38b15acbabf8b7cc211856fa5368de47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

GPS Integrity RAIM, WAAS, and GBAS: Concepts and Status Federal Aviation Administration Presentation to: CAAC ATMB March 8, 2011 Presented By: John Warburton FAA Engineering Development Services Navigation Group AJP-652 john. warburton@faa. gov GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 0 0

Overview • GPS Basics • GPS with Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring • FAA GPS Augmentation Systems • Wide Area Augmentation System • Ground Based Augmentation System • Summary GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 1 1

Global Positioning System Basics • Space Segment • • 24 Satellites 6 Orbital Planes 4 Satellites per Plane SVs Orbit at approximately 20 million meters above the earth • Each SV Orbits the earth twice a day • Ground Control Segment • Master Control Station, Colorado Springs • Monitor Stations; Hawaii, Ascension Island, Diego Garcia, and Kwajalein GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 2 2
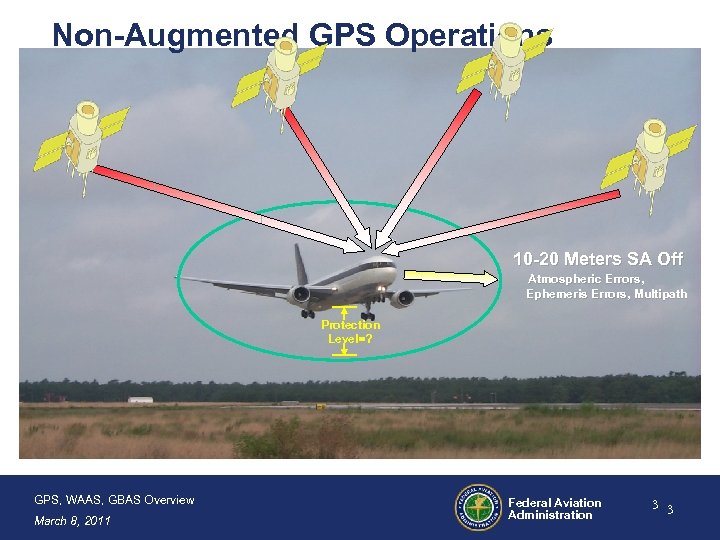
Non-Augmented GPS Operations 10 -20 Meters SA Off Atmospheric Errors, Ephemeris Errors, Multipath Protection Level=? GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 3 3
GPS Operations and RAIM • Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) provides GPS solution integrity without additional augmentation • RAIM functions include Fault Detection (FD) and Fault Detection and Exclusion (FDE) • Fault detection algorithms determine if there is an error in the GPS solution • Fault detection and exclusion algorithms determine if there is an error in the solution and can isolate and exclude satellites from the solution GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 4 4
RAIM Information • RAIM Prediction Link http: //www. raimprediction. net/ac 90 -100/ GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 5 5

Satellite Navigation WAAS / LAAS Implementation Space-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 6 6
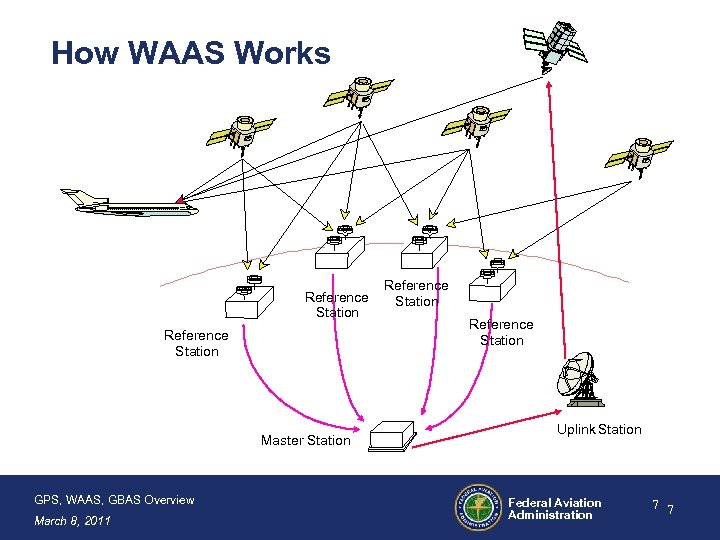
How WAAS Works Reference Station Master Station GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Reference Station Uplink Station Federal Aviation Administration 7 7

WAAS Status • Continuing to make pre planned upgrades/enhancements to the system • New GEO satellite (AMR, PRN 133) added to the system in November 2009 • CRW (PRN 135) GEO • Satellite operator, Intelsat, lost all command control of satellite in April 2010 • WAAS L-band payload continued to operate • Satellite drifted east • Original location was 133 degrees west longitude • Intelsat was able to regain command control in December 2010 • Satellite now returning to its original location • It is ready to return to service GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 8 8
WAAS Status – User Services • LNAV Procedures: • LNAV • GPS Only 4976 400 • LPV procedure status: • Cumulative LPVs Published to Date • • 2367 LPVs Published to non-ILS Runways LPVs Published to <250’ Decision Altitude LPVs Published to exactly 200’ DA 1470 897 433 422 • First LP procedure published 1/13/11 • Peter O Knight, Tampa FL runway 36 • Over 61, 206 WAAS receivers have been sold GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 9 9
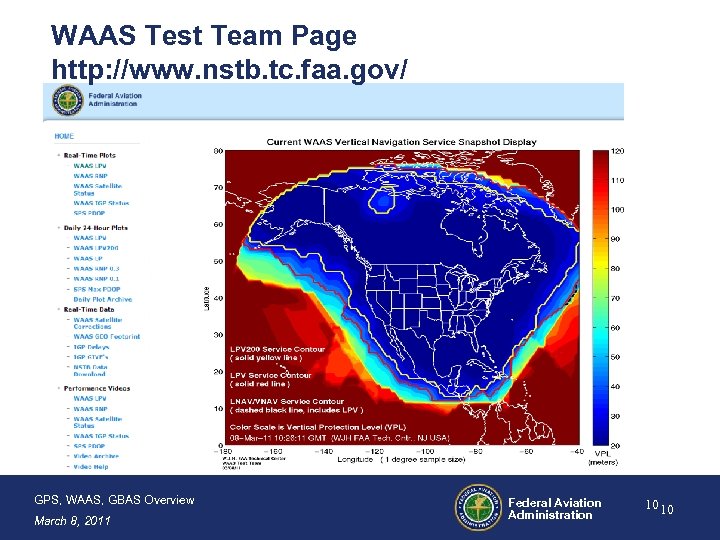
WAAS Test Team Page http: //www. nstb. tc. faa. gov/ GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 10 10
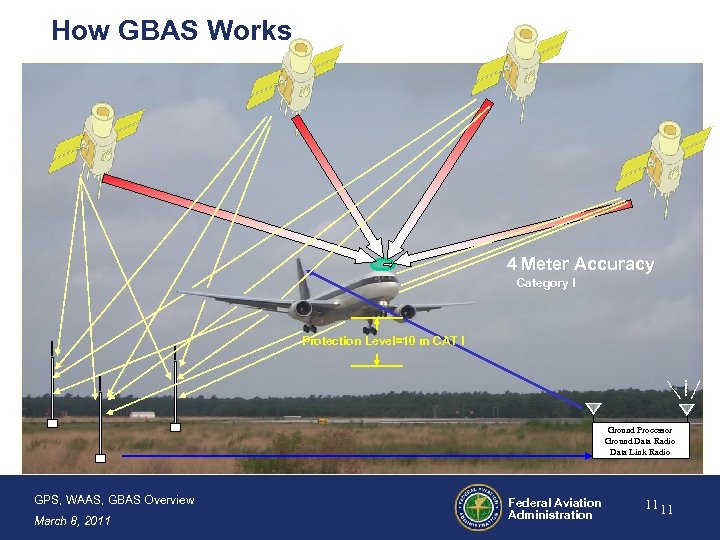
How GBAS Works 4 Meter Accuracy Category I Protection Level=10 m CAT I Ground Processor Ground Data Radio Data Link Radio GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 11 11
Ground Based Augmentation System Service • Provides Precision Approach Capability, CAT I/II/III Service. • Performance equivalent to existing Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) radionavigation landing aids. • Complements the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) • Provides CAT I where WAAS is not available. • Uses WAAS integrity information when in coverage of a WAAS GEO. • Requirements were coordinated internationally to support harmonization efforts. • CAT I/II/III Architectures Have Common Baseline Configuration and are fully interoperable. GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 12 12

GBAS CAT I Approval Status • Full Category I Non-Federal GBAS system design approval was completed in September 2009. • Honeywell SLS-4000 is the first approved GBAS. • SLS-4000 was installed at the FAA Technical Center in September 2008 • Being used as a platform to support FAA review of Honeywell design artifacts, Integrity Monitor Verification, and a CAT III development system • Hazardously Misleading Information (HMI) Report was completed December 2008 • Fully describes the integrity safety case for the SLS-4000 • SLS-4000 was installed at Newark Liberty International Airport (EWR) in November 2009 • FAA is working to resolve environmental interference at EWR GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 13 13
GBAS CAT II/III Status • Requirements Development and Validation • Acquisition Documentation to support a Federal Procurement of GBAS CAT III • Investment Analysis and other Acquisition Management System (AMS) required documentation • Requirements Validation - ICAO standards • Technical validation of proposed CAT III standards completed May 2010 • Operational Validation via prototypes • Prototype Development • CAT III GBAS Ground Facility (Honeywell) • Perform analysis on the existing Honeywell SLS-4000 algorithms to validate ICAO Annex 10 and LAAS CAT III Federal Specification requirements • POP: May 2010 - Nov 2012 • CAT III GBAS Avionics (Honeywell) • Produce red-label Airborne Equipment Class (AEC) D avionics to validate MOPS compliance • POP: August 2010 to February 2013 GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 14 14
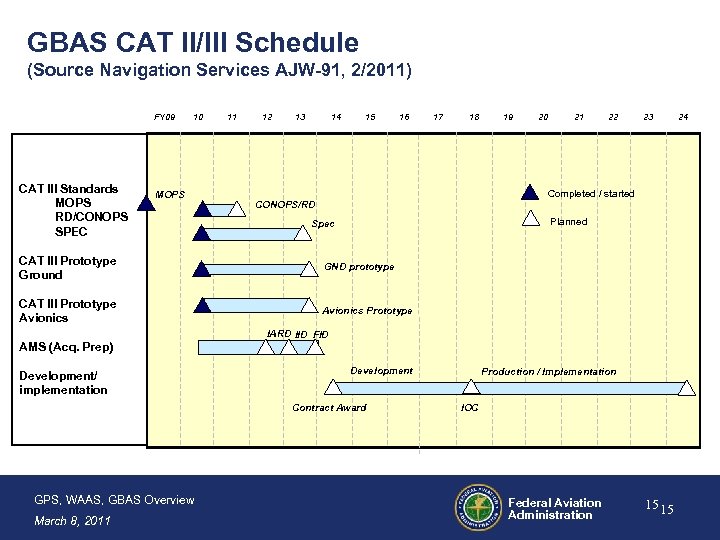
GBAS CAT II/III Schedule (Source Navigation Services AJW-91, 2/2011) FY 09 CAT III Standards MOPS RD/CONOPS SPEC 10 MOPS 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Completed / started CONOPS/RD Planned Spec CAT III Prototype Ground GND prototype CAT III Prototype Avionics Prototype IARD IID FID AMS (Acq. Prep) Development/ implementation Development Contract Award GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Production / Implementation IOC Federal Aviation Administration 15 15 24

GBAS Operational Projects • Project Newark • Partnership Participants: The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (PANYNJ), Continental Airlines, Honeywell and FAA Navigation Service’s Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) Program Office. • A GBAS was installed at Newark Airport to: • Demonstrate the improved performance and precision and interoperability with other GNSS capabilities. • Provide data to support FAA decisions on ground equipage and airline decisions on avionics. GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 16 16

GBAS Operational Projects • Project Houston • Partnership Participants: Houston Airport System (HAS), Continental Airlines, Honeywell, and FAA Navigation Service’s Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) Program Office. • A GBAS will be installed at Houston Intercontinental Airport (IAH) to: • Provide an effective city pair to support Continental equipage development • Continental taking delivery of GBAS capable 737 NG (30 total by February) GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 17 17
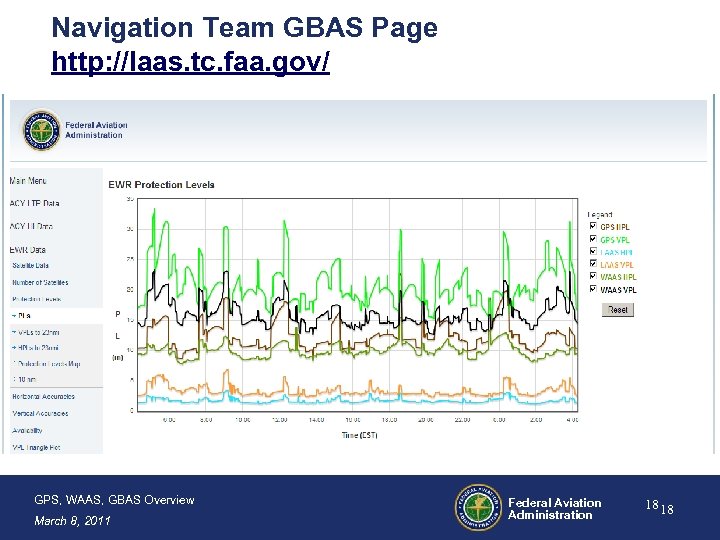
Navigation Team GBAS Page http: //laas. tc. faa. gov/ GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 18 18

Summary • Discussion of GPS, RAIM, WAAS, and LAAS • High-level concepts and overview • Provided links for additional information • Contact Information at the FAA Technical Center • Navigation Engineering Development Services John Warburton (609) 485 6782 john. warburton@faa. gov • Navigation Test and Evaluation Services Bill Wanner (609) 485 5514 bill. wanner@faa. gov GPS, WAAS, GBAS Overview March 8, 2011 Federal Aviation Administration 19 19
38b15acbabf8b7cc211856fa5368de47.ppt