eb747188acadc36ce61f582e35018f0d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86
 Good Clinical Practice (GCP) A whistle stop tour! St George’s University of London, UK Debbie Rolfe Regulatory Assurance Manager, Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) A whistle stop tour! St George’s University of London, UK Debbie Rolfe Regulatory Assurance Manager, Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 What is GCP? Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is an international ethical scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording and reporting trials that involve the participation of human subjects. . Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
What is GCP? Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is an international ethical scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording and reporting trials that involve the participation of human subjects. . Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 What is GCP? The objective of ICH GCP is to provide a unified standard for - USA - European Union - Japan To facilitate the mutual acceptance of clinical data by the regulatory authorities in these jurisdictions. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
What is GCP? The objective of ICH GCP is to provide a unified standard for - USA - European Union - Japan To facilitate the mutual acceptance of clinical data by the regulatory authorities in these jurisdictions. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 13 Principles of GCP 1. Ethical Principles of Declaration of Helsinki 8. Researcher training, education and experience 2. Benefit justifies risk 9. Freely given informed consent 3. Rights, safety, wellbeing 4. Adequate information to support trial 10. Accurate data handling and storage 5. Clear, scientifically sound protocol 6. Favourable ethics approval 7. 11. Data Protection and confidentiality 12. Good Manufacturing Practice 13. Quality assurance systems Qualified Chief Investigator ICH GCP Section 2 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
13 Principles of GCP 1. Ethical Principles of Declaration of Helsinki 8. Researcher training, education and experience 2. Benefit justifies risk 9. Freely given informed consent 3. Rights, safety, wellbeing 4. Adequate information to support trial 10. Accurate data handling and storage 5. Clear, scientifically sound protocol 6. Favourable ethics approval 7. 11. Data Protection and confidentiality 12. Good Manufacturing Practice 13. Quality assurance systems Qualified Chief Investigator ICH GCP Section 2 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 What is a clinical trial? ICH GCP 1. 13: Any investigation in human subjects intended to discover or verify the clinical, pharmacological and/or pharmacodynamic effects of an investigational product and/or to identify any adverse reactions to an investigational product, and/or to study absorption; distribution; metabolism; and excretion of an investigational product with the object of ascertaining its safety and efficacy. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
What is a clinical trial? ICH GCP 1. 13: Any investigation in human subjects intended to discover or verify the clinical, pharmacological and/or pharmacodynamic effects of an investigational product and/or to identify any adverse reactions to an investigational product, and/or to study absorption; distribution; metabolism; and excretion of an investigational product with the object of ascertaining its safety and efficacy. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 1 • Clinical Trials should be conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, that are consistent with GCP and the applicable regulatory requirements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 1 • Clinical Trials should be conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, that are consistent with GCP and the applicable regulatory requirements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 DECLARATION OF HELSINKI • • Leading international ethical standard 1 st adopted in 1964 – 7 revisions current 2013 The Declaration provides guidance for research on humans, their material and/or their data: – Safeguarding research participants – Adhering to an approved research protocol – Benefits > risks – Full informed consent, including assent where appropriate – Publishing findings – Use of placebos – Post-trial access to treatment Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
DECLARATION OF HELSINKI • • Leading international ethical standard 1 st adopted in 1964 – 7 revisions current 2013 The Declaration provides guidance for research on humans, their material and/or their data: – Safeguarding research participants – Adhering to an approved research protocol – Benefits > risks – Full informed consent, including assent where appropriate – Publishing findings – Use of placebos – Post-trial access to treatment Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
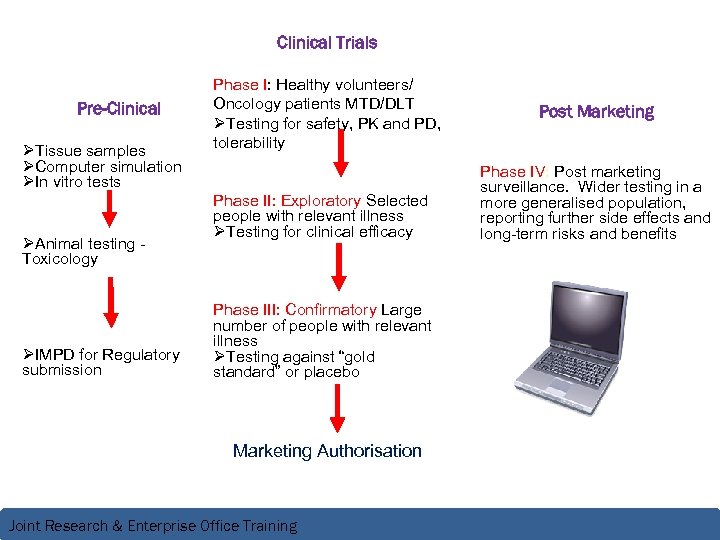 Clinical Trials Pre-Clinical ØTissue samples ØComputer simulation ØIn vitro tests ØAnimal testing Toxicology ØIMPD for Regulatory submission Phase I: Healthy volunteers/ Oncology patients MTD/DLT ØTesting for safety, PK and PD, tolerability Phase II: Exploratory Selected people with relevant illness ØTesting for clinical efficacy Phase III: Confirmatory Large number of people with relevant illness ØTesting against “gold standard” or placebo Marketing Authorisation Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training Post Marketing Phase IV: Post marketing surveillance. Wider testing in a more generalised population, reporting further side effects and long-term risks and benefits
Clinical Trials Pre-Clinical ØTissue samples ØComputer simulation ØIn vitro tests ØAnimal testing Toxicology ØIMPD for Regulatory submission Phase I: Healthy volunteers/ Oncology patients MTD/DLT ØTesting for safety, PK and PD, tolerability Phase II: Exploratory Selected people with relevant illness ØTesting for clinical efficacy Phase III: Confirmatory Large number of people with relevant illness ØTesting against “gold standard” or placebo Marketing Authorisation Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training Post Marketing Phase IV: Post marketing surveillance. Wider testing in a more generalised population, reporting further side effects and long-term risks and benefits
 Principle 2 • Before a trial is initiated, foreseeable risks and inconveniences should be weighed against anticipated benefit for the individual trial subject and society. A trial should be initiated and continued only if the anticipated benefits justify the risks Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 2 • Before a trial is initiated, foreseeable risks and inconveniences should be weighed against anticipated benefit for the individual trial subject and society. A trial should be initiated and continued only if the anticipated benefits justify the risks Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 3 • Rights , safety and well-being of the trial subjects are the most important considerations and should prevail over interests of science and society Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 3 • Rights , safety and well-being of the trial subjects are the most important considerations and should prevail over interests of science and society Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 4 • The available non-clinical and clinical information on an investigational product should be adequate to support the proposed clinical trial Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 4 • The available non-clinical and clinical information on an investigational product should be adequate to support the proposed clinical trial Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 5 • Clinical trials should be scientifically sound, and described in a clear, detailed protocol Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 5 • Clinical trials should be scientifically sound, and described in a clear, detailed protocol Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 6 • A trial should be conducted in compliance with the protocol that has received prior institutional review board (IRB)/ Independent ethics committee (IEC) approval/ favourable opinion. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 6 • A trial should be conducted in compliance with the protocol that has received prior institutional review board (IRB)/ Independent ethics committee (IEC) approval/ favourable opinion. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 7 • The medical care given to, and medical decisions made on behalf of, subjects should always be the responsibility of a qualified physician or, where appropriate, of a qualified dentist. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 7 • The medical care given to, and medical decisions made on behalf of, subjects should always be the responsibility of a qualified physician or, where appropriate, of a qualified dentist. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 8 • Each individual in conducting a trial should be qualified by education, training, and experience to perform his or her respective tasks. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 8 • Each individual in conducting a trial should be qualified by education, training, and experience to perform his or her respective tasks. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Role of the IRB/REC • Who are the ethics committee/ Review board? Ø At least 5 members with at least 1 non-scientific member, at least 1 member independent of trial site or institution can be clinicians, nurses, pharmacists and other interested parties • Ethical approval: Ø Gives balanced independent view of research following review of the trial protocol, information provided to the subjects, subject recruitment procedures e. g. advertisements, informed consent forms and proposed process and available safety information Ø Ensures Investigator suitable qualified and experienced Ø Clear documented approval listing documents and version numbers approved for use ial subjects well being of all tr rights, safety and safeguard the An IRB/IEC should. ICH GCP: 3. 1. 1 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Role of the IRB/REC • Who are the ethics committee/ Review board? Ø At least 5 members with at least 1 non-scientific member, at least 1 member independent of trial site or institution can be clinicians, nurses, pharmacists and other interested parties • Ethical approval: Ø Gives balanced independent view of research following review of the trial protocol, information provided to the subjects, subject recruitment procedures e. g. advertisements, informed consent forms and proposed process and available safety information Ø Ensures Investigator suitable qualified and experienced Ø Clear documented approval listing documents and version numbers approved for use ial subjects well being of all tr rights, safety and safeguard the An IRB/IEC should. ICH GCP: 3. 1. 1 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 9 • Freely given informed consent should be obtained from every subject prior to clinical trial participation. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 9 • Freely given informed consent should be obtained from every subject prior to clinical trial participation. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Informed Consent “a process by which a participant voluntarily confirms his or her willingness to participate in a particular trial, after having been informed of all aspects of the trial that are relevant to the participant’s decision to participate. Informed consent is documented by means of a written, signed and dated consent form” ICH GCP Section 1. 28 • • Must be obtained before any research related activity occurs Copy to participant, copy in ISF and original in medical notes Continuous process throughout the study. What if consent is withdrawn? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Informed Consent “a process by which a participant voluntarily confirms his or her willingness to participate in a particular trial, after having been informed of all aspects of the trial that are relevant to the participant’s decision to participate. Informed consent is documented by means of a written, signed and dated consent form” ICH GCP Section 1. 28 • • Must be obtained before any research related activity occurs Copy to participant, copy in ISF and original in medical notes Continuous process throughout the study. What if consent is withdrawn? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
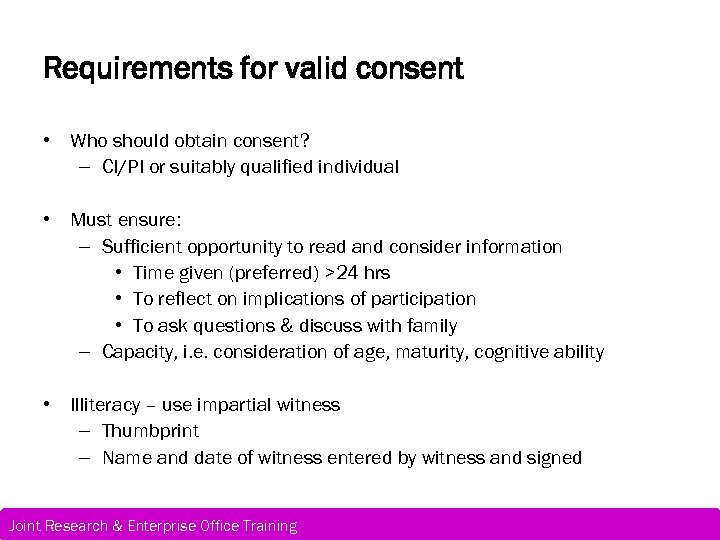 Requirements for valid consent • Who should obtain consent? – CI/PI or suitably qualified individual • Must ensure: – Sufficient opportunity to read and consider information • Time given (preferred) >24 hrs • To reflect on implications of participation • To ask questions & discuss with family – Capacity, i. e. consideration of age, maturity, cognitive ability • Illiteracy – use impartial witness – Thumbprint – Name and date of witness entered by witness and signed Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Requirements for valid consent • Who should obtain consent? – CI/PI or suitably qualified individual • Must ensure: – Sufficient opportunity to read and consider information • Time given (preferred) >24 hrs • To reflect on implications of participation • To ask questions & discuss with family – Capacity, i. e. consideration of age, maturity, cognitive ability • Illiteracy – use impartial witness – Thumbprint – Name and date of witness entered by witness and signed Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Adults without Capacity • • Mental Illness / Mental Disability / Brain Damage Country-specific regulations – Legally designated person to give consent for another adult – Hierarchy: 1. Personal legal representative • Suitable by virtue of relationship • Willing 2. Professional legal representative • Not connected with study • Primarily responsible for person’s medical care OR • Nominated by relevant health care provider Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Adults without Capacity • • Mental Illness / Mental Disability / Brain Damage Country-specific regulations – Legally designated person to give consent for another adult – Hierarchy: 1. Personal legal representative • Suitable by virtue of relationship • Willing 2. Professional legal representative • Not connected with study • Primarily responsible for person’s medical care OR • Nominated by relevant health care provider Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Requirements for valid Unconscious Patients consent • Research should relate directly to life-threatening condition of participant • Legal representative (personal or professional) to give consent • Waiver accepted if allowed by IEC/IRB • Emergency research should be re-consented – Follow-up Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Requirements for valid Unconscious Patients consent • Research should relate directly to life-threatening condition of participant • Legal representative (personal or professional) to give consent • Waiver accepted if allowed by IEC/IRB • Emergency research should be re-consented – Follow-up Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Assent of Minors • Only research that directly relates to the child’s clinical condition should be conducted • Parent’s signature sufficient in law – Best practice: assent of child (if deemed competent) – Assent is not legally binding, however, favoured by ethics committees • Child should be involved as much as possible – use of age related information sheets • Parental consent should reflect wishes of the child, these may overrule parents’ wishes Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Assent of Minors • Only research that directly relates to the child’s clinical condition should be conducted • Parent’s signature sufficient in law – Best practice: assent of child (if deemed competent) – Assent is not legally binding, however, favoured by ethics committees • Child should be involved as much as possible – use of age related information sheets • Parental consent should reflect wishes of the child, these may overrule parents’ wishes Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Inspection Findings • Missing consent forms – not possible to verify subjects had consented • Lack of subject or Investigator signature to demonstrate agreement to participate • Unapproved consent form used • Consent form referencing wrong Patient information sheet • Consent taken by persons not listed on delegation log – therefore no evidence of training to obtain consent Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Inspection Findings • Missing consent forms – not possible to verify subjects had consented • Lack of subject or Investigator signature to demonstrate agreement to participate • Unapproved consent form used • Consent form referencing wrong Patient information sheet • Consent taken by persons not listed on delegation log – therefore no evidence of training to obtain consent Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 10 • All clinical trial information should be recorded, handled, and stored in a way that allows its accurate reporting, interpretation and verification Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 10 • All clinical trial information should be recorded, handled, and stored in a way that allows its accurate reporting, interpretation and verification Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Essential Documents Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Essential Documents Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 What are Essential Documents? “Essential documents are those which individually and collectively permit evaluation of the conduct of a trial and the quality of the data produced. These documents serve to demonstrate the compliance of the investigator, sponsor and monitor with the standards of Good Clinical Practice and with all applicable regulatory requirements. ” Filing essential documents in a timely manner greatly assists in the successful management of a trial by the investigator, Sponsor and monitor. Normally it will be these documents that are inspected by the regulatory authorities as part of the process to confirm the validity of the trial conduct and integrity of the data collected ICH GCP Section 8 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
What are Essential Documents? “Essential documents are those which individually and collectively permit evaluation of the conduct of a trial and the quality of the data produced. These documents serve to demonstrate the compliance of the investigator, sponsor and monitor with the standards of Good Clinical Practice and with all applicable regulatory requirements. ” Filing essential documents in a timely manner greatly assists in the successful management of a trial by the investigator, Sponsor and monitor. Normally it will be these documents that are inspected by the regulatory authorities as part of the process to confirm the validity of the trial conduct and integrity of the data collected ICH GCP Section 8 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Why Bother? • First thing inspectors, auditors & monitors look at • Organises the paperwork – Saves time – Saves effort – Facilitates organisation of the study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Why Bother? • First thing inspectors, auditors & monitors look at • Organises the paperwork – Saves time – Saves effort – Facilitates organisation of the study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Trial Master File • Trial master files should be established at the beginning of the trial BOTH at the Investigator site and at the Sponsor office • Essential documents are generally grouped in 3 stages of the trial (normally where generated) – Prior to Clinical phase – Clinical conduct – Following completion/ trial termination • Description & purpose of each document and whether kept at Sponsor office or Investigator site or both is described in ICH GCP Section 8. 2 -8. 4 • All documents described should be subject to and available for audit by the Sponsor’s monitor and inspection by the regulatory authorities Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Trial Master File • Trial master files should be established at the beginning of the trial BOTH at the Investigator site and at the Sponsor office • Essential documents are generally grouped in 3 stages of the trial (normally where generated) – Prior to Clinical phase – Clinical conduct – Following completion/ trial termination • Description & purpose of each document and whether kept at Sponsor office or Investigator site or both is described in ICH GCP Section 8. 2 -8. 4 • All documents described should be subject to and available for audit by the Sponsor’s monitor and inspection by the regulatory authorities Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 11 • Confidentiality of records that could identify subjects should be protected, respecting the privacy and confidentiality rules in accordance with the applicable regulatory requirements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 11 • Confidentiality of records that could identify subjects should be protected, respecting the privacy and confidentiality rules in accordance with the applicable regulatory requirements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC • Was created to regulate the progression of personal data within the European Union and is part of the EU privacy and human rights law. • • • New EU data protection regulation (draft) To harmonise current data protection laws across the EU member states. Regulation means it will be directly applicable to all EU member states without need for national implementing legislation. 2012/0011(COD) Awaiting council 1 st reading position • – http: //www. europarl. europa. eu/registre/docs_autres_institutions/commission_europeenne/co m/2012/0011/COM_COM%282012%290011_EN. pdf Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC • Was created to regulate the progression of personal data within the European Union and is part of the EU privacy and human rights law. • • • New EU data protection regulation (draft) To harmonise current data protection laws across the EU member states. Regulation means it will be directly applicable to all EU member states without need for national implementing legislation. 2012/0011(COD) Awaiting council 1 st reading position • – http: //www. europarl. europa. eu/registre/docs_autres_institutions/commission_europeenne/co m/2012/0011/COM_COM%282012%290011_EN. pdf Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Investigator Site File • • • Contact Lists Protocol and any Amendments Ethics and Regulatory Approvals Participant Information Sheets and Consent forms Agreements and contracts Delegation & duty Logs Participant master file – Participant ID log Data Management Case Report Forms Serious Adverse Events Correspondence and Communication (both Sponsor and Internal Team meetings) Study specific SOPs & Training logs Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Investigator Site File • • • Contact Lists Protocol and any Amendments Ethics and Regulatory Approvals Participant Information Sheets and Consent forms Agreements and contracts Delegation & duty Logs Participant master file – Participant ID log Data Management Case Report Forms Serious Adverse Events Correspondence and Communication (both Sponsor and Internal Team meetings) Study specific SOPs & Training logs Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Protocol A document that describes the objective(s), design, methodology, statistical considerations and organisation of a trial. The protocol usually also gives the background and rationale for the trial, but these could be provided in other protocol referenced documents. ICH GCP 1. 44 Contents of a protocol are suggested in ICH GCP Section 6 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Protocol A document that describes the objective(s), design, methodology, statistical considerations and organisation of a trial. The protocol usually also gives the background and rationale for the trial, but these could be provided in other protocol referenced documents. ICH GCP 1. 44 Contents of a protocol are suggested in ICH GCP Section 6 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Document Control • All documents should have: – Version number – Date • Standard numbering system – Ensures only current ethically approved version in use – Format consistent • e. g. v 1. 1; 27/09/2010 DRAFT – Method/ approved procedure for amending version numbers • Approval and distribution procedures defined Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Document Control • All documents should have: – Version number – Date • Standard numbering system – Ensures only current ethically approved version in use – Format consistent • e. g. v 1. 1; 27/09/2010 DRAFT – Method/ approved procedure for amending version numbers • Approval and distribution procedures defined Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Amendments Substantial An amendment to the protocol or any other supporting documentation that is likely to affect to a significant degree the: 1. 2. 3. Safety or physical or mental integrity of the trial subjects Scientific value of the trial Conduct or management of the trial Non-substantial • Requires notification only (e. g. typos, amending members of research teams except CI & PIs) • Retain all documents in the ISF/TMF – documents that are no longer approved for use MUST be clearly marked as superseded • Pharmacy MUST be included on the circulation list of approved Protocols, updated Reference Safety Information Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
Amendments Substantial An amendment to the protocol or any other supporting documentation that is likely to affect to a significant degree the: 1. 2. 3. Safety or physical or mental integrity of the trial subjects Scientific value of the trial Conduct or management of the trial Non-substantial • Requires notification only (e. g. typos, amending members of research teams except CI & PIs) • Retain all documents in the ISF/TMF – documents that are no longer approved for use MUST be clearly marked as superseded • Pharmacy MUST be included on the circulation list of approved Protocols, updated Reference Safety Information Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Inspection Findings • Lack of essential docs e. g. IMP shipment receipt, blood sample shipments to central labs • Incomplete trial subject screening lists • Missing source documents • Discrepancies between source data and data reported in Clinical Study Report • Lack of evidence of Sponsor SOP use • Poor document control – documents not superseded/removed from circulation update Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Inspection Findings • Lack of essential docs e. g. IMP shipment receipt, blood sample shipments to central labs • Incomplete trial subject screening lists • Missing source documents • Discrepancies between source data and data reported in Clinical Study Report • Lack of evidence of Sponsor SOP use • Poor document control – documents not superseded/removed from circulation update Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 12 • Investigational products should be manufactured, handled and stored in accordance with applicable good manufacturing practice (GMP). They should be used in accordance with the approved protocol. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 12 • Investigational products should be manufactured, handled and stored in accordance with applicable good manufacturing practice (GMP). They should be used in accordance with the approved protocol. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 PHARMACY ! • All IMPs (including comparators and placebo) is manufactured in accordance with any applicable GMP and is coded, labelled in a manner that protects the blinding and in accordance with applicable regulatory requirements. • Decoding/unblinding of treatment in case of medical emergency • Storage temperatures, storage conditions e. g. Protect from light, reconstitution fluids and procedures and stability information. • IMP accountability and chain of custody details Sponsors responsibility ICH GCP 5. 12 -5. 14 Recommend to include your Pharmacy department early on! Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
PHARMACY ! • All IMPs (including comparators and placebo) is manufactured in accordance with any applicable GMP and is coded, labelled in a manner that protects the blinding and in accordance with applicable regulatory requirements. • Decoding/unblinding of treatment in case of medical emergency • Storage temperatures, storage conditions e. g. Protect from light, reconstitution fluids and procedures and stability information. • IMP accountability and chain of custody details Sponsors responsibility ICH GCP 5. 12 -5. 14 Recommend to include your Pharmacy department early on! Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Pharmacy Site File – • • • RSI -IB IMPD or Summary of Product Characteristics (Sm. PC) Protocol and Amendments Submission and approval documentation in accordance with local & regional requirements Approved label (Annexe 13) Template Certificate of Analysis IMP QP release Instructions for Use Dose & administration Approved prescription template & copies of participant prescriptions Approved prescribers signature samples Recommended storage conditions Training log • • • Delivery notes Drug accountability forms Chain of Custody Treatment Allocation. Participant lists Drug destruction procedure Drug destruction log Code break Procedure Pharmacy delegation log Contact Lists Correspondence & communications Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Pharmacy Site File – • • • RSI -IB IMPD or Summary of Product Characteristics (Sm. PC) Protocol and Amendments Submission and approval documentation in accordance with local & regional requirements Approved label (Annexe 13) Template Certificate of Analysis IMP QP release Instructions for Use Dose & administration Approved prescription template & copies of participant prescriptions Approved prescribers signature samples Recommended storage conditions Training log • • • Delivery notes Drug accountability forms Chain of Custody Treatment Allocation. Participant lists Drug destruction procedure Drug destruction log Code break Procedure Pharmacy delegation log Contact Lists Correspondence & communications Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Product Accountability • Should determine: – Storage temperatures – Storage conditions ICH GCP Section 5. 19 – Storage times – Reconstitution fluids and procedures – Devices for infusion • Site should receive appropriate instructions • Document shipment, receipt, delivery, distribution- dispensing, Subject returned IMP and destruction ICH GCP Section 5. 13 -5. 14 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Product Accountability • Should determine: – Storage temperatures – Storage conditions ICH GCP Section 5. 19 – Storage times – Reconstitution fluids and procedures – Devices for infusion • Site should receive appropriate instructions • Document shipment, receipt, delivery, distribution- dispensing, Subject returned IMP and destruction ICH GCP Section 5. 13 -5. 14 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Risk Adaptive Approach ~(UK) • Type A – Routine prescribing on licensed IMPs (or established off-label use supported by published evidence/guidelines) • Type B – licensed IMP – new indication, substantial dose modifications, combinations in which interactions are suspected • Type C – Unlicensed IMPs in any EU MS Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Risk Adaptive Approach ~(UK) • Type A – Routine prescribing on licensed IMPs (or established off-label use supported by published evidence/guidelines) • Type B – licensed IMP – new indication, substantial dose modifications, combinations in which interactions are suspected • Type C – Unlicensed IMPs in any EU MS Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Principle 13 • Systems with procedures that assure the quality of every aspect of the trial should be implemented. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Principle 13 • Systems with procedures that assure the quality of every aspect of the trial should be implemented. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Trial Management Group (TMG) • Every trial should have a TMG • Normally includes individuals who are responsible for the day to day management of the trial – CI – Trial manager – Statistician – Research nurse – Data manager • Role is to: – Monitor conduct and progress of the trial – Ensure that the protocol is adhered to – Take appropriate action to safeguard participants Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Trial Management Group (TMG) • Every trial should have a TMG • Normally includes individuals who are responsible for the day to day management of the trial – CI – Trial manager – Statistician – Research nurse – Data manager • Role is to: – Monitor conduct and progress of the trial – Ensure that the protocol is adhered to – Take appropriate action to safeguard participants Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
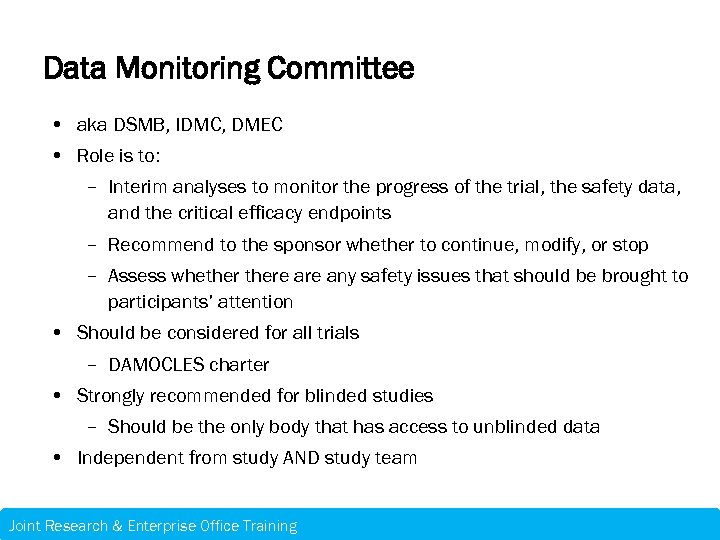 Data Monitoring Committee • aka DSMB, IDMC, DMEC • Role is to: – Interim analyses to monitor the progress of the trial, the safety data, and the critical efficacy endpoints – Recommend to the sponsor whether to continue, modify, or stop – Assess whethere any safety issues that should be brought to participants’ attention • Should be considered for all trials – DAMOCLES charter • Strongly recommended for blinded studies – Should be the only body that has access to unblinded data • Independent from study AND study team Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Data Monitoring Committee • aka DSMB, IDMC, DMEC • Role is to: – Interim analyses to monitor the progress of the trial, the safety data, and the critical efficacy endpoints – Recommend to the sponsor whether to continue, modify, or stop – Assess whethere any safety issues that should be brought to participants’ attention • Should be considered for all trials – DAMOCLES charter • Strongly recommended for blinded studies – Should be the only body that has access to unblinded data • Independent from study AND study team Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Trial Steering Committee (TSC) • Role is to: – Provide overall supervision of the trial – Ensure that it is being conducted in accordance with the principles of GCP and the relevant regulations • Should agree the trial’s protocol and any protocol amendments • Provide advice to the investigators on all aspects of the trial • The TSC may have members who are independent of the investigators, in particular an independent chairperson Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Trial Steering Committee (TSC) • Role is to: – Provide overall supervision of the trial – Ensure that it is being conducted in accordance with the principles of GCP and the relevant regulations • Should agree the trial’s protocol and any protocol amendments • Provide advice to the investigators on all aspects of the trial • The TSC may have members who are independent of the investigators, in particular an independent chairperson Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Compliance with GCP provides public assurance that the rights, safety and wellbeing of trial subjects are protected, consistent with the principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, and that the clinical trial data are credible Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Compliance with GCP provides public assurance that the rights, safety and wellbeing of trial subjects are protected, consistent with the principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, and that the clinical trial data are credible Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Safety Reporting Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Safety Reporting Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Pharmacovigilance (PV) is the process and science of monitoring the safety of medicines and taking action to reduce the risks and increase the benefits of medicines Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Pharmacovigilance (PV) is the process and science of monitoring the safety of medicines and taking action to reduce the risks and increase the benefits of medicines Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 What's it all about? • • Collect and manage data on safety of medicines Interrogate data to detect ‘signals’ (new or changing issues) Evaluation and decision making with regards to Safety Issues Pro-active risk management to minimise potential risk associated with medicine use • Acting to protect public health (including regulatory action) • Communication with and informing stakeholders & the public • Audit, both outcomes of actions taken & processes involved Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
What's it all about? • • Collect and manage data on safety of medicines Interrogate data to detect ‘signals’ (new or changing issues) Evaluation and decision making with regards to Safety Issues Pro-active risk management to minimise potential risk associated with medicine use • Acting to protect public health (including regulatory action) • Communication with and informing stakeholders & the public • Audit, both outcomes of actions taken & processes involved Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Acronyms • AE – Adverse Event • AR / ADR/ADE – Adverse Reaction / Adverse Drug Reaction/Adverse Device Event • SAE/SADE – Serious Adverse Event/Serious Adverse Device Event • SAR/SADR – Serious Adverse Drug Reaction • SUSAR – Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reaction • USADE – Unanticipated Serious Adverse device effect Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Acronyms • AE – Adverse Event • AR / ADR/ADE – Adverse Reaction / Adverse Drug Reaction/Adverse Device Event • SAE/SADE – Serious Adverse Event/Serious Adverse Device Event • SAR/SADR – Serious Adverse Drug Reaction • SUSAR – Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reaction • USADE – Unanticipated Serious Adverse device effect Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 AEs and ARs/ADRs ADE/SADE Any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical trial participant administered a medicinal product • AE: Does not need to be related to a drug • AR: Related to any dose administered of medicinal product For Non-CE marked devices or CE marked devices used outside the Intended use covered by the CE marking • ADE: Includes any events resulting from insufficiencies or inadequacies in instructions for use, deployment, installation the operation, or any malfunction. It also includes user error or intentional misuse • SADE: Adverse device event has resulted in any consequences characteristic of an SAE Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
AEs and ARs/ADRs ADE/SADE Any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical trial participant administered a medicinal product • AE: Does not need to be related to a drug • AR: Related to any dose administered of medicinal product For Non-CE marked devices or CE marked devices used outside the Intended use covered by the CE marking • ADE: Includes any events resulting from insufficiencies or inadequacies in instructions for use, deployment, installation the operation, or any malfunction. It also includes user error or intentional misuse • SADE: Adverse device event has resulted in any consequences characteristic of an SAE Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 SAEs • Any AE that at any dose: – Results in death – Is life threatening – Requires hospitalisation, or prolongation of existing inpatients’ hospitalisation – Results in persistent or significant disability or incapacity – Is a congenital anomaly or birth defect – Is otherwise considered medically significant by the investigator Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
SAEs • Any AE that at any dose: – Results in death – Is life threatening – Requires hospitalisation, or prolongation of existing inpatients’ hospitalisation – Results in persistent or significant disability or incapacity – Is a congenital anomaly or birth defect – Is otherwise considered medically significant by the investigator Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 SARs/SADRs • Any adverse reaction that is classed as serious AND is consistent* with the information about the IMP listed in the Reference Safety Information (Sm. PC or IB or IMPD) *i. e. it is expected • Investigator Brochure should be reviewed & updated annually to include aggregated safety information – PI should ensure all study team members are updated and familiar with new information – record on training log kept in the TMF– ensure all participating sites receive updated information especially participating pharmacy departments Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
SARs/SADRs • Any adverse reaction that is classed as serious AND is consistent* with the information about the IMP listed in the Reference Safety Information (Sm. PC or IB or IMPD) *i. e. it is expected • Investigator Brochure should be reviewed & updated annually to include aggregated safety information – PI should ensure all study team members are updated and familiar with new information – record on training log kept in the TMF– ensure all participating sites receive updated information especially participating pharmacy departments Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 SUSARs Any adverse reaction that is classed as serious and is suspected to be caused by the IMP and is NOT consistent with the information about the IMP in the Reference Safety Information e. g. Sm. PC/IB/IMPD ØSuspected and Unexpected USADE (Unanticipated Serious Adverse Device Effect Serious adverse device effect which by its nature, incidence, severity or outcome has not been identified in the current version of the risk analysis report. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
SUSARs Any adverse reaction that is classed as serious and is suspected to be caused by the IMP and is NOT consistent with the information about the IMP in the Reference Safety Information e. g. Sm. PC/IB/IMPD ØSuspected and Unexpected USADE (Unanticipated Serious Adverse Device Effect Serious adverse device effect which by its nature, incidence, severity or outcome has not been identified in the current version of the risk analysis report. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Causality Factors to consider: • Nature of the reaction – ARs commonly caused by medicines, eg skin reactions • Timing – e. g. anaphylaxis usually occurs within minutes • Relationship to dose – Positive dechallenge – Positive rechallenge • Disagreement between CI and PI then reporting weighted in favour of greatest risk Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Causality Factors to consider: • Nature of the reaction – ARs commonly caused by medicines, eg skin reactions • Timing – e. g. anaphylaxis usually occurs within minutes • Relationship to dose – Positive dechallenge – Positive rechallenge • Disagreement between CI and PI then reporting weighted in favour of greatest risk Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Causality Description of relationship of IMP with SAE Definitely Clear evidence of causal relationship & other possible factors can be ruled out Probably Evidence suggests causal relationship and other possible factors is unlikely Possibly Some evidence to suggest a causal relationship as event occurred within a reasonable time following IMP administration however, other factors cannot be ruled out. Unlikely Little evidence as the event did not occur within a reasonable time frame and another reasonable explanation exists Unrelated No evidence of causal relationship Not Assessable NB: If this description is used the Sponsor will assume event IS related until subsequent follow up information suggests otherwise
Causality Description of relationship of IMP with SAE Definitely Clear evidence of causal relationship & other possible factors can be ruled out Probably Evidence suggests causal relationship and other possible factors is unlikely Possibly Some evidence to suggest a causal relationship as event occurred within a reasonable time following IMP administration however, other factors cannot be ruled out. Unlikely Little evidence as the event did not occur within a reasonable time frame and another reasonable explanation exists Unrelated No evidence of causal relationship Not Assessable NB: If this description is used the Sponsor will assume event IS related until subsequent follow up information suggests otherwise
 Recording AEs and ARs • Trial Planning – In the protocol list expected SAEs & SARs - in relation to known IMP side effects, - in relation to the disease - State which expected SAEs will not be reported or do not require immediate reporting but do state when and how they will be reported (outcome data or within x days of event) - Reference procedures to be followed in event of SAE - Clearly state responsibilities Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Recording AEs and ARs • Trial Planning – In the protocol list expected SAEs & SARs - in relation to known IMP side effects, - in relation to the disease - State which expected SAEs will not be reported or do not require immediate reporting but do state when and how they will be reported (outcome data or within x days of event) - Reference procedures to be followed in event of SAE - Clearly state responsibilities Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Recording AEs and ARs continued • Data Collection – Maintain listing of all AEs/ARs that occur during the study – AEs/ARs do not need to be reported but may require notification to the Sponsor in accordance with the monitoring plan & protocol. – AE logs should be clinically reviewed by the CI to rule out trends/increase in frequency or severity- Document any reviews in TMF and adverse findings should be reported to the Sponsor within 24 hours. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Recording AEs and ARs continued • Data Collection – Maintain listing of all AEs/ARs that occur during the study – AEs/ARs do not need to be reported but may require notification to the Sponsor in accordance with the monitoring plan & protocol. – AE logs should be clinically reviewed by the CI to rule out trends/increase in frequency or severity- Document any reviews in TMF and adverse findings should be reported to the Sponsor within 24 hours. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Reporting SAEs and SARs • Assess AE for – seriousness – causality – Expectedness • Report to CI/Sponsor within 24 hrs on specific form – Except when listed in protocol as not requiring immediate reporting ICH GCP Section 4. 11 & 5. 17 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Reporting SAEs and SARs • Assess AE for – seriousness – causality – Expectedness • Report to CI/Sponsor within 24 hrs on specific form – Except when listed in protocol as not requiring immediate reporting ICH GCP Section 4. 11 & 5. 17 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Reporting SAEs/SUSARs • Assess AE for – seriousness – causality – expectedness • If serious, suspected causally related and NOT expected • Expedited reporting to CA and REC – fatal or life threatening = 7 days, follow-up in 8 days – other = 15 days – Report even if occurred outside MS – Follow up until resolution – Included on DSUR in line listing ICH GCP Section 4. 11 & 5. 17 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Reporting SAEs/SUSARs • Assess AE for – seriousness – causality – expectedness • If serious, suspected causally related and NOT expected • Expedited reporting to CA and REC – fatal or life threatening = 7 days, follow-up in 8 days – other = 15 days – Report even if occurred outside MS – Follow up until resolution – Included on DSUR in line listing ICH GCP Section 4. 11 & 5. 17 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 DEVICES- Reportable Events under Annex 7 & X of directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC respectively • The following events are considered reportable – Any SAE – Any Investigational Medical Device Deficiency that may have led to an SAE if • a/ suitable action had not been taken • b/ intervention had not been made • c/ if circumstances had been less fortunate – New findings/updates in relation to already reportable events • Reportable events occurring in 3 rd countries in which a clinical investigation is performed under the same clinical investigation plan have to reported as above Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
DEVICES- Reportable Events under Annex 7 & X of directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC respectively • The following events are considered reportable – Any SAE – Any Investigational Medical Device Deficiency that may have led to an SAE if • a/ suitable action had not been taken • b/ intervention had not been made • c/ if circumstances had been less fortunate – New findings/updates in relation to already reportable events • Reportable events occurring in 3 rd countries in which a clinical investigation is performed under the same clinical investigation plan have to reported as above Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 DEVICES- Reportable Events under Annex 7 & X of directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC respectively • Report to CI/Sponsor & Manufacturer within 3 days after occurrence on specific form supplied by manufacturer – Except when listed in protocol as not requiring immediate reporting • Reported by Sponsor simultaneously to each National CA & NB where investigations have occurred immediately (or no later than 2 calendar days) where death or imminent risk of serious injury has occurred, any other reportable events no later than 7 days following awareness of event Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
DEVICES- Reportable Events under Annex 7 & X of directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC respectively • Report to CI/Sponsor & Manufacturer within 3 days after occurrence on specific form supplied by manufacturer – Except when listed in protocol as not requiring immediate reporting • Reported by Sponsor simultaneously to each National CA & NB where investigations have occurred immediately (or no later than 2 calendar days) where death or imminent risk of serious injury has occurred, any other reportable events no later than 7 days following awareness of event Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Special Situations • Pregnancy or impregnation – Follow up to birth (& beyond if stipulated in protocol) • Lack of efficacy – May be a significant hazard to the subject population if IMP used to treat life threatening disease • Overdose / abuse / misuse – Protocol should include guidance Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Special Situations • Pregnancy or impregnation – Follow up to birth (& beyond if stipulated in protocol) • Lack of efficacy – May be a significant hazard to the subject population if IMP used to treat life threatening disease • Overdose / abuse / misuse – Protocol should include guidance Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Special Situations • Expected SAE, but unexpected outcome • Increase in frequency or severity of SAE (hence regular AE log review by CI encouraged for signal detection) • URGENT SAFETY MEASURES Can be implemented immediately for the protection of trial subjects however IRB/REC/CA must be notified within 3 days via submission of amendment Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Special Situations • Expected SAE, but unexpected outcome • Increase in frequency or severity of SAE (hence regular AE log review by CI encouraged for signal detection) • URGENT SAFETY MEASURES Can be implemented immediately for the protection of trial subjects however IRB/REC/CA must be notified within 3 days via submission of amendment Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Why do we need to monitor safety post marketing? REAL LIFE IS NOT LIKE A CLINICAL TRIAL • Clinical trials only encompass a very TIGHTLY CONTROLLED section of a population • No pregnancy • Concomitant medications are controlled • Long term use UK • Yellow card scheme via the MHRA website https: //yellowcard. mhra. gov. uk/ Report – Side effects for a medicine, vaccine, herbal or homeopathic remedy Report - Medical Device adverse incident Report – Defective medicines of unacceptable quality Report – Counterfeit or fake medicine or medical device Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Why do we need to monitor safety post marketing? REAL LIFE IS NOT LIKE A CLINICAL TRIAL • Clinical trials only encompass a very TIGHTLY CONTROLLED section of a population • No pregnancy • Concomitant medications are controlled • Long term use UK • Yellow card scheme via the MHRA website https: //yellowcard. mhra. gov. uk/ Report – Side effects for a medicine, vaccine, herbal or homeopathic remedy Report - Medical Device adverse incident Report – Defective medicines of unacceptable quality Report – Counterfeit or fake medicine or medical device Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Common Inspection Findings • Failure to report SUSARs • Failure to follow up pregnancy outcomes • Subject confidentiality – i. e. SAE reports in the TMF with Subject names • Failure to submit ASR’s/DSUR’s in a timely fashion • Inadequate instruction or procedure contained in the protocols to ensure Adverse Events recorded or reported appropriately • Lack of sponsor oversight/process to ensure and monitor compliance of SUSAR reporting and ASR/DSUR submissions Source MHRA GCP Inspections Metrics Reports 2009 -2012
Common Inspection Findings • Failure to report SUSARs • Failure to follow up pregnancy outcomes • Subject confidentiality – i. e. SAE reports in the TMF with Subject names • Failure to submit ASR’s/DSUR’s in a timely fashion • Inadequate instruction or procedure contained in the protocols to ensure Adverse Events recorded or reported appropriately • Lack of sponsor oversight/process to ensure and monitor compliance of SUSAR reporting and ASR/DSUR submissions Source MHRA GCP Inspections Metrics Reports 2009 -2012
 DSURs Replaces Annual Safety Reports – Anniversary of first international birth date (regulatory approval) =DIBD – Paediatric studies may require 6 monthly reports – If listing multiple studies – then Data Lock Point (DLP) Include each study until declaration of end of that study – DSUR per IMP to the MHRA (although for some investigator led studies MHRA may accept report on anniversary of MHRA CTA) – Aggregate Reporting - Ensure all SAEs and SUSARs for that reporting period are line listed/tabulated in suggested format – Check for any new information/publications during that reporting period and updates on Sm. PC’s if using licensed medicines Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
DSURs Replaces Annual Safety Reports – Anniversary of first international birth date (regulatory approval) =DIBD – Paediatric studies may require 6 monthly reports – If listing multiple studies – then Data Lock Point (DLP) Include each study until declaration of end of that study – DSUR per IMP to the MHRA (although for some investigator led studies MHRA may accept report on anniversary of MHRA CTA) – Aggregate Reporting - Ensure all SAEs and SUSARs for that reporting period are line listed/tabulated in suggested format – Check for any new information/publications during that reporting period and updates on Sm. PC’s if using licensed medicines Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Progress Reports, Declaration of End of Study and Final Report Annual progress reports to IRB/REC Ø Within 30 days of Anniversary of IRB/REC approval Ø Until end of study Declaration of End of Study to IRB/REC Ø Appropriate form within 90 days of the end of the study Ø Or within 15 days if the study is terminated early Final report on the research to IRB/REC Ø Within 12 months of the end of the study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
Progress Reports, Declaration of End of Study and Final Report Annual progress reports to IRB/REC Ø Within 30 days of Anniversary of IRB/REC approval Ø Until end of study Declaration of End of Study to IRB/REC Ø Appropriate form within 90 days of the end of the study Ø Or within 15 days if the study is terminated early Final report on the research to IRB/REC Ø Within 12 months of the end of the study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 End Of Study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
End Of Study Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
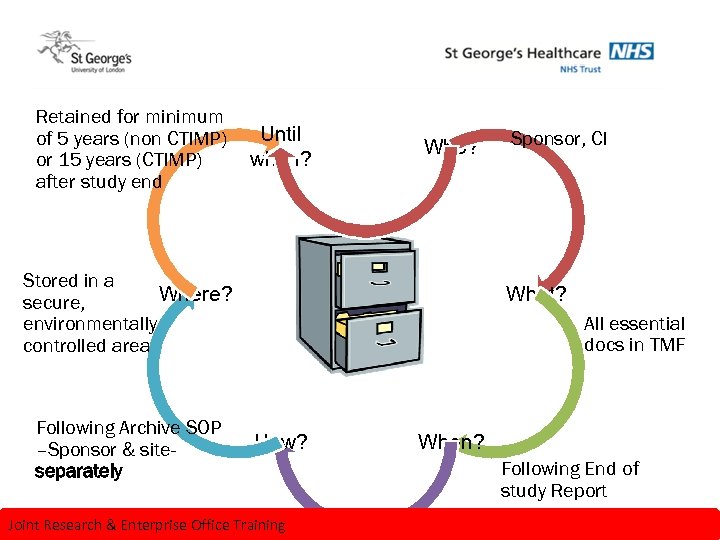 Archiving principles Retained for minimum of 5 years (non CTIMP) or 15 years (CTIMP) after study end Until when? Who? Stored in a Where? secure, environmentally controlled area Following Archive SOP –Sponsor & siteseparately Sponsor, CI What? All essential docs in TMF How? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training When? Following End of study Report
Archiving principles Retained for minimum of 5 years (non CTIMP) or 15 years (CTIMP) after study end Until when? Who? Stored in a Where? secure, environmentally controlled area Following Archive SOP –Sponsor & siteseparately Sponsor, CI What? All essential docs in TMF How? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training When? Following End of study Report
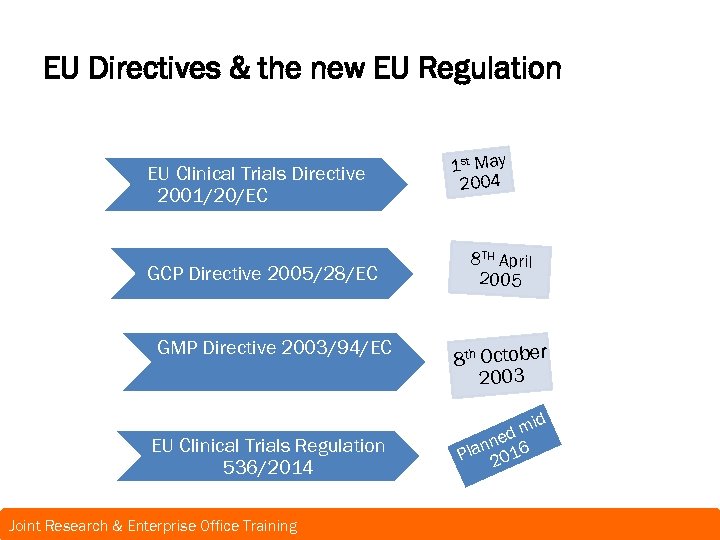 EU Directives & the new EU Regulation EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC GCP Directive 2005/28/EC GMP Directive 2003/94/EC EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training 1 st May 2004 8 TH April 2005 8 th October 2003 m ned 6 n Pla 201 id
EU Directives & the new EU Regulation EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC GCP Directive 2005/28/EC GMP Directive 2003/94/EC EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training 1 st May 2004 8 TH April 2005 8 th October 2003 m ned 6 n Pla 201 id
 EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC • Simplify and standardised Clinical Trial applications for both commercial & academic Sponsors across EU • To protect safety and well being of participants and improve quality of emerging data However • Increased documentation burden for academic partners • Increased financial burden for academics & their host institutions acting as Sponsor • One size fits All ? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC • Simplify and standardised Clinical Trial applications for both commercial & academic Sponsors across EU • To protect safety and well being of participants and improve quality of emerging data However • Increased documentation burden for academic partners • Increased financial burden for academics & their host institutions acting as Sponsor • One size fits All ? Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC EFGCP compared data between 2003 and 2007 – Commercial studies submitted and conducted increased by 11% and 30% respectively – Academic studies submitted remained unchanged but studies conducted decreased by 25% • EORTC – New trials fell by 63% between 2004 -5 • Academic CT fell by 75% in Finland, 70% in Ireland, 25% in Sweden and 66% in Austria 1 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC EFGCP compared data between 2003 and 2007 – Commercial studies submitted and conducted increased by 11% and 30% respectively – Academic studies submitted remained unchanged but studies conducted decreased by 25% • EORTC – New trials fell by 63% between 2004 -5 • Academic CT fell by 75% in Finland, 70% in Ireland, 25% in Sweden and 66% in Austria 1 Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Why? • CT directive intended to harmonise process across Europe • Each MS interpretation has led to need for country specific document requirements increasing administrative burden and Europe seems increasingly less attractive Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Why? • CT directive intended to harmonise process across Europe • Each MS interpretation has led to need for country specific document requirements increasing administrative burden and Europe seems increasingly less attractive Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Regulation removes “ interpretation” and introduces true uniformity Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Regulation removes “ interpretation” and introduces true uniformity Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Highlights Ø Will not apply to non-interventional studies Ø Clinical Study = investigation in relation to humans intended: : Ø To discover or verify the clinical, pharmacological or other pharmacodynamic effects of one or more medicinal products Ø To identify any adverse reactions to one or more medicinal products or Ø To study absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of one or more medicinal products with the objective of ascertaining safety and efficacy of those medicinal products Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Highlights Ø Will not apply to non-interventional studies Ø Clinical Study = investigation in relation to humans intended: : Ø To discover or verify the clinical, pharmacological or other pharmacodynamic effects of one or more medicinal products Ø To identify any adverse reactions to one or more medicinal products or Ø To study absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of one or more medicinal products with the objective of ascertaining safety and efficacy of those medicinal products Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 What is covered Ø Clinical Trial : Ø Assignment of a subject to a particular therapeutic strategy decided in advance and does not fall within normal clinical practice in MS concerned (in a non interventional study the patient is usually treated within normal clinical practice) Or Ø decision to prescribe the IMP is taken together with decision to include the subject in the clinical study (in a non interventional study the decision to prescribe a treatment is taken before entry into the study) Or Ø diagnostic or monitoring procedures in addition to normal clinical practice are applied to the subjects (this would be noninterventional and so is a Clinical Trial) Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 What is covered Ø Clinical Trial : Ø Assignment of a subject to a particular therapeutic strategy decided in advance and does not fall within normal clinical practice in MS concerned (in a non interventional study the patient is usually treated within normal clinical practice) Or Ø decision to prescribe the IMP is taken together with decision to include the subject in the clinical study (in a non interventional study the decision to prescribe a treatment is taken before entry into the study) Or Ø diagnostic or monitoring procedures in addition to normal clinical practice are applied to the subjects (this would be noninterventional and so is a Clinical Trial) Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Low Intervention Trial Ø IMPs excluding placebos are authorised according to the protocol of the Clinical Trial, Ø The IMPs are used in accordance with the terms of the marketing authorisation Or Ø The use of the IMPs is evidence based and published by scientific evidence on the safety and efficacy of those IMPs in any MS concerned; and Ø The additional diagnostic or monitoring procedures do not pose more than minimal additional risk or burden to the safety of the subjects compared to normal practice in any MS Ø In the UK CA-(MHRA) already using “Risk adaptive approach” Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Low Intervention Trial Ø IMPs excluding placebos are authorised according to the protocol of the Clinical Trial, Ø The IMPs are used in accordance with the terms of the marketing authorisation Or Ø The use of the IMPs is evidence based and published by scientific evidence on the safety and efficacy of those IMPs in any MS concerned; and Ø The additional diagnostic or monitoring procedures do not pose more than minimal additional risk or burden to the safety of the subjects compared to normal practice in any MS Ø In the UK CA-(MHRA) already using “Risk adaptive approach” Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 A single electronic application will be submitted via EU portal Sponsor can propose a Reporting Member State (RMS) to conduct assessment in co-ordination with other CMS 2 part application - Part I – Scientific – to include Application form, Protocol, IMPD, Investigator’s brochure, examples of trial labels, Manufacturing authorisation/QP declaration, copy of scientific advice or paediatric investigation plan, proof of fee, cover letter and Statement of compliance with the EU data protection Regulation - Part II – Country specific – feasibility & Ethics - Recruitment arrangements, Patient information sheet, Informed consent Form, Investigator/site information, proof of insurance, Financial arrangements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 A single electronic application will be submitted via EU portal Sponsor can propose a Reporting Member State (RMS) to conduct assessment in co-ordination with other CMS 2 part application - Part I – Scientific – to include Application form, Protocol, IMPD, Investigator’s brochure, examples of trial labels, Manufacturing authorisation/QP declaration, copy of scientific advice or paediatric investigation plan, proof of fee, cover letter and Statement of compliance with the EU data protection Regulation - Part II – Country specific – feasibility & Ethics - Recruitment arrangements, Patient information sheet, Informed consent Form, Investigator/site information, proof of insurance, Financial arrangements Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
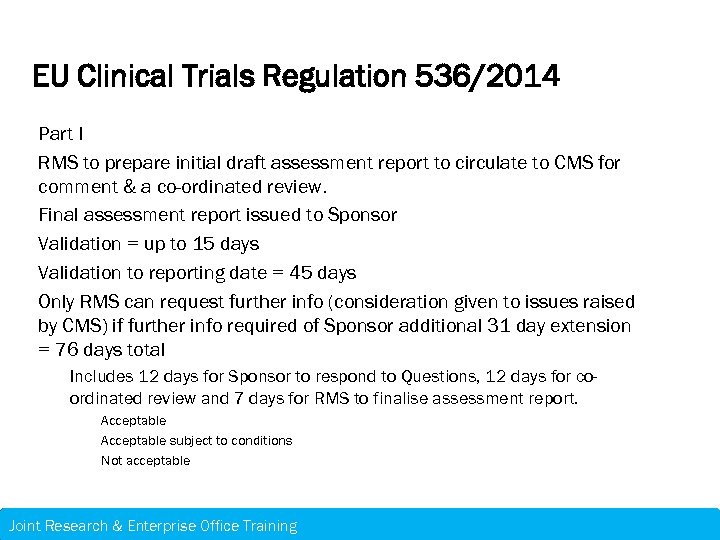 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Part I RMS to prepare initial draft assessment report to circulate to CMS for comment & a co-ordinated review. Final assessment report issued to Sponsor Validation = up to 15 days Validation to reporting date = 45 days Only RMS can request further info (consideration given to issues raised by CMS) if further info required of Sponsor additional 31 day extension = 76 days total Includes 12 days for Sponsor to respond to Questions, 12 days for coordinated review and 7 days for RMS to finalise assessment report. Acceptable subject to conditions Not acceptable Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Part I RMS to prepare initial draft assessment report to circulate to CMS for comment & a co-ordinated review. Final assessment report issued to Sponsor Validation = up to 15 days Validation to reporting date = 45 days Only RMS can request further info (consideration given to issues raised by CMS) if further info required of Sponsor additional 31 day extension = 76 days total Includes 12 days for Sponsor to respond to Questions, 12 days for coordinated review and 7 days for RMS to finalise assessment report. Acceptable subject to conditions Not acceptable Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
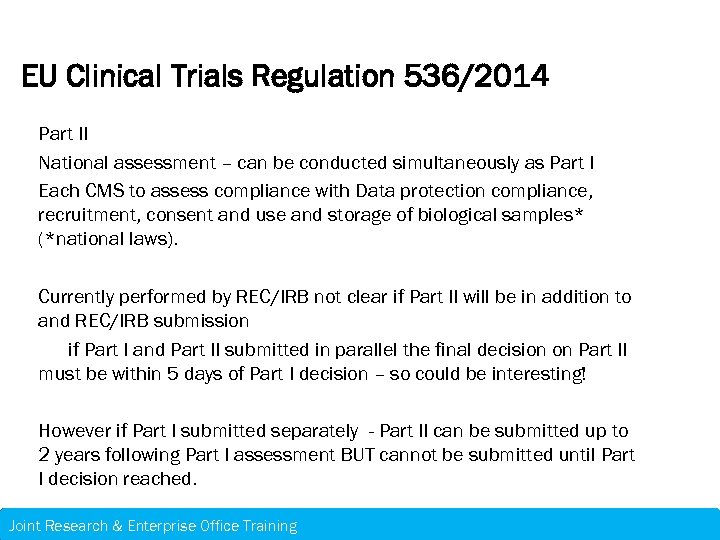 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Part II National assessment – can be conducted simultaneously as Part I Each CMS to assess compliance with Data protection compliance, recruitment, consent and use and storage of biological samples* (*national laws). Currently performed by REC/IRB not clear if Part II will be in addition to and REC/IRB submission if Part I and Part II submitted in parallel the final decision on Part II must be within 5 days of Part I decision – so could be interesting! However if Part I submitted separately - Part II can be submitted up to 2 years following Part I assessment BUT cannot be submitted until Part I decision reached. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Part II National assessment – can be conducted simultaneously as Part I Each CMS to assess compliance with Data protection compliance, recruitment, consent and use and storage of biological samples* (*national laws). Currently performed by REC/IRB not clear if Part II will be in addition to and REC/IRB submission if Part I and Part II submitted in parallel the final decision on Part II must be within 5 days of Part I decision – so could be interesting! However if Part I submitted separately - Part II can be submitted up to 2 years following Part I assessment BUT cannot be submitted until Part I decision reached. Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training – 21 st November 2013 Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 • Substantial Amendments • Part I – 38 days +31 days if questions raised & decision within 5 days of assessment report • Part II – 38 days (plus extension for questions) Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 • Substantial Amendments • Part I – 38 days +31 days if questions raised & decision within 5 days of assessment report • Part II – 38 days (plus extension for questions) Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
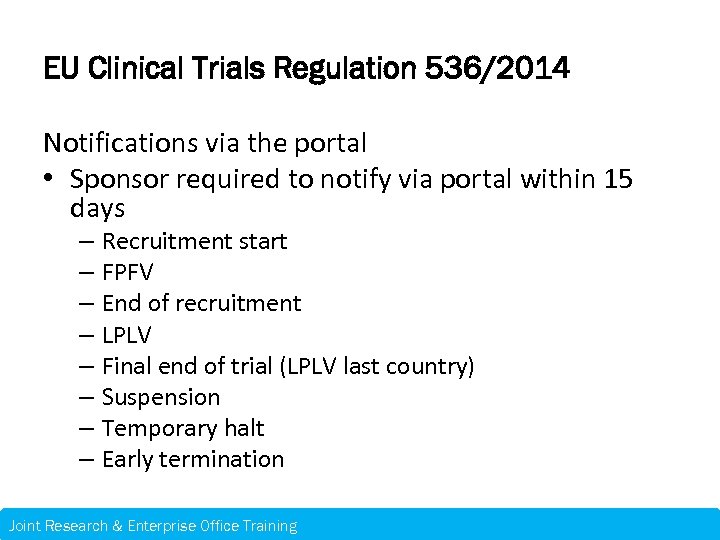 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Notifications via the portal • Sponsor required to notify via portal within 15 days – Recruitment start – FPFV – End of recruitment – LPLV – Final end of trial (LPLV last country) – Suspension – Temporary halt – Early termination Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Notifications via the portal • Sponsor required to notify via portal within 15 days – Recruitment start – FPFV – End of recruitment – LPLV – Final end of trial (LPLV last country) – Suspension – Temporary halt – Early termination Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Other Notifications Required by the Sponsor – SUSARs to the EMA via the Eudravigilance database. – Annual Safety Reports. EMA will forward reports to the MS – 3 rd country inspection reports Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Other Notifications Required by the Sponsor – SUSARs to the EMA via the Eudravigilance database. – Annual Safety Reports. EMA will forward reports to the MS – 3 rd country inspection reports Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Headline Trial Management Changes • All previous trial data in the submission must be registered on a database e. g. Eudra. CT or clinicaltrials. gov • Public access to EU CT database- results must be available in lay summary – subjects must be told how to find results • Serious breaches to be reported within 7 calendar days • TMF archived for 25 years minimum Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Headline Trial Management Changes • All previous trial data in the submission must be registered on a database e. g. Eudra. CT or clinicaltrials. gov • Public access to EU CT database- results must be available in lay summary – subjects must be told how to find results • Serious breaches to be reported within 7 calendar days • TMF archived for 25 years minimum Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Implementation • Timetable dependant on EU submission portal set up • Planned 6 months after but no earlier than 28 th May 2016 • Transition period to allow anything submitted before effective date to continue under the existing directive for 3 years • 1 year overlap of 2 systems so current submissions until at least 28 th May 2017 governed by directive for up to 42 months from declaration of portal being ready Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
EU Clinical Trials Regulation 536/2014 Implementation • Timetable dependant on EU submission portal set up • Planned 6 months after but no earlier than 28 th May 2016 • Transition period to allow anything submitted before effective date to continue under the existing directive for 3 years • 1 year overlap of 2 systems so current submissions until at least 28 th May 2017 governed by directive for up to 42 months from declaration of portal being ready Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
 Thank you for listening Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training
Thank you for listening Joint Research & Enterprise Office Training


