69d99bb555ba1d1de7d2f4de62e6cb24.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Governance in Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) Jeremy Collymore, Coordinator Caribbean Disaster Emergency Response Agency (CDERA) Caribbean Conference on Comprehensive Disaster Management and Reducing Disasters Knowledge Fair The Hilton Barbados, Barbados December 12 – 14, 2006
Governance in Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) Jeremy Collymore, Coordinator Caribbean Disaster Emergency Response Agency (CDERA) Caribbean Conference on Comprehensive Disaster Management and Reducing Disasters Knowledge Fair The Hilton Barbados, Barbados December 12 – 14, 2006
 GOVERNANCE n n n Exercise of society in managing its socio-economic political affairs Comprises the values, policies, institutions and mechanisms through which society Articulates interest Mediates differences Exercises legal rights and obligations
GOVERNANCE n n n Exercise of society in managing its socio-economic political affairs Comprises the values, policies, institutions and mechanisms through which society Articulates interest Mediates differences Exercises legal rights and obligations
 ELEMENTS OF GOVERNANCE n n n Economic – decision making processes that inform internal and external economic activities and relationships Political – decision making to formulate policies Administrative - system of policy implementation
ELEMENTS OF GOVERNANCE n n n Economic – decision making processes that inform internal and external economic activities and relationships Political – decision making to formulate policies Administrative - system of policy implementation
 INTRINSIC PROCESSES n Participation n Consultation n Shared Responsibility
INTRINSIC PROCESSES n Participation n Consultation n Shared Responsibility
 DESIRED OUTCOMES n Equity n Reduced Poverty n Improved Quality of Life
DESIRED OUTCOMES n Equity n Reduced Poverty n Improved Quality of Life
 CDM DEFINED Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) involves all actions required to ensure that a country/jurisdiction has a capability to deal with all types of hazards, all phases of the Disaster Management Cycle by coordinating the wide-ranging actions and utilising all necessary resources.
CDM DEFINED Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) involves all actions required to ensure that a country/jurisdiction has a capability to deal with all types of hazards, all phases of the Disaster Management Cycle by coordinating the wide-ranging actions and utilising all necessary resources.
 CDM INTER-RELATED COMPONENTS n n n n Multi-Hazard Multi-faceted Multi-Disciplinary Multi-sectoral Integrated Comprehensive Management
CDM INTER-RELATED COMPONENTS n n n n Multi-Hazard Multi-faceted Multi-Disciplinary Multi-sectoral Integrated Comprehensive Management
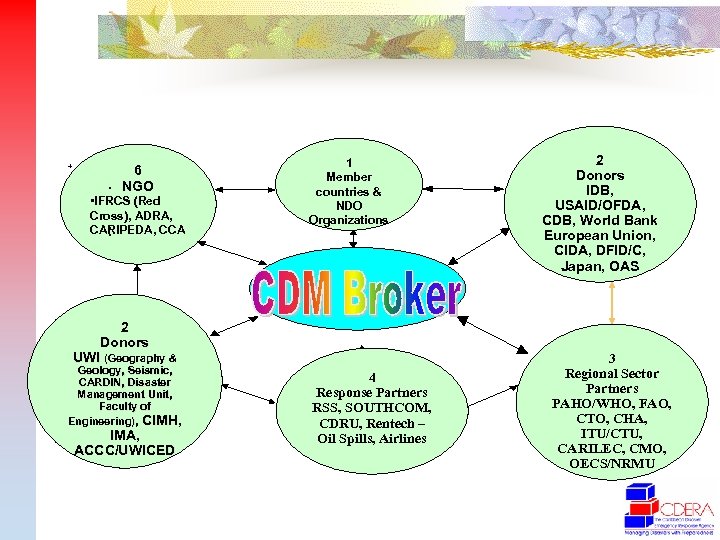 + § 6 NGO § • IFRCS (Red Cross), ADRA, § CARIPEDA, CCA § 1 Member countries & NDO Organizations 2 Donors UWI (Geography & Geology, Seismic, CARDIN, Disaster Management Unit, Faculty of Engineering), CIMH, IMA, ACCC/UWICED 4 Response Partners RSS, SOUTHCOM, CDRU, Rentech – Oil Spills, Airlines 2 Donors IDB, USAID/OFDA, CDB, World Bank European Union, CIDA, DFID/C, Japan, OAS 3 Regional Sector Partners PAHO/WHO, FAO, CTO, CHA, ITU/CTU, CARILEC, CMO, OECS/NRMU
+ § 6 NGO § • IFRCS (Red Cross), ADRA, § CARIPEDA, CCA § 1 Member countries & NDO Organizations 2 Donors UWI (Geography & Geology, Seismic, CARDIN, Disaster Management Unit, Faculty of Engineering), CIMH, IMA, ACCC/UWICED 4 Response Partners RSS, SOUTHCOM, CDRU, Rentech – Oil Spills, Airlines 2 Donors IDB, USAID/OFDA, CDB, World Bank European Union, CIDA, DFID/C, Japan, OAS 3 Regional Sector Partners PAHO/WHO, FAO, CTO, CHA, ITU/CTU, CARILEC, CMO, OECS/NRMU
 ISSUES IN REALIZING CDM n Recognising linkages between disaster management, environment and development n Broadens the range of actors n A revised mandate for the national and regional organisations, incorporating the CDM Policy
ISSUES IN REALIZING CDM n Recognising linkages between disaster management, environment and development n Broadens the range of actors n A revised mandate for the national and regional organisations, incorporating the CDM Policy
 ISSUES IN REALIZING CDM (Cont’d) n Introduces new decision making approaches to n Requires an inventory of mandates n Clear allocation of responsibilities, possibly within a legislative framework
ISSUES IN REALIZING CDM (Cont’d) n Introduces new decision making approaches to n Requires an inventory of mandates n Clear allocation of responsibilities, possibly within a legislative framework
 CDM IMPLEMENTATION ESSENTIALS n More effective use of all resources, including those of the private sector and other relevant organisations n The identification and definition of a coordination mechanism involving all new stakeholders
CDM IMPLEMENTATION ESSENTIALS n More effective use of all resources, including those of the private sector and other relevant organisations n The identification and definition of a coordination mechanism involving all new stakeholders
 CRITICAL IMPLEMENTATION STEPS n Consensus on a regional strategic framework informed by the collective priorised needs of stakeholders n Inclusion in the Public and Private Sector Reform agenda
CRITICAL IMPLEMENTATION STEPS n Consensus on a regional strategic framework informed by the collective priorised needs of stakeholders n Inclusion in the Public and Private Sector Reform agenda
 GOVERNANCE ISSUES IN CDM: What are they? n Who are the actors? n What are the decision-making roles of the actors? n What are the instruments used to engage discourse? n How is the contribution of the stakeholders fashioned into policy and programme? n What voice is given to the partners and when?
GOVERNANCE ISSUES IN CDM: What are they? n Who are the actors? n What are the decision-making roles of the actors? n What are the instruments used to engage discourse? n How is the contribution of the stakeholders fashioned into policy and programme? n What voice is given to the partners and when?
 CDM GOVERNANCE REQUIREMENTS How n Internal Dialogue n Policy and Programme Mainstreaming n Performance Culture
CDM GOVERNANCE REQUIREMENTS How n Internal Dialogue n Policy and Programme Mainstreaming n Performance Culture
 CDM Governance Requirements n Results Based Management (RBM) n Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) n Reporting n Joint Missions n Cooperative Programming n Aid Flows Aligned to Agreed Priorities`
CDM Governance Requirements n Results Based Management (RBM) n Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) n Reporting n Joint Missions n Cooperative Programming n Aid Flows Aligned to Agreed Priorities`
 CDM Governance Requirements n Results Based Management Tools n Monitoring and Evaluation n Programme Design n Proposal Writing n System Wide Assessments
CDM Governance Requirements n Results Based Management Tools n Monitoring and Evaluation n Programme Design n Proposal Writing n System Wide Assessments
 GOVERNANCE PROCESS Consultation/Participation n Document Sharing or Development n Townhall Meetings (How Structured) n Iterative n Limited to Implementation or Design and Evaluation
GOVERNANCE PROCESS Consultation/Participation n Document Sharing or Development n Townhall Meetings (How Structured) n Iterative n Limited to Implementation or Design and Evaluation
 LEGAL/INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK (A) n Are the empowered adequate for managing the change? n Do they represent potential impositions? n How are equity issues decided?
LEGAL/INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK (A) n Are the empowered adequate for managing the change? n Do they represent potential impositions? n How are equity issues decided?
 LEGAL/INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK (B) n Know coping capacity n Utilize existing policy or support policy development n Harmonise tools for assessment n Embrace transparency at all points of support
LEGAL/INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK (B) n Know coping capacity n Utilize existing policy or support policy development n Harmonise tools for assessment n Embrace transparency at all points of support
 STRUCTURING CDM AID DELIVERY n Assistance Linked to Outcomes n Not time driven n Making a difference rather than expending funds n Know legal/institutional framework n Grievance procedures mechanism n Evaluation of support in anchored outcomes rather than solely outputs to
STRUCTURING CDM AID DELIVERY n Assistance Linked to Outcomes n Not time driven n Making a difference rather than expending funds n Know legal/institutional framework n Grievance procedures mechanism n Evaluation of support in anchored outcomes rather than solely outputs to
 SCALING ISSUES n Sub-regions n n Regional n n Association of Caribbean States Pan-American n n Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States IACN International n United Nations
SCALING ISSUES n Sub-regions n n Regional n n Association of Caribbean States Pan-American n n Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States IACN International n United Nations
 HUMANITARIAN GOVERNANCE n Who sets response times? n Why is response not linked to recovery? n What is the conflict between clean-up and DANA? n Is food for labour real participation? n What is the institutional dislocation potential of the cluster approach?
HUMANITARIAN GOVERNANCE n Who sets response times? n Why is response not linked to recovery? n What is the conflict between clean-up and DANA? n Is food for labour real participation? n What is the institutional dislocation potential of the cluster approach?
 Perceptions of Donors: A Challenge n Host Government organisations are too weak and personnel insufficiently trained n Governments are corrupt n Bureaucracy is an obstacle to free exercise of development and humanitarian assistance n Donor and aid organisations do not have to be accountable to Government
Perceptions of Donors: A Challenge n Host Government organisations are too weak and personnel insufficiently trained n Governments are corrupt n Bureaucracy is an obstacle to free exercise of development and humanitarian assistance n Donor and aid organisations do not have to be accountable to Government
 Key Areas of Mainstreaming n Policy n Strategy n Spatial Planning n Project Cycle Management n External Relations n Institutional Capacity
Key Areas of Mainstreaming n Policy n Strategy n Spatial Planning n Project Cycle Management n External Relations n Institutional Capacity
 Key Influences on Mainstreaming n n n n Staff Ownership Cross-Organisational Buy-in Workload Organisation Champion Leadership by Line-managers Integration vs. Bullying Staff Skills Development Time
Key Influences on Mainstreaming n n n n Staff Ownership Cross-Organisational Buy-in Workload Organisation Champion Leadership by Line-managers Integration vs. Bullying Staff Skills Development Time
 Governance in Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) Caribbean Disaster Emergency Response Agency Building #1, Manor Lodge Hill, Saint Michael, Barbados Tel No: (246) 425 -0386 Email: cdera@caribsurf. com www. cdera. org
Governance in Comprehensive Disaster Management (CDM) Caribbean Disaster Emergency Response Agency Building #1, Manor Lodge Hill, Saint Michael, Barbados Tel No: (246) 425 -0386 Email: cdera@caribsurf. com www. cdera. org


