b1e4531cbf1d905d64a09cc259b7916a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
© Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 4 Pregnancy © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
4 Pregnancy © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Conception • Cell is the smallest unit of life that is able to reproduce itself • Sperm is the male germ cell • Ovum is the female germ cell • Conception occurs when ovum and sperm combine • Zygote is a single cell formed at conception – also called a fertilized egg © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Conception • Cell is the smallest unit of life that is able to reproduce itself • Sperm is the male germ cell • Ovum is the female germ cell • Conception occurs when ovum and sperm combine • Zygote is a single cell formed at conception – also called a fertilized egg © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
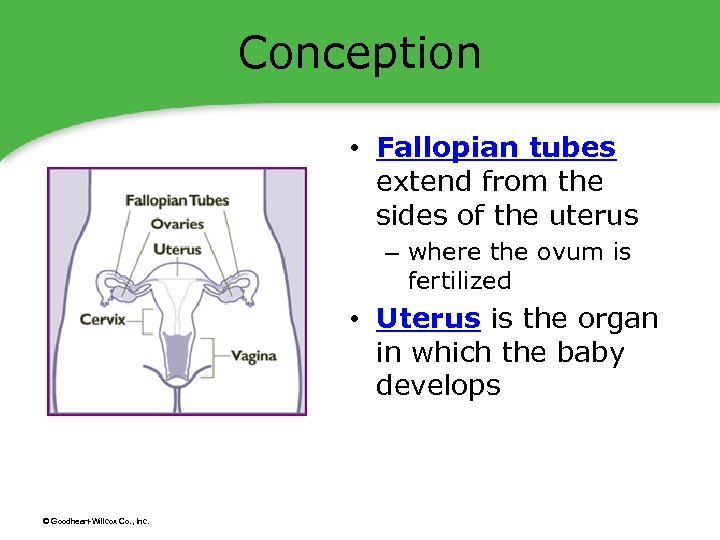 Conception • Fallopian tubes extend from the sides of the uterus – where the ovum is fertilized • Uterus is the organ in which the baby develops © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Conception • Fallopian tubes extend from the sides of the uterus – where the ovum is fertilized • Uterus is the organ in which the baby develops © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Genetic Factors and the Unborn Baby • Genetic factors are traits passed through the genes – affect all stages of growth and development • Genome is a genetic blueprint that guides growth and development during pregnancy – gives cells instructions for family-like traits that will unfold throughout life © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Genetic Factors and the Unborn Baby • Genetic factors are traits passed through the genes – affect all stages of growth and development • Genome is a genetic blueprint that guides growth and development during pregnancy – gives cells instructions for family-like traits that will unfold throughout life © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
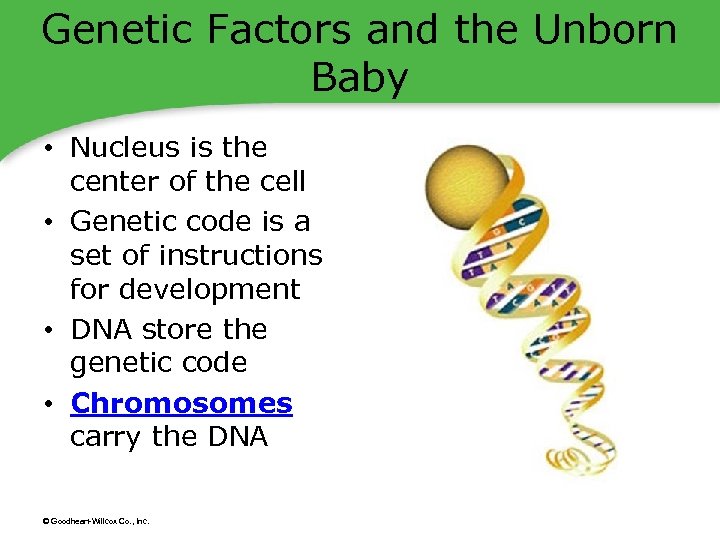 Genetic Factors and the Unborn Baby • Nucleus is the center of the cell • Genetic code is a set of instructions for development • DNA store the genetic code • Chromosomes carry the DNA © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Genetic Factors and the Unborn Baby • Nucleus is the center of the cell • Genetic code is a set of instructions for development • DNA store the genetic code • Chromosomes carry the DNA © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Objective • Describe how a person inherits traits through genes. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Objective • Describe how a person inherits traits through genes. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Chromosomes and Genes • Chromosomes – each person has 46, pairs of 23 – half from sperm, half from egg – contains 20, 000 genes • Genes – each human cell contains about 1 million genes – a gene, or group of genes, decides a trait © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Chromosomes and Genes • Chromosomes – each person has 46, pairs of 23 – half from sperm, half from egg – contains 20, 000 genes • Genes – each human cell contains about 1 million genes – a gene, or group of genes, decides a trait © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Dominant and Recessive Traits • Dominant traits always show in a person even if only one gene of the pair is inherited for that trait • Recessive traits typically do not show in a person unless both genes for the trait are inherited – one from each parent – person who inherits only one recessive gene for a trait becomes a carrier of that trait © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Dominant and Recessive Traits • Dominant traits always show in a person even if only one gene of the pair is inherited for that trait • Recessive traits typically do not show in a person unless both genes for the trait are inherited – one from each parent – person who inherits only one recessive gene for a trait becomes a carrier of that trait © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Sex Chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine genetic sex of baby – XX female • ovum always carries only X chromosomes – XY male • sperm can carry either X or Y chromosome • boys’ sex-linked traits are determined only by their mothers © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Sex Chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine genetic sex of baby – XX female • ovum always carries only X chromosomes – XY male • sperm can carry either X or Y chromosome • boys’ sex-linked traits are determined only by their mothers © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Multiple Pregnancy • Multiple pregnancy occurs when two or more babies develop in the same pregnancy © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Multiple Pregnancy • Multiple pregnancy occurs when two or more babies develop in the same pregnancy © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
 Multiple Pregnancy • Fraternal children develop from two or more ova – most common – each baby has own chorion • Identical children develop from same ova and sperm • Mixed types of pregnancy must include fraternal and identical babies © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Multiple Pregnancy • Fraternal children develop from two or more ova – most common – each baby has own chorion • Identical children develop from same ova and sperm • Mixed types of pregnancy must include fraternal and identical babies © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 What Do You Think? How can parents help identical twins maintain separate identities while still nurturing a close sibling relationship? © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
What Do You Think? How can parents help identical twins maintain separate identities while still nurturing a close sibling relationship? © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Stages in Prenatal Development • Prenatal development takes place between conception and birth – germinal stage – embryonic stage – fetal stage © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Stages in Prenatal Development • Prenatal development takes place between conception and birth – germinal stage – embryonic stage – fetal stage © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
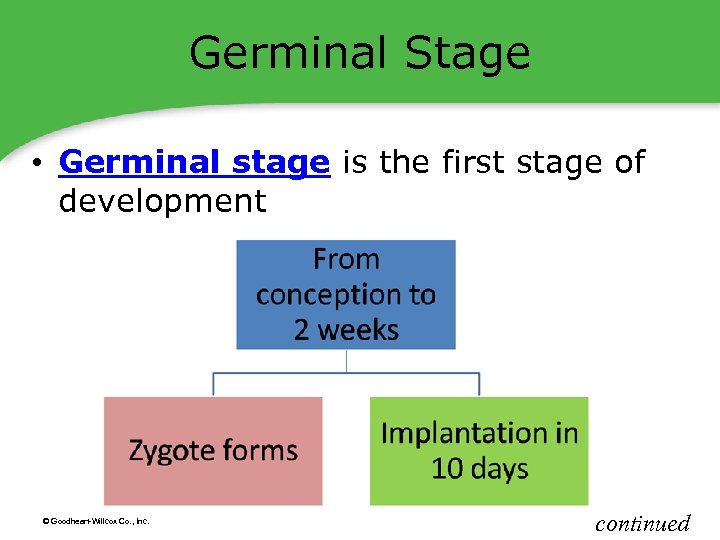 Germinal Stage • Germinal stage is the first stage of development © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Germinal Stage • Germinal stage is the first stage of development © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
 Germinal Stage • Amnion is a fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby in the uterus • Placenta is an organ filled with blood vessels that nourish the baby in the uterus • Umbilical cord is a cord that connects the baby to the placenta © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Germinal Stage • Amnion is a fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby in the uterus • Placenta is an organ filled with blood vessels that nourish the baby in the uterus • Umbilical cord is a cord that connects the baby to the placenta © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Embryonic Stage • Embryonic stage is the second stage of development, lasts about six weeks – most crucial to development – baby is called an embryo – development of most body systems – heart begins to beat – cartilage is present before bones form – substances pass from mother’s placenta through the umbilical cord © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Embryonic Stage • Embryonic stage is the second stage of development, lasts about six weeks – most crucial to development – baby is called an embryo – development of most body systems – heart begins to beat – cartilage is present before bones form – substances pass from mother’s placenta through the umbilical cord © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Fetal Stage • Fetal stage is the third stage of pregnancy, lasts from about nine weeks after conception until birth – bone starts to replace cartilage – baby is known as a fetus © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Fetal Stage • Fetal stage is the third stage of pregnancy, lasts from about nine weeks after conception until birth – bone starts to replace cartilage – baby is known as a fetus © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
 Fetal Stage • During the fetal stage, – all parts of the body mature – overall size increases quickly – heartbeat in the third month – quickening begins between the fourth and fifth months © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
Fetal Stage • During the fetal stage, – all parts of the body mature – overall size increases quickly – heartbeat in the third month – quickening begins between the fourth and fifth months © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. continued
 Fetal Stage • Age of viability is the age at which a baby could survive if born, 28 weeks – still need extensive medical care – better chance of survival each week the baby is not born • During last two months of pregnancy, – inner layer of lungs produces substance that allows for breathing air – receives immunities from mother in the ninth month © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Fetal Stage • Age of viability is the age at which a baby could survive if born, 28 weeks – still need extensive medical care – better chance of survival each week the baby is not born • During last two months of pregnancy, – inner layer of lungs produces substance that allows for breathing air – receives immunities from mother in the ninth month © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 What Do You Think? • Pregnancies that end before 20 weeks are considered a miscarriage, resulting in no record of the life, such as a birth or death certificate. • How do you think this impacts a parent after the loss of a wanted pregnancy? © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
What Do You Think? • Pregnancies that end before 20 weeks are considered a miscarriage, resulting in no record of the life, such as a birth or death certificate. • How do you think this impacts a parent after the loss of a wanted pregnancy? © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • age of viability. Age at which most babies could survive if they were born (28 th week of pregnancy). • amnion. Fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby in the uterus. • cartilage. Soft, elastic, flexible tissue that provides structure for the body. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • age of viability. Age at which most babies could survive if they were born (28 th week of pregnancy). • amnion. Fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby in the uterus. • cartilage. Soft, elastic, flexible tissue that provides structure for the body. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • cell. Smallest unit of life that is able to reproduce itself. • chorion. Membrane that surrounds the baby in the uterus. • chromosomes. Threadlike structures that carry genes in living cells. • conception. Union of the ovum and sperm cells. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • cell. Smallest unit of life that is able to reproduce itself. • chorion. Membrane that surrounds the baby in the uterus. • chromosomes. Threadlike structures that carry genes in living cells. • conception. Union of the ovum and sperm cells. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • dominant traits. Traits that always show in a person even if only one gene of the pair is inherited for that trait. • embryo. Medical term used to describe the unborn baby in the embryonic stage of development (week 3 through 8 of pregnancy). © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • dominant traits. Traits that always show in a person even if only one gene of the pair is inherited for that trait. • embryo. Medical term used to describe the unborn baby in the embryonic stage of development (week 3 through 8 of pregnancy). © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • embryonic stage. Second stage of prenatal development, lasting about six weeks. • fallopian tubes. Two hollow tubes that connect to the uterus and have fingerlike projections that reach toward each ovary. • fetal stage. Third stage of pregnancy, lasting from about nine weeks after conception until birth. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • embryonic stage. Second stage of prenatal development, lasting about six weeks. • fallopian tubes. Two hollow tubes that connect to the uterus and have fingerlike projections that reach toward each ovary. • fetal stage. Third stage of pregnancy, lasting from about nine weeks after conception until birth. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • fetus. Medical term used to describe the unborn baby in the fetal stage of development (week 9 until the end of pregnancy). • fraternal. Term used to describe children from multiple pregnancies who develop from two or more fertilized ova and differ in genetic makeup. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • fetus. Medical term used to describe the unborn baby in the fetal stage of development (week 9 until the end of pregnancy). • fraternal. Term used to describe children from multiple pregnancies who develop from two or more fertilized ova and differ in genetic makeup. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • genetic factors. Traits that are passed through the genes. • germinal stage. First stage of prenatal development, lasting about two weeks after conception. • identical. Term used to describe children from multiple pregnancies who develop from one fertilized ovum and have the same genetic makeup. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • genetic factors. Traits that are passed through the genes. • germinal stage. First stage of prenatal development, lasting about two weeks after conception. • identical. Term used to describe children from multiple pregnancies who develop from one fertilized ovum and have the same genetic makeup. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • multiple pregnancy. Pregnancy in which two or more babies develop. • ovum. Female sex cell; also called egg. • placenta. Organ filled with blood vessels that nourish baby in the uterus. • prenatal development. Development that takes place between conception and birth. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • multiple pregnancy. Pregnancy in which two or more babies develop. • ovum. Female sex cell; also called egg. • placenta. Organ filled with blood vessels that nourish baby in the uterus. • prenatal development. Development that takes place between conception and birth. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • quickening. Movements of the fetus that can be felt by the mother. • recessive traits. Traits that typically do not show in a person unless both genes for the trait are inherited. • sperm. Male sex cell. • umbilical cord. Cord that connects the baby to the placenta. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • quickening. Movements of the fetus that can be felt by the mother. • recessive traits. Traits that typically do not show in a person unless both genes for the trait are inherited. • sperm. Male sex cell. • umbilical cord. Cord that connects the baby to the placenta. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
 Glossary of Key Terms • uterus. Organ in which the baby develops and is protected until birth. • zygote. Single cell formed at conception; also called fertilized egg. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.
Glossary of Key Terms • uterus. Organ in which the baby develops and is protected until birth. • zygote. Single cell formed at conception; also called fertilized egg. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc.


