6b2a4130751e19542790b659e249cefd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Governance and Risk Management End to end Application Security: a pre-emptive approach Michael Weider, Director of Security Products IBM Rational © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance and Risk Management End to end Application Security: a pre-emptive approach Michael Weider, Director of Security Products IBM Rational © 2008 IBM Corporation
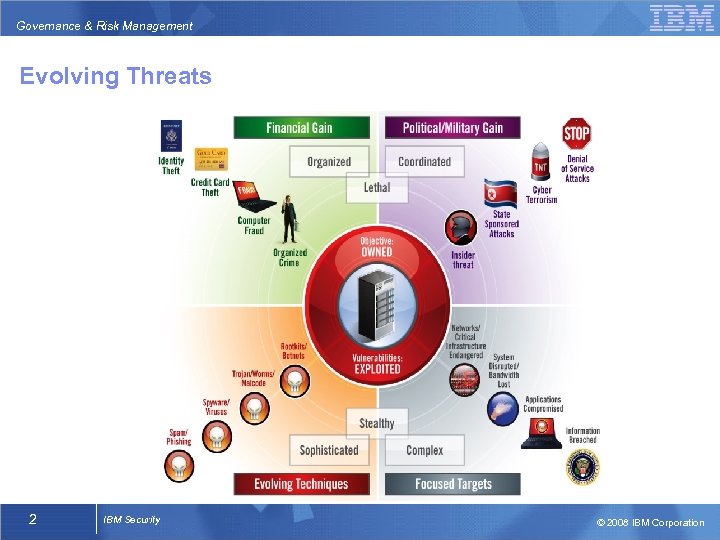 Governance & Risk Management Evolving Threats 2 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Evolving Threats 2 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 3 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 3 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
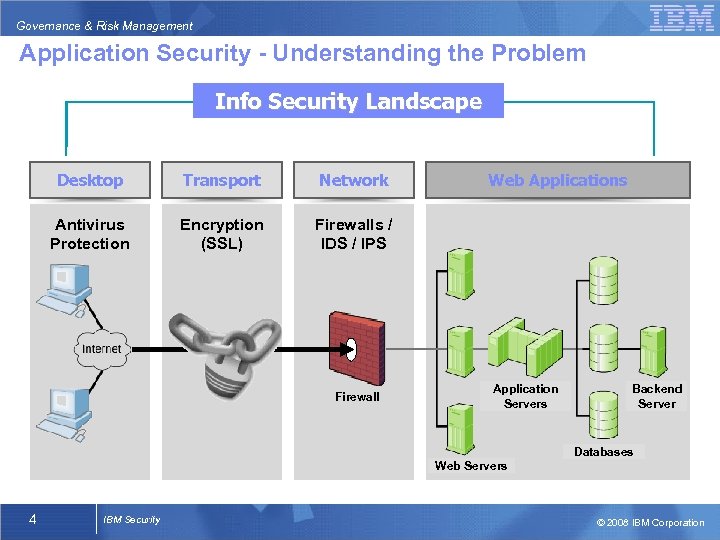 Governance & Risk Management Application Security - Understanding the Problem Info Security Landscape Desktop Transport Network Antivirus Protection Encryption (SSL) Firewalls / IDS / IPS Firewall Web Applications Application Servers Backend Server Databases Web Servers 4 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Application Security - Understanding the Problem Info Security Landscape Desktop Transport Network Antivirus Protection Encryption (SSL) Firewalls / IDS / IPS Firewall Web Applications Application Servers Backend Server Databases Web Servers 4 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
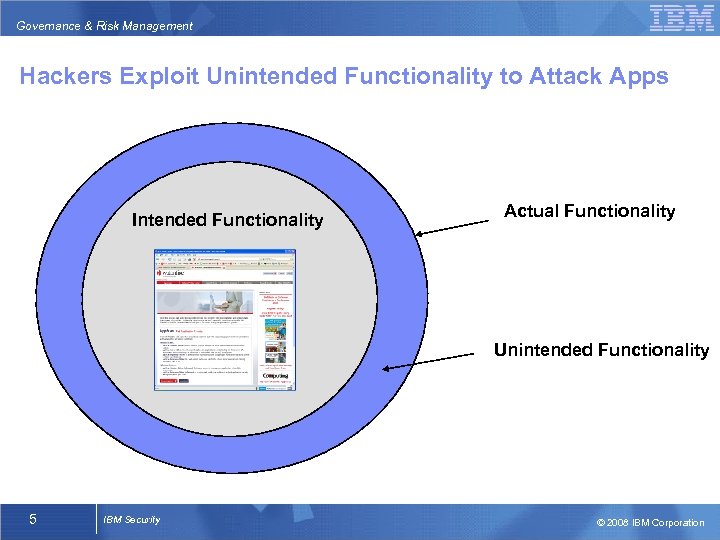 Governance & Risk Management Hackers Exploit Unintended Functionality to Attack Apps Intended Functionality Actual Functionality Unintended Functionality 5 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Hackers Exploit Unintended Functionality to Attack Apps Intended Functionality Actual Functionality Unintended Functionality 5 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance and Risk Management Application Security Hacking Example © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance and Risk Management Application Security Hacking Example © 2008 IBM Corporation
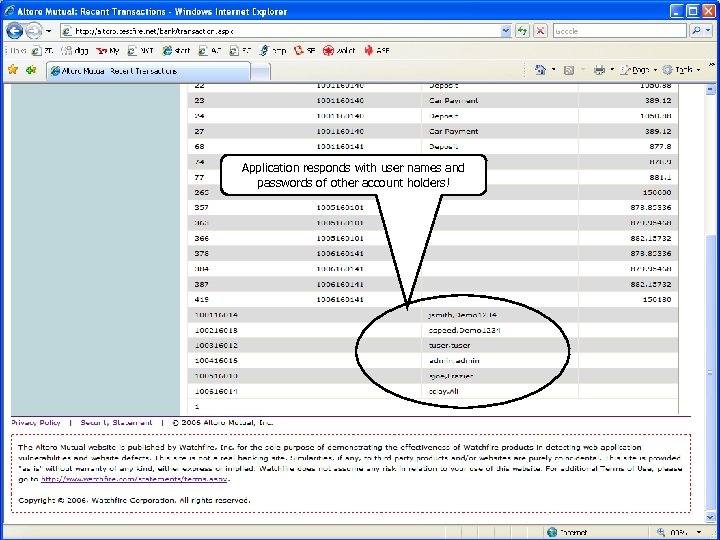 Governance & Risk Management 01/01/2006 union select userid, null, username+', '+password, null from users-Application responds with user names and passwords of other account holders! 7 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management 01/01/2006 union select userid, null, username+', '+password, null from users-Application responds with user names and passwords of other account holders! 7 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management The OWASP Top 10 Application Threat Example Impact Cross Site scripting Identity Theft, Sensitive Information Leakage, … Hackers can impersonate legitimate users, and control their accounts. Injection Flaws Attacker can manipulate queries to the DB / LDAP / Other system Hackers can access backend database information, alter it or steal it. Malicious File Execution Execute shell commands on server, up to full control Site modified to transfer all interactions to the hacker. Insecure Direct Object Reference Attacker can access sensitive files and resources Web application returns contents of sensitive file (instead of harmless one) Cross-Site Request Forgery Attacker can invoke “blind” actions on web applications, impersonating as a trusted user Blind requests to bank account transfer money to hacker Information Leakage and Improper Error Handling Attackers can gain detailed system information Malicious system reconnaissance may assist in developing further attacks Broken Authentication & Session Management Session tokens not guarded or invalidated properly Hacker can “force” session token on victim; session tokens can be stolen after logout Insecure Cryptographic Storage Weak encryption techniques may lead to broken encryption Confidential information (SSN, Credit Cards) can be decrypted by malicious users Insecure Communications Sensitive info sent unencrypted over insecure channel Unencrypted credentials “sniffed” and used by hacker to impersonate user Failure to Restrict URL Access 8 Negative Impact Hacker can access unauthorized resources Hacker can forcefully browse and access a page past the login page IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management The OWASP Top 10 Application Threat Example Impact Cross Site scripting Identity Theft, Sensitive Information Leakage, … Hackers can impersonate legitimate users, and control their accounts. Injection Flaws Attacker can manipulate queries to the DB / LDAP / Other system Hackers can access backend database information, alter it or steal it. Malicious File Execution Execute shell commands on server, up to full control Site modified to transfer all interactions to the hacker. Insecure Direct Object Reference Attacker can access sensitive files and resources Web application returns contents of sensitive file (instead of harmless one) Cross-Site Request Forgery Attacker can invoke “blind” actions on web applications, impersonating as a trusted user Blind requests to bank account transfer money to hacker Information Leakage and Improper Error Handling Attackers can gain detailed system information Malicious system reconnaissance may assist in developing further attacks Broken Authentication & Session Management Session tokens not guarded or invalidated properly Hacker can “force” session token on victim; session tokens can be stolen after logout Insecure Cryptographic Storage Weak encryption techniques may lead to broken encryption Confidential information (SSN, Credit Cards) can be decrypted by malicious users Insecure Communications Sensitive info sent unencrypted over insecure channel Unencrypted credentials “sniffed” and used by hacker to impersonate user Failure to Restrict URL Access 8 Negative Impact Hacker can access unauthorized resources Hacker can forcefully browse and access a page past the login page IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Where Do These Problems Exist? Type: § Customer facing services § Partner portals § Employee intranets Source: 1. Applications you buy – e. g. COTS 2. Applications you build internally 3. Applications you outsource 9 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Where Do These Problems Exist? Type: § Customer facing services § Partner portals § Employee intranets Source: 1. Applications you buy – e. g. COTS 2. Applications you build internally 3. Applications you outsource 9 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
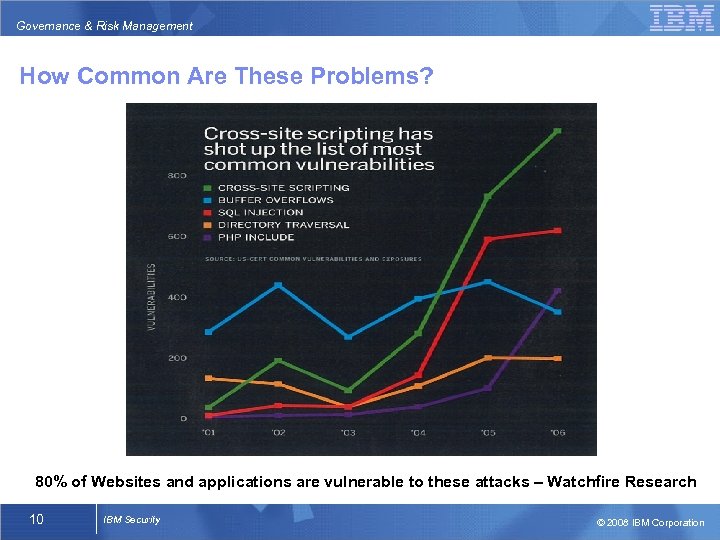 Governance & Risk Management How Common Are These Problems? 80% of Websites and applications are vulnerable to these attacks – Watchfire Research 10 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management How Common Are These Problems? 80% of Websites and applications are vulnerable to these attacks – Watchfire Research 10 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
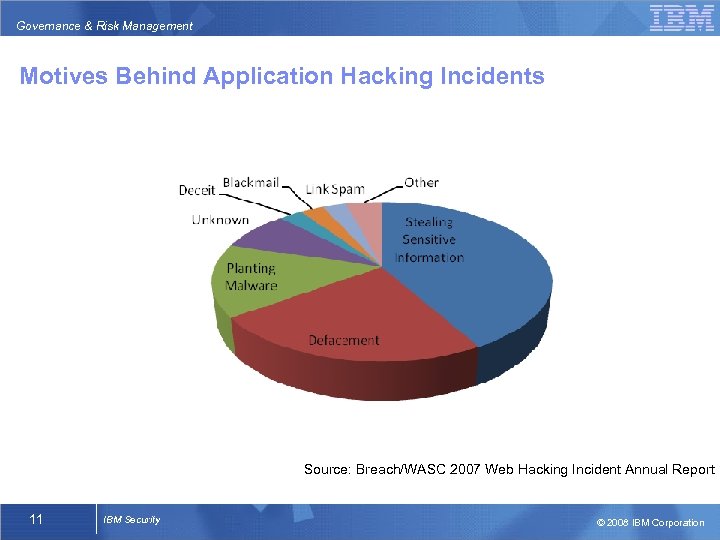 Governance & Risk Management Motives Behind Application Hacking Incidents Source: Breach/WASC 2007 Web Hacking Incident Annual Report 11 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Motives Behind Application Hacking Incidents Source: Breach/WASC 2007 Web Hacking Incident Annual Report 11 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
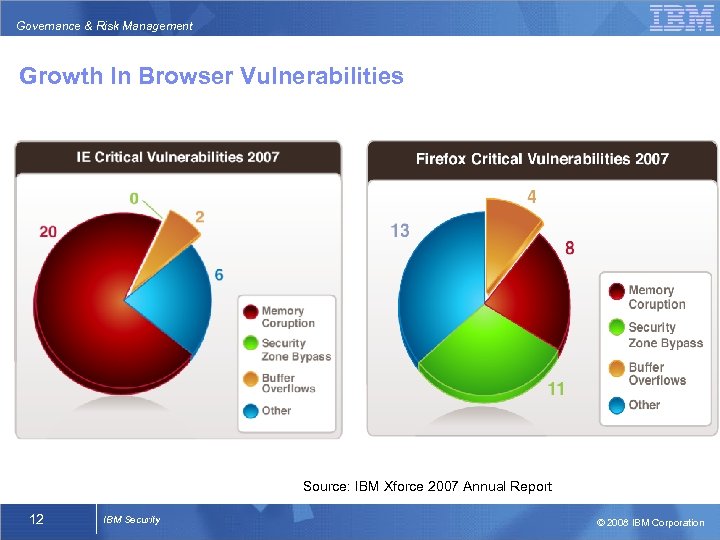 Governance & Risk Management Growth In Browser Vulnerabilities Source: IBM Xforce 2007 Annual Report 12 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Growth In Browser Vulnerabilities Source: IBM Xforce 2007 Annual Report 12 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
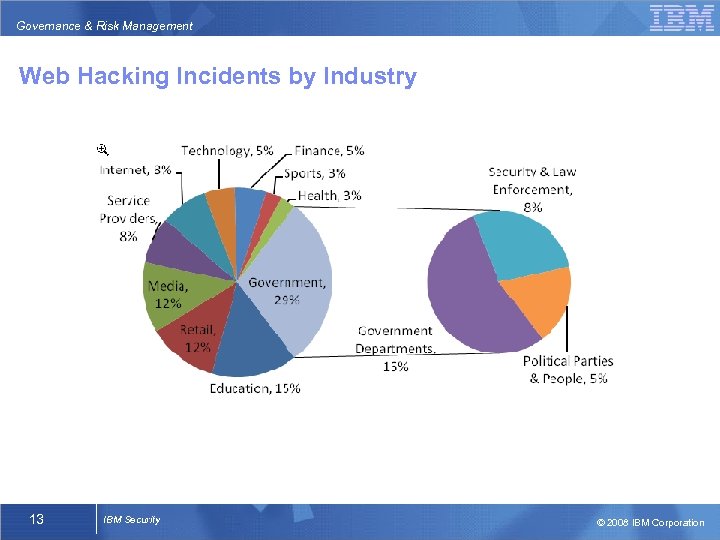 Governance & Risk Management Web Hacking Incidents by Industry Source: WASC 2007 Web Hacking Incident Annual Report 13 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Web Hacking Incidents by Industry Source: WASC 2007 Web Hacking Incident Annual Report 13 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management PCI Application Security Requirements 14 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management PCI Application Security Requirements 14 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management What is the Root Cause? 1. Developers not trained in security § Most computer science curricula have no security courses 2. Under investment from security teams § Lack of tools, policies, process, etc. 3. Growth in complex, mission critical online applications § Online banking, commerce, Web 2. 0, etc 4. Number one focus by hackers § 75% of attacks focused on applications - Gartner Result: Application security incidents and lost data on the rise 15 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management What is the Root Cause? 1. Developers not trained in security § Most computer science curricula have no security courses 2. Under investment from security teams § Lack of tools, policies, process, etc. 3. Growth in complex, mission critical online applications § Online banking, commerce, Web 2. 0, etc 4. Number one focus by hackers § 75% of attacks focused on applications - Gartner Result: Application security incidents and lost data on the rise 15 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 16 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 16 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
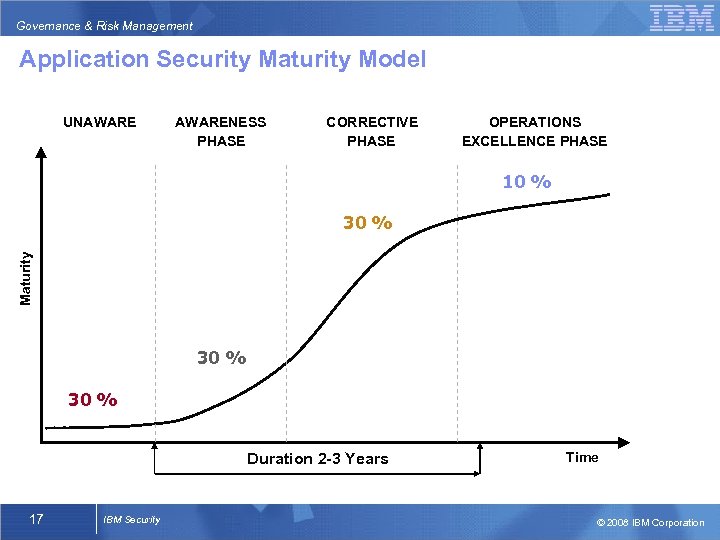 Governance & Risk Management Application Security Maturity Model UNAWARENESS PHASE CORRECTIVE PHASE OPERATIONS EXCELLENCE PHASE 10 % Maturity 30 % Duration 2 -3 Years 17 IBM Security Time © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Application Security Maturity Model UNAWARENESS PHASE CORRECTIVE PHASE OPERATIONS EXCELLENCE PHASE 10 % Maturity 30 % Duration 2 -3 Years 17 IBM Security Time © 2008 IBM Corporation
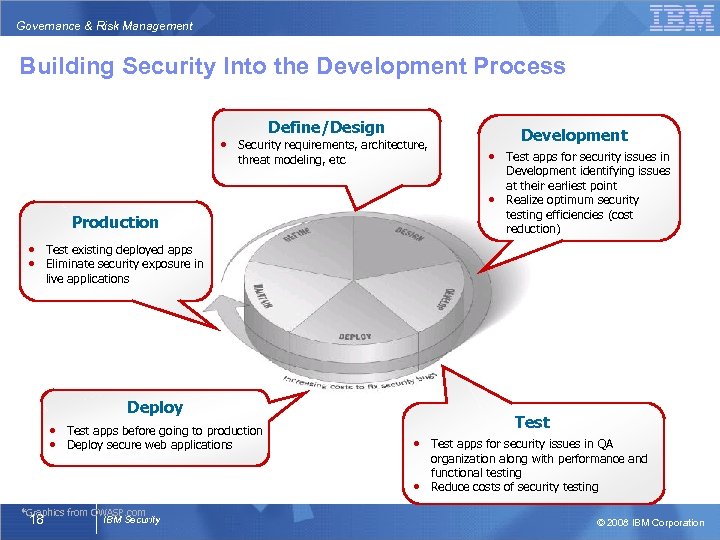 Governance & Risk Management Building Security Into the Development Process • Define/Design Security requirements, architecture, threat modeling, etc Development • • Production • • Test apps for security issues in Development identifying issues at their earliest point Realize optimum security testing efficiencies (cost reduction) Test existing deployed apps Eliminate security exposure in live applications Deploy • • Test apps before going to production Deploy secure web applications Test • • *Graphics from OWASP. com IBM Security 18 Test apps for security issues in QA organization along with performance and functional testing Reduce costs of security testing © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Building Security Into the Development Process • Define/Design Security requirements, architecture, threat modeling, etc Development • • Production • • Test apps for security issues in Development identifying issues at their earliest point Realize optimum security testing efficiencies (cost reduction) Test existing deployed apps Eliminate security exposure in live applications Deploy • • Test apps before going to production Deploy secure web applications Test • • *Graphics from OWASP. com IBM Security 18 Test apps for security issues in QA organization along with performance and functional testing Reduce costs of security testing © 2008 IBM Corporation
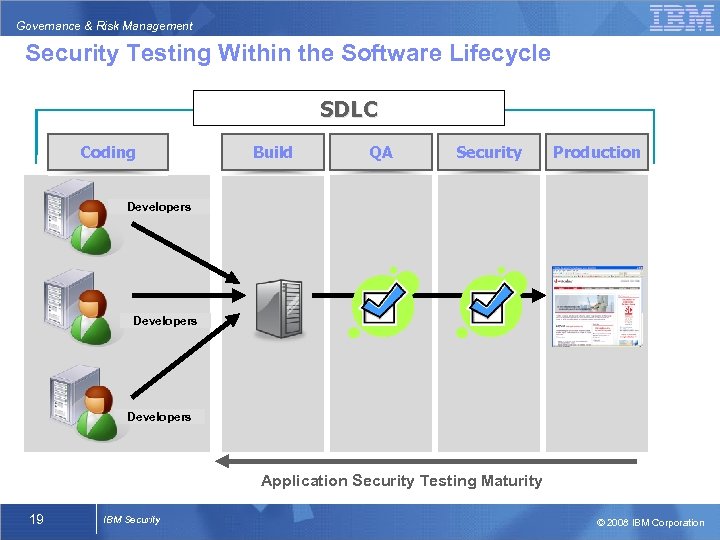 Governance & Risk Management Security Testing Within the Software Lifecycle SDLC Coding Build QA Security Production Developers Application Security Testing Maturity 19 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Security Testing Within the Software Lifecycle SDLC Coding Build QA Security Production Developers Application Security Testing Maturity 19 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
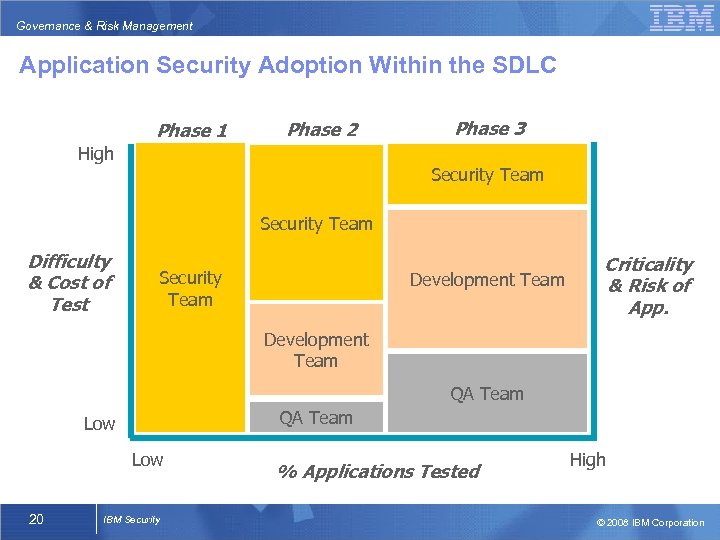 Governance & Risk Management Application Security Adoption Within the SDLC Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 High Security Team Difficulty & Cost of Test Security Team Development Team Criticality & Risk of App. Development Team QA Team Low 20 IBM Security % Applications Tested High © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Application Security Adoption Within the SDLC Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 High Security Team Difficulty & Cost of Test Security Team Development Team Criticality & Risk of App. Development Team QA Team Low 20 IBM Security % Applications Tested High © 2008 IBM Corporation
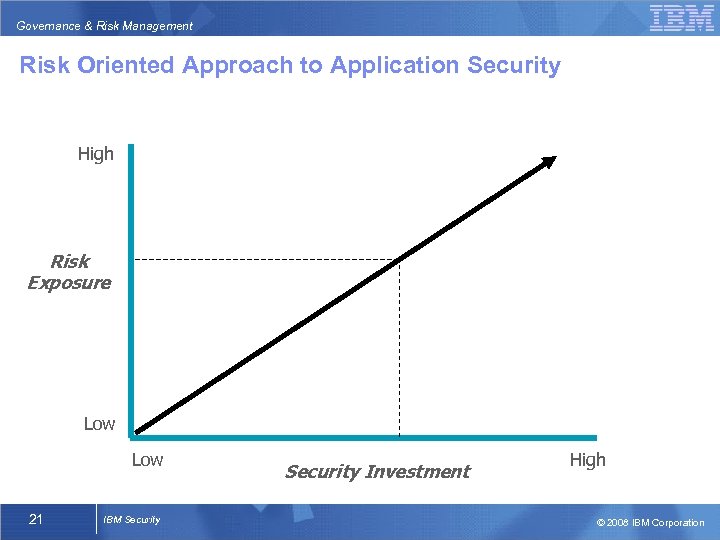 Governance & Risk Management Risk Oriented Approach to Application Security High Risk Exposure Low 21 IBM Security Investment High © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Risk Oriented Approach to Application Security High Risk Exposure Low 21 IBM Security Investment High © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Educating Developers and Getting “Buy in” § Establish security accountability and stds for shipping § Create a “security architect” role § Create a security community of practice § Create a secure development portal or wiki § Conduct hacking demos to demonstrate risks § Online & offline courses for secure coding § Put developers through secure coding exams § Security reviews of real applications § Pay premiums for security architects 22 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Educating Developers and Getting “Buy in” § Establish security accountability and stds for shipping § Create a “security architect” role § Create a security community of practice § Create a secure development portal or wiki § Conduct hacking demos to demonstrate risks § Online & offline courses for secure coding § Put developers through secure coding exams § Security reviews of real applications § Pay premiums for security architects 22 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 23 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Agenda § Introduction to Application Security § Application Security Best Practices § IBM Vision for Application Security 23 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
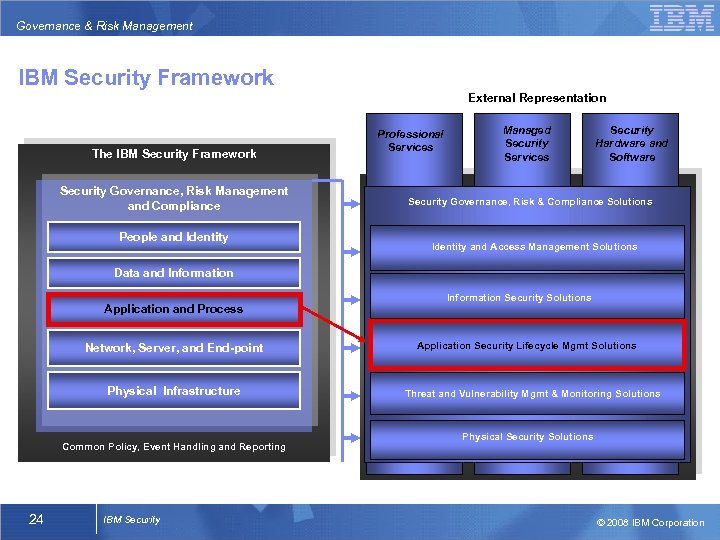 Governance & Risk Management IBM Security Framework External Representation The IBM Security Framework Security Governance, Risk Management and Compliance People and Identity Professional Services Managed Security Services Security Hardware and Software Security Governance, Risk & Compliance Solutions Identity and Access Management Solutions Data and Information Application and Process Network, Server, and End-point Physical Infrastructure Common Policy, Event Handling and Reporting 24 IBM Security Information Security Solutions Application Security Lifecycle Mgmt Solutions Threat and Vulnerability Mgmt & Monitoring Solutions Physical Security Solutions © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management IBM Security Framework External Representation The IBM Security Framework Security Governance, Risk Management and Compliance People and Identity Professional Services Managed Security Services Security Hardware and Software Security Governance, Risk & Compliance Solutions Identity and Access Management Solutions Data and Information Application and Process Network, Server, and End-point Physical Infrastructure Common Policy, Event Handling and Reporting 24 IBM Security Information Security Solutions Application Security Lifecycle Mgmt Solutions Threat and Vulnerability Mgmt & Monitoring Solutions Physical Security Solutions © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Software Security Development Ecosystem Control, Monitor and Report Developers Coding Build System Build Quality Assurance Testing QA Security Auditor scanning Security Web Based Security Training 25 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Software Security Development Ecosystem Control, Monitor and Report Developers Coding Build System Build Quality Assurance Testing QA Security Auditor scanning Security Web Based Security Training 25 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management Product and Services § Products: – App. Scan: Application Security Vulnerability Assessment Tools § Services: – App. Scan On. Demand § Training: – Application security Web based training and onsite courses For more information see: www. watchfire. com 26 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management Product and Services § Products: – App. Scan: Application Security Vulnerability Assessment Tools § Services: – App. Scan On. Demand § Training: – Application security Web based training and onsite courses For more information see: www. watchfire. com 26 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
 Governance & Risk Management 27 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation
Governance & Risk Management 27 IBM Security © 2008 IBM Corporation


