2054f48e3f61fc142cd846635bfe414b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Good Governance and Anti-Corruption Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 1
Good Governance and Anti-Corruption Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 1
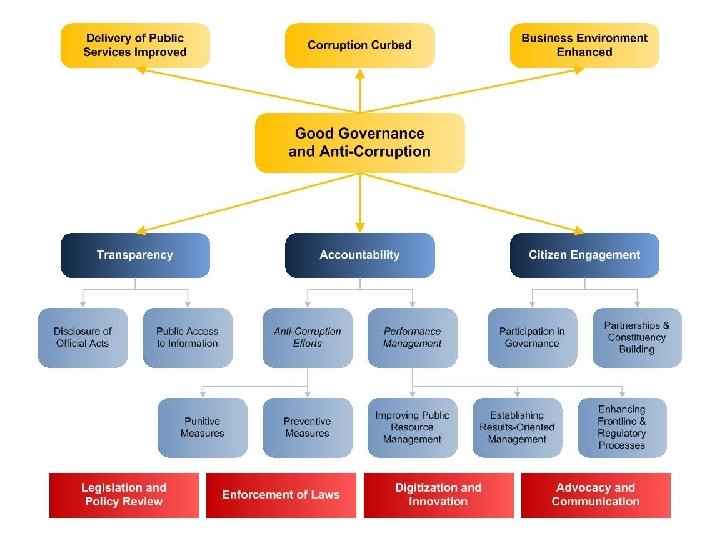
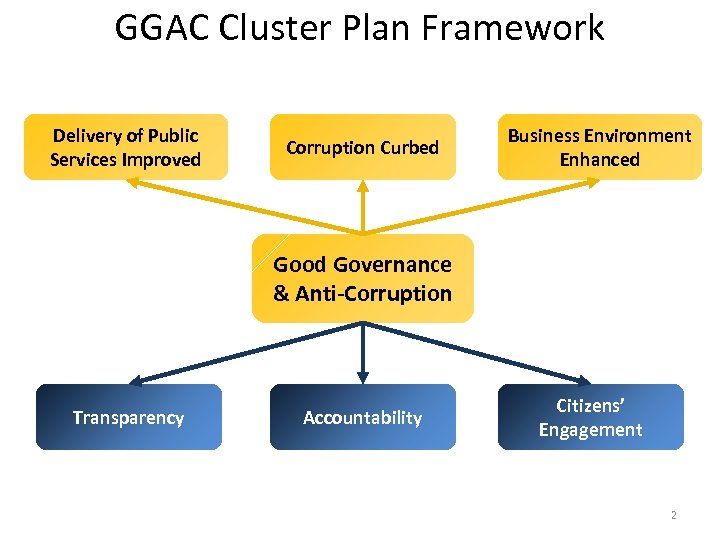 GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Transparency Accountability Citizens’ Engagement 2
GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Transparency Accountability Citizens’ Engagement 2
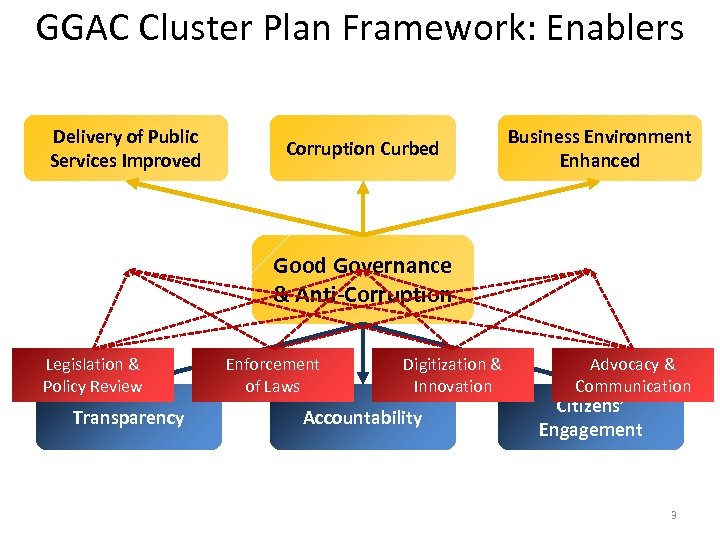 GGAC Cluster Plan Framework: Enablers Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Legislation & Policy Review Transparency Enforcement of Laws Digitization & Innovation Accountability Advocacy & Communication Citizens’ Engagement 3
GGAC Cluster Plan Framework: Enablers Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Legislation & Policy Review Transparency Enforcement of Laws Digitization & Innovation Accountability Advocacy & Communication Citizens’ Engagement 3
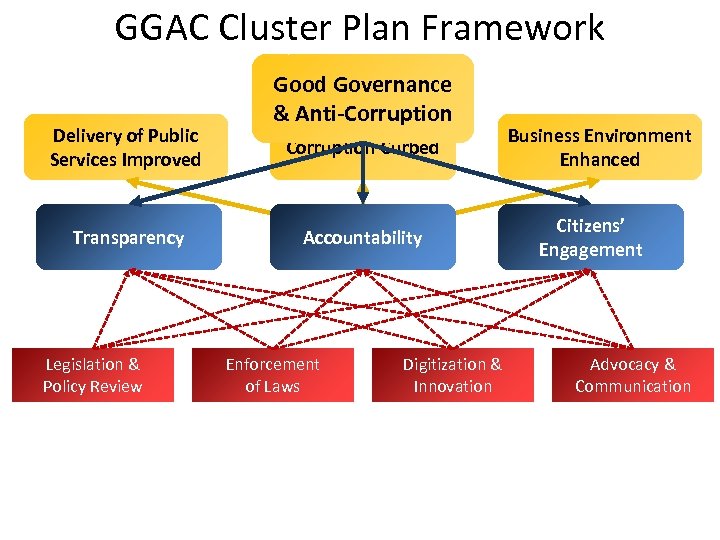 GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Transparency Legislation & Policy Review Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Curbed Accountability Enforcement of Laws Digitization & Innovation Business Environment Enhanced Citizens’ Engagement Advocacy & Communication
GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Transparency Legislation & Policy Review Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Curbed Accountability Enforcement of Laws Digitization & Innovation Business Environment Enhanced Citizens’ Engagement Advocacy & Communication
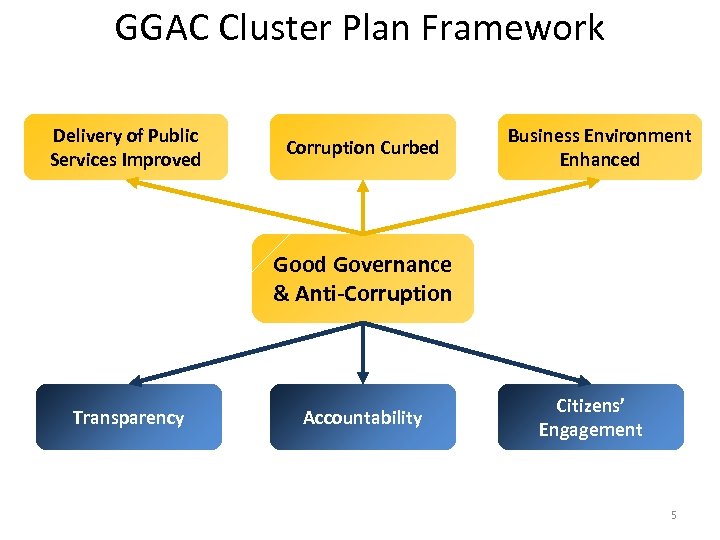 GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Transparency Accountability Citizens’ Engagement 5
GGAC Cluster Plan Framework Delivery of Public Services Improved Corruption Curbed Business Environment Enhanced Good Governance & Anti-Corruption Transparency Accountability Citizens’ Engagement 5
 The GGAC Cluster Plan and the Open Government Partnership GGAC Cluster Plan mother plan for 2012 -2016 Phl Action Plan for OGP 2012 one-year slice of GGAC Cluster Plan 6
The GGAC Cluster Plan and the Open Government Partnership GGAC Cluster Plan mother plan for 2012 -2016 Phl Action Plan for OGP 2012 one-year slice of GGAC Cluster Plan 6
 GGAC Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 & Phil OGP Plan 2012: Stakeholder Consultations Undertaken • Consultation with Cabinet and NGAs – Agencies requested for their inputs to the Action Plan • Consultations with Business Leaders – Primarily Makati Business Club and private sector-side of National Competitiveness Council • Consultations with Civil Society Organizations – Over 10 National Civil Society Organization Networks consulted • Consultation with Development Partners – through Phl Development Forum Governance Working Group • Consultation with Local Government Units – through DILG which consults LGUs on various initiatives 7
GGAC Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 & Phil OGP Plan 2012: Stakeholder Consultations Undertaken • Consultation with Cabinet and NGAs – Agencies requested for their inputs to the Action Plan • Consultations with Business Leaders – Primarily Makati Business Club and private sector-side of National Competitiveness Council • Consultations with Civil Society Organizations – Over 10 National Civil Society Organization Networks consulted • Consultation with Development Partners – through Phl Development Forum Governance Working Group • Consultation with Local Government Units – through DILG which consults LGUs on various initiatives 7
 Good Governance and Anti-Corruption Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 KEY INITIATIVES Note: items with OGP logo (left) are proposed OGP commitments for 2012. 8
Good Governance and Anti-Corruption Cluster Plan 2012 -2016 KEY INITIATIVES Note: items with OGP logo (left) are proposed OGP commitments for 2012. 8
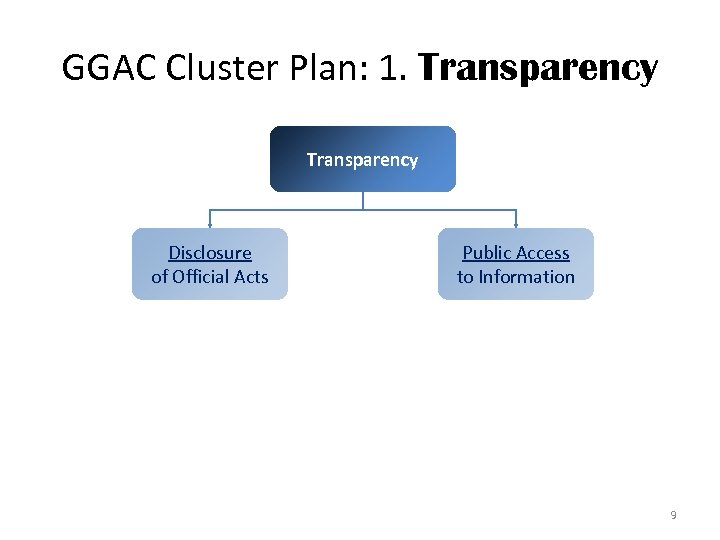 GGAC Cluster Plan: 1. Transparency Disclosure of Official Acts Public Access to Information 9
GGAC Cluster Plan: 1. Transparency Disclosure of Official Acts Public Access to Information 9
 Transparency: Disclosure • Mandatory Disclosure of Budget Info – By 2012, all 24 departments fully complying with the disclosure requirements, from only 4 departments publishing all required info • Full Disclosure Policy for LGUs – By 2012, all LGUs (provinces, cities and municipalities) comply 100% with disclosure standards) 10
Transparency: Disclosure • Mandatory Disclosure of Budget Info – By 2012, all 24 departments fully complying with the disclosure requirements, from only 4 departments publishing all required info • Full Disclosure Policy for LGUs – By 2012, all LGUs (provinces, cities and municipalities) comply 100% with disclosure standards) 10
 Transparency: Disclosure • Expansion of Phl Government Electronic Procurement System (Phil. GEPS) – By 2012, DBM to expand Phil. GEPS to include e-bidding functions (electronic bids submission, supplier registry, virtual store, etc. ) from present bulletin board of bid notices and award • E-Transparency & Accountability Initiative for Lump-sum Funds System (E-TAILS) – By 2012, DBM to expand E-TAILS to include automatic disclosure of School Building Fund and Internal Revenue Allocation, from the present PDAF disclosure. 11
Transparency: Disclosure • Expansion of Phl Government Electronic Procurement System (Phil. GEPS) – By 2012, DBM to expand Phil. GEPS to include e-bidding functions (electronic bids submission, supplier registry, virtual store, etc. ) from present bulletin board of bid notices and award • E-Transparency & Accountability Initiative for Lump-sum Funds System (E-TAILS) – By 2012, DBM to expand E-TAILS to include automatic disclosure of School Building Fund and Internal Revenue Allocation, from the present PDAF disclosure. 11
 Transparency: Disclosure • Increase NGAs compliance with the Anti. Red Tape Act (ARTA), especially the posting of Citizens’ Charters – By 2012, Report Card Survey on front line services conducted by CSC in 433 offices. • Monitor ARTA Compliance of LGUs – BY 2016, 100% of provinces, cities and municipalities comply with the policy 12
Transparency: Disclosure • Increase NGAs compliance with the Anti. Red Tape Act (ARTA), especially the posting of Citizens’ Charters – By 2012, Report Card Survey on front line services conducted by CSC in 433 offices. • Monitor ARTA Compliance of LGUs – BY 2016, 100% of provinces, cities and municipalities comply with the policy 12
 Transparency: Access • Single Portal for Government Info – Official Gazette (gov. ph) to be converted into a one-stop source of information and service delivery within 2012. • Public Access to Information Initiative – By Q 1 2012, GGAC Cluster to review existing info policies and procedures, and craft roadmap to improve access to information across the board – Roadmap to include setting-up of enabling systems (e. g. ICT) and mechanisms (e. g. delegated info officers); and establishing a comprehensive policy on access to info 13
Transparency: Access • Single Portal for Government Info – Official Gazette (gov. ph) to be converted into a one-stop source of information and service delivery within 2012. • Public Access to Information Initiative – By Q 1 2012, GGAC Cluster to review existing info policies and procedures, and craft roadmap to improve access to information across the board – Roadmap to include setting-up of enabling systems (e. g. ICT) and mechanisms (e. g. delegated info officers); and establishing a comprehensive policy on access to info 13
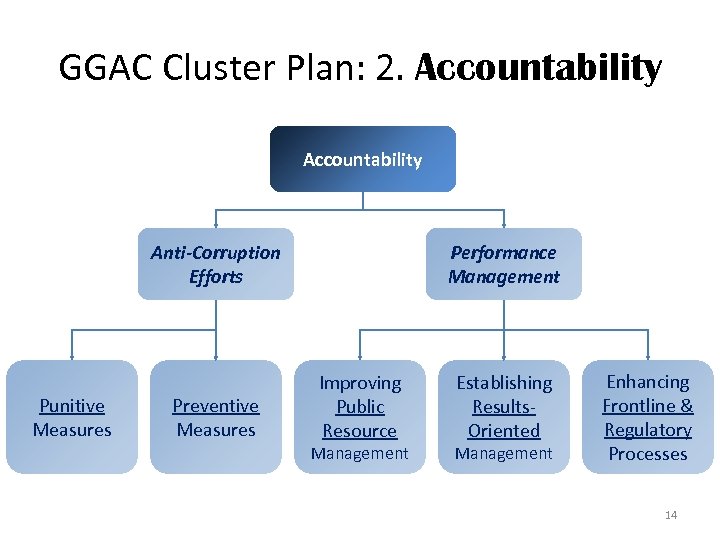 GGAC Cluster Plan: 2. Accountability Anti-Corruption Efforts Punitive Measures Preventive Measures Performance Management Improving Public Resource Management Establishing Results. Oriented Management Enhancing Frontline & Regulatory Processes 14
GGAC Cluster Plan: 2. Accountability Anti-Corruption Efforts Punitive Measures Preventive Measures Performance Management Improving Public Resource Management Establishing Results. Oriented Management Enhancing Frontline & Regulatory Processes 14
 Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Punitive • Speedy Resolution of Corruption Cases, especially Special Cases of Grand Corruption – High profile cases resolved within their prescribed periods – Annual DOJ resolution rate improved to 85% • Revenue Integrity Protection Service – By 2012, increase coverage – Reduce time to complete investigation from 120 to 60 days 15
Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Punitive • Speedy Resolution of Corruption Cases, especially Special Cases of Grand Corruption – High profile cases resolved within their prescribed periods – Annual DOJ resolution rate improved to 85% • Revenue Integrity Protection Service – By 2012, increase coverage – Reduce time to complete investigation from 120 to 60 days 15
 Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Punitive Legislation: • Pass Whistleblower Protection Law • Strengthen Witness Protection Program 16
Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Punitive Legislation: • Pass Whistleblower Protection Law • Strengthen Witness Protection Program 16
 Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Preventive • Strengthen Internal Controls – By 2012, Internal Audit Units in 6 Departments have been organized (on top of the current 14 Departments with Internal Audit Units) – By 2016, National Guidelines on Internal Control Systems and Philippine Government Internal Audit Manual are adopted by all government agencies through capacitybuilding activities. Note: All programs under Transparency & Citizen Engagement Pillars contribute to preventing corruption 17
Accountability (Anti-Corruption): Preventive • Strengthen Internal Controls – By 2012, Internal Audit Units in 6 Departments have been organized (on top of the current 14 Departments with Internal Audit Units) – By 2016, National Guidelines on Internal Control Systems and Philippine Government Internal Audit Manual are adopted by all government agencies through capacitybuilding activities. Note: All programs under Transparency & Citizen Engagement Pillars contribute to preventing corruption 17
 Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management • Institutionalize Public Financial and Expenditure Management Reforms – Zero Based Budgeting – Medium-Term Expenditure Framework – Organizational Performance Indicator Framework • Develop a Government Integrated Financial Management System (GIFMIS) – By 2012, core system (single platform for information sharing between COA, DBM and BTr) developed. – By 2016, full implementation of GIFMIS in all agencies 18
Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management • Institutionalize Public Financial and Expenditure Management Reforms – Zero Based Budgeting – Medium-Term Expenditure Framework – Organizational Performance Indicator Framework • Develop a Government Integrated Financial Management System (GIFMIS) – By 2012, core system (single platform for information sharing between COA, DBM and BTr) developed. – By 2016, full implementation of GIFMIS in all agencies 18
 Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management Various ICT Projects • Government Manpower Info System (GMIS) and National Payroll System – DBM is developing the National Payroll System, piloted in COA, DBM and DOF-BTR in the 3 rd quarter. Other agencies (e. g. Dep. Ed, DPWH, AFP, PNP) to adopt within the year. • Cashless Purchase Cards – DBM to pilot cashless purchase card system in DBM, AFP and several other agencies within the year. 19
Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management Various ICT Projects • Government Manpower Info System (GMIS) and National Payroll System – DBM is developing the National Payroll System, piloted in COA, DBM and DOF-BTR in the 3 rd quarter. Other agencies (e. g. Dep. Ed, DPWH, AFP, PNP) to adopt within the year. • Cashless Purchase Cards – DBM to pilot cashless purchase card system in DBM, AFP and several other agencies within the year. 19
 Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management Various ICT Projects: • Develop a Registry System for Basic Sectors in Agriculture (RSBSA) – By 2012, NSO maps 54 provinces and 3. 5 M farmers. All provinces mapped by 2013 – MOA between DBM, DAR and NSO forged • On-line X-ray Imaging System – By 2012, system piloted at the Port of Manila and Manila International Container Port • Petroleum Inventory System – By 2012, system implemented at Subic 20
Accountability (Performance): Public Resource Management Various ICT Projects: • Develop a Registry System for Basic Sectors in Agriculture (RSBSA) – By 2012, NSO maps 54 provinces and 3. 5 M farmers. All provinces mapped by 2013 – MOA between DBM, DAR and NSO forged • On-line X-ray Imaging System – By 2012, system piloted at the Port of Manila and Manila International Container Port • Petroleum Inventory System – By 2012, system implemented at Subic 20
 Accountability (Performance): Results-Oriented Management • Harmonize Government Performance Management Systems – AO 25 creates a Task Force to develop Results-Based Performance Management System in six months • Embed Accountability in LGUs – By 2012, 689 LGUs w/ Seal of Good Housekeeping are able to access the Performance Challenge Fund – All LGUs assessed for their eligibility for the Seal of Good Housekeeping. 21
Accountability (Performance): Results-Oriented Management • Harmonize Government Performance Management Systems – AO 25 creates a Task Force to develop Results-Based Performance Management System in six months • Embed Accountability in LGUs – By 2012, 689 LGUs w/ Seal of Good Housekeeping are able to access the Performance Challenge Fund – All LGUs assessed for their eligibility for the Seal of Good Housekeeping. 21
 Accountability (Performance): Results-Oriented Management • National Justice Information System – Phase I (2012 -2015): database systems of law enforcement, prosecution and corrections agencies of DOJ are established and/or interconnected • By 2012, criminal database systems among National Prosecution Service, National Bureau of Investigation and Bureau of Immigration established • President directed that systems for PNP and NBI Clearances be integrated – Phase II starting 2015: Databases with other criminal justice agencies (PNP, PDEA, BJMP, Judiciary, etc) are interconnected. 22
Accountability (Performance): Results-Oriented Management • National Justice Information System – Phase I (2012 -2015): database systems of law enforcement, prosecution and corrections agencies of DOJ are established and/or interconnected • By 2012, criminal database systems among National Prosecution Service, National Bureau of Investigation and Bureau of Immigration established • President directed that systems for PNP and NBI Clearances be integrated – Phase II starting 2015: Databases with other criminal justice agencies (PNP, PDEA, BJMP, Judiciary, etc) are interconnected. 22
 Accountability (Performance): Frontline and Regulatory Processes • Streamline Business Permits and Licensing – By 2012, an additional 227 LGUs adopt reforms in Business Permits and Licensing Systems – By 2016, total of 1, 634 LGUs to adopt reforms • Enhance Quality of Public Service in Tourism – By 2012, craft a roadmap to improve the frontline systems and procedures involved in the tourism sector, from arrival of tourists to their departure. • Pursue National Competition Policy – Enactment of an Anti-Trust Law – Recently-established Competition Authority in DOJ pursues 23 prosecution and resolution of anti-trust cases
Accountability (Performance): Frontline and Regulatory Processes • Streamline Business Permits and Licensing – By 2012, an additional 227 LGUs adopt reforms in Business Permits and Licensing Systems – By 2016, total of 1, 634 LGUs to adopt reforms • Enhance Quality of Public Service in Tourism – By 2012, craft a roadmap to improve the frontline systems and procedures involved in the tourism sector, from arrival of tourists to their departure. • Pursue National Competition Policy – Enactment of an Anti-Trust Law – Recently-established Competition Authority in DOJ pursues 23 prosecution and resolution of anti-trust cases
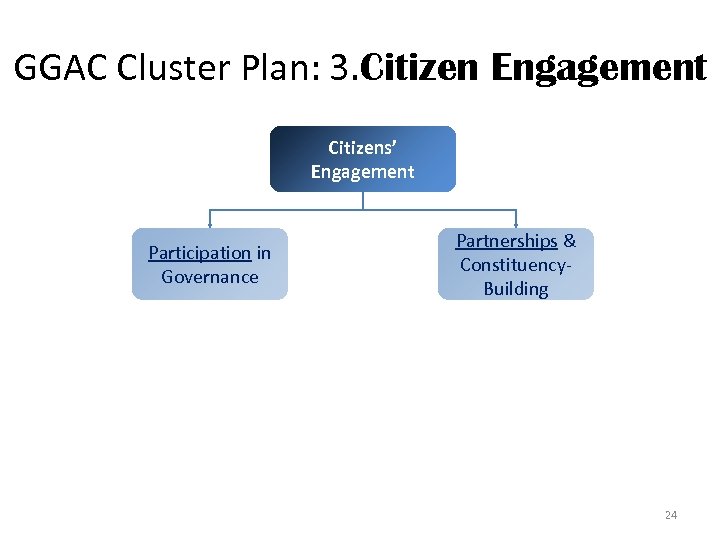 GGAC Cluster Plan: 3. Citizen Engagement Citizens’ Engagement Participation in Governance Partnerships & Constituency. Building 24
GGAC Cluster Plan: 3. Citizen Engagement Citizens’ Engagement Participation in Governance Partnerships & Constituency. Building 24
 Citizen Engagement: Participatory Governance • CSO Engagement in Budget Process – For 2012: NGAs and GOCCs implementing the consultative budget preparation process doubled to 12 & 6 – Guidelines for CSO participation in all phases of the budget developed and implemented • Bottom-Up Planning & Budgeting – In preparing the 2013 national budget, 609 city/municipal will come up with their Local Poverty Reduction Action Plans and the priority projects included in the departments’ budget. • P 250 -M Empowerment Fund Established 25
Citizen Engagement: Participatory Governance • CSO Engagement in Budget Process – For 2012: NGAs and GOCCs implementing the consultative budget preparation process doubled to 12 & 6 – Guidelines for CSO participation in all phases of the budget developed and implemented • Bottom-Up Planning & Budgeting – In preparing the 2013 national budget, 609 city/municipal will come up with their Local Poverty Reduction Action Plans and the priority projects included in the departments’ budget. • P 250 -M Empowerment Fund Established 25
 Citizen Engagement: Participatory Governance • Institutionalize Participatory Audits Infrastructure Projects for – By 2012, participatory audits jointly undertaken by COA and CSOs in select projects of the DPWH and DA • Pera ng Bayan website – Tips reported through the website resulted in filing of 16 cases (vs. smugglers, tax evaders, erring revenue officers) • Budget ng Bayan website – By 2012, DBM will develop and implement the website 26
Citizen Engagement: Participatory Governance • Institutionalize Participatory Audits Infrastructure Projects for – By 2012, participatory audits jointly undertaken by COA and CSOs in select projects of the DPWH and DA • Pera ng Bayan website – Tips reported through the website resulted in filing of 16 cases (vs. smugglers, tax evaders, erring revenue officers) • Budget ng Bayan website – By 2012, DBM will develop and implement the website 26
 Citizen Engagement: Partnerships & Constituency-Building • International: Active participation and leadership in OGP as Steering Committee Member • Domestic: Convene a Philippine OGP – Broad coalition of government, CSO and private sector – Philippine OGP Assembly to be held in 2012 27
Citizen Engagement: Partnerships & Constituency-Building • International: Active participation and leadership in OGP as Steering Committee Member • Domestic: Convene a Philippine OGP – Broad coalition of government, CSO and private sector – Philippine OGP Assembly to be held in 2012 27
 Citizen Engagement: Partnerships & Constituency-Building • Implement Integrity Initiative with Business – By 2012, Industry Integrity pact signed – By 2014, Unified standard on Integrity and Corporate Governance (including accreditation system) created • CSOs - People's Participation Partnership for LGUs – By 2012, DILG to develop and implements Citizens’ Satisfaction and Index System – By 2012, CSO Participation Fund established 28
Citizen Engagement: Partnerships & Constituency-Building • Implement Integrity Initiative with Business – By 2012, Industry Integrity pact signed – By 2014, Unified standard on Integrity and Corporate Governance (including accreditation system) created • CSOs - People's Participation Partnership for LGUs – By 2012, DILG to develop and implements Citizens’ Satisfaction and Index System – By 2012, CSO Participation Fund established 28
 Thank you! 29
Thank you! 29


