93212ede715f5dacc9f09c244d3c8a4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 GOVERNANCE, CIVIL SOCIETY AND THE "NEW" AFRICA PIA 2574 “An End of Class Editorial”
GOVERNANCE, CIVIL SOCIETY AND THE "NEW" AFRICA PIA 2574 “An End of Class Editorial”
 Corny but…
Corny but…
 The Primacy of the African Nation-State- How sovereign a. Impact of trans-national actors b. Issue of micro-states c. Rational Actor model- public or social choice theory
The Primacy of the African Nation-State- How sovereign a. Impact of trans-national actors b. Issue of micro-states c. Rational Actor model- public or social choice theory
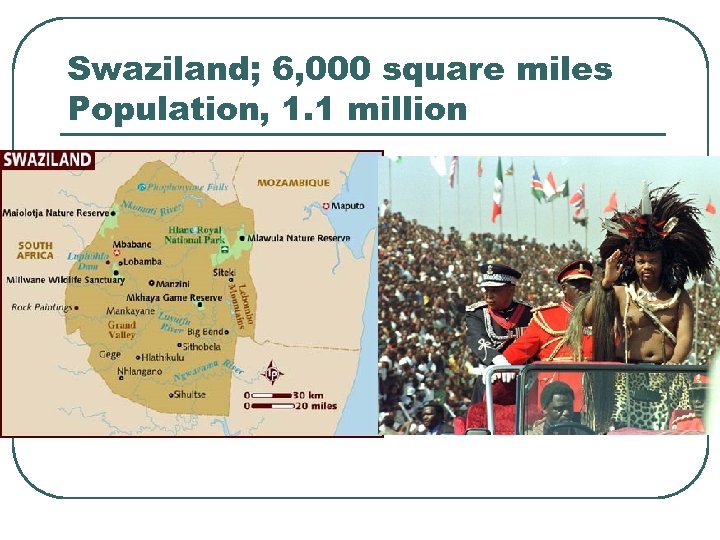 Swaziland; 6, 000 square miles Population, 1. 1 million
Swaziland; 6, 000 square miles Population, 1. 1 million
 The Primacy of the African Nation-State- How sovereign d. Collective choice is it non-rational? Is it more than an aggregate of individuals? e. The role of international regimes- UN, World Bank, IMF, etc. New International Order (NIO)
The Primacy of the African Nation-State- How sovereign d. Collective choice is it non-rational? Is it more than an aggregate of individuals? e. The role of international regimes- UN, World Bank, IMF, etc. New International Order (NIO)
 Targeting Economic Groups
Targeting Economic Groups
 Democracy: What is it? Democracy and: l 1. Governance l 2. Local Government l 3. Civil Society
Democracy: What is it? Democracy and: l 1. Governance l 2. Local Government l 3. Civil Society
 Types of Democracy • Direct Democracy • Indirect Democracy • Pluralism vs. Polyarchy • Civil Society • Cooperative Movement
Types of Democracy • Direct Democracy • Indirect Democracy • Pluralism vs. Polyarchy • Civil Society • Cooperative Movement
 Review: James Madison and Democracy: l The problem with majorities l Tyranny l Factions
Review: James Madison and Democracy: l The problem with majorities l Tyranny l Factions
 Direct Democracy vs. Representative Democracy l Populism vs. Minority rights l Shifting majorities l Problem with Plebiscites Guinea 1958 “No” Vote
Direct Democracy vs. Representative Democracy l Populism vs. Minority rights l Shifting majorities l Problem with Plebiscites Guinea 1958 “No” Vote
 Definitions of Democracy in Africa l The First Issue: Opposition vs. Consensus l The Second Issue: “A Chief is a Chief by the People”
Definitions of Democracy in Africa l The First Issue: Opposition vs. Consensus l The Second Issue: “A Chief is a Chief by the People”
 Ashante, Ghana
Ashante, Ghana
 Definitions of Democracy: Review l Presidential Systems- Separation of Powers l Parliamentary systems. Representation and Fusion l Traditional Africa- Consensus and hierarchy
Definitions of Democracy: Review l Presidential Systems- Separation of Powers l Parliamentary systems. Representation and Fusion l Traditional Africa- Consensus and hierarchy
 South Africa’s Parliament
South Africa’s Parliament
 Defining Democracy l Village democracy and talking things out l Ubuntu, Ujamaa and Humanism l How Collective, How Market Friendly
Defining Democracy l Village democracy and talking things out l Ubuntu, Ujamaa and Humanism l How Collective, How Market Friendly
 THE INSTITUTIONAL STATE l What is the "Institutional State? “ l Why is it important?
THE INSTITUTIONAL STATE l What is the "Institutional State? “ l Why is it important?
 The Institutional State: l Civil Society l Institutionalized Norms l Stable Government
The Institutional State: l Civil Society l Institutionalized Norms l Stable Government
 The Institutional State: l Permanent Government: The Administrative apparatus l Goal: Muted Cultural Differences l Defining Bureaucracy- the permanent government
The Institutional State: l Permanent Government: The Administrative apparatus l Goal: Muted Cultural Differences l Defining Bureaucracy- the permanent government
 The Institutional State: The Reality l Breakdown of Governance l Bureaucracy and Corruption l Military Coups
The Institutional State: The Reality l Breakdown of Governance l Bureaucracy and Corruption l Military Coups
 The Institutional State: The Reality l Self Serving Bureaucrats l Bureaucratic Elites l Civil War-Violence: Inter-state Conflict and African Development
The Institutional State: The Reality l Self Serving Bureaucrats l Bureaucratic Elites l Civil War-Violence: Inter-state Conflict and African Development
 Governance and Sovereigntyl Rules of the Game politics: Zero/sum vs. sum/sum politics l "Splintering"- the break up of statescentrifugal forces l Interest Group Liberalism-how real? l Civil Society as organizational, not individual, or the mass.
Governance and Sovereigntyl Rules of the Game politics: Zero/sum vs. sum/sum politics l "Splintering"- the break up of statescentrifugal forces l Interest Group Liberalism-how real? l Civil Society as organizational, not individual, or the mass.
 Congo Wars
Congo Wars
 Governance and Sovereigntyl The need for apathy? l Constitutional vs. social stability l Institutional structures and Checks and balances:
Governance and Sovereigntyl The need for apathy? l Constitutional vs. social stability l Institutional structures and Checks and balances:
 Traditional Society: l Forms of Traditional Influence in Local Government l Grass Roots- traditional governance mechanisms governance in sub. Saharan Africa l The Answer or the Problem?
Traditional Society: l Forms of Traditional Influence in Local Government l Grass Roots- traditional governance mechanisms governance in sub. Saharan Africa l The Answer or the Problem?

 Traditional Influence-Review 1. Full Meeting (Town Hall style)- Direct Democracy 2. Pure Form- Traditional Councils (Appointed) 3. Partial- Half Elected/Half Traditional 4. Technical- deconcentrated. Department heads and Traditional (No Elections
Traditional Influence-Review 1. Full Meeting (Town Hall style)- Direct Democracy 2. Pure Form- Traditional Councils (Appointed) 3. Partial- Half Elected/Half Traditional 4. Technical- deconcentrated. Department heads and Traditional (No Elections
 African Justice?
African Justice?
 Traditional Influence 5. Specialized- Judicial Function 6. Specialized Partial- Land Board (2 Trad. , 2 LG, 2 Cen. Gov. ) 7. Bicameral- Traditional as an upper house
Traditional Influence 5. Specialized- Judicial Function 6. Specialized Partial- Land Board (2 Trad. , 2 LG, 2 Cen. Gov. ) 7. Bicameral- Traditional as an upper house
 J. M. Coetzee, Disgrace (London: Penguin, 1999). l Born, 1940
J. M. Coetzee, Disgrace (London: Penguin, 1999). l Born, 1940
 Cyprian Ekwensi, People of the City (London: Heineman, 1954) l 1921 -2007
Cyprian Ekwensi, People of the City (London: Heineman, 1954) l 1921 -2007
 Peter Abrahams, Mine Boy (London: Heineman, 1946) l Born: 1919
Peter Abrahams, Mine Boy (London: Heineman, 1946) l Born: 1919
 Discussion Points l HOW IMPORTANT IS DEMOCRACY FOR DEVELOPMENT? l HOW REALISTIC IS CIVIL SOCIETY IN AFRICA? l CAN GOVERNMENT BE STABILIZED?
Discussion Points l HOW IMPORTANT IS DEMOCRACY FOR DEVELOPMENT? l HOW REALISTIC IS CIVIL SOCIETY IN AFRICA? l CAN GOVERNMENT BE STABILIZED?
 Discussion l What have you been Reading? l What Should your colleagues read? l Logistics?
Discussion l What have you been Reading? l What Should your colleagues read? l Logistics?


