GPRS, EGPRS integration in BSC.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

GPRS/EGPRS Integration in BSC BSS S 14 1 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLN 0

Objectives After studying this module participant should be able to: • Create Gb Interface within the BSC • Enable GPRS on cell level • Enable EGPRS on cell level • Handle dynamic Abis pools 2 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
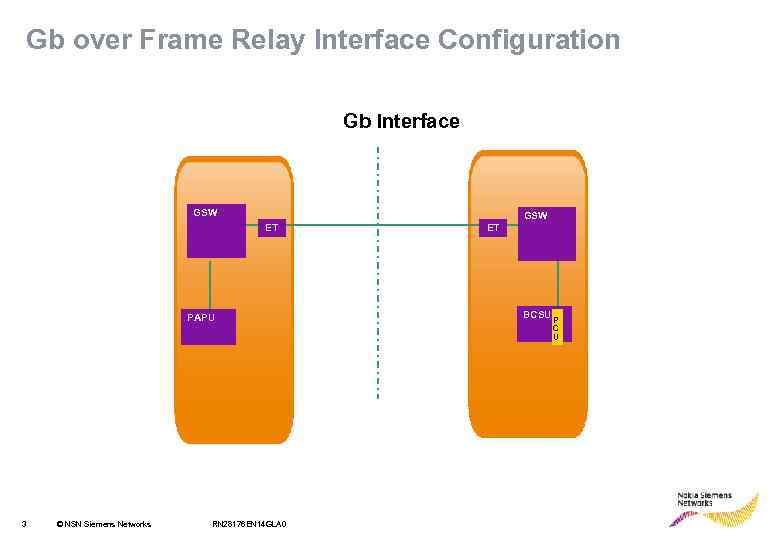
Gb over Frame Relay Interface Configuration Gb Interface GSW ET PAPU ET BCSU P C U 3 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Steps to Enable GPRS in BSC (FR) Start Connect the Gb interface ET Create and Activate Gb Interface Activating GPRS/EGPRS on a cell level End 4 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
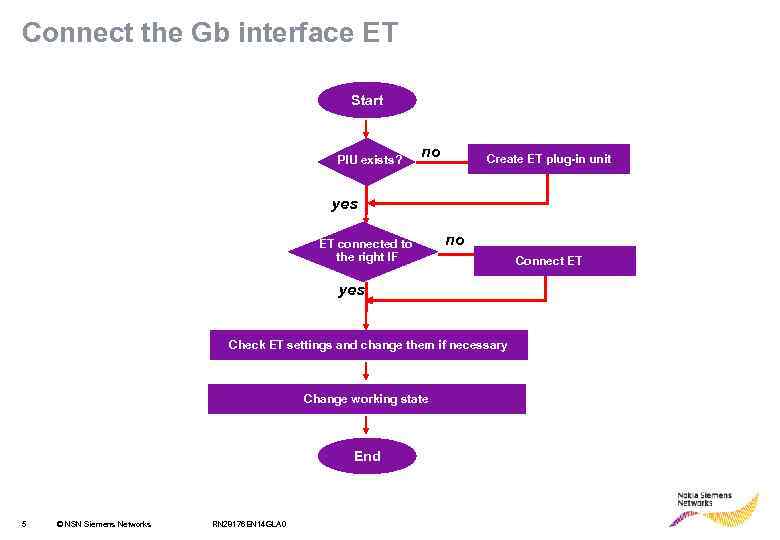
Connect the Gb interface ET Start PIU exists? no Create ET plug-in unit yes ET connected to the right IF no yes Check ET settings and change them if necessary Change working state End 5 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Connect ET
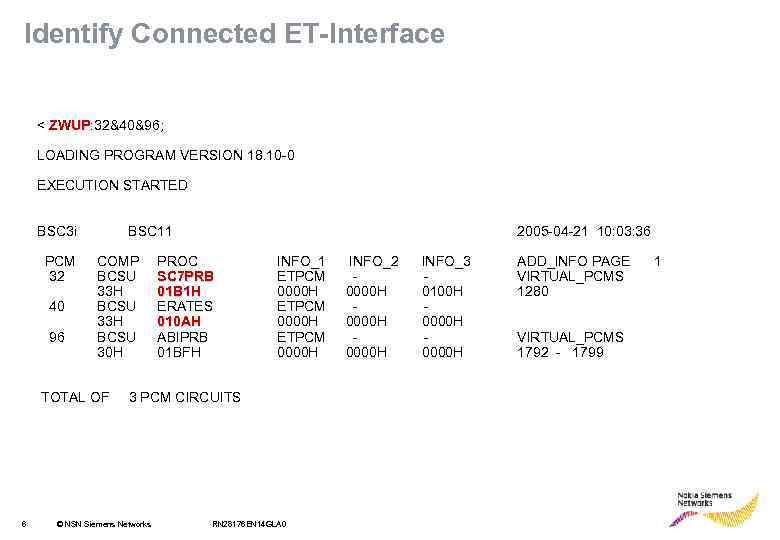
Identify Connected ET-Interface < ZWUP: 32&40&96; ZWUP LOADING PROGRAM VERSION 18. 10 -0 EXECUTION STARTED BSC 3 i PCM 32 40 96 BSC 11 COMP BCSU 33 H BCSU 30 H TOTAL OF 6 2005 -04 -21 10: 03: 36 PROC SC 7 PRB 01 B 1 H ERATES 010 AH ABIPRB 01 BFH INFO_1 ETPCM 0000 H 3 PCM CIRCUITS © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 INFO_2 0000 H INFO_3 0100 H 0000 H ADD_INFO PAGE VIRTUAL_PCMS 1280 VIRTUAL_PCMS 1792 - 1799 1
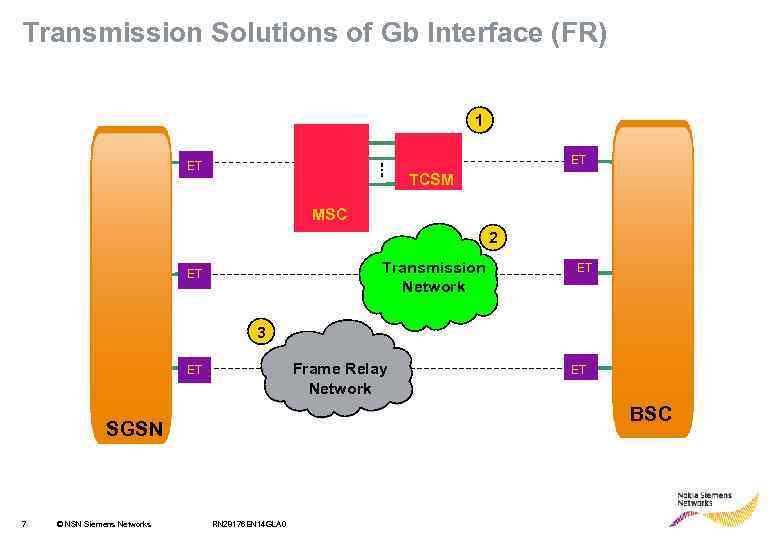
Transmission Solutions of Gb Interface (FR) 1 ET ET TCSM MSC 2 Transmission Network ET ET 3 Frame Relay Network ET BSC SGSN 7 © NSN Siemens Networks ET RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
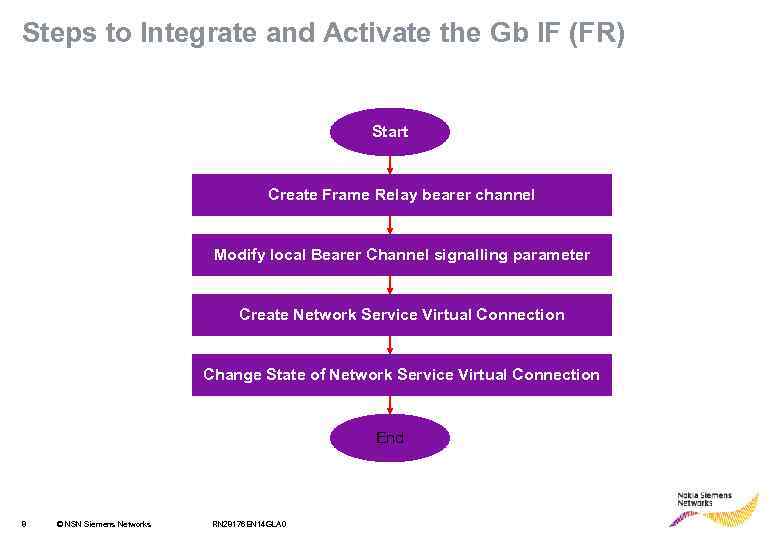
Steps to Integrate and Activate the Gb IF (FR) Start Create Frame Relay bearer channel Modify local Bearer Channel signalling parameter Create Network Service Virtual Connection Change State of Network Service Virtual Connection End 8 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
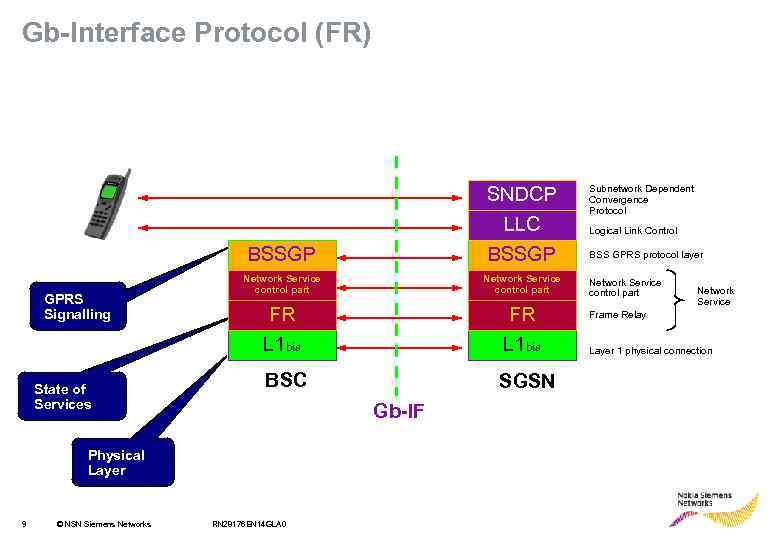
Gb-Interface Protocol (FR) BSSGP GPRS Signalling State of Services SNDCP LLC BSSGP Network Service control part FR L 1 bis BSC SGSN Gb-IF Physical Layer 9 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Subnetwork Dependent Convergence Protocol Logical Link Control BSS GPRS protocol layer Network Service control part Network Service Frame Relay Layer 1 physical connection
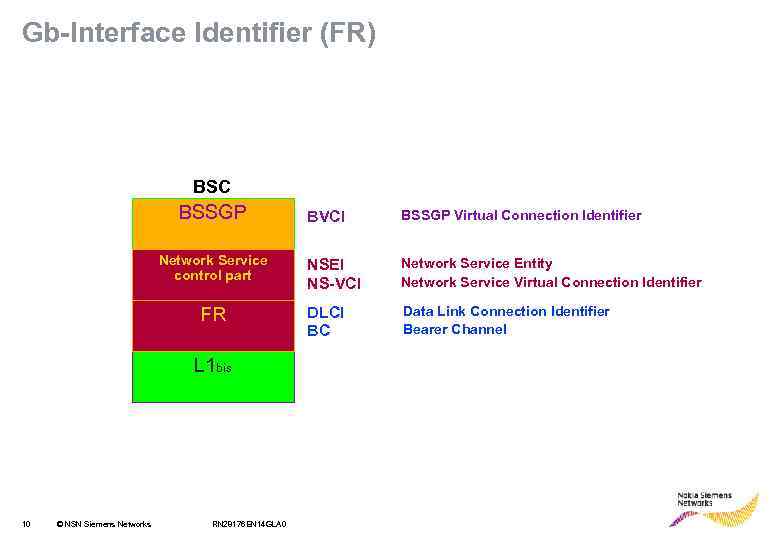
Gb-Interface Identifier (FR) BSC BSSGP Network Service control part FR L 1 bis 10 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 BVCI BSSGP Virtual Connection Identifier NSEI NS-VCI Network Service Entity Network Service Virtual Connection Identifier DLCI BC Data Link Connection Identifier Bearer Channel
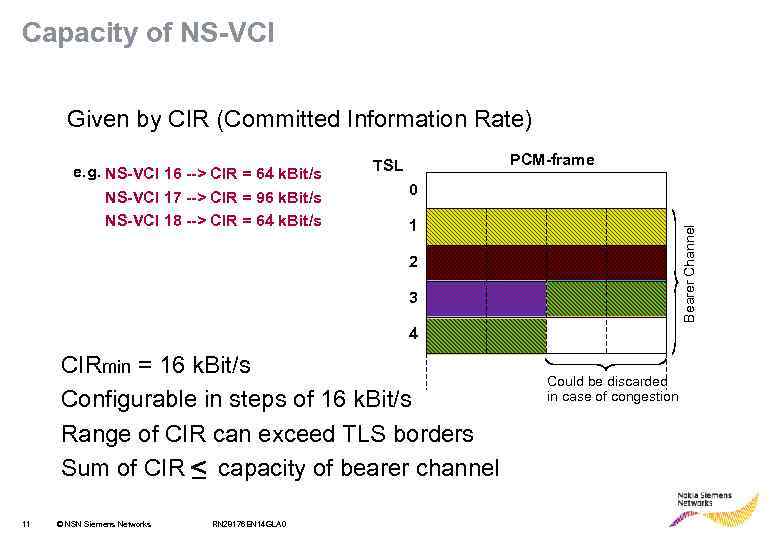
Capacity of NS-VCI Given by CIR (Committed Information Rate) NS-VCI 17 --> CIR = 96 k. Bit/s NS-VCI 18 --> CIR = 64 k. Bit/s PCM-frame TSL 0 1 Bearer Channel e. g. NS-VCI 16 --> CIR = 64 k. Bit/s 2 3 4 CIRmin = 16 k. Bit/s Configurable in steps of 16 k. Bit/s Range of CIR can exceed TLS borders Sum of CIR capacity of bearer channel 11 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Could be discarded in case of congestion
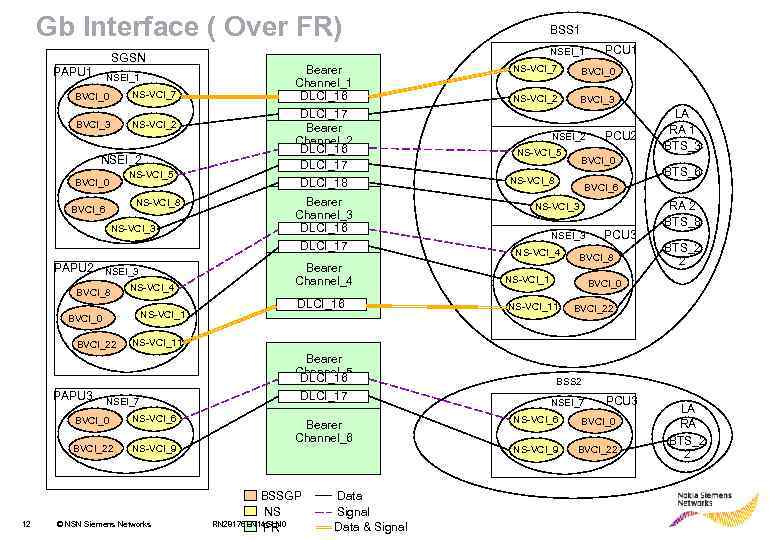
Gb Interface ( Over FR) SGSN PAPU 1 NSEI_1 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_7 BVCI_3 NS-VCI_2 NSEI_2 NS-VCI_5 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_8 BVCI_6 NS-VCI_3 PAPU 2 NSEI_3 BVCI_8 NS-VCI_4 NS-VCI_1 BVCI_0 BVCI_22 PAPU 3 NSEI_1 Bearer Channel_1 DLCI_16 DLCI_17 Bearer Channel_2 DLCI_16 DLCI_17 DLCI_18 Bearer Channel_3 DLCI_16 DLCI_17 Bearer Channel_4 DLCI_16 PCU 1 NS-VCI_7 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_2 BVCI_3 NSEI_2 NS-VCI_5 PCU 2 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_8 LA RA 1 BTS_3 BTS_6 BVCI_6 NS-VCI_3 NSEI_3 NS-VCI_4 PCU 3 BVCI_8 NS-VCI_1 RA 2 BTS_8 BTS_2 2 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_11 BVCI_22 NS-VCI_11 NSEI_7 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_6 BVCI_22 12 BSS 1 NS-VCI_9 © NSN Siemens Networks Bearer Channel_5 DLCI_16 DLCI_17 Bearer Channel_6 BSSGP NS RN 28176 EN 14 GLN 0 FR Data Signal Data & Signal BSS 2 NSEI_7 PCU 3 NS-VCI_6 BVCI_0 NS-VCI_9 BVCI_22 LA RA BTS_2 2
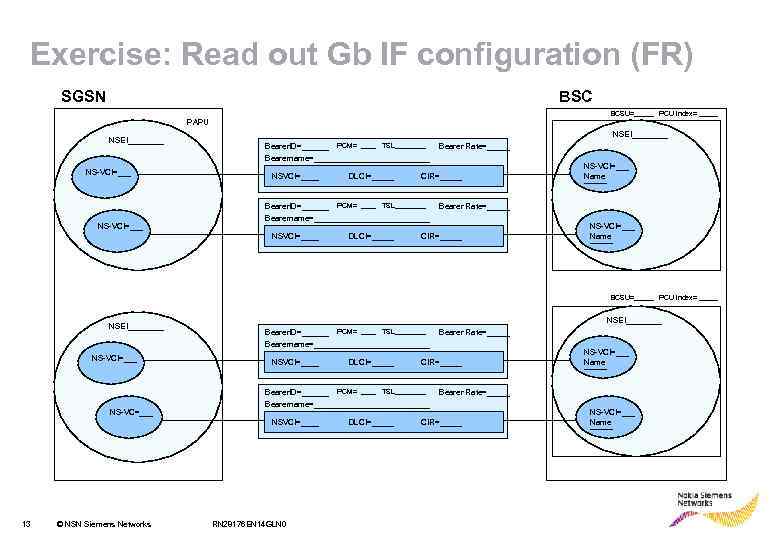
Exercise: Read out Gb IF configuration (FR) SGSN BSC BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ PAPU NSEI____ NS-VCI=___ NSEI____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= ____ TSL____ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=____ DLCI=_____ CIR=_____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= ____ TSL____ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=____ DLCI=_____ Bearer Rate=_____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ Bearer Rate=_____ CIR=_____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ NSEI____ NS-VCI=___ NS-VC=___ NSEI____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= ____ TSL____ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=____ © NSN Siemens Networks CIR=_____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= ____ TSL____ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=____ 13 DLCI=_____ RN 28176 EN 14 GLN 0 DLCI=_____ Bearer Rate=_____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ Bearer Rate=_____ CIR=_____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____

Gb over IP Considerations • Gb over IP license must be installed and activated • In dynamic IP configurations the SGSN side must be created • • 14 first In static IP configurations it does not matter which end (BSC/SGSN) is created first Static configuration can use only logical IP addresses Both IPv 4 and IPv 6 are supported in the NSN implementation of Gb over IP DNS names can be used instead of IP addresses if a DNS server address is specified in the BSC © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Gb over IP interface configuration (BSC 2 i) Gb Interface SGSN BSC 2 i IP Networks PAPU External LAN BCSU P BCSU C U 15 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
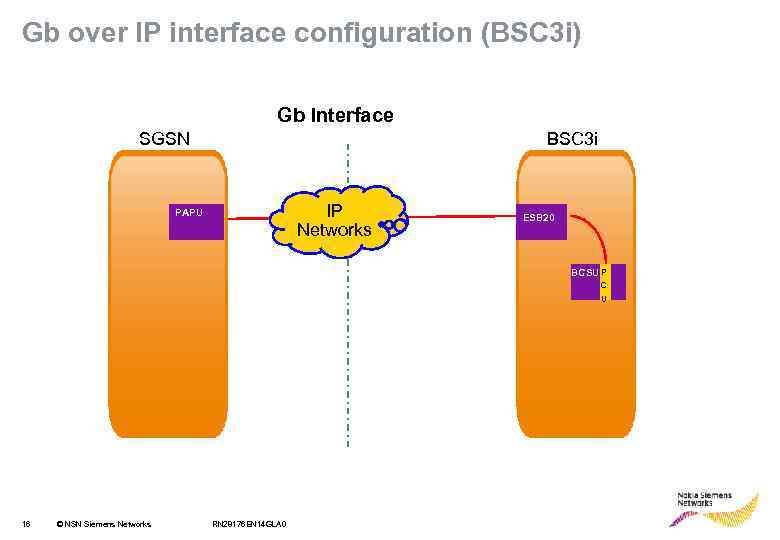
Gb over IP interface configuration (BSC 3 i) Gb Interface SGSN BSC 3 i IP Networks PAPU ESB 20 BCSU P BCSU C U 16 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
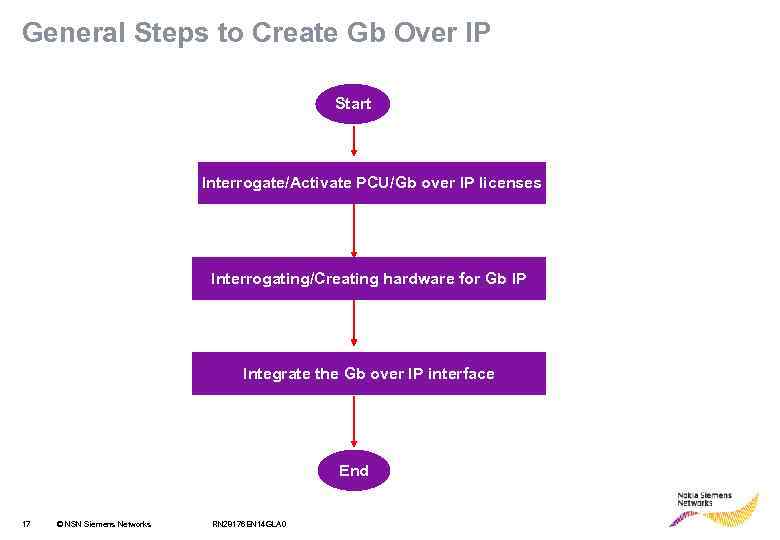
General Steps to Create Gb Over IP Start Interrogate/Activate PCU/Gb over IP licenses Interrogating/Creating hardware for Gb IP Integrate the Gb over IP interface End 17 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Transmission Solutions of Gb Interface (IP) LAN Switch 1 Point to Point Ethernet LAN Switch SGSN 18 © NSN Siemens Networks 2 IP Network LAN Switch BSC RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
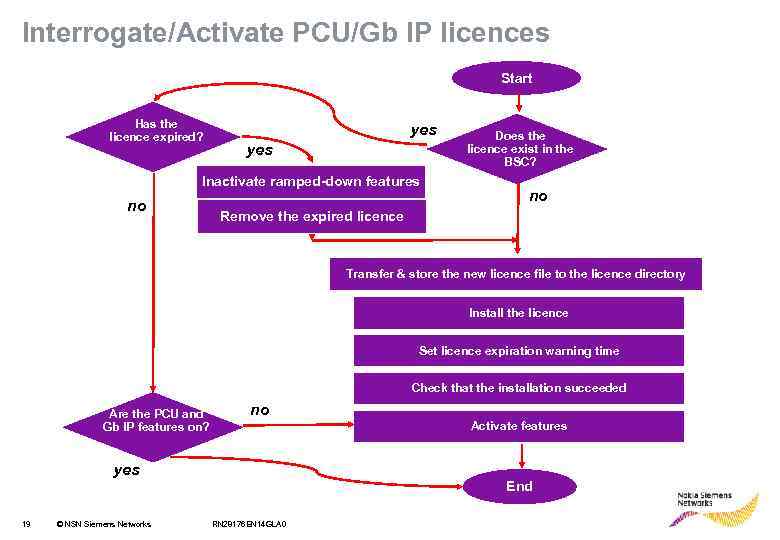
Interrogate/Activate PCU/Gb IP licences Start Has the licence expired? yes Inactivate ramped-down features no Does the licence exist in the BSC? no Remove the expired licence Transfer & store the new licence file to the licence directory Install the licence Set licence expiration warning time Check that the installation succeeded Are the PCU and Gb IP features on? no Activate features yes End 19 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
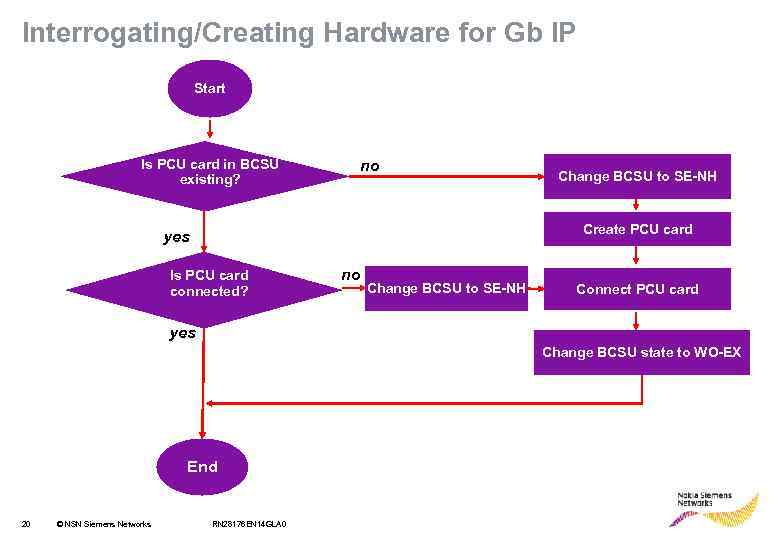
Interrogating/Creating Hardware for Gb IP Start Is PCU card in BCSU existing? no Change BCSU to SE-NH Create PCU card yes Is PCU card connected? no Change BCSU to SE-NH Connect PCU card yes Change BCSU state to WO-EX End 20 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
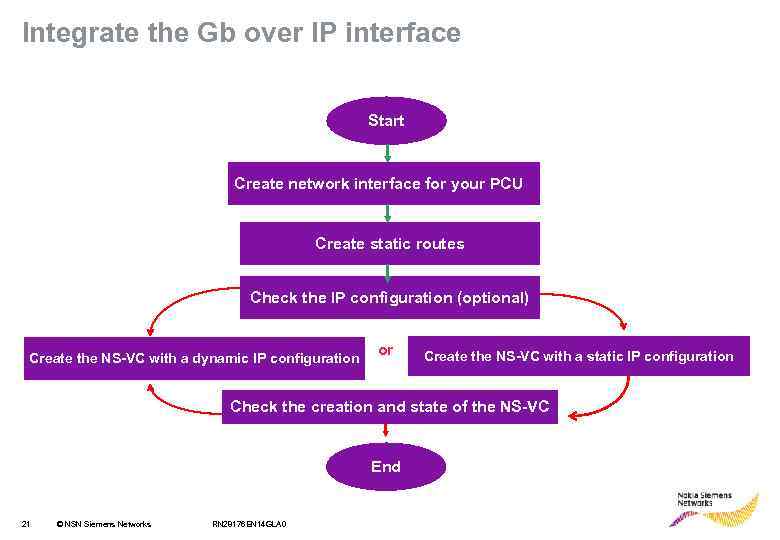
Integrate the Gb over IP interface Start Create network interface for your PCU Create static routes Check the IP configuration (optional) Create the NS-VC with a dynamic IP configuration or Create the NS-VC with a static IP configuration Check the creation and state of the NS-VC End 21 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
Static Gb IP configuration • Configuration parameters are configured to both ends statically and not transferred over Gb. • Operator creates all NS-VCs with fixed remote IP endpoints: address, port number, signaling weight and data weight. • BSC software can decide that static configuration is used, if PRE parameter is set to No (N) in creation of first NS-VC in NSE. • NS-VC configurations on both sides (BSS and SGSN) must match 22 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
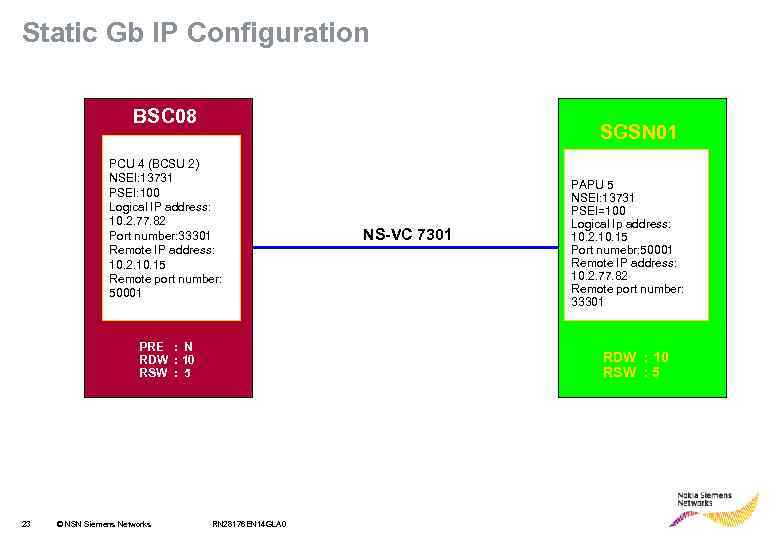
Static Gb IP Configuration BSC 08 SGSN 01 PCU 4 (BCSU 2) NSEI: 13731 PSEI: 100 Logical IP address: 10. 2. 77. 82 Port number: 33301 Remote IP address: 10. 2. 10. 15 Remote port number: 50001 PRE : N RDW : 10 RSW : 5 23 © NSN Siemens Networks NS-VC 7301 PAPU 5 NSEI: 13731 PSEI=100 Logical Ip address: 10. 2. 10. 15 Port numebr: 50001 Remote IP address: 10. 2. 77. 82 Remote port number: 33301 RDW : 10 RSW : 5 RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Gb IP NS-VC static configuration (BSC) FXI: ; BSC 3 i BSC 31 -LAB NETWORK SERVICE VIRTUAL LINK PARAMETERS: EQOS ENABLED PSE-00 NSE-01755 NS-VL-05500 COMMAND EXECUTED 24 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
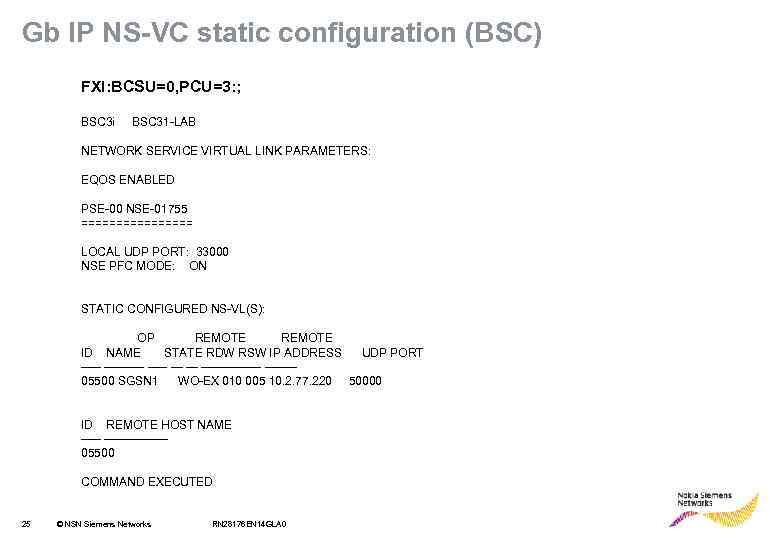
Gb IP NS-VC static configuration (BSC) FXI: BCSU=0, PCU=3: ; BSC 3 i BSC 31 -LAB NETWORK SERVICE VIRTUAL LINK PARAMETERS: EQOS ENABLED PSE-00 NSE-01755 ======== LOCAL UDP PORT: 33000 NSE PFC MODE: ON STATIC CONFIGURED NS-VL(S): OP REMOTE ID NAME STATE RDW RSW IP ADDRESS UDP PORT ---------- -------05500 SGSN 1 WO-EX 010 005 10. 2. 77. 220 50000 ID REMOTE HOST NAME ----------05500 COMMAND EXECUTED 25 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Dynamic Gb IP Configuration • • • 26 Configuration parameters are transferred over Gb in the initialization phase. Only one address and port pair of the remote end SGSN is needed to establish NS-VC configuration on Gb. These parameters are attributes of the preconfigured SGSN IP endpoint. BSC software can decide that dynamic configuration is used, if PRE parameter is set to Yes (Y) when creating the first NSVC in NSE. © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
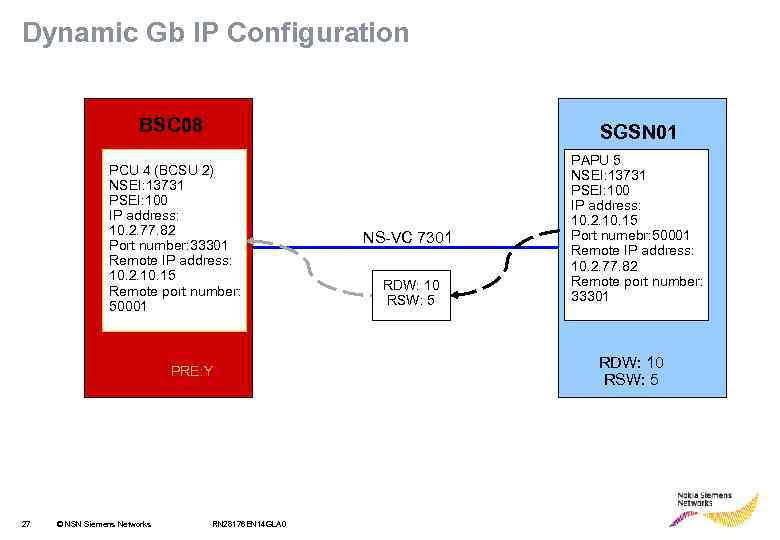
Dynamic Gb IP Configuration BSC 08 SGSN 01 PCU 4 (BCSU 2) NSEI: 13731 PSEI: 100 IP address: 10. 2. 77. 82 Port number: 33301 Remote IP address: 10. 2. 10. 15 Remote port number: 50001 PRE: Y 27 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 NS-VC 7301 RDW: 10 RSW: 5 PAPU 5 NSEI: 13731 PSEI: 100 IP address: 10. 2. 10. 15 Port numebr: 50001 Remote IP address: 10. 2. 77. 82 Remote port number: 33301 RDW: 10 RSW: 5

Dynamic Gb IP configuration BSC 08 NETWORK SERVICE VIRTUAL CONNECTION CREATION NSEI-13731 BCSU-2 PCU-4 PRE CONFIGURED NS-VC: NS-VC LOCAL REMOTE ID NAME UDP PORT IP ADDRESS UDP PORT ---------- -------07301 GBOVERIP 50000 10. 2. 10. 15 50001 REMOTE HOST NAME: /*** WARNING ***/ /*** BSC DB AND PCU CONFIGURED OK BUT NO RESPONSE RECEIVED FROM SGSN, STILL TRYING ***/ COMMAND EXECUTED 28 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
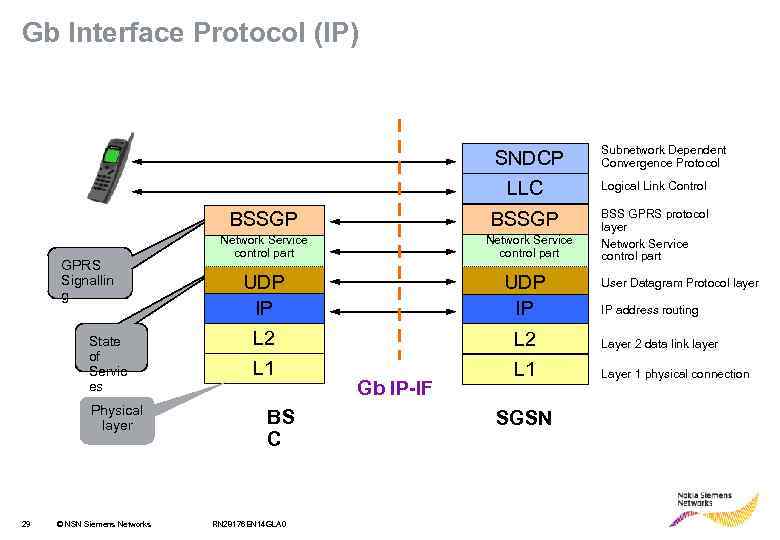
Gb Interface Protocol (IP) SNDCP LLC BSSGP GPRS Signallin g State of Servic es Physical layer 29 © NSN Siemens Network Service control part Subnetwork Dependent Convergence Protocol Logical Link Control BSS GPRS protocol layer Network Service control part UDP IP L 2 Layer 2 data link layer L 1 Layer 1 physical connection BS C RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Gb IP-IF SGSN User Datagram Protocol layer IP address routing
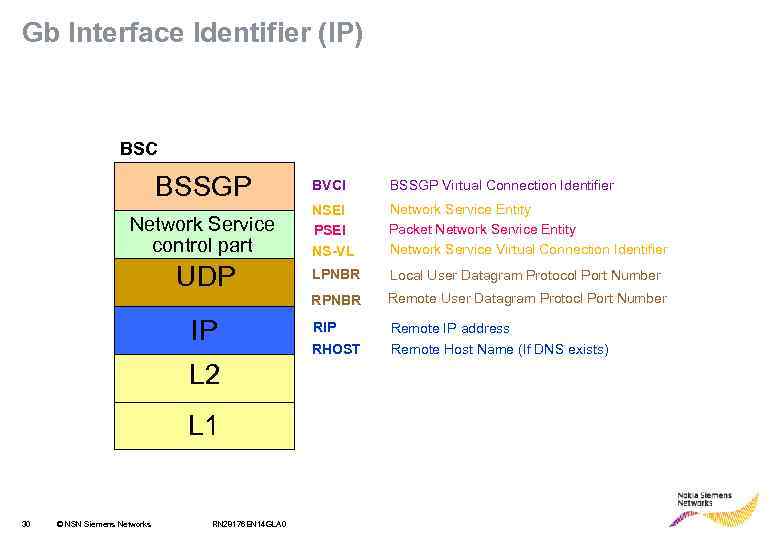
Gb Interface Identifier (IP) BSC BSSGP BVCI BSSGP Virtual Connection Identifier Network Service control part NSEI PSEI NS-VL Network Service Entity Packet Network Service Entity Network Service Virtual Connection Identifier UDP LPNBR Local User Datagram Protocol Port Number RPNBR Remote User Datagram Protocl Port Number RIP Remote IP address RHOST Remote Host Name (If DNS exists) IP L 2 L 1 30 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
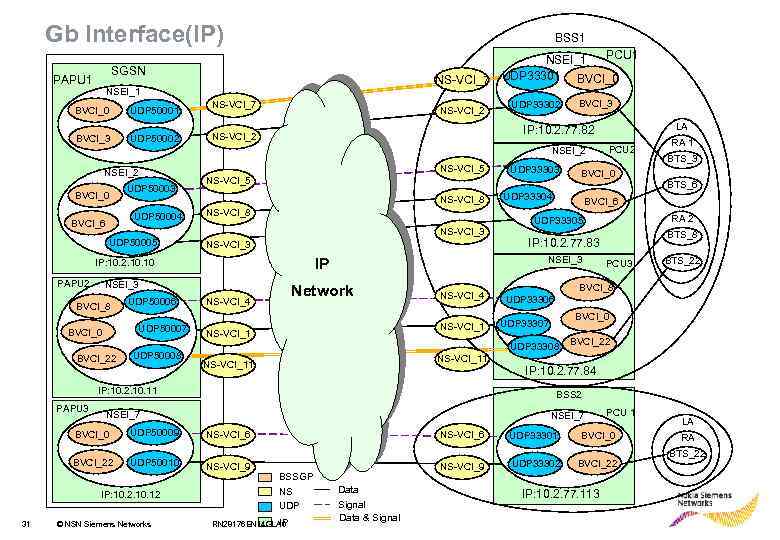
Gb Interface(IP) BSS 1 SGSN PAPU 1 NS-VCI_7 NSEI_1 BVCI_0 UDP 50001 BVCI_3 UDP 50002 NS-VCI_7 NS-VCI_2 PCU 1 NSEI_1 UDP 33301 BVCI_0 UDP 33302 BVCI_3 NSEI_2 BVCI_0 UDP 50003 BVCI_6 NS-VCI_5 NS-VCI_8 UDP 50004 UDP 50005 NS-VCI_8 NS-VCI_3 NSEI_3 BVCI_8 UDP 50006 UDP 50007 BVCI_0 BVCI_22 UDP 50008 Network NS-VCI_4 NS-VCI_1 PCU 2 BVCI_0 UDP 33304 BTS_8 IP: 10. 2. 77. 83 PCU 3 BTS_22 BVCI_8 UDP 33306 BVCI_0 UDP 33307 BVCI_22 IP: 10. 2. 77. 84 BSS 2 NSEI_7 PCU 1 UDP 50009 NS-VCI_6 UDP 33301 BVCI_0 BVCI_22 UDP 50010 NS-VCI_9 UDP 33302 BVCI_22 © NSN Siemens Networks BTS_6 RA 2 UDP 33305 BVCI_0 31 BTS_3 NS-VCI_11 NSEI_7 IP: 10. 2. 10. 12 RA 1 BVCI_6 UDP 33308 IP: 10. 2. 10. 11 PAPU 3 UDP 33303 NSEI_3 IP IP: 10. 2. 10 PAPU 2 LA IP: 10. 2. 77. 82 NS-VCI_2 BSSGP NS UDP IP RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Data Signal Data & Signal IP: 10. 2. 77. 113 LA RA BTS_22
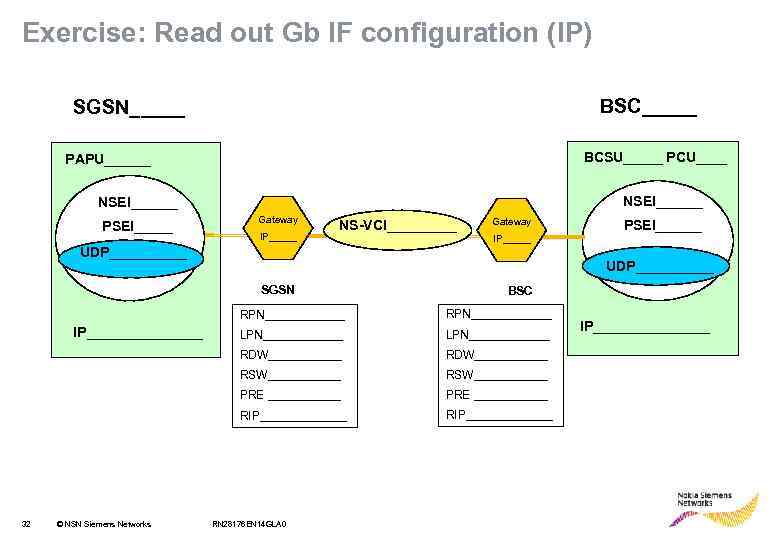
Exercise: Read out Gb IF configuration (IP) BSC_____ SGSN_____ BCSU_____ PCU____ PAPU______ NSEI______ PSEI_____ Gateway IP_____ NS-VCI_____ Gateway IP_____ UDP__________ SGSN BSC RPN______ LPN______ RDW______ RSW___________ PRE ______ RIP_______ © NSN Siemens Networks LPN______ RSW______ 32 RPN______ RDW______ IP________ PSEI______ RIP_______ RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 IP________
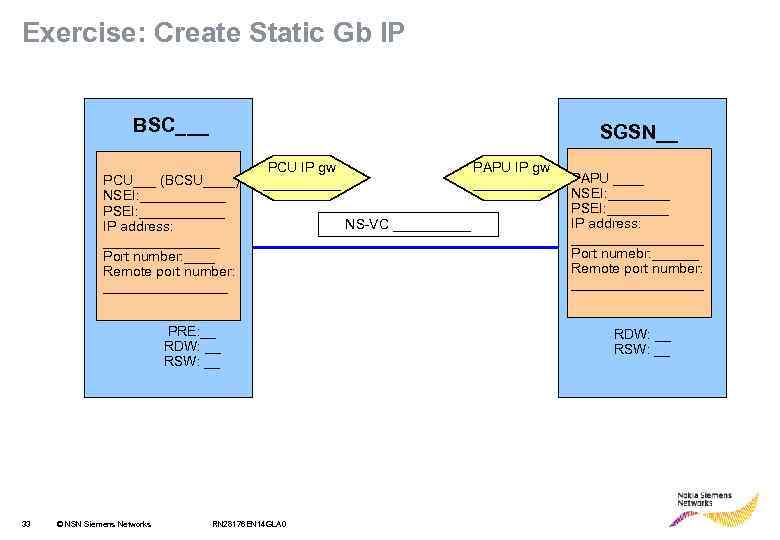
Exercise: Create Static Gb IP BSC___ SGSN__ PCU___ (BCSU____) NSEI: ______ PSEI: ______ IP address: ________ Port number: ____ Remote port number: ________ PCU IP gw _____ PRE: __ RDW: __ RSW: __ 33 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 PAPU IP gw _____ NS-VC _____ PAPU ____ NSEI: ____ PSEI: ____ IP address: _________ Port numebr: ______ Remote port number: _________ RDW: __ RSW: __
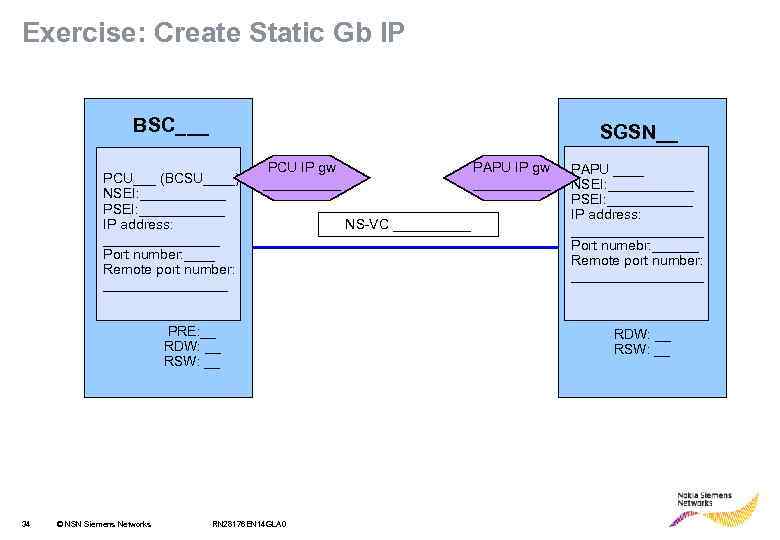
Exercise: Create Static Gb IP BSC___ SGSN__ PCU___ (BCSU____) NSEI: ______ PSEI: ______ IP address: ________ Port number: ____ Remote port number: ________ PCU IP gw _____ PRE: __ RDW: __ RSW: __ 34 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 PAPU IP gw _____ NS-VC _____ PAPU ____ NSEI: ______ PSEI: ______ IP address: _________ Port numebr: ______ Remote port number: _________ RDW: __ RSW: __
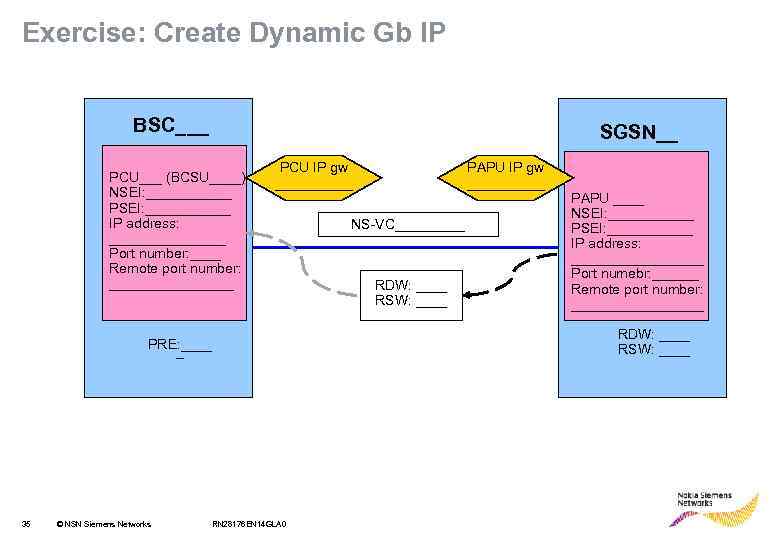
Exercise: Create Dynamic Gb IP BSC___ SGSN__ PCU___ (BCSU____) NSEI: ______ PSEI: ______ IP address: ________ Port number: ____ Remote port number: ________ PCU IP gw _____ © NSN Siemens Networks NS-VC_____ RDW: ____ RSW: ____ PAPU ____ NSEI: ______ PSEI: ______ IP address: _________ Port numebr: ______ Remote port number: _________ RDW: ____ RSW: ____ PRE: ____ _ 35 PAPU IP gw _____ RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
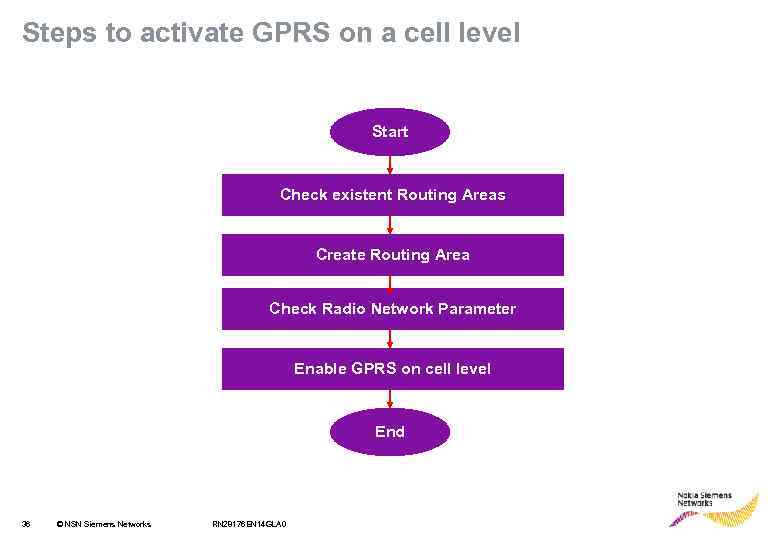
Steps to activate GPRS on a cell level Start Check existent Routing Areas Create Routing Area Check Radio Network Parameter Enable GPRS on cell level End 36 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Routing Area RAI = MCC+MNC+LAC+RAC Routing Area PCU n Cell RA 2 BTS SGSN BTS PCU 1 RA n RA 1 BTS PCU 0 BTS BSC Rules: Routing Area 37 Location Area Cell © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 LA Location Area
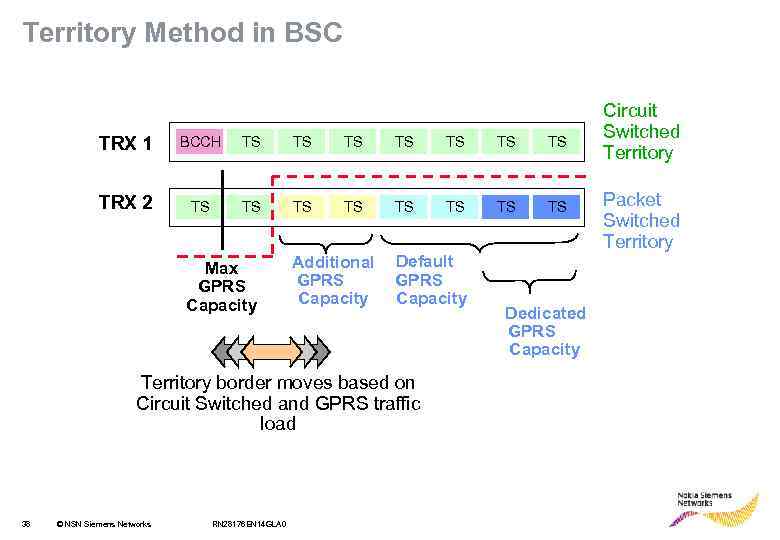
Territory Method in BSC TRX 1 BCCH TS TS TRX 2 TS TS Max GPRS Capacity Additional GPRS Capacity Default GPRS Capacity Territory border moves based on Circuit Switched and GPRS traffic load 38 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Dedicated GPRS Capacity Circuit Switched Territory Packet Switched Territory

GPRS Capable Traffic Channel Within a cell, all the Full Rate and Dual Rate traffic channels are GPRS capable. GPRS territory is a set of consecutive TSLs, excluding • TSLs that are not capable of full rate traffic • non-TCH channels (BCCH, SDCCH) • permanent half rate TSLs • blocked TSLs • TSL 0 when BB Hopping is used • transparent HSCSD calls. 39 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
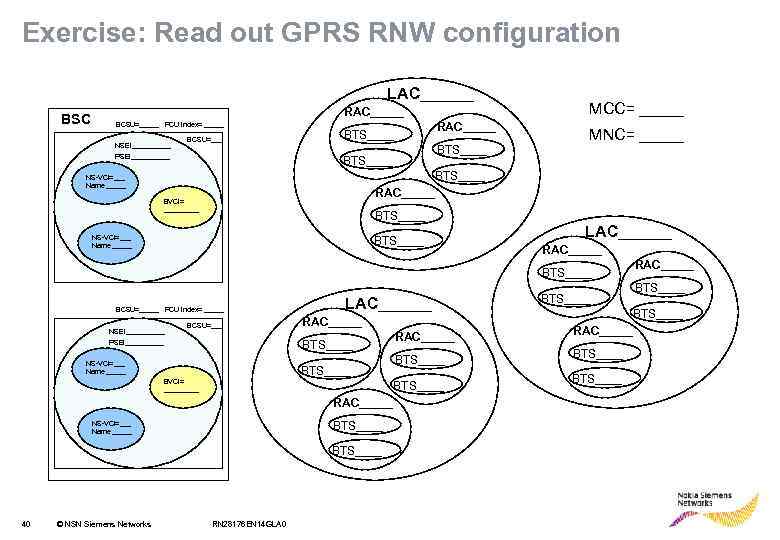
Exercise: Read out GPRS RNW configuration LAC______ BSC RAC_____ BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ NSEI_____ BCSU=___ PSEI_____ BTS____ MCC= _____ MNC= _____ BTS____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ RAC_____ BVCI= _____ BTS____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ BTS____ LAC______ RAC_____ BTS____ BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ NSEI_____ BCSU=___ LAC______ RAC_____ BTS____ PSEI_____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ BTS____ BVCI= _____ BTS____ NS-VCI=___ Name _____ BTS____ © NSN Siemens Networks BTS____ RAC_____ 40 RAC_____ RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 BTS____ RAC_____ BTS____
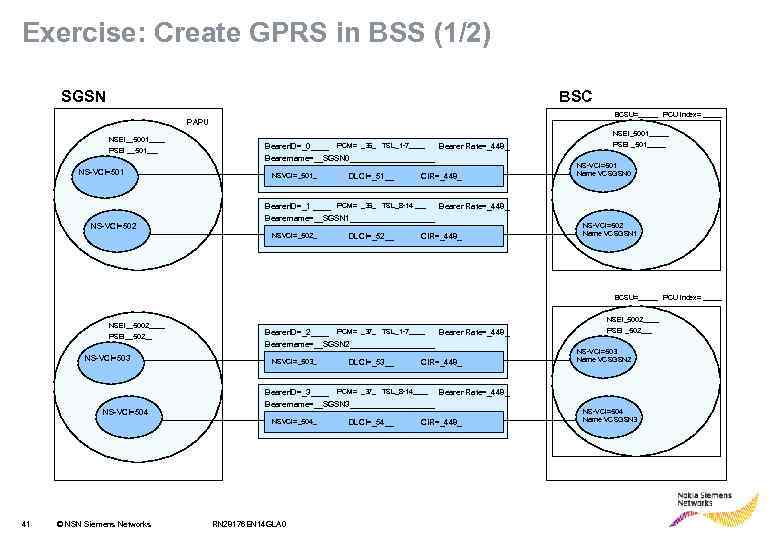
Exercise: Create GPRS in BSS (1/2) SGSN BSC BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ PAPU NSEI__5001____ PSEI __501___ NS-VCI=501 NS-VCI=___ NS-VCI=502 NS-VCI=___ NSEI_5001_____ Bearer. ID=_0____ Bearer Rate=_448_ Bearername=__SGSN 0__________ PSEI _501_____ PCM= _36_ TSL_1 -7____ NSVCI=_501_ DLCI=_51__ CIR=_448_ Bearer. ID=_1 ____ PCM= _36_ TSL_8 -14 ___ Bearer Rate=_448_ Bearername=__SGSN 1__________ NSVCI=_502_ DLCI=_52__ CIR=_448_ NS-VCI=501 Name VCSGSN 0 NS-VCI=502 NS-VCI=___ Name VCSGSN 1 Name _____ BCSU=_____ PCU index= _____ NSEI__5002____ PSEI__502__ NS-VCI=503 NS-VCI=___ NSEI_5002____ Bearer. ID=_2____ PCM= ____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= _37_ TSL_1 -7____ Bearer Rate=_____ Rate=_448_ TSL____ Bearername=__SGSN 2__________ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=_503_ NSVCI=____ _ NS-VCI=504 NS-VC=___ _ © NSN Siemens Networks CIR=_448_ CIR=_____ Bearer. ID=_3____ PCM= ____ Bearer. ID=______ PCM= _37_ TSL_8 -14____ Bearer Rate=_____ Rate=_448_ TSL____ Bearername=__SGSN 3__________ Bearername=_____________ NSVCI=_504_ NSVCI=____ 41 DLCI=_53__ DLCI=_____ RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 DLCI=_54__ DLCI=_____ CIR=_448_ CIR=_____ PSEI _502___ NS-VCI=503 NS-VCI=___ Name VCSGSN 2 Name _____ NS-VCI=504 NS-VCI=___ Name VCSGSN 3 Name _____
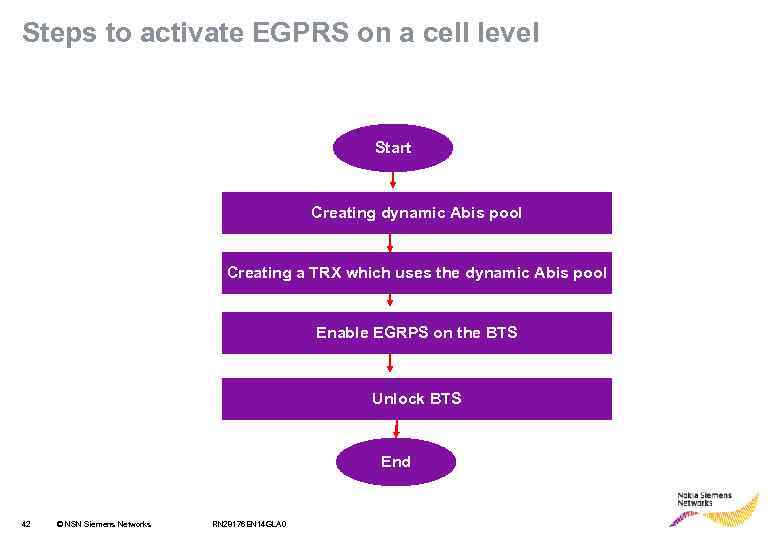
Steps to activate EGPRS on a cell level Start Creating dynamic Abis pool Creating dynamic Abis Creating a TRX which uses the dynamic Abis pool Enable EGRPS on the BTS Unlock BTS End 42 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
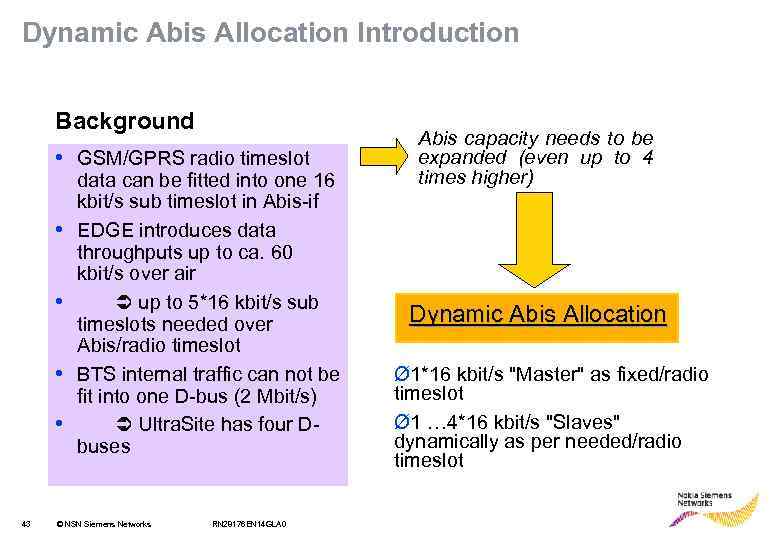
Dynamic Abis Allocation Introduction Background • GSM/GPRS radio timeslot • • 43 data can be fitted into one 16 kbit/s sub timeslot in Abis-if EDGE introduces data throughputs up to ca. 60 kbit/s over air up to 5*16 kbit/s sub timeslots needed over Abis/radio timeslot BTS internal traffic can not be fit into one D-bus (2 Mbit/s) Ultra. Site has four Dbuses © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0 Abis capacity needs to be expanded (even up to 4 times higher) Dynamic Abis Allocation Ø 1*16 kbit/s "Master" as fixed/radio timeslot Ø 1 … 4*16 kbit/s "Slaves" dynamically as per needed/radio timeslot

Dynamic Abis solution PCU frame types • PCU data frame • used when TRX not in EDGE mode • only able to carry CS-1 and CS-2 • PCU master data frame • used when TRX is attached to Dynamic Abis and Edge or/CS 3 CS 4 is enabled in BTS • carries CS-1 or MCS-1 on its own and CS 2. . . CS-4 and MCS-2. . . MCS-9 with the help of slave frame(s) • includes pointers to the slave frames • PCU slave data frame • carries additional data that does not fit in PCU master data frames • PCU random access frame • PCU synchronisation frame 44 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Dynamic Abis solution Fixed channels and EDAP • For each GPRS radio timeslot on each EDGE TRX, one fixed 16 -kbps channel is allocated on the Abis for the transfer for PCU master data frames. • PCU slave data frames are allocated in a common pool, the EDAP (EDGE Dynamic Abis Pool). • 12 PCM timeslots as the maximum size of EDAP. • A master channel and its slave channels and therefore the entire EDAP must be on the same Abis PCM. 45 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
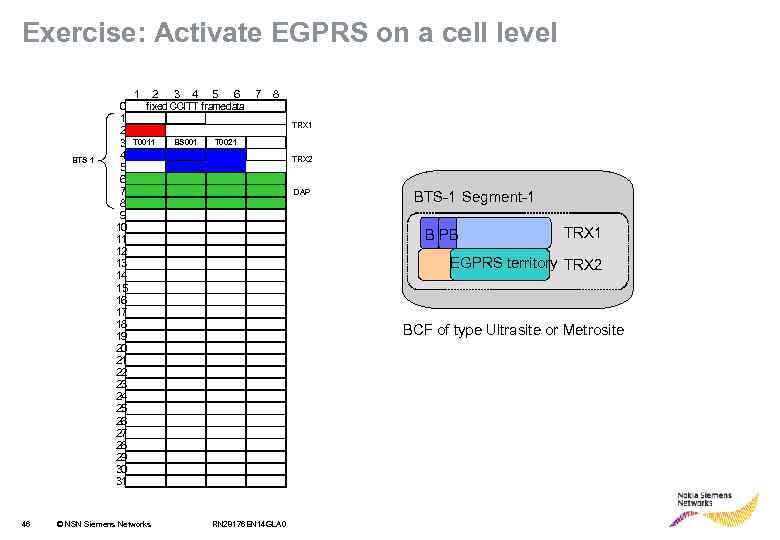
Exercise: Activate EGPRS on a cell level BTS 1 46 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 fixed CCITT framedata 8 TRX 1 T 0011 © NSN Siemens Networks BS 001 T 0021 TRX 2 DAP BTS-1 Segment-1 B PB TRX 1 EGPRS territory TRX 2 BCF of type Ultrasite or Metrosite RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
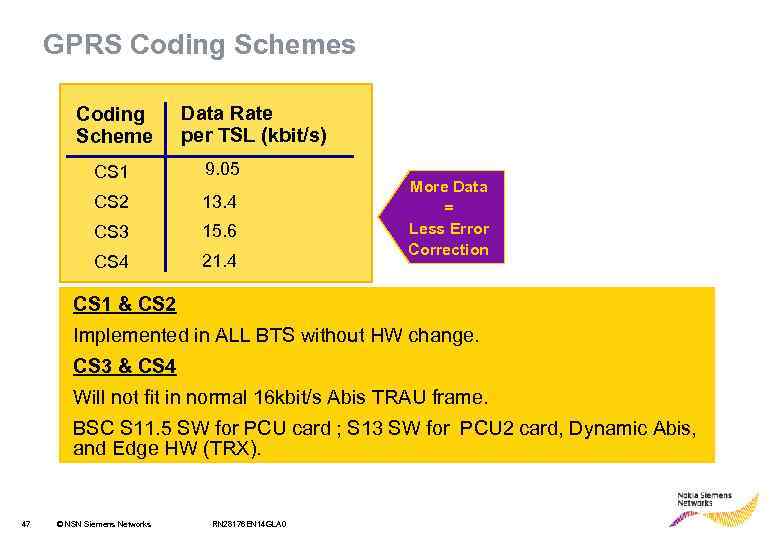
GPRS Coding Schemes Coding Scheme Data Rate per TSL (kbit/s) CS 1 9. 05 CS 2 13. 4 CS 3 15. 6 CS 4 21. 4 More Data = Less Error Correction CS 1 & CS 2 Implemented in ALL BTS without HW change. CS 3 & CS 4 Will not fit in normal 16 kbit/s Abis TRAU frame. BSC S 11. 5 SW for PCU card ; S 13 SW for PCU 2 card, Dynamic Abis, and Edge HW (TRX). 47 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0

Functional Description • When CS 3 -CS 4 option is on, and the Dynamic Abis pool and (E)GPRS territories are created then all GPRS coding schemes (CS 1 -CS 4) are available for data transfer. • The current GPRS Link Adaptation algorithm in the PCU/RLC is replaced with a new one, which covers also CS 3 and CS 4. • A data block of CS 2 -CS 4 is transferred in one PCU master Data Frame and one PCU Slave Data Frame through the Abis interface. CS 1 data block fits in one PCU Master Data Frame. 48 © NSN Siemens Networks RN 28176 EN 14 GLA 0
GPRS, EGPRS integration in BSC.ppt