21884f485de1b68f7427d708502f19c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Good practice examples of developing local SMEs and opportunities for local business to become part of the supply chain Experiences of the Linkages Program in Cajamarca María Cecilia Araujo M. Washington D. C. , June 19 th 2006
Good practice examples of developing local SMEs and opportunities for local business to become part of the supply chain Experiences of the Linkages Program in Cajamarca María Cecilia Araujo M. Washington D. C. , June 19 th 2006
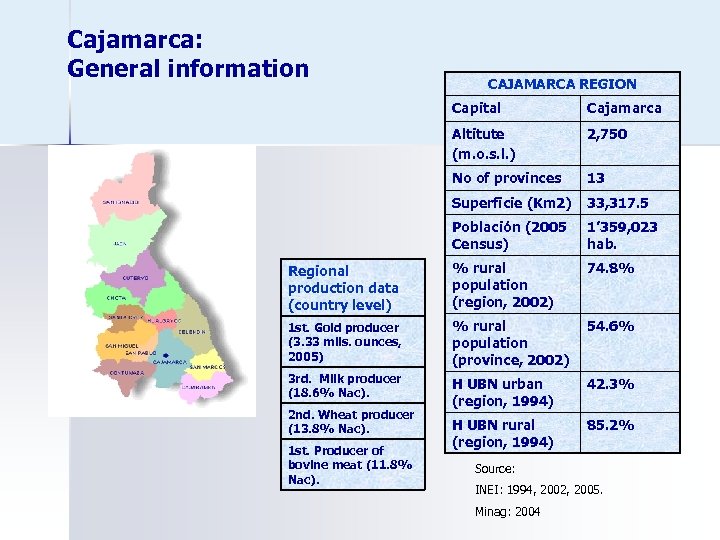 Cajamarca: General information CAJAMARCA REGION Capital Cajamarca Altitute (m. o. s. l. ) 2, 750 No of provinces 13 Superficie (Km 2) 33, 317. 5 Población (2005 Census) 1’ 359, 023 hab. Regional production data (country level) % rural population (region, 2002) 74. 8% 1 st. Gold producer (3. 33 mlls. ounces, 2005) % rural population (province, 2002) 54. 6% 3 rd. Milk producer (18. 6% Nac). H UBN urban (region, 1994) 42. 3% H UBN rural (region, 1994) 85. 2% 2 nd. Wheat producer (13. 8% Nac). 1 st. Producer of bovine meat (11. 8% Nac). Source: INEI: 1994, 2002, 2005. Minag: 2004
Cajamarca: General information CAJAMARCA REGION Capital Cajamarca Altitute (m. o. s. l. ) 2, 750 No of provinces 13 Superficie (Km 2) 33, 317. 5 Población (2005 Census) 1’ 359, 023 hab. Regional production data (country level) % rural population (region, 2002) 74. 8% 1 st. Gold producer (3. 33 mlls. ounces, 2005) % rural population (province, 2002) 54. 6% 3 rd. Milk producer (18. 6% Nac). H UBN urban (region, 1994) 42. 3% H UBN rural (region, 1994) 85. 2% 2 nd. Wheat producer (13. 8% Nac). 1 st. Producer of bovine meat (11. 8% Nac). Source: INEI: 1994, 2002, 2005. Minag: 2004
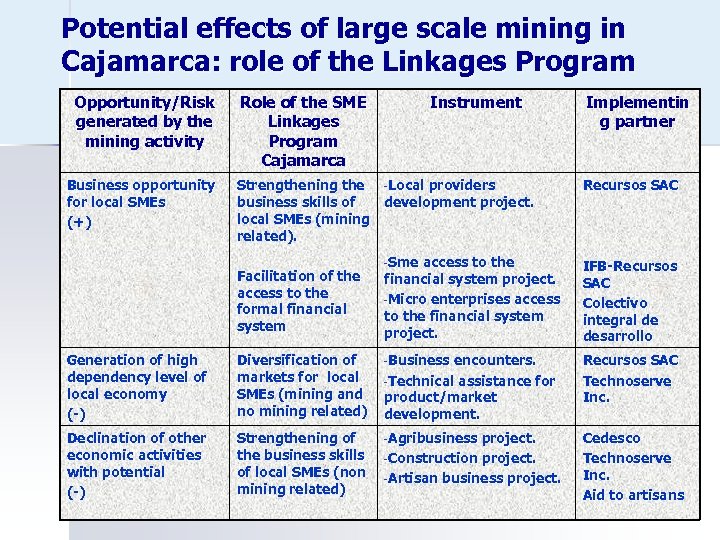 Potential effects of large scale mining in Cajamarca: role of the Linkages Program Opportunity/Risk generated by the mining activity Business opportunity for local SMEs (+) Role of the SME Linkages Program Cajamarca Instrument Strengthening the -Local providers business skills of development project. local SMEs (mining related). Facilitation of the access to the formal financial system Implementin g partner Recursos SAC -Sme access to the financial system project. -Micro enterprises access to the financial system project. IFB-Recursos SAC Colectivo integral de desarrollo Generation of high dependency level of local economy (-) Diversification of markets for local SMEs (mining and no mining related) -Business encounters. -Technical assistance for product/market development. Recursos SAC Technoserve Inc. Declination of other economic activities with potential (-) Strengthening of the business skills of local SMEs (non mining related) -Agribusiness Cedesco Technoserve Inc. Aid to artisans project. -Construction project. -Artisan business project.
Potential effects of large scale mining in Cajamarca: role of the Linkages Program Opportunity/Risk generated by the mining activity Business opportunity for local SMEs (+) Role of the SME Linkages Program Cajamarca Instrument Strengthening the -Local providers business skills of development project. local SMEs (mining related). Facilitation of the access to the formal financial system Implementin g partner Recursos SAC -Sme access to the financial system project. -Micro enterprises access to the financial system project. IFB-Recursos SAC Colectivo integral de desarrollo Generation of high dependency level of local economy (-) Diversification of markets for local SMEs (mining and no mining related) -Business encounters. -Technical assistance for product/market development. Recursos SAC Technoserve Inc. Declination of other economic activities with potential (-) Strengthening of the business skills of local SMEs (non mining related) -Agribusiness Cedesco Technoserve Inc. Aid to artisans project. -Construction project. -Artisan business project.
 Linkages experience: Suppliers development project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Minera Yanacocha. -Printing services (Foto Andina, Publiser). -Engineering services (Ceyca). -Garment products (Jy. R). -Heavy equipment maintenance (Urteaga). -General services (American services). Local/regional demand. - Printing services (Foto Andina, Publiser). - Engineering services (Ceyca, Santa Martha). - Garment products (Jy. R, Nic. Nor). -Heavy equipment maintenance (Urteaga). -General services (American services). Some facts: Number of assisted SMEs: 119 Number of employments involved: 506 Number of new employments generated: 35 Sales generated: US$ 12’ 748, 755 (US$ 6’ 500. 000 baseline data)
Linkages experience: Suppliers development project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Minera Yanacocha. -Printing services (Foto Andina, Publiser). -Engineering services (Ceyca). -Garment products (Jy. R). -Heavy equipment maintenance (Urteaga). -General services (American services). Local/regional demand. - Printing services (Foto Andina, Publiser). - Engineering services (Ceyca, Santa Martha). - Garment products (Jy. R, Nic. Nor). -Heavy equipment maintenance (Urteaga). -General services (American services). Some facts: Number of assisted SMEs: 119 Number of employments involved: 506 Number of new employments generated: 35 Sales generated: US$ 12’ 748, 755 (US$ 6’ 500. 000 baseline data)
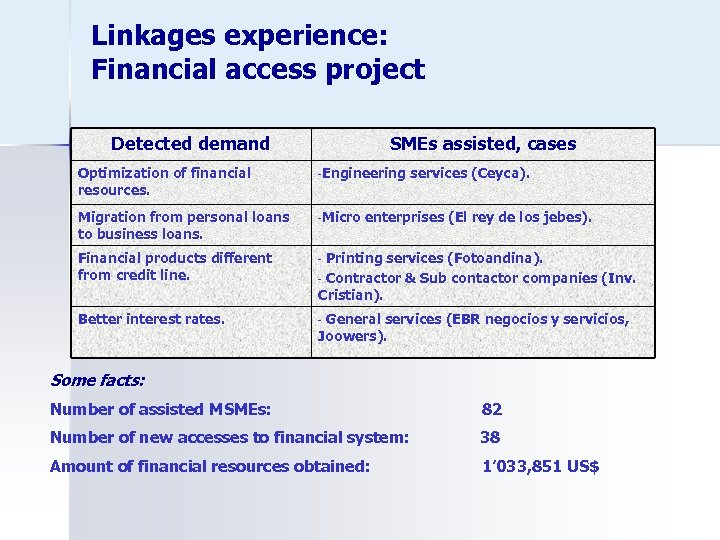 Linkages experience: Financial access project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Optimization of financial resources. -Engineering Migration from personal loans to business loans. -Micro Financial products different from credit line. - Better interest rates. services (Ceyca). - enterprises (El rey de los jebes). Printing services (Fotoandina). - Contractor & Sub contactor companies (Inv. Cristian). General services (EBR negocios y servicios, Joowers). Some facts: Number of assisted MSMEs: 82 Number of new accesses to financial system: 38 Amount of financial resources obtained: 1’ 033, 851 US$
Linkages experience: Financial access project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Optimization of financial resources. -Engineering Migration from personal loans to business loans. -Micro Financial products different from credit line. - Better interest rates. services (Ceyca). - enterprises (El rey de los jebes). Printing services (Fotoandina). - Contractor & Sub contactor companies (Inv. Cristian). General services (EBR negocios y servicios, Joowers). Some facts: Number of assisted MSMEs: 82 Number of new accesses to financial system: 38 Amount of financial resources obtained: 1’ 033, 851 US$
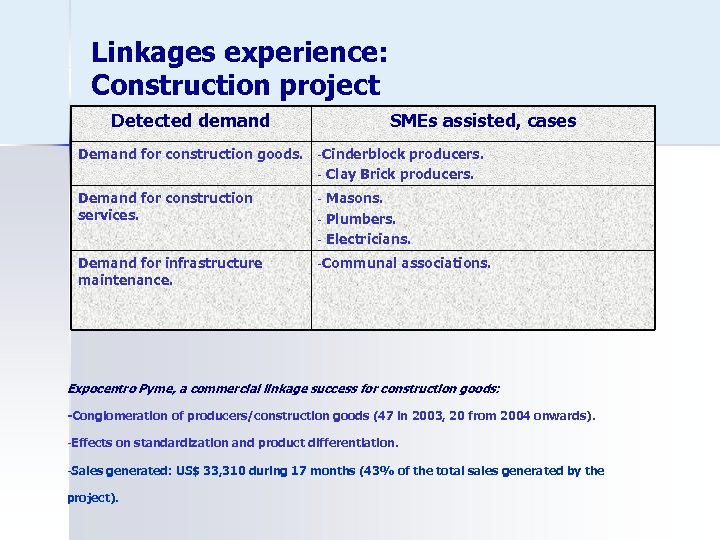 Linkages experience: Construction project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Demand for construction goods. -Cinderblock producers. - Clay Brick producers. Demand for construction services. - Demand for infrastructure maintenance. -Communal Masons. - Plumbers. - Electricians. associations. Expocentro Pyme, a commercial linkage success for construction goods: -Conglomeration of producers/construction goods (47 in 2003, 20 from 2004 onwards). -Effects on standardization and product differentiation. -Sales generated: US$ 33, 310 during 17 months (43% of the total sales generated by the project).
Linkages experience: Construction project Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Demand for construction goods. -Cinderblock producers. - Clay Brick producers. Demand for construction services. - Demand for infrastructure maintenance. -Communal Masons. - Plumbers. - Electricians. associations. Expocentro Pyme, a commercial linkage success for construction goods: -Conglomeration of producers/construction goods (47 in 2003, 20 from 2004 onwards). -Effects on standardization and product differentiation. -Sales generated: US$ 33, 310 during 17 months (43% of the total sales generated by the project).
 Linkages experience: Artisan project (Aid to artisans) Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Local market (tourism, institutional demands, hotel exhibits). -Clay products (Keramic Makkas). Domestic market (national fairs) -Textile products (La Collpa, Granja Porcón, Yuracyacu, Atoctambo, Cañafisto , Cuyumalca). International market (Create and Barrel, San Diego Zoo) Challenges: Some facts: -Product standardization: in site assistance. Number of assisted artisans: 51 -Independence in the commercial relationships (exporters). Number of employments involved: 51 Number of new employments generated: 14 -Delivery timing. -Volume of production. Sales generated: 47, 912 US$
Linkages experience: Artisan project (Aid to artisans) Detected demand SMEs assisted, cases Local market (tourism, institutional demands, hotel exhibits). -Clay products (Keramic Makkas). Domestic market (national fairs) -Textile products (La Collpa, Granja Porcón, Yuracyacu, Atoctambo, Cañafisto , Cuyumalca). International market (Create and Barrel, San Diego Zoo) Challenges: Some facts: -Product standardization: in site assistance. Number of assisted artisans: 51 -Independence in the commercial relationships (exporters). Number of employments involved: 51 Number of new employments generated: 14 -Delivery timing. -Volume of production. Sales generated: 47, 912 US$
 Beyond the provision of Business Development Services: n Do local governments have a role in the local economic development? – Centralization problem in Peru. – Modernization process, including the Local Economic Development promotion role. – Capacity building requirements of local governments. Case: Business licensing in Cajamarca. n Development of other income-generating opportunities. – Mining activities complementing the development of tourism supply chain. Case: Tourist development in Huaraz and the involvement of Cía Minera Antamina.
Beyond the provision of Business Development Services: n Do local governments have a role in the local economic development? – Centralization problem in Peru. – Modernization process, including the Local Economic Development promotion role. – Capacity building requirements of local governments. Case: Business licensing in Cajamarca. n Development of other income-generating opportunities. – Mining activities complementing the development of tourism supply chain. Case: Tourist development in Huaraz and the involvement of Cía Minera Antamina.
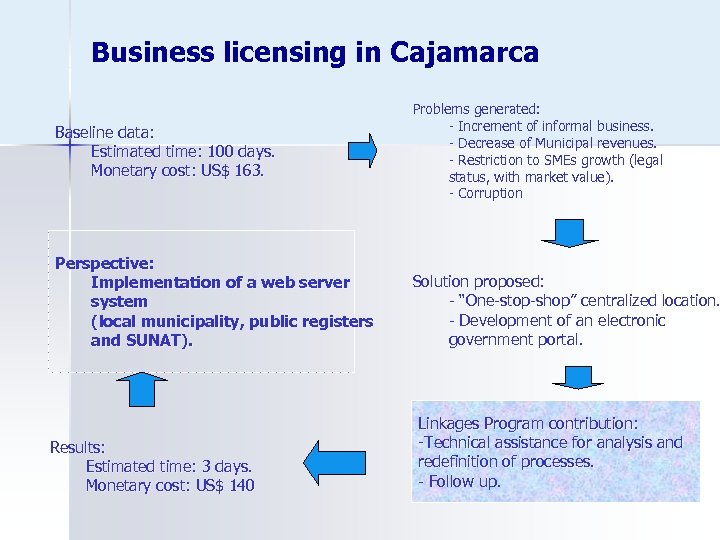 Business licensing in Cajamarca Baseline data: Estimated time: 100 days. Monetary cost: US$ 163. Perspective: Implementation of a web server system (local municipality, public registers and SUNAT). Results: Estimated time: 3 days. Monetary cost: US$ 140 Problems generated: - Increment of informal business. - Decrease of Municipal revenues. - Restriction to SMEs growth (legal status, with market value). - Corruption Solution proposed: - “One-stop-shop” centralized location. - Development of an electronic government portal. Linkages Program contribution: -Technical assistance for analysis and redefinition of processes. - Follow up.
Business licensing in Cajamarca Baseline data: Estimated time: 100 days. Monetary cost: US$ 163. Perspective: Implementation of a web server system (local municipality, public registers and SUNAT). Results: Estimated time: 3 days. Monetary cost: US$ 140 Problems generated: - Increment of informal business. - Decrease of Municipal revenues. - Restriction to SMEs growth (legal status, with market value). - Corruption Solution proposed: - “One-stop-shop” centralized location. - Development of an electronic government portal. Linkages Program contribution: -Technical assistance for analysis and redefinition of processes. - Follow up.
 Sustainable tourism in Huaraz: Gestur General information: -Ancash is a region with a population of 1’ 039, 415 (70% of poorness incidence). -Limited use of tourist resources (Huascarán, Huayhuash). -Presence of high scale mining activities (Cía Minera Antamina). Gestur strategy: -Alliance with the regional actors (mining company vg). Gestur project: -Incorporation of rural population in the supply chain of tour operators (through BDS provision). -Technical assistance to Local governments (implementation of tourism development plans). -Development of new alternative tourist circuits (rural approach). -Alliance with tour operators. -Improvement of the business environment. -Articulation to BDS providers.
Sustainable tourism in Huaraz: Gestur General information: -Ancash is a region with a population of 1’ 039, 415 (70% of poorness incidence). -Limited use of tourist resources (Huascarán, Huayhuash). -Presence of high scale mining activities (Cía Minera Antamina). Gestur strategy: -Alliance with the regional actors (mining company vg). Gestur project: -Incorporation of rural population in the supply chain of tour operators (through BDS provision). -Technical assistance to Local governments (implementation of tourism development plans). -Development of new alternative tourist circuits (rural approach). -Alliance with tour operators. -Improvement of the business environment. -Articulation to BDS providers.
 Lessons learned: • Joint definition of objectives and goals (IFC/invested company) is crucial. • A linkages program can go further than the suppliers development experience, contributing to sustainable local economic development. Sustainability of the results lies on: • Market approach of the SMEs capacity building process (linked to actual & potential market requirements, not only to the mining demand). • Contribution to the improvement of the business environment, generation of synergies with public and private sector (not conclave).
Lessons learned: • Joint definition of objectives and goals (IFC/invested company) is crucial. • A linkages program can go further than the suppliers development experience, contributing to sustainable local economic development. Sustainability of the results lies on: • Market approach of the SMEs capacity building process (linked to actual & potential market requirements, not only to the mining demand). • Contribution to the improvement of the business environment, generation of synergies with public and private sector (not conclave).
 Thanks for your attention We create opportunities
Thanks for your attention We create opportunities


