a436fae2306381b6783df0a808044e0e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Government of Canada • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • PWGSC - Korea Joint Cooperation Committee Seoul, Korea November 15, 2006 François Audet Director General, Government of Canada Marketplace Government of Canada
Government of Canada • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • PWGSC - Korea Joint Cooperation Committee Seoul, Korea November 15, 2006 François Audet Director General, Government of Canada Marketplace Government of Canada
 Agenda • The Government of Canada (GC) & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 2
Agenda • The Government of Canada (GC) & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 2
 Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 3
Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 3
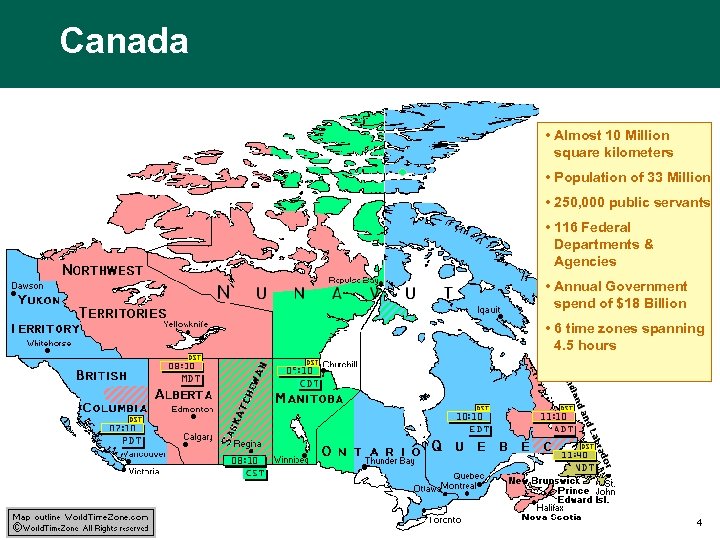 Canada • Almost 10 Million square kilometers • Population of 33 Million • 250, 000 public servants • 116 Federal Departments & Agencies • Annual Government spend of $18 Billion • 6 time zones spanning 4. 5 hours 4
Canada • Almost 10 Million square kilometers • Population of 33 Million • 250, 000 public servants • 116 Federal Departments & Agencies • Annual Government spend of $18 Billion • 6 time zones spanning 4. 5 hours 4
 Government of Canada Web Presence • As a result of an earlier government-wide initiative called Government On-line, Canadians, businesses and international clients are now: – provided with a more accessible government, where information and services are organized according to their needs, and are available 24/7 around the world, in English or French; – delivered better and more responsive services as 130 of the most commonly used services are now available on line; – offered electronic transactions that are protected and secure while their personal information is safeguarded. 5
Government of Canada Web Presence • As a result of an earlier government-wide initiative called Government On-line, Canadians, businesses and international clients are now: – provided with a more accessible government, where information and services are organized according to their needs, and are available 24/7 around the world, in English or French; – delivered better and more responsive services as 130 of the most commonly used services are now available on line; – offered electronic transactions that are protected and secure while their personal information is safeguarded. 5
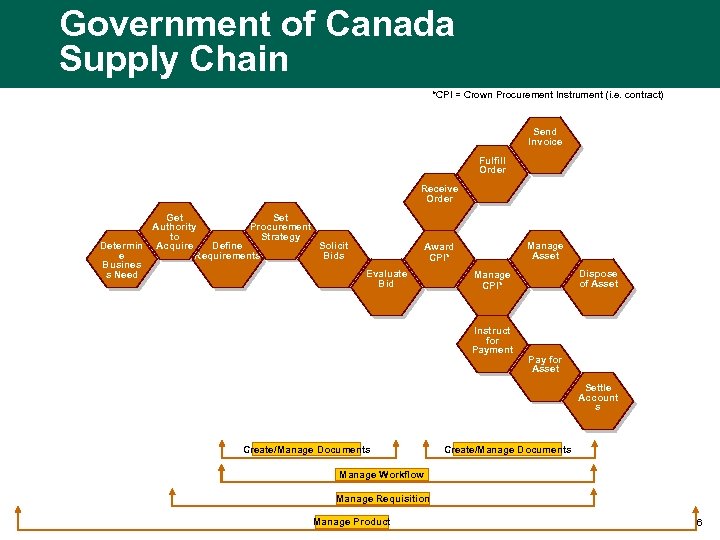 Government of Canada Supply Chain *CPI = Crown Procurement Instrument (i. e. contract) Send Invoice Fulfill Order Receive Order Get Set Authority Procurement to Strategy Define Determin Acquire Solicit Requirements e Bids Busines s Need Manage Asset Award CPI* Evaluate Bid Dispose of Asset Manage CPI* Instruct for Payment Pay for Asset Settle Account s Create/Manage Documents Manage Workflow Manage Requisition Manage Product 6
Government of Canada Supply Chain *CPI = Crown Procurement Instrument (i. e. contract) Send Invoice Fulfill Order Receive Order Get Set Authority Procurement to Strategy Define Determin Acquire Solicit Requirements e Bids Busines s Need Manage Asset Award CPI* Evaluate Bid Dispose of Asset Manage CPI* Instruct for Payment Pay for Asset Settle Account s Create/Manage Documents Manage Workflow Manage Requisition Manage Product 6
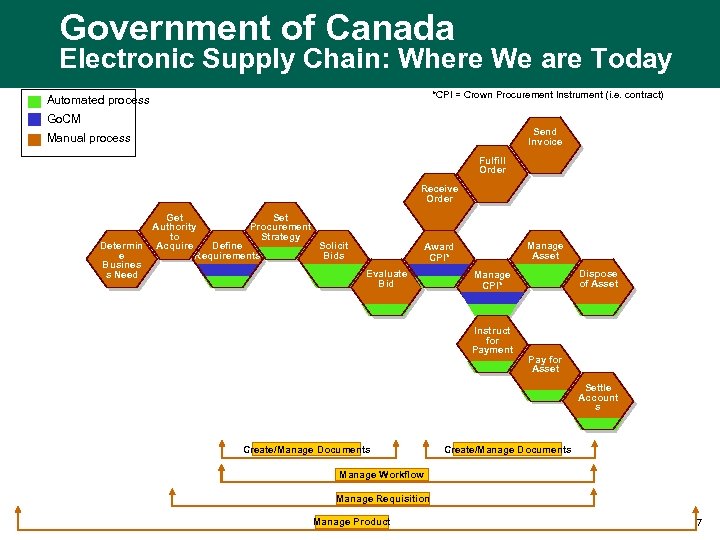 Government of Canada Electronic Supply Chain: Where We are Today *CPI = Crown Procurement Instrument (i. e. contract) Automated process Go. CM Send Invoice Manual process Fulfill Order Receive Order Get Set Authority Procurement to Strategy Define Determin Acquire Solicit Requirements e Bids Busines s Need Manage Asset Award CPI* Evaluate Bid Dispose of Asset Manage CPI* Instruct for Payment Pay for Asset Settle Account s Create/Manage Documents Manage Workflow Manage Requisition Manage Product 7
Government of Canada Electronic Supply Chain: Where We are Today *CPI = Crown Procurement Instrument (i. e. contract) Automated process Go. CM Send Invoice Manual process Fulfill Order Receive Order Get Set Authority Procurement to Strategy Define Determin Acquire Solicit Requirements e Bids Busines s Need Manage Asset Award CPI* Evaluate Bid Dispose of Asset Manage CPI* Instruct for Payment Pay for Asset Settle Account s Create/Manage Documents Manage Workflow Manage Requisition Manage Product 7
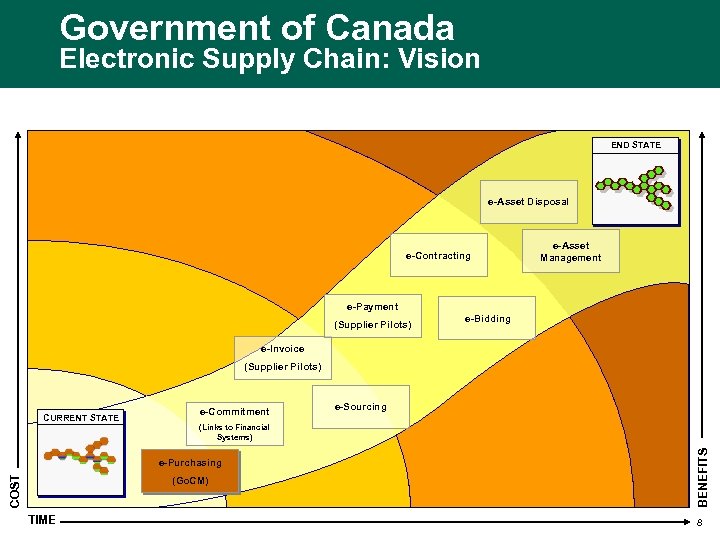 Government of Canada Electronic Supply Chain: Vision END STATE CURRENT STATE Information e-Asset Disposal Application Technology e-Contracting e-Asset Management e-Payment (Supplier Pilots) e-Bidding e-Invoice (Supplier Pilots) COST Information Application Technology TIME e-Commitment e-Sourcing (Links to Financial Systems) e-Purchasing (Go. CM) BENEFITS CURRENT STATE 8
Government of Canada Electronic Supply Chain: Vision END STATE CURRENT STATE Information e-Asset Disposal Application Technology e-Contracting e-Asset Management e-Payment (Supplier Pilots) e-Bidding e-Invoice (Supplier Pilots) COST Information Application Technology TIME e-Commitment e-Sourcing (Links to Financial Systems) e-Purchasing (Go. CM) BENEFITS CURRENT STATE 8
 Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 9
Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 9
 What is the Go. CM The Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) is an on-line service offering authorized Government of Canada (GC) users a common point of access to an electronic catalogue where they can browse, search and compare preapproved goods and services from Mandatory Standing Offers and Supply Arrangements. 10
What is the Go. CM The Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) is an on-line service offering authorized Government of Canada (GC) users a common point of access to an electronic catalogue where they can browse, search and compare preapproved goods and services from Mandatory Standing Offers and Supply Arrangements. 10
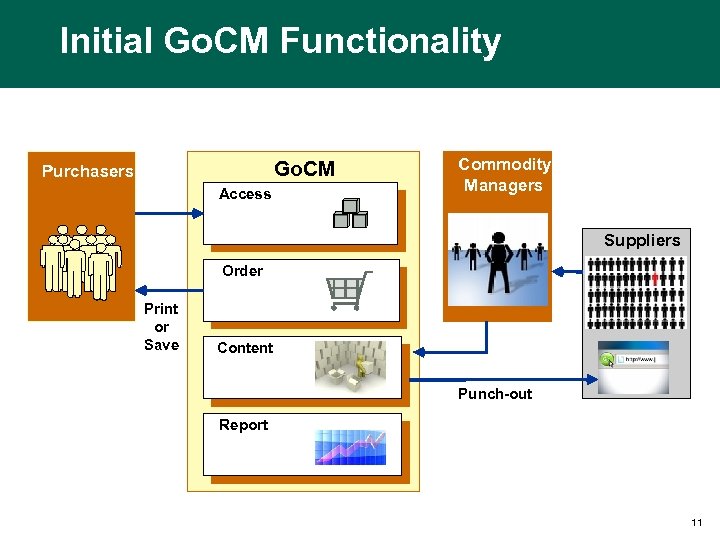 Initial Go. CM Functionality Go. CM Purchasers Access Commodity Managers Suppliers Order Print or Save Content Punch-out Report 11
Initial Go. CM Functionality Go. CM Purchasers Access Commodity Managers Suppliers Order Print or Save Content Punch-out Report 11
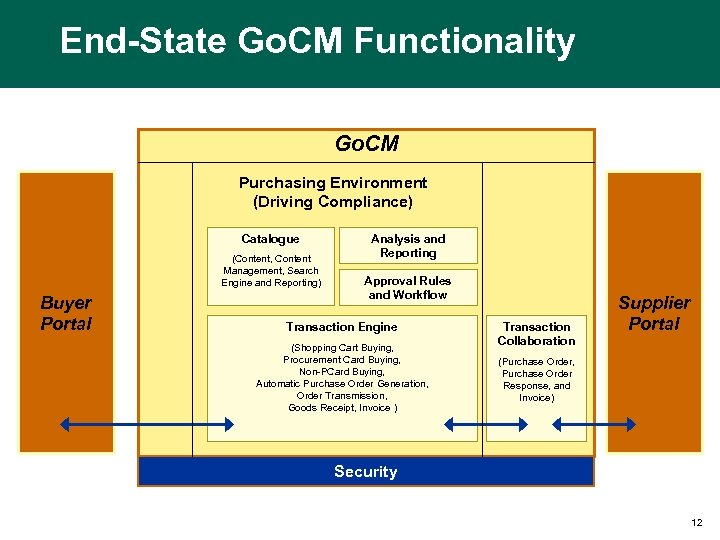 End-State Go. CM Functionality Go. CM Purchasing Environment (Driving Compliance) Catalogue (Content, Content Management, Search Engine and Reporting) Buyer Portal Analysis and Reporting Approval Rules and Workflow Transaction Engine (Shopping Cart Buying, Procurement Card Buying, Non-PCard Buying, Automatic Purchase Order Generation, Order Transmission, Goods Receipt, Invoice ) Transaction Collaboration Supplier Portal (Purchase Order, Purchase Order Response, and Invoice) Security 12
End-State Go. CM Functionality Go. CM Purchasing Environment (Driving Compliance) Catalogue (Content, Content Management, Search Engine and Reporting) Buyer Portal Analysis and Reporting Approval Rules and Workflow Transaction Engine (Shopping Cart Buying, Procurement Card Buying, Non-PCard Buying, Automatic Purchase Order Generation, Order Transmission, Goods Receipt, Invoice ) Transaction Collaboration Supplier Portal (Purchase Order, Purchase Order Response, and Invoice) Security 12
 Go. CM: an Outsourced Solution • The Government of Canada (GC) has made a strategic decision to contract to private sector firms for the provision of systems and services with a magnitude similar to that of the Go. CM. The Government Electronic Tendering Service (GETS) is another example of such an outsourced solution. • The Go. CM has been outsourced to: – Leverage the expert knowledge of industry, – Ensure that the Go. CM solution is scaleable both in scope and in transaction volume, – Increase the probability of success. • The Go. CM contract has been separated into four (4) tasks – – Task 1: Definition (Business Case) Task 2: Configuration & Implementation Task 3: Population & Expansion Task 4: Operation, Maintenance & Support • The Go. CM Project is currently in Task 2 13
Go. CM: an Outsourced Solution • The Government of Canada (GC) has made a strategic decision to contract to private sector firms for the provision of systems and services with a magnitude similar to that of the Go. CM. The Government Electronic Tendering Service (GETS) is another example of such an outsourced solution. • The Go. CM has been outsourced to: – Leverage the expert knowledge of industry, – Ensure that the Go. CM solution is scaleable both in scope and in transaction volume, – Increase the probability of success. • The Go. CM contract has been separated into four (4) tasks – – Task 1: Definition (Business Case) Task 2: Configuration & Implementation Task 3: Population & Expansion Task 4: Operation, Maintenance & Support • The Go. CM Project is currently in Task 2 13
 Legal Considerations • Procurement – – – Trade agreements Partnering Ownership of assets (renting vs. buying) Supplier relationships Liability Legal clauses for standing offers regarding electronic catalogues and services • An e-Marketplace Service – Digital signatures – Non-repudiation – System of record 14
Legal Considerations • Procurement – – – Trade agreements Partnering Ownership of assets (renting vs. buying) Supplier relationships Liability Legal clauses for standing offers regarding electronic catalogues and services • An e-Marketplace Service – Digital signatures – Non-repudiation – System of record 14
 Future Opportunities for the Go. CM • Financial System Integration • Electronic Supplier Portal • Electronic Bidding • Request for Volume Discounts (RVDs) • Near-dynamic Updates 15
Future Opportunities for the Go. CM • Financial System Integration • Electronic Supplier Portal • Electronic Bidding • Request for Volume Discounts (RVDs) • Near-dynamic Updates 15
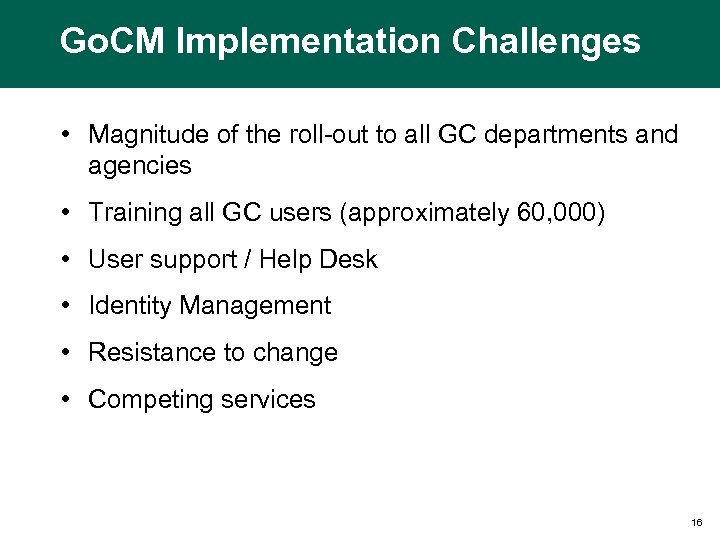 Go. CM Implementation Challenges • Magnitude of the roll-out to all GC departments and agencies • Training all GC users (approximately 60, 000) • User support / Help Desk • Identity Management • Resistance to change • Competing services 16
Go. CM Implementation Challenges • Magnitude of the roll-out to all GC departments and agencies • Training all GC users (approximately 60, 000) • User support / Help Desk • Identity Management • Resistance to change • Competing services 16
 Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 17
Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 17
 Current Situation • No specific role for PDA’s • Not a common tool / device for purchasers – Not all employees have cell phones – PDA’s are normally reserved for senior staff – Most purchasing is done by junior staff • PDA’s may be used by suppliers to receive bidding information 18
Current Situation • No specific role for PDA’s • Not a common tool / device for purchasers – Not all employees have cell phones – PDA’s are normally reserved for senior staff – Most purchasing is done by junior staff • PDA’s may be used by suppliers to receive bidding information 18
 Wireless Environment in the GC • Wireless spans several layers • Use of devices in Personal Area emerging • Pilots conducted for Wireless LAN • Satellite services for remote connectivity highly successful • Large implementation of Black. Berry services both in private sector and in government for email and cell-phone • Concern with meeting government high security requirements for information protection • Commercial infrastructure is generally land-based, with wireless service providers emerging in large market areas and commercial buildings (airports, hotels, convention centers) 19
Wireless Environment in the GC • Wireless spans several layers • Use of devices in Personal Area emerging • Pilots conducted for Wireless LAN • Satellite services for remote connectivity highly successful • Large implementation of Black. Berry services both in private sector and in government for email and cell-phone • Concern with meeting government high security requirements for information protection • Commercial infrastructure is generally land-based, with wireless service providers emerging in large market areas and commercial buildings (airports, hotels, convention centers) 19
 Drivers & Challenges Drivers • Increase efficiencies • Continue to be a world leader in electronic commerce Challenges • Non-repudiation • Security of Bid Contents • Identity Management 20
Drivers & Challenges Drivers • Increase efficiencies • Continue to be a world leader in electronic commerce Challenges • Non-repudiation • Security of Bid Contents • Identity Management 20
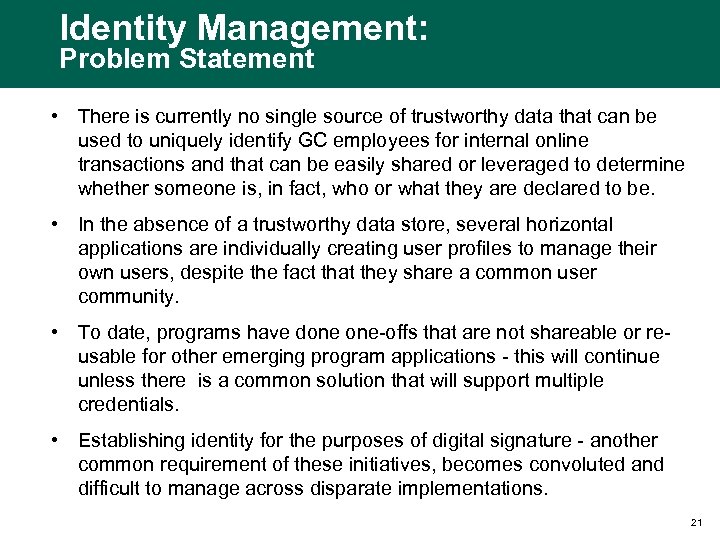 Identity Management: Problem Statement • There is currently no single source of trustworthy data that can be used to uniquely identify GC employees for internal online transactions and that can be easily shared or leveraged to determine whether someone is, in fact, who or what they are declared to be. • In the absence of a trustworthy data store, several horizontal applications are individually creating user profiles to manage their own users, despite the fact that they share a common user community. • To date, programs have done one-offs that are not shareable or reusable for other emerging program applications - this will continue unless there is a common solution that will support multiple credentials. • Establishing identity for the purposes of digital signature - another common requirement of these initiatives, becomes convoluted and difficult to manage across disparate implementations. 21
Identity Management: Problem Statement • There is currently no single source of trustworthy data that can be used to uniquely identify GC employees for internal online transactions and that can be easily shared or leveraged to determine whether someone is, in fact, who or what they are declared to be. • In the absence of a trustworthy data store, several horizontal applications are individually creating user profiles to manage their own users, despite the fact that they share a common user community. • To date, programs have done one-offs that are not shareable or reusable for other emerging program applications - this will continue unless there is a common solution that will support multiple credentials. • Establishing identity for the purposes of digital signature - another common requirement of these initiatives, becomes convoluted and difficult to manage across disparate implementations. 21
 Identity Management: Vision Enrolment and Authorization Services intends to support a networked Government in which GC employees can easily conduct on-line transactions with key “shared services” applications with multiple credentials, while protecting the privacy and security of their identity information and enabling the authorization of transactions using secure electronic signatures. Specifically, the Identity Management project will support: • Common identity profile management • Authentication services • Support for digital signature services • Access control • Self-serve profile management 22
Identity Management: Vision Enrolment and Authorization Services intends to support a networked Government in which GC employees can easily conduct on-line transactions with key “shared services” applications with multiple credentials, while protecting the privacy and security of their identity information and enabling the authorization of transactions using secure electronic signatures. Specifically, the Identity Management project will support: • Common identity profile management • Authentication services • Support for digital signature services • Access control • Self-serve profile management 22
 Identity Management: Objectives Enrolment and Authorization Services will define, architect and guide the implementation of services and tools that will provide the following specific functionality: • Authenticate a user at a central policy enforcement point common to participating applications • Support electronic chain of evidence requirements for sessions brokered by the common authentication solution • Meaningfully identify a user accessing any of the participating applications with a level of assurance appropriate to the application (common solution for supporting multiple credentials) • Manage and provide self-management to users who have been meaningfully identified by the common identification solution • Digitally sign an authorization of a business transaction through a web browser session 23
Identity Management: Objectives Enrolment and Authorization Services will define, architect and guide the implementation of services and tools that will provide the following specific functionality: • Authenticate a user at a central policy enforcement point common to participating applications • Support electronic chain of evidence requirements for sessions brokered by the common authentication solution • Meaningfully identify a user accessing any of the participating applications with a level of assurance appropriate to the application (common solution for supporting multiple credentials) • Manage and provide self-management to users who have been meaningfully identified by the common identification solution • Digitally sign an authorization of a business transaction through a web browser session 23
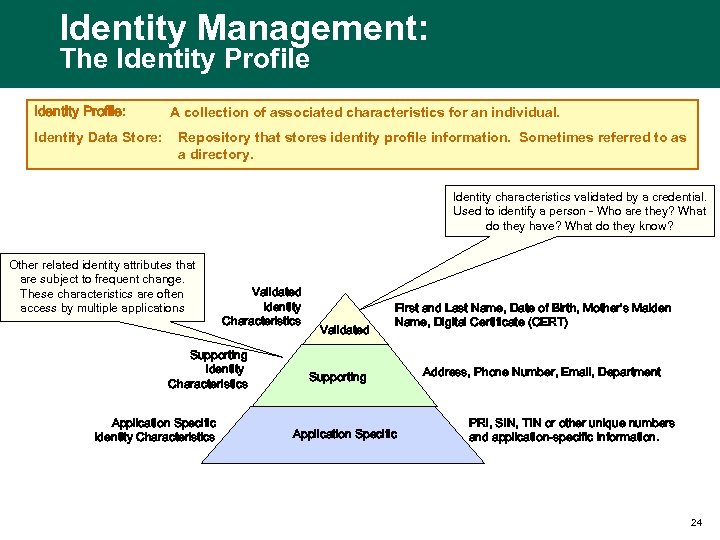 Identity Management: The Identity Profile: Identity Data Store: A collection of associated characteristics for an individual. Repository that stores identity profile information. Sometimes referred to as a directory. Identity characteristics validated by a credential. Used to identify a person - Who are they? What do they have? What do they know? Other related identity attributes that are subject to frequent change. These characteristics are often access by multiple applications Validated Identity Characteristics Supporting Identity Characteristics Application Specific Identity Characteristics Validated First and Last Name, Date of Birth, Mother’s Maiden Name, Digital Certificate (CERT) Supporting Application Specific Address, Phone Number, Email, Department PRI, SIN, TIN or other unique numbers and application-specific information. 24
Identity Management: The Identity Profile: Identity Data Store: A collection of associated characteristics for an individual. Repository that stores identity profile information. Sometimes referred to as a directory. Identity characteristics validated by a credential. Used to identify a person - Who are they? What do they have? What do they know? Other related identity attributes that are subject to frequent change. These characteristics are often access by multiple applications Validated Identity Characteristics Supporting Identity Characteristics Application Specific Identity Characteristics Validated First and Last Name, Date of Birth, Mother’s Maiden Name, Digital Certificate (CERT) Supporting Application Specific Address, Phone Number, Email, Department PRI, SIN, TIN or other unique numbers and application-specific information. 24
 Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 25
Agenda • The Government of Canada & e. Procurement • Government of Canada Marketplace (Go. CM) Project Update • Mobile Devices in Procurement • In your experience… 25
 When implementing GEPS… • What was your implementation approach • How did you train all users? • How did you set-up systems support and help desk? • How do you handle digital signatures? • Were interfaces to the external systems difficult to develop? • Were there any privacy issues? • What was your biggest challenge? 26
When implementing GEPS… • What was your implementation approach • How did you train all users? • How did you set-up systems support and help desk? • How do you handle digital signatures? • Were interfaces to the external systems difficult to develop? • Were there any privacy issues? • What was your biggest challenge? 26


