f43faedb2fbb8b188e6d6a46227b1b28.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Documentation and Records: u Preparation of process documents: Productive Process Plan (HACCP) u Generate, file, conserve and store process records > Production and Process Control: u Food risks control u Requirements of raw material - relationship with suppliers & conservation of raw materials u Production process control - control of the processes of production u Storage and distribution control
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Documentation and Records: u Preparation of process documents: Productive Process Plan (HACCP) u Generate, file, conserve and store process records > Production and Process Control: u Food risks control u Requirements of raw material - relationship with suppliers & conservation of raw materials u Production process control - control of the processes of production u Storage and distribution control
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > GMP is based on the processing activities of the enterprise. > Taking as a reference the Recommended General Principles of Food Hygiene of Codex Alimentarius (FAO/OMS): CAC/RCP 1 -1969, Rev. 3 (1997) > Following the Systems Focus > Following the Continuous Improvement route
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > GMP is based on the processing activities of the enterprise. > Taking as a reference the Recommended General Principles of Food Hygiene of Codex Alimentarius (FAO/OMS): CAC/RCP 1 -1969, Rev. 3 (1997) > Following the Systems Focus > Following the Continuous Improvement route
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > General hygiene status of Infrastructure: > Building & Surroundings in Good Repair > Production Area With Adequate Drainage > Storage (Raw & Cooked Products, Packaging Materials, Clothing, Personal Belongings, Chemicals Etc) > Toilet and Hand Washing Facilities With Selfclosing Doors, Dressing Rooms > Eating Area > Signs
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > General hygiene status of Infrastructure: > Building & Surroundings in Good Repair > Production Area With Adequate Drainage > Storage (Raw & Cooked Products, Packaging Materials, Clothing, Personal Belongings, Chemicals Etc) > Toilet and Hand Washing Facilities With Selfclosing Doors, Dressing Rooms > Eating Area > Signs
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY s General hygiene status of Infrastructure s Equipment (tools and utensils)
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY s General hygiene status of Infrastructure s Equipment (tools and utensils)
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY v General hygiene status of SERVICES/ UTILITIES: § Water (meets municipal standard) § Waste (collection, treatment and disposal), § Chemicals - labelling & residues, § Lighting, § Screening and ventilation to avoid contamination
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY v General hygiene status of SERVICES/ UTILITIES: § Water (meets municipal standard) § Waste (collection, treatment and disposal), § Chemicals - labelling & residues, § Lighting, § Screening and ventilation to avoid contamination
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Sanitation plan for: >food contact surfaces >Floors >Equipment & utensils
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Sanitation plan for: >food contact surfaces >Floors >Equipment & utensils
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Pest control - no pests in plant
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Pest control - no pests in plant
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Staff Hygiene FDisease Control: health condition of personnel ensuring that no communicable infections, infected lesions and other source of microbial contamination occur. FCleanliness: FHand washing before start of work, after each absence from the workstation and after hands are soiled or contaminated. FMaintaining adequate personal cleanliness
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Staff Hygiene FDisease Control: health condition of personnel ensuring that no communicable infections, infected lesions and other source of microbial contamination occur. FCleanliness: FHand washing before start of work, after each absence from the workstation and after hands are soiled or contaminated. FMaintaining adequate personal cleanliness
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY § Cleanliness cont’d 1. Appropriate Clothing, Suitable to the Operation in a Manner That Protects Against Contamination of Food, Food-contact Surfaces or Food Packaging Materials. This Includes Gloves, Boots, Aprons, Hair Restraints, No Jewelry or Other Objects That May Fall Into the Product 2. Designated Eating & Smoking Areas - Outside of Production Area 3. Designated Storage Area for Clothing and Personal Belongings
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY § Cleanliness cont’d 1. Appropriate Clothing, Suitable to the Operation in a Manner That Protects Against Contamination of Food, Food-contact Surfaces or Food Packaging Materials. This Includes Gloves, Boots, Aprons, Hair Restraints, No Jewelry or Other Objects That May Fall Into the Product 2. Designated Eating & Smoking Areas - Outside of Production Area 3. Designated Storage Area for Clothing and Personal Belongings
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Training: FNecessity for systematic detection of contamination caused by biological, physical and chemical contaminants FPlanned Training in Food Hygiene education and training are important elements in developing and implementing a good food hygiene programme
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY >Training: FNecessity for systematic detection of contamination caused by biological, physical and chemical contaminants FPlanned Training in Food Hygiene education and training are important elements in developing and implementing a good food hygiene programme
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY • Training – Personnel responsible for identifying sanitation failure or food contamination should have a background of education or experience, or a combination thereof, to provide a level of competency necessary for production of clean and safe food. – Food handlers and supervisors should receive appropriate training in proper food handling techniques and food-protection principles and should be informed of the danger of poor personal hygiene and unsanitary practices
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY • Training – Personnel responsible for identifying sanitation failure or food contamination should have a background of education or experience, or a combination thereof, to provide a level of competency necessary for production of clean and safe food. – Food handlers and supervisors should receive appropriate training in proper food handling techniques and food-protection principles and should be informed of the danger of poor personal hygiene and unsanitary practices
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY • Supervision – Responsibility for assuring compliance by all personnel with all requirements of good manufacturing practices shall be clearly assigned to competent supervisory personnel
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY • Supervision – Responsibility for assuring compliance by all personnel with all requirements of good manufacturing practices shall be clearly assigned to competent supervisory personnel
 Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Control of measuring devices: >Equipment Control, Maintenance and Calibration >Traceability of calibrated equipment > Identification and traceability of products: >Processes identification and traceability of product at all stages of production and delivery. >Mechanisms for Recall: to remove products from the market when necessary.
Good Manufacture Practices FOOD INDUSTRY > Control of measuring devices: >Equipment Control, Maintenance and Calibration >Traceability of calibrated equipment > Identification and traceability of products: >Processes identification and traceability of product at all stages of production and delivery. >Mechanisms for Recall: to remove products from the market when necessary.
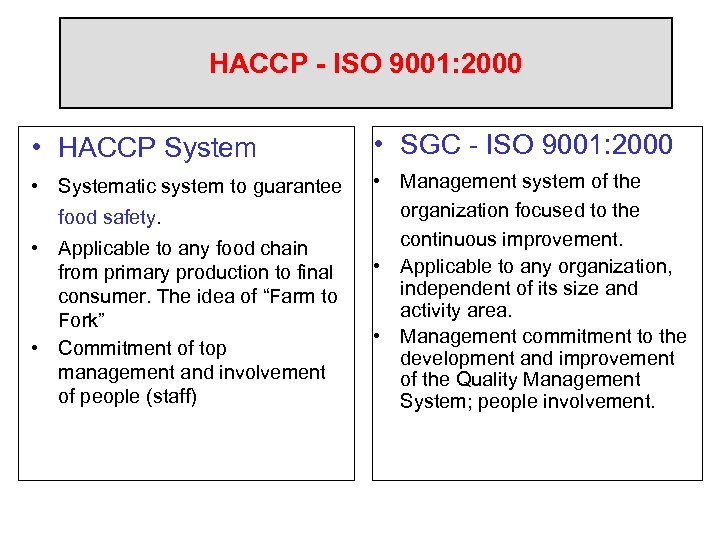 HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC - ISO 9001: 2000 • Systematic system to guarantee • Management system of the organization focused to the continuous improvement. • Applicable to any organization, independent of its size and activity area. • Management commitment to the development and improvement of the Quality Management System; people involvement. food safety. • Applicable to any food chain from primary production to final consumer. The idea of “Farm to Fork” • Commitment of top management and involvement of people (staff)
HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC - ISO 9001: 2000 • Systematic system to guarantee • Management system of the organization focused to the continuous improvement. • Applicable to any organization, independent of its size and activity area. • Management commitment to the development and improvement of the Quality Management System; people involvement. food safety. • Applicable to any food chain from primary production to final consumer. The idea of “Farm to Fork” • Commitment of top management and involvement of people (staff)
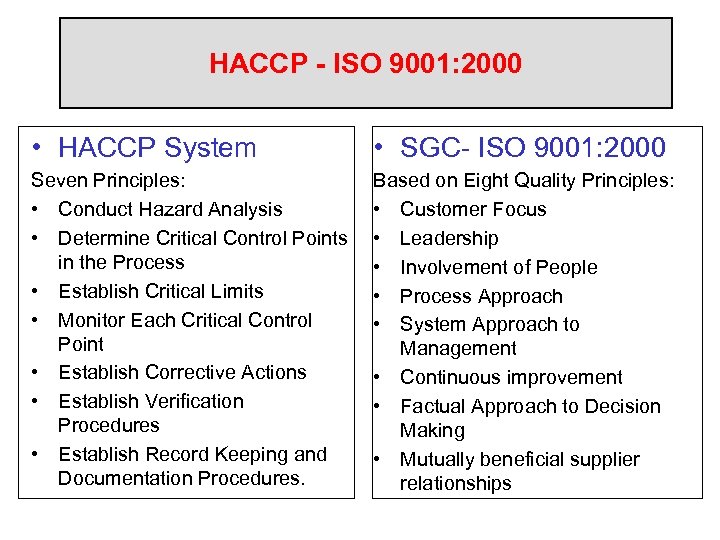 HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 Seven Principles: • Conduct Hazard Analysis • Determine Critical Control Points in the Process • Establish Critical Limits • Monitor Each Critical Control Point • Establish Corrective Actions • Establish Verification Procedures • Establish Record Keeping and Documentation Procedures. Based on Eight Quality Principles: • Customer Focus • Leadership • Involvement of People • Process Approach • System Approach to Management • Continuous improvement • Factual Approach to Decision Making • Mutually beneficial supplier relationships
HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 Seven Principles: • Conduct Hazard Analysis • Determine Critical Control Points in the Process • Establish Critical Limits • Monitor Each Critical Control Point • Establish Corrective Actions • Establish Verification Procedures • Establish Record Keeping and Documentation Procedures. Based on Eight Quality Principles: • Customer Focus • Leadership • Involvement of People • Process Approach • System Approach to Management • Continuous improvement • Factual Approach to Decision Making • Mutually beneficial supplier relationships
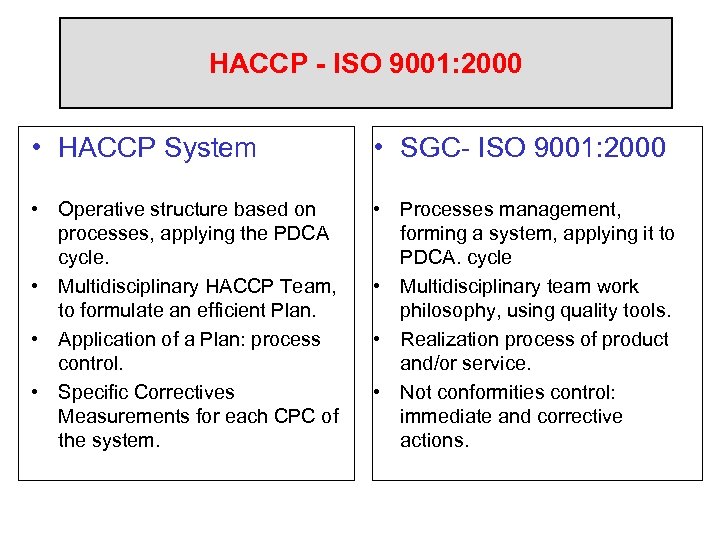 HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 • Operative structure based on processes, applying the PDCA cycle. • Multidisciplinary HACCP Team, to formulate an efficient Plan. • Application of a Plan: process control. • Specific Correctives Measurements for each CPC of the system. • Processes management, forming a system, applying it to PDCA. cycle • Multidisciplinary team work philosophy, using quality tools. • Realization process of product and/or service. • Not conformities control: immediate and corrective actions.
HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 • Operative structure based on processes, applying the PDCA cycle. • Multidisciplinary HACCP Team, to formulate an efficient Plan. • Application of a Plan: process control. • Specific Correctives Measurements for each CPC of the system. • Processes management, forming a system, applying it to PDCA. cycle • Multidisciplinary team work philosophy, using quality tools. • Realization process of product and/or service. • Not conformities control: immediate and corrective actions.
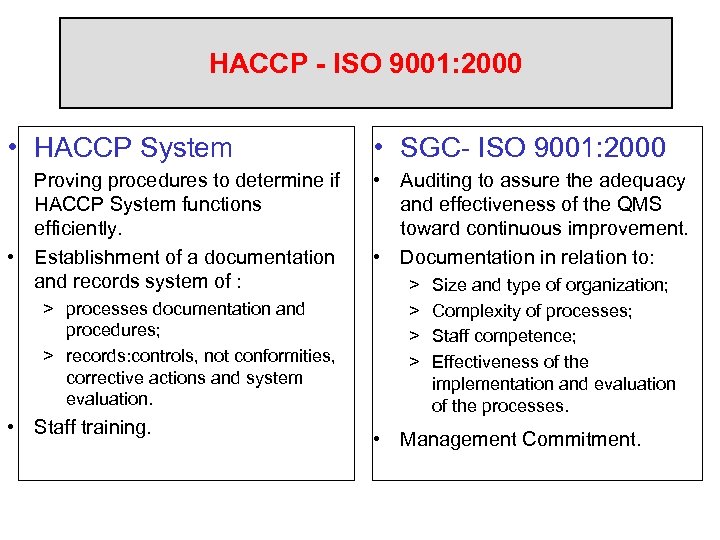 HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 Proving procedures to determine if HACCP System functions efficiently. • Establishment of a documentation and records system of : • Auditing to assure the adequacy and effectiveness of the QMS toward continuous improvement. • Documentation in relation to: > processes documentation and procedures; > records: controls, not conformities, corrective actions and system evaluation. • Staff training. > > Size and type of organization; Complexity of processes; Staff competence; Effectiveness of the implementation and evaluation of the processes. • Management Commitment.
HACCP - ISO 9001: 2000 • HACCP System • SGC- ISO 9001: 2000 Proving procedures to determine if HACCP System functions efficiently. • Establishment of a documentation and records system of : • Auditing to assure the adequacy and effectiveness of the QMS toward continuous improvement. • Documentation in relation to: > processes documentation and procedures; > records: controls, not conformities, corrective actions and system evaluation. • Staff training. > > Size and type of organization; Complexity of processes; Staff competence; Effectiveness of the implementation and evaluation of the processes. • Management Commitment.


