b457c50eda8a9ce7523fd3718f3a4a3d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Goree Island The Door of No Return
Goree Island The Door of No Return
 "Take up the White Man's Burden. Send forth the best ye breed. Go blind your sons to exile To serve your captives' need. . . " -Joseph Rudyard Kipling
"Take up the White Man's Burden. Send forth the best ye breed. Go blind your sons to exile To serve your captives' need. . . " -Joseph Rudyard Kipling
 Portuguese Traders o o Age of Exploration Europeans were in search of a new route to India. Arrived in the 1400 s for gold, cotton, and ivory By the 1650 s, the slave trade was the most lucrative enterprise
Portuguese Traders o o Age of Exploration Europeans were in search of a new route to India. Arrived in the 1400 s for gold, cotton, and ivory By the 1650 s, the slave trade was the most lucrative enterprise
 Slavery o o Common in ancient China, Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome Arabs, Egyptians, and Kushites all held slaves Slave caravans were a common sight in East Africa and the Sahara NO TRADE in slaves was more extensive or more brutal than the TRANS-ATLANTIC trade that took place between 1600 -1800 s.
Slavery o o Common in ancient China, Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome Arabs, Egyptians, and Kushites all held slaves Slave caravans were a common sight in East Africa and the Sahara NO TRADE in slaves was more extensive or more brutal than the TRANS-ATLANTIC trade that took place between 1600 -1800 s.
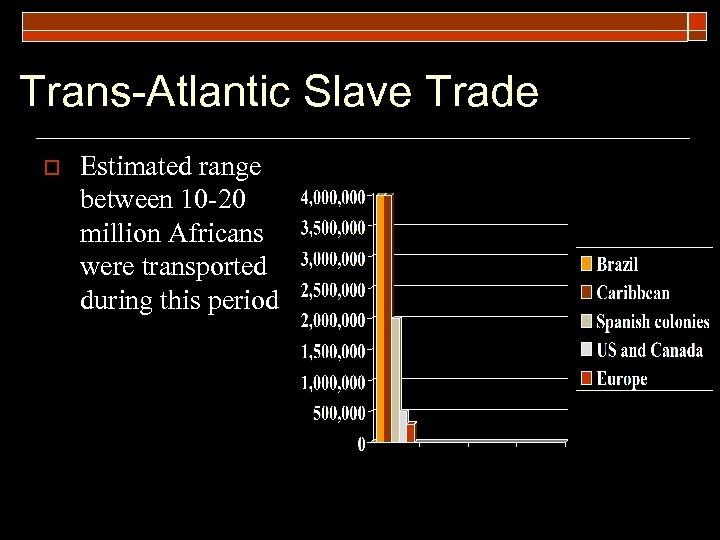 Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade o Estimated range between 10 -20 million Africans were transported during this period
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade o Estimated range between 10 -20 million Africans were transported during this period
 o o Portuguese traders bought slaves in Benin and the Niger delta to sell elsewhere. Slaves were needed for sugar plantations in Latin America and Caribbean at first, then others were used in North America
o o Portuguese traders bought slaves in Benin and the Niger delta to sell elsewhere. Slaves were needed for sugar plantations in Latin America and Caribbean at first, then others were used in North America
 How were the slaves obtained? o o Traders organized and operated their own slave raids. Traders bought slaves from African kings and chiefs. n n n Some were prisoners of wars between tribes Some tribes raided other groups’ villages in order to capture slaves to sell Some sold their own family members or themselves
How were the slaves obtained? o o Traders organized and operated their own slave raids. Traders bought slaves from African kings and chiefs. n n n Some were prisoners of wars between tribes Some tribes raided other groups’ villages in order to capture slaves to sell Some sold their own family members or themselves
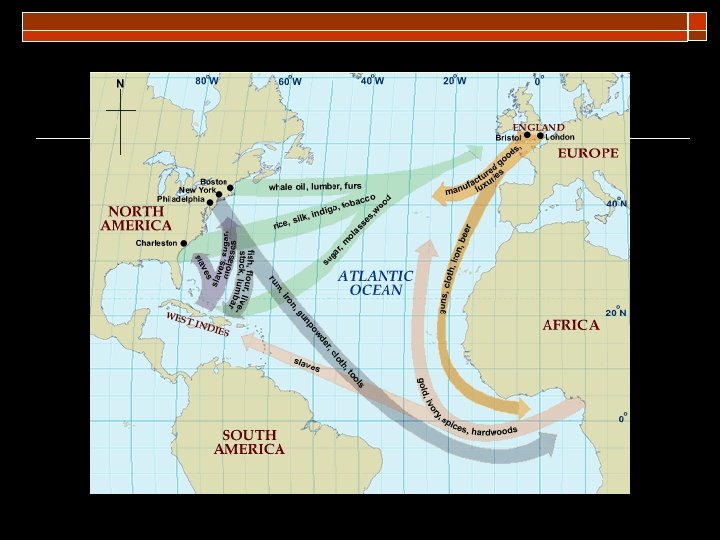
 Triangular Trade o o o Europeans brought goods (usually guns and trinkets) to Africa in exchange for slaves Slaves were brought to plantations in S. America, Caribbean, and U. S. Sugar, rum, tobacco, and molasses were shipped to Europe to trade for manufactured products
Triangular Trade o o o Europeans brought goods (usually guns and trinkets) to Africa in exchange for slaves Slaves were brought to plantations in S. America, Caribbean, and U. S. Sugar, rum, tobacco, and molasses were shipped to Europe to trade for manufactured products
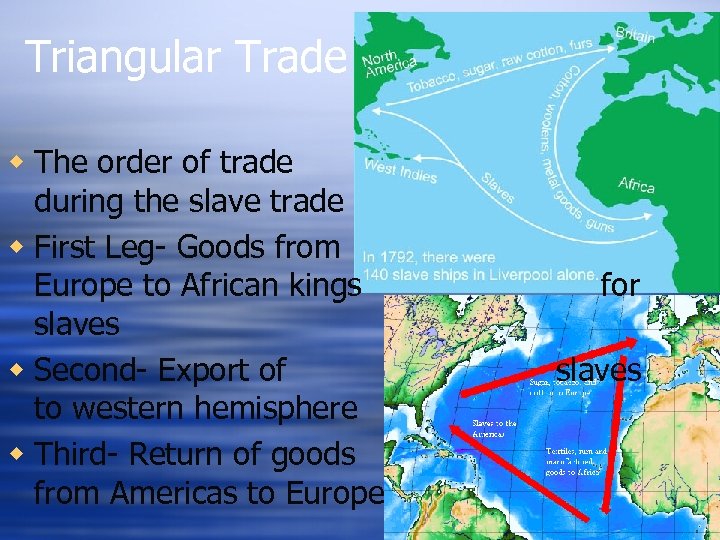 Triangular Trade w The order of trade during the slave trade w First Leg- Goods from Europe to African kings slaves w Second- Export of to western hemisphere w Third- Return of goods from Americas to Europe for slaves
Triangular Trade w The order of trade during the slave trade w First Leg- Goods from Europe to African kings slaves w Second- Export of to western hemisphere w Third- Return of goods from Americas to Europe for slaves
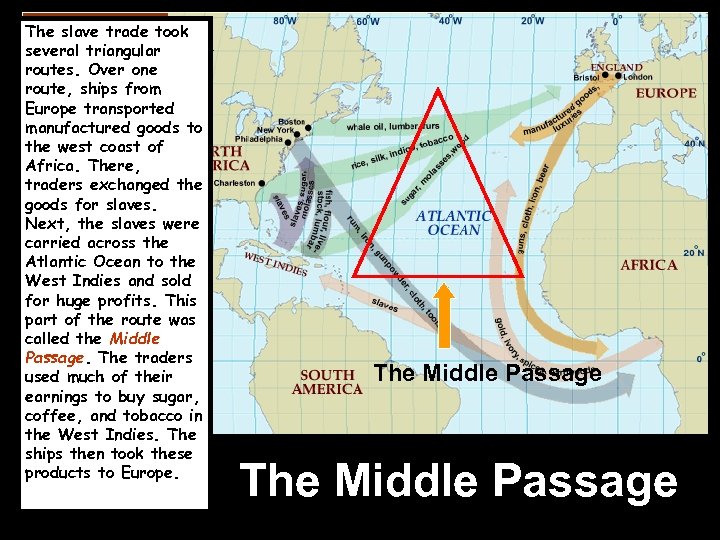 The slave trade took several triangular routes. Over one route, ships from Europe transported manufactured goods to the west coast of Africa. There, traders exchanged the goods for slaves. Next, the slaves were carried across the Atlantic Ocean to the West Indies and sold for huge profits. This part of the route was called the Middle Passage. The traders used much of their earnings to buy sugar, coffee, and tobacco in the West Indies. The ships then took these products to Europe. The Middle Passage
The slave trade took several triangular routes. Over one route, ships from Europe transported manufactured goods to the west coast of Africa. There, traders exchanged the goods for slaves. Next, the slaves were carried across the Atlantic Ocean to the West Indies and sold for huge profits. This part of the route was called the Middle Passage. The traders used much of their earnings to buy sugar, coffee, and tobacco in the West Indies. The ships then took these products to Europe. The Middle Passage
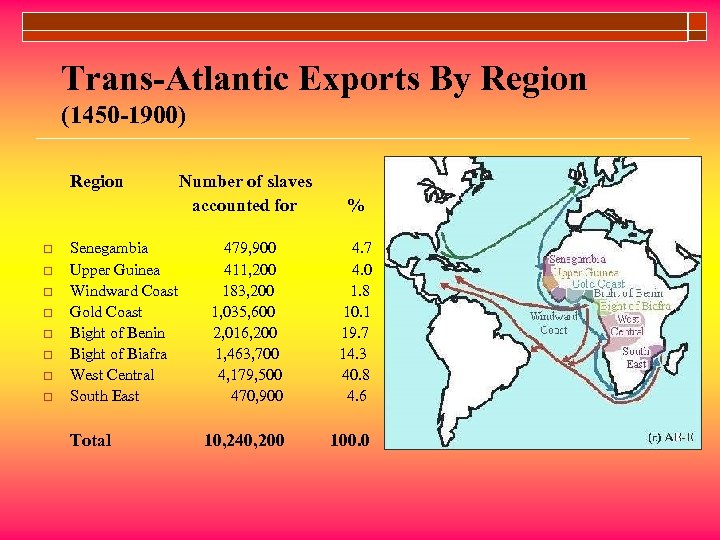 Trans-Atlantic Exports By Region (1450 -1900) Region o o o o Senegambia Upper Guinea Windward Coast Gold Coast Bight of Benin Bight of Biafra West Central South East Total Number of slaves accounted for % 479, 900 411, 200 183, 200 1, 035, 600 2, 016, 200 1, 463, 700 4, 179, 500 470, 900 4. 7 4. 0 1. 8 10. 1 19. 7 14. 3 40. 8 4. 6 10, 240, 200 100. 0
Trans-Atlantic Exports By Region (1450 -1900) Region o o o o Senegambia Upper Guinea Windward Coast Gold Coast Bight of Benin Bight of Biafra West Central South East Total Number of slaves accounted for % 479, 900 411, 200 183, 200 1, 035, 600 2, 016, 200 1, 463, 700 4, 179, 500 470, 900 4. 7 4. 0 1. 8 10. 1 19. 7 14. 3 40. 8 4. 6 10, 240, 200 100. 0
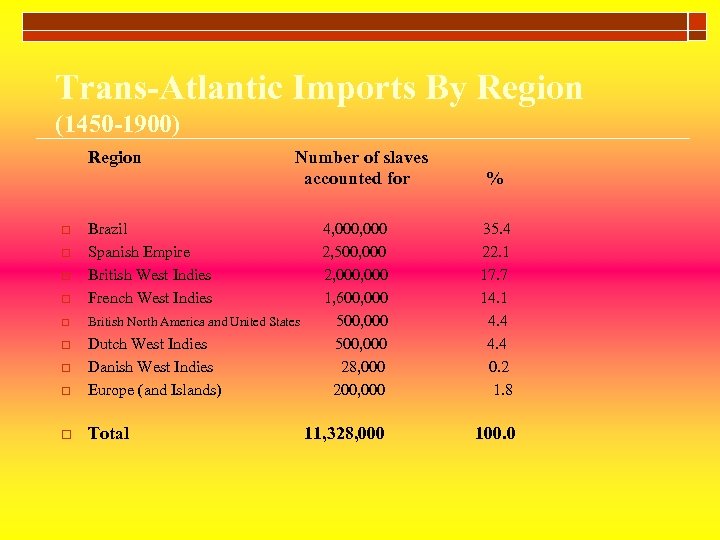 Trans-Atlantic Imports By Region (1450 -1900) Region Number of slaves accounted for o Brazil Spanish Empire British West Indies French West Indies o British North America and United States o o Dutch West Indies Danish West Indies Europe (and Islands) o Total o o % 4, 000 2, 500, 000 2, 000 1, 600, 000 500, 000 28, 000 200, 000 35. 4 22. 1 17. 7 14. 1 4. 4 0. 2 1. 8 11, 328, 000 100. 0
Trans-Atlantic Imports By Region (1450 -1900) Region Number of slaves accounted for o Brazil Spanish Empire British West Indies French West Indies o British North America and United States o o Dutch West Indies Danish West Indies Europe (and Islands) o Total o o % 4, 000 2, 500, 000 2, 000 1, 600, 000 500, 000 28, 000 200, 000 35. 4 22. 1 17. 7 14. 1 4. 4 0. 2 1. 8 11, 328, 000 100. 0
 Tonight o Review your ethnic group notes for the quiz tomorrow. o Start working on reading pages 507 -516 and taking notes. They are due on Friday.
Tonight o Review your ethnic group notes for the quiz tomorrow. o Start working on reading pages 507 -516 and taking notes. They are due on Friday.


