16627c3330ed5774b1542d7a5f8a3a5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Governmental Influencers AP Government Unit III
Governmental Influencers AP Government Unit III
 Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • The Fourth Estate of Government • Global Media Phenomenon • Who has freer press? ? Homework: • Federalist 10 Factor of Interest Groups • Pillar of Democracy Due 12/20/17
Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • The Fourth Estate of Government • Global Media Phenomenon • Who has freer press? ? Homework: • Federalist 10 Factor of Interest Groups • Pillar of Democracy Due 12/20/17
 Welcome to K Street, Washington DC Alex de Tocqueville in 1834 stated - “In no country of the world has the principle of association been more successfully used…than in America. ” - Alex de Tocqueville, 1834 • 2/3 rds of all Americans belong to some sort of organization • There are over 22, 000 interest groups in the U. S.
Welcome to K Street, Washington DC Alex de Tocqueville in 1834 stated - “In no country of the world has the principle of association been more successfully used…than in America. ” - Alex de Tocqueville, 1834 • 2/3 rds of all Americans belong to some sort of organization • There are over 22, 000 interest groups in the U. S.
 Interest Groups - Why • Groups of people who join together in support of a single issue. Factors for existence ▫ Many kinds of cleavages in the US ▫ Constitution creates many protected access points ▫ Political parties are weak
Interest Groups - Why • Groups of people who join together in support of a single issue. Factors for existence ▫ Many kinds of cleavages in the US ▫ Constitution creates many protected access points ▫ Political parties are weak
 The Three Headed Hydra • Interest groups’ tactics to gain access ▫ The United States Government has multiple access points ▫ First Amendment protections ▫ Tactics Electioneering: PACS, Super PACs, Issue Advocacy Lobbying: direct appeal Shape public opinion: mass mailing, issue advocacy Litigation: civil suits
The Three Headed Hydra • Interest groups’ tactics to gain access ▫ The United States Government has multiple access points ▫ First Amendment protections ▫ Tactics Electioneering: PACS, Super PACs, Issue Advocacy Lobbying: direct appeal Shape public opinion: mass mailing, issue advocacy Litigation: civil suits
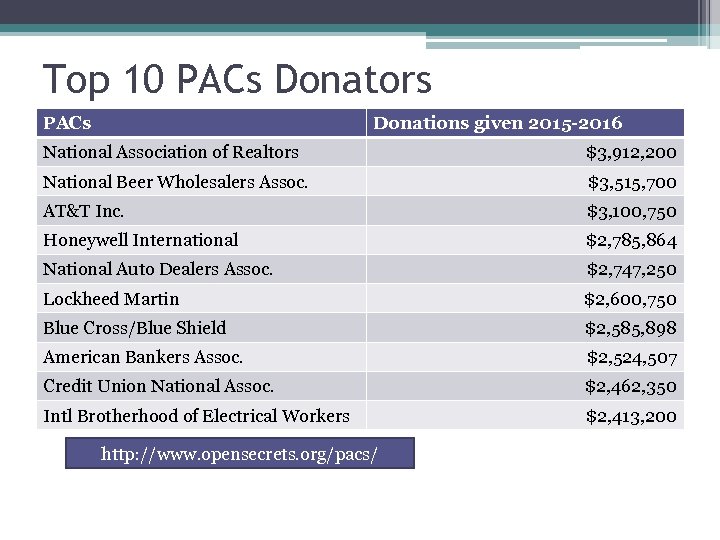 Top 10 PACs Donators PACs Donations given 2015 -2016 National Association of Realtors $3, 912, 200 National Beer Wholesalers Assoc. $3, 515, 700 AT&T Inc. $3, 100, 750 Honeywell International $2, 785, 864 National Auto Dealers Assoc. $2, 747, 250 Lockheed Martin $2, 600, 750 Blue Cross/Blue Shield $2, 585, 898 American Bankers Assoc. $2, 524, 507 Credit Union National Assoc. $2, 462, 350 Intl Brotherhood of Electrical Workers $2, 413, 200 http: //www. opensecrets. org/pacs/
Top 10 PACs Donators PACs Donations given 2015 -2016 National Association of Realtors $3, 912, 200 National Beer Wholesalers Assoc. $3, 515, 700 AT&T Inc. $3, 100, 750 Honeywell International $2, 785, 864 National Auto Dealers Assoc. $2, 747, 250 Lockheed Martin $2, 600, 750 Blue Cross/Blue Shield $2, 585, 898 American Bankers Assoc. $2, 524, 507 Credit Union National Assoc. $2, 462, 350 Intl Brotherhood of Electrical Workers $2, 413, 200 http: //www. opensecrets. org/pacs/
 Group think politics • • • The schools of thought - Pluralism - Elite - Hyper-pluralism Write statement the represents each school of group think politics and how it counters the others
Group think politics • • • The schools of thought - Pluralism - Elite - Hyper-pluralism Write statement the represents each school of group think politics and how it counters the others
 Group Think Theory: identify theory • Interest groups, Congressional committees, and bureaucratic agencies form iron triangles to achieve their goals. These have now expand to include more groups and create issue networks • Interest groups form Super PACS to fund electioneering • There are over 7000 interest groups in the United States and many counter each other – example pro-choice and pro-life
Group Think Theory: identify theory • Interest groups, Congressional committees, and bureaucratic agencies form iron triangles to achieve their goals. These have now expand to include more groups and create issue networks • Interest groups form Super PACS to fund electioneering • There are over 7000 interest groups in the United States and many counter each other – example pro-choice and pro-life
 Group Think Theories • Elites – Only a wealth few people, key groups, and institutions hold power (even their policies prompt their power) •
Group Think Theories • Elites – Only a wealth few people, key groups, and institutions hold power (even their policies prompt their power) •
 Group Think Theories • Pluralism – there are competing groups, but no one is dominant. • - Groups play by the rules • - Group competition • - Groups are links between the people and government • - Groups do not have an equal distribution of power
Group Think Theories • Pluralism – there are competing groups, but no one is dominant. • - Groups play by the rules • - Group competition • - Groups are links between the people and government • - Groups do not have an equal distribution of power
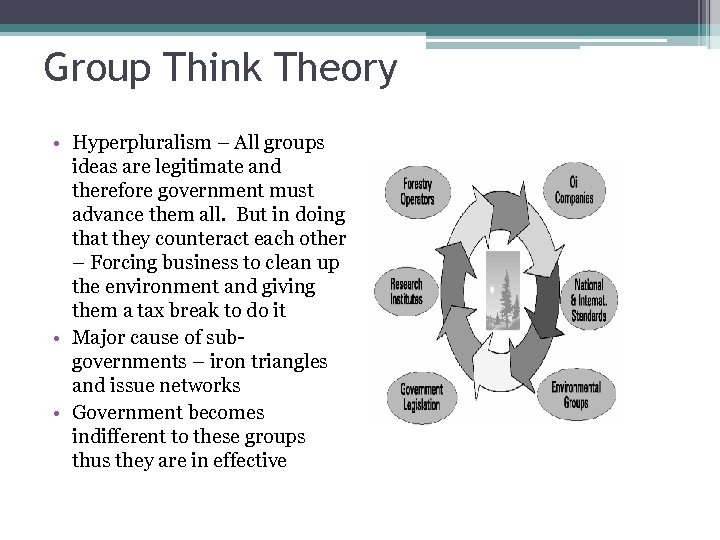 Group Think Theory • Hyperpluralism – All groups ideas are legitimate and therefore government must advance them all. But in doing that they counteract each other – Forcing business to clean up the environment and giving them a tax break to do it • Major cause of subgovernments – iron triangles and issue networks • Government becomes indifferent to these groups thus they are in effective
Group Think Theory • Hyperpluralism – All groups ideas are legitimate and therefore government must advance them all. But in doing that they counteract each other – Forcing business to clean up the environment and giving them a tax break to do it • Major cause of subgovernments – iron triangles and issue networks • Government becomes indifferent to these groups thus they are in effective
 Know THY Interest • Describe two ways an interest group is unlike a political party. • Which group think theory supports the idea that because government has deal with counteracting groups (ex. Pro environment and corporations) that become indifferent to both? • According to Madison what is a major cause of interest groups?
Know THY Interest • Describe two ways an interest group is unlike a political party. • Which group think theory supports the idea that because government has deal with counteracting groups (ex. Pro environment and corporations) that become indifferent to both? • According to Madison what is a major cause of interest groups?
 Types of Membership – Classification Institutional • • • The most usual organization represents a business or corporation. (Other examples – universities, foundations, and government) They share lobbyist, lawyers, and public relations experts Ex. Cities - National League of Cities, and counties National Association of Counties
Types of Membership – Classification Institutional • • • The most usual organization represents a business or corporation. (Other examples – universities, foundations, and government) They share lobbyist, lawyers, and public relations experts Ex. Cities - National League of Cities, and counties National Association of Counties
 Types of Membership – Classification Individual • We are a nation of joiners – (churches, political association, clubs) • These focus on are own personal interest and can be some of the most powerful groups: Ex. NAACP, NRA, AFL -CIO
Types of Membership – Classification Individual • We are a nation of joiners – (churches, political association, clubs) • These focus on are own personal interest and can be some of the most powerful groups: Ex. NAACP, NRA, AFL -CIO
 Success in interest groups • What three factors determine the effectiveness of an interest group? • How does Olson Law explain the ineffectiveness of consumer advocacy groups? • Why does intensity effect whether politicians will listen to an interest group? • How does the elite group theory apply to interest groups?
Success in interest groups • What three factors determine the effectiveness of an interest group? • How does Olson Law explain the ineffectiveness of consumer advocacy groups? • Why does intensity effect whether politicians will listen to an interest group? • How does the elite group theory apply to interest groups?
 TOP 10 – Why are they always the same • • • 2001 National Rifle Association (No. 1) American Association of Retired People-AARP - (No. 2) National Federation of Independent Business (No. 3) American Israel Foreign Affairs Committee (No. 4) Association of Trial Lawyers of America (No. 5) American Federation of Labor- Congress of Industrial Organizations AFL-CIO (No. 6) Chamber of Commerce of the United States of America (No. 7) National Beer Wholesalers of America (No. 8) National Association of Realtors (No. 9) • National Association of Manufacturers (No. 10)
TOP 10 – Why are they always the same • • • 2001 National Rifle Association (No. 1) American Association of Retired People-AARP - (No. 2) National Federation of Independent Business (No. 3) American Israel Foreign Affairs Committee (No. 4) Association of Trial Lawyers of America (No. 5) American Federation of Labor- Congress of Industrial Organizations AFL-CIO (No. 6) Chamber of Commerce of the United States of America (No. 7) National Beer Wholesalers of America (No. 8) National Association of Realtors (No. 9) • National Association of Manufacturers (No. 10)
 Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Test analysis • The benefit of membership • Effective interest group test Homework: • Pillar of Democracy Assignment
Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Test analysis • The benefit of membership • Effective interest group test Homework: • Pillar of Democracy Assignment
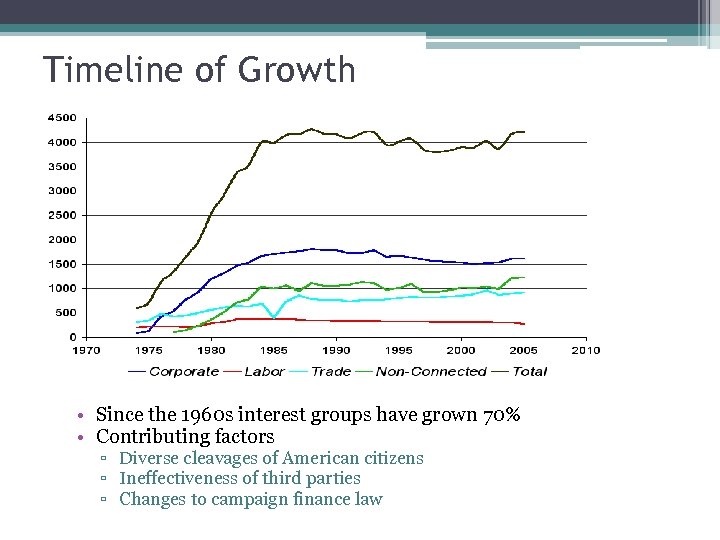 Timeline of Growth • Since the 1960 s interest groups have grown 70% • Contributing factors ▫ Diverse cleavages of American citizens ▫ Ineffectiveness of third parties ▫ Changes to campaign finance law
Timeline of Growth • Since the 1960 s interest groups have grown 70% • Contributing factors ▫ Diverse cleavages of American citizens ▫ Ineffectiveness of third parties ▫ Changes to campaign finance law
 Factors of the rise • Board economic developments: cash crops and mass production • Government policy itself - Wars-veterans groups Encourage the creation of the farmers bureau Launched Chamber of Commerce Favored the growth of unions • Emergence of strong leaders in uncertain times (civil rights) • Expanding role of government • Technology and media
Factors of the rise • Board economic developments: cash crops and mass production • Government policy itself - Wars-veterans groups Encourage the creation of the farmers bureau Launched Chamber of Commerce Favored the growth of unions • Emergence of strong leaders in uncertain times (civil rights) • Expanding role of government • Technology and media
 Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Pillar of Democracy • Beer or Consumer Safety • Tactics of influence Homework: • Zip – Happy Holiday
Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Pillar of Democracy • Beer or Consumer Safety • Tactics of influence Homework: • Zip – Happy Holiday
 No Party in an Interest Group • Major differences: ▫ They do not run candidates for political office ▫ Parties generate and support a broad spectrum of policies; interest groups support one or a few related policies.
No Party in an Interest Group • Major differences: ▫ They do not run candidates for political office ▫ Parties generate and support a broad spectrum of policies; interest groups support one or a few related policies.
 Why join? 1. Solidary incentives: pleasure, companionship (League of Women Voters (LWV), NAACP, Rotary, Parent-Teacher Association, American Legion) 2. Material incentives: money, things, services (farm organizations, AARP) 3. Purposive incentives: goal /purpose of the organization itself ▫ Passionate about goal ▫ Strong sense of civic duty ▫ Cost of joining minimal
Why join? 1. Solidary incentives: pleasure, companionship (League of Women Voters (LWV), NAACP, Rotary, Parent-Teacher Association, American Legion) 2. Material incentives: money, things, services (farm organizations, AARP) 3. Purposive incentives: goal /purpose of the organization itself ▫ Passionate about goal ▫ Strong sense of civic duty ▫ Cost of joining minimal
 Effective Interest Groups Safety v. Beer • Choose which interest group is most effective and give three reasons why. ▫ Consumer advocacy ▫ National Beer Wholesalers or
Effective Interest Groups Safety v. Beer • Choose which interest group is most effective and give three reasons why. ▫ Consumer advocacy ▫ National Beer Wholesalers or
 A successful interest • 3 main factors determine the success of an interest groups • - Size of groups • - Intensity • - Financial resources • Money and intensity can be major factors of success, but usually the most successful groups are small in size
A successful interest • 3 main factors determine the success of an interest groups • - Size of groups • - Intensity • - Financial resources • Money and intensity can be major factors of success, but usually the most successful groups are small in size
 Small groups are successful • Safety v. Beer • Smaller groups have organizational advantages • Potential group = all people who could join v. actual group = those that actual join ▫ Ex. Consumer advocacy groups – Free rider problem: you don’t have to join to get the benefit ▫ Suffers of Olson’s Law: potential members gain the collective good without joining, hence smaller is better
Small groups are successful • Safety v. Beer • Smaller groups have organizational advantages • Potential group = all people who could join v. actual group = those that actual join ▫ Ex. Consumer advocacy groups – Free rider problem: you don’t have to join to get the benefit ▫ Suffers of Olson’s Law: potential members gain the collective good without joining, hence smaller is better
 Small group wins – Elite ***#$% • The National Beer Wholesalers Association is highly effective because they are few beer producers and they have potential members are fewer and more likely to join because the common good is worth securing ( if they get sued the effect is greater to them) • Selective benefits – large groups find special benefits (discounts on car rentals) to get potential members to become actual members
Small group wins – Elite ***#$% • The National Beer Wholesalers Association is highly effective because they are few beer producers and they have potential members are fewer and more likely to join because the common good is worth securing ( if they get sued the effect is greater to them) • Selective benefits – large groups find special benefits (discounts on car rentals) to get potential members to become actual members
 Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Truth in the Media • Making Public Policy Sausage • Using good strategery Homework: • None – Happy a HIPPY HOLIDAY
Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • Truth in the Media • Making Public Policy Sausage • Using good strategery Homework: • None – Happy a HIPPY HOLIDAY
 Fact v. Fiction of Media Impact ▫ Media has effect on elections v. Media has no effect on elections ▫ Media has created a more candidate center trend v. media has no influence on candidates or the party ▫ Media effects how politics are conducted v. media has no effect on how politics are conducted ▫ Issues that are important to the media are the same for the people or what media values as important is completely worthless to us ▫ Newspaper watchers see a larger difference between candidates than TV watchers v. TV watchers see bigger differences than newspaper readers ▫ TV news has an effect on popularity v. TV news reporting has no effect on popularity
Fact v. Fiction of Media Impact ▫ Media has effect on elections v. Media has no effect on elections ▫ Media has created a more candidate center trend v. media has no influence on candidates or the party ▫ Media effects how politics are conducted v. media has no effect on how politics are conducted ▫ Issues that are important to the media are the same for the people or what media values as important is completely worthless to us ▫ Newspaper watchers see a larger difference between candidates than TV watchers v. TV watchers see bigger differences than newspaper readers ▫ TV news has an effect on popularity v. TV news reporting has no effect on popularity
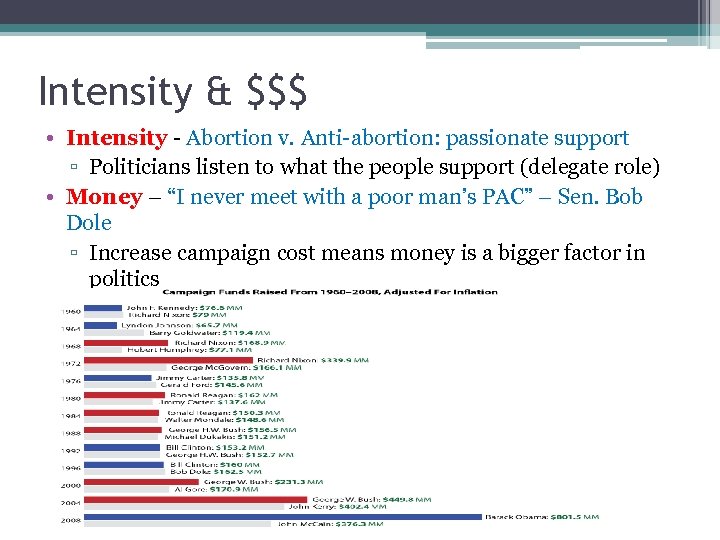 Intensity & $$$ • Intensity - Abortion v. Anti-abortion: passionate support ▫ Politicians listen to what the people support (delegate role) • Money – “I never meet with a poor man’s PAC” – Sen. Bob Dole ▫ Increase campaign cost means money is a bigger factor in politics
Intensity & $$$ • Intensity - Abortion v. Anti-abortion: passionate support ▫ Politicians listen to what the people support (delegate role) • Money – “I never meet with a poor man’s PAC” – Sen. Bob Dole ▫ Increase campaign cost means money is a bigger factor in politics
 Money Talks and we know what happens to the bull • Former Senator Bob Dole put it best when he said he has never been approached by a poor mans PAC. • Wealthy interest groups get more time with elected officials because of their potential fund re-election bids
Money Talks and we know what happens to the bull • Former Senator Bob Dole put it best when he said he has never been approached by a poor mans PAC. • Wealthy interest groups get more time with elected officials because of their potential fund re-election bids
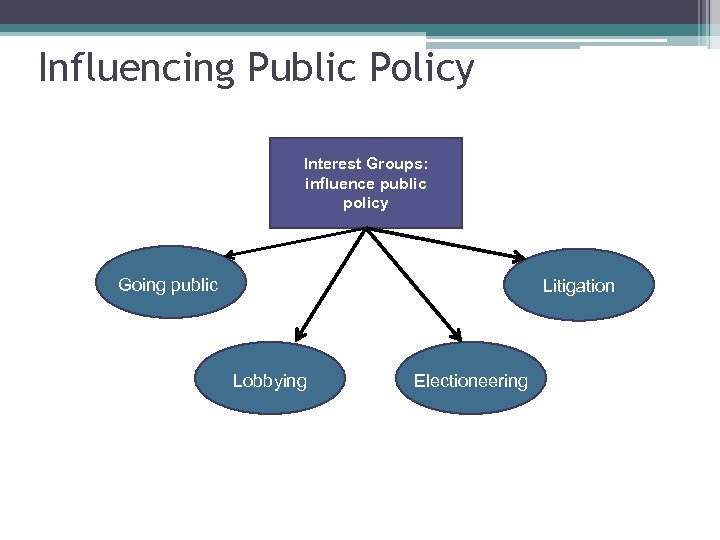 Influencing Public Policy Interest Groups: influence public policy Going public Litigation Lobbying Electioneering
Influencing Public Policy Interest Groups: influence public policy Going public Litigation Lobbying Electioneering
 Public policy • Interest groups work within an ever changing society, therefore always working garner support for their issue. • • • ▫ Evaluate the following five interest groups and determine which tactic work best them in our current political climate. Be sure to explain using relevant examples. American Medical Association (AMA) National Rifle Association (NRA) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) Sierra Club Arab Americans Political Action Committee (AAPAC)
Public policy • Interest groups work within an ever changing society, therefore always working garner support for their issue. • • • ▫ Evaluate the following five interest groups and determine which tactic work best them in our current political climate. Be sure to explain using relevant examples. American Medical Association (AMA) National Rifle Association (NRA) National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) Sierra Club Arab Americans Political Action Committee (AAPAC)
 Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • 21 Terms • Tactics of influence • Number 1 interest Homework: • Read pages 341 -349 – distinctions of interest groups & Lobbyist Disclosure Act, & Ethics in Government Act
Essential Questions: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibit the voice of the people? Students Can: • Formulate argument premises over how democracy is swayed by linkage institutions • Evaluate the validity of interest groups in the political process • Decipher how interest groups impact public policy Agenda • 21 Terms • Tactics of influence • Number 1 interest Homework: • Read pages 341 -349 – distinctions of interest groups & Lobbyist Disclosure Act, & Ethics in Government Act
 We are in the lobby • Interest groups hire individuals to sway elected officials opinion on potential legislation • Assistance ▫ ▫ - ideas for legislation - information about legislation (think tanks) - provide strategies to get legislation passed - campaign strategy
We are in the lobby • Interest groups hire individuals to sway elected officials opinion on potential legislation • Assistance ▫ ▫ - ideas for legislation - information about legislation (think tanks) - provide strategies to get legislation passed - campaign strategy
 Electioneering • Aiding candidates in re-election bids ▫ Form a PAC – Political Action Committee to raise and donate campaign funds (campaign cost keep rising) ▫ Form a 527 – created to influence election by advocacy groups ▫ Carry out issue advocacy ▫ Grassroots mobilization campaigns ▫ Campaign support (volunteering, endorsements, etc…) ▫ Focus on incumbents (influence)
Electioneering • Aiding candidates in re-election bids ▫ Form a PAC – Political Action Committee to raise and donate campaign funds (campaign cost keep rising) ▫ Form a 527 – created to influence election by advocacy groups ▫ Carry out issue advocacy ▫ Grassroots mobilization campaigns ▫ Campaign support (volunteering, endorsements, etc…) ▫ Focus on incumbents (influence)
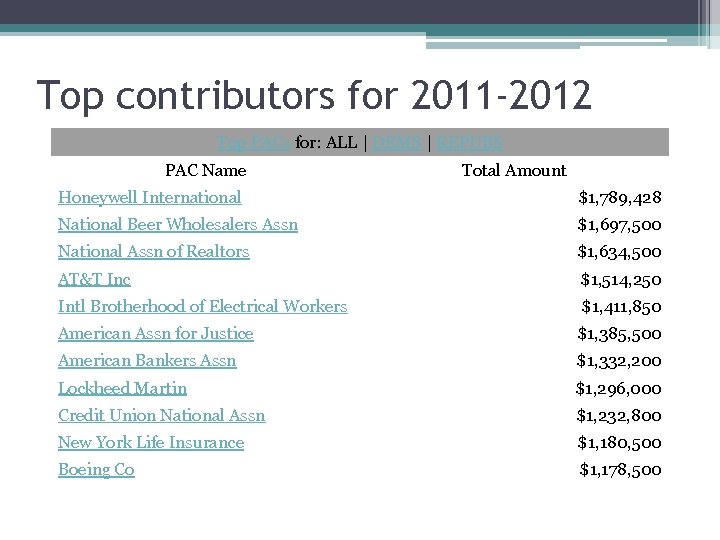 Top contributors for 2011 -2012 Top PACs for: ALL | DEMS | REPUBS PAC Name Total Amount Honeywell International $1, 789, 428 National Beer Wholesalers Assn $1, 697, 500 National Assn of Realtors $1, 634, 500 AT&T Inc $1, 514, 250 Intl Brotherhood of Electrical Workers $1, 411, 850 American Assn for Justice $1, 385, 500 American Bankers Assn $1, 332, 200 Lockheed Martin $1, 296, 000 Credit Union National Assn $1, 232, 800 New York Life Insurance $1, 180, 500 Boeing Co $1, 178, 500
Top contributors for 2011 -2012 Top PACs for: ALL | DEMS | REPUBS PAC Name Total Amount Honeywell International $1, 789, 428 National Beer Wholesalers Assn $1, 697, 500 National Assn of Realtors $1, 634, 500 AT&T Inc $1, 514, 250 Intl Brotherhood of Electrical Workers $1, 411, 850 American Assn for Justice $1, 385, 500 American Bankers Assn $1, 332, 200 Lockheed Martin $1, 296, 000 Credit Union National Assn $1, 232, 800 New York Life Insurance $1, 180, 500 Boeing Co $1, 178, 500
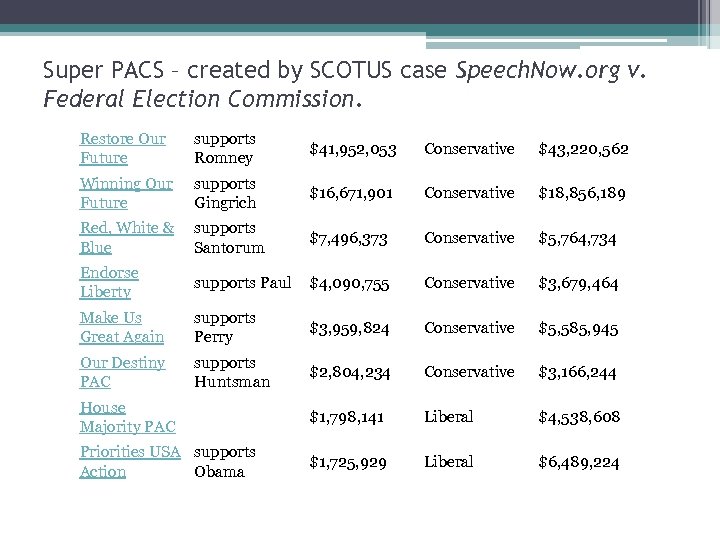 Super PACS – created by SCOTUS case Speech. Now. org v. Federal Election Commission. Restore Our Future supports Romney $41, 952, 053 Conservative $43, 220, 562 Winning Our Future supports Gingrich $16, 671, 901 Conservative $18, 856, 189 Red, White & Blue supports Santorum $7, 496, 373 Conservative $5, 764, 734 Endorse Liberty supports Paul $4, 090, 755 Conservative $3, 679, 464 Make Us Great Again supports Perry $3, 959, 824 Conservative $5, 585, 945 Our Destiny PAC supports Huntsman $2, 804, 234 Conservative $3, 166, 244 House Majority PAC $1, 798, 141 Liberal $4, 538, 608 Priorities USA supports Action Obama $1, 725, 929 Liberal $6, 489, 224
Super PACS – created by SCOTUS case Speech. Now. org v. Federal Election Commission. Restore Our Future supports Romney $41, 952, 053 Conservative $43, 220, 562 Winning Our Future supports Gingrich $16, 671, 901 Conservative $18, 856, 189 Red, White & Blue supports Santorum $7, 496, 373 Conservative $5, 764, 734 Endorse Liberty supports Paul $4, 090, 755 Conservative $3, 679, 464 Make Us Great Again supports Perry $3, 959, 824 Conservative $5, 585, 945 Our Destiny PAC supports Huntsman $2, 804, 234 Conservative $3, 166, 244 House Majority PAC $1, 798, 141 Liberal $4, 538, 608 Priorities USA supports Action Obama $1, 725, 929 Liberal $6, 489, 224
 Litigation – I will sue • Litigation: class-action lawsuits, constitutional appeals to federal courts in order to get laws to changed or protect laws to support their cause ▫ Ex. Brown v. Board (NAACP) • Amicus Curiae briefs: friend of the court briefs that explain a groups view on a case being heard by the Supreme Court in which they do not have standing. ▫ Precedents for cases
Litigation – I will sue • Litigation: class-action lawsuits, constitutional appeals to federal courts in order to get laws to changed or protect laws to support their cause ▫ Ex. Brown v. Board (NAACP) • Amicus Curiae briefs: friend of the court briefs that explain a groups view on a case being heard by the Supreme Court in which they do not have standing. ▫ Precedents for cases
 Today’s Focus • NCSCS Goal 3: The learner will analyze political parties, elections, interest groups, and mass media. • Objectives 3. 03 Evaluate the role of the interest groups in the political system. ▫ ▫ The ranges of interest represented The activities of interest groups The effects of interest groups on political process The unique characteristics and role of PACS in the political process • EQ: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibits the voice of the people? • Students can: decipher how interest groups influence public policy to achieve their policy agenda • Outline for the day • ▫ Interest groups reloading ▫ Classifying and evaluating the power of interest groups ▫ Olson’s law mystique Homework: • Complete IG Blood Typing Chart (your section only) • UNIT IIIB TEST – Wed. January 11
Today’s Focus • NCSCS Goal 3: The learner will analyze political parties, elections, interest groups, and mass media. • Objectives 3. 03 Evaluate the role of the interest groups in the political system. ▫ ▫ The ranges of interest represented The activities of interest groups The effects of interest groups on political process The unique characteristics and role of PACS in the political process • EQ: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibits the voice of the people? • Students can: decipher how interest groups influence public policy to achieve their policy agenda • Outline for the day • ▫ Interest groups reloading ▫ Classifying and evaluating the power of interest groups ▫ Olson’s law mystique Homework: • Complete IG Blood Typing Chart (your section only) • UNIT IIIB TEST – Wed. January 11
 John Q Public • Interest groups develop public opinion which ultimately sway legislators • 1. Grassroots Lobbying – developing the grassroots movement (take it to the people) • 2. Astroturf lobbying – intended to build grassroots, but done by corporations to advance their own agenda • 3. Write-in campaign • 4. Issue ads • 5. Image molding/agenda setting • 6. The Ratings Game – interest groups will rate elected officials as to the support they have given to their issue (Litmus test)
John Q Public • Interest groups develop public opinion which ultimately sway legislators • 1. Grassroots Lobbying – developing the grassroots movement (take it to the people) • 2. Astroturf lobbying – intended to build grassroots, but done by corporations to advance their own agenda • 3. Write-in campaign • 4. Issue ads • 5. Image molding/agenda setting • 6. The Ratings Game – interest groups will rate elected officials as to the support they have given to their issue (Litmus test)
 Regulating Interest Groups Protected by the First Amendment Limitations: • Required to register with the federal government • Must disclose finance support • Campaign finance laws Revolving Door issue: interest groups lure former members of Congress and staffers to work as lobbyists Ethics in Government Act: bars ex federal government employees from working with interest groups for a period of two years Lobbying Disclosure Act: lobbyists must register with the federal government and disclose financial activity relating to lobbying
Regulating Interest Groups Protected by the First Amendment Limitations: • Required to register with the federal government • Must disclose finance support • Campaign finance laws Revolving Door issue: interest groups lure former members of Congress and staffers to work as lobbyists Ethics in Government Act: bars ex federal government employees from working with interest groups for a period of two years Lobbying Disclosure Act: lobbyists must register with the federal government and disclose financial activity relating to lobbying
 Interest Group Think Challenge • How do interest groups represent each group think theory? • Which group think theory is most likely to lead to subgovernment groups, such as iron triangles?
Interest Group Think Challenge • How do interest groups represent each group think theory? • Which group think theory is most likely to lead to subgovernment groups, such as iron triangles?
 Types of Interest • • Institutional Membership Social Movement (environmental, economic, equality Consumer and public interest
Types of Interest • • Institutional Membership Social Movement (environmental, economic, equality Consumer and public interest
 Economic • The economy is always a primary topic that most Americans worry about • Issues: wages, profits, taxes, regulation, and jobs • Labor: unions (collective bargaining) weakened by right to work laws • Business: (may prove elite theorist correct) – lots of financial resources, few members with a focused message, well organized
Economic • The economy is always a primary topic that most Americans worry about • Issues: wages, profits, taxes, regulation, and jobs • Labor: unions (collective bargaining) weakened by right to work laws • Business: (may prove elite theorist correct) – lots of financial resources, few members with a focused message, well organized
 Environmental • Save the Earth: • Focused on protecting the planet from corrosive forces (air pollution, extinction, etc. ) • Intense message, but lack the financial resources and suffer from Olson’s law
Environmental • Save the Earth: • Focused on protecting the planet from corrosive forces (air pollution, extinction, etc. ) • Intense message, but lack the financial resources and suffer from Olson’s law
 Social Interest Groups • These interest groups are interested in gaining equality for a specific group • EX. AARP, NAACP, NOW • They have an intense message but suffer from having potential members
Social Interest Groups • These interest groups are interested in gaining equality for a specific group • EX. AARP, NAACP, NOW • They have an intense message but suffer from having potential members
 Consumer and Public Interest • Ralph Nader Consumer Advocacy has lead to a growth in this group • Product safety the driving force
Consumer and Public Interest • Ralph Nader Consumer Advocacy has lead to a growth in this group • Product safety the driving force
 Membership • These run by actual members and are supported by individual citizens • America was a nation of joiners • Examples: religious, civic, and unions • We have greater sense of efficacy and duty (civic groups)
Membership • These run by actual members and are supported by individual citizens • America was a nation of joiners • Examples: religious, civic, and unions • We have greater sense of efficacy and duty (civic groups)
 Incentive to join • Material incentive (benefits) • Use selective benefit to keep members paying their dues and overcome free rider problem • Solidary groups – people like to belong (companionship) • Purpose of organization – ideology – reason to get involved
Incentive to join • Material incentive (benefits) • Use selective benefit to keep members paying their dues and overcome free rider problem • Solidary groups – people like to belong (companionship) • Purpose of organization – ideology – reason to get involved
 Single-issue group • Focus on a narrowly define issue, dislike compromise, and single-minded pursues its goal • The have high intensity because their issue and message a very clear cut
Single-issue group • Focus on a narrowly define issue, dislike compromise, and single-minded pursues its goal • The have high intensity because their issue and message a very clear cut
 Today’s Focus • NCSCS Goal 3: The learner will analyze political parties, elections, interest groups, and mass media. • Objectives 3. 03 Evaluate the role of the interest groups in the political system. ▫ ▫ The ranges of interest represented The activities of interest groups The effects of interest groups on political process The unique characteristics and role of PACS in the political process • EQ: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibits the voice of the people? • Students can: decipher how interest groups influence public policy to achieve their policy agenda • Outline for the day • ▫ Debatable influence ▫ Classifying and evaluating the power of interest groups ▫ Breaking the FRQ Homework: • Read David Mayhew’s “From Congress: The Electoral • • Connection” and complete a journal review Complete FRQ break down (Due Monday) UNIT IIIB TEST – Wed. January 11
Today’s Focus • NCSCS Goal 3: The learner will analyze political parties, elections, interest groups, and mass media. • Objectives 3. 03 Evaluate the role of the interest groups in the political system. ▫ ▫ The ranges of interest represented The activities of interest groups The effects of interest groups on political process The unique characteristics and role of PACS in the political process • EQ: How do linkage institutions play a connecting role in the United States political process that both grants and inhibits the voice of the people? • Students can: decipher how interest groups influence public policy to achieve their policy agenda • Outline for the day • ▫ Debatable influence ▫ Classifying and evaluating the power of interest groups ▫ Breaking the FRQ Homework: • Read David Mayhew’s “From Congress: The Electoral • • Connection” and complete a journal review Complete FRQ break down (Due Monday) UNIT IIIB TEST – Wed. January 11



