 04 from CSR, GFZ, and JPL all continue and improve – Some center-center differences that users should note • Alternate solutions becoming more common and useful – offer potentially improved solutions in ranges of spatial wavelengths – full statistical characterization typically not available or well understood • Users should definitely take a look at multiple solutions and compare • SDS is always interested to hear from users about issues GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 24
Overall GRACE SDS Status Summary • GRACE L 1 B data flowing well in automated system • AODRL 04 has become primary dealiasing product • L 2 Gravity Field releases RL 04 from CSR, GFZ, and JPL all continue and improve – Some center-center differences that users should note • Alternate solutions becoming more common and useful – offer potentially improved solutions in ranges of spatial wavelengths – full statistical characterization typically not available or well understood • Users should definitely take a look at multiple solutions and compare • SDS is always interested to hear from users about issues GRACE Science Team Meeting Potsdam October 2007 24


