e4ad2710a524112a800fa963b7bb7af3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84

“God could cause us considerable embarrassment by revealing all the secrets of nature to us: we should not know what to do for sheer apathy and boredom. ” -- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe

Systems Biology of Osmotic Shock in Antibody Producing Cell Lines Candidacy Proposal Thomas R. Kiehl NSF Graduate Research Fellow, Multidisciplinary Science Ph. D. Program
What is an Antibody? • Antibodies are an important component of the body’s natural defenses. • These glycoproteins recognize foreign substances and tag them for remediation by other parts of the immune system. • m. Ab’s are an effective part of a growing number of medical treatments, lab techniques, diagnostics and imaging. Image source: Wikipedia

Roche buys antibody technology company for $56. 6 mln, Apr 2, 2007 ZURICH (Market. Watch) -- Swiss drugmaker Roche Holding AG (RHHBY) Monday said it has acquired privately-held Therapeutic Human Polyclonals Inc, an emerging biotechnology company focused on research in human antibody technologies, for $56. 6 million in cash. Roche, based in Basel, said it plans to fully integrate THP, which is based in Germany and the U. S. , into its protein research center in Penzberg, Germany. "We are delighted about this acquisition as it builds on our strength in therapeutic antibodies, " said Jonathan Knowles, head of global research at Roche. The development of therapeutic proteins and antibodies is an important area of research for the company, Roche said. At 0826 GMT, Roche shares were CHF 1. 80, or 0. 8% higher, at CHF 216. 80, in a slightly lower broader market. THP focuses on research in the field of human antibody technologies, where drugs made out of antibodies fight infectious agents, including bacteria and viruses, by seeking them out and helping the body to destroy them. THP says it has developed a unique transgenic mammalian platform to create human antibodies. The technology will enable the generation of both monoclonal and polyclonal antibody drugs with enhanced efficacy, Roche said. Monoclonal antibodies are identical because they were produced by one type of immune cell and are all clones of a single parent cell. "Improved monoclonal antibody companies are hot commodities, " said Denise Anderson, pharmaceutical analyst in Zurich with broker Kepler Equities, who has a buy rating on the stock, pointing to a string of deals over the past twelve months. Roche itself paid $181 million last year to acquire Glyc. Art Biotechnology AG of Zurich, which also had a crop of early-stage antibodies. In May, Merck & Co. (MRK) agreed to pay a combined $480 million to acquire Abmaxis and Glyco. Fi, two biotechnology firms that brought the drug maker new methods to discover and produce drugs. Merck, based in Whitehouse Station, N. J. , isn't affiliated with its German namesake. Also in the second quarter of 2006, Pfizer inc. (PFE) acquired Bioren, a small specialist in the discovery of monoclonal antibodies. "We think the deal makes good strategic sense for Roche, where top drugs Rituxan, Herceptin and Avastin are all antibodies, Anderson said. At a time when many traditional drugs made from small molecules are facing the loss of patent. protection, medicines made out of large proteins are still protected from this threat not only because they've only entered the market over the past decade but also because they are more complex to imitate. Monday (Roche) said it has acquired privately-held Therapeutic Human Polyclonals Inc, an emerging biotechnology company focused on Roche itself paid $181 million research in human antibody last year to acquire Glyc. Art technologies, for $56. 6 million in cash. Biotechnology AG of Zurich, which also had a crop of earlystage antibodies. In May, Merck & Co. (MRK) agreed to pay a combined $480 million to acquire Abmaxis and Glyco. Fi, two biotechnology firms that brought the Also in the second quarter of 2006, drug maker new methods to discover Pfizer inc. (PFE) acquired Bioren, a and produce drugs. small specialist in the discovery of monoclonal antibodies

2005 Market, $13 Billion • ½ of that from just two drugs – Rituxan ($3. 3 Bn) – non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (CD 20) – Remicade ($3. 4 Bn) - rheumatoid arthritis (TNF-α) • 17 therapeutic monoclonal antibodies have received FDA approval and are on the market in the U. S. • Several antibodies have been approved for use in diagnostic imaging applications. • Report does not mention BMS’ Abatacept which is a fusion protein composed of an immunoglobulin fused to the extracellular domain of CTLA-4 (Sales for the second quarter of 2006 were $18 million, sales could reach US$ 1 billion by 2009/2010, ) Market Report: Monoclonal Antibodies: From Magic Bullets to Successful Drugs Abatacept: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 5, 185 -186 (March 2006)

Herceptin, A prototypical Antibody Therapeutic • This m. Ab targets a receptor which is over expressed in certain breast cancers (Bange 2001, Sliwkowski 1999). • Herceptin targets the epidermal growth factor receptor, HER 2, which is part of the Erb. B family of tyrosine kinases. • This targeting results in cell cycle arrest and suppression of tumor growth.

Systems Biology of Osmotic Shock in Antibody Producing Cell Lines Candidacy Proposal Thomas R. Kiehl NSF Graduate Research Fellow, Multidisciplinary Science Ph. D. Program

How do you make m. Ab’s? • In 1975 Köhler and Milstein first developed cell lines which could reliably produce monoclonal antibodies • These cell lines, known as hybridomas, were a fusion of an antibody-secreting murine lymphocyte cell with an murine myleoma cell. • From this process emerges an immortalized cell line which secretes identical antibodies that have been raised against a specific antigen.

Systems Biology of Osmotic Shock in Antibody Producing Cell Lines Candidacy Proposal Thomas R. Kiehl NSF Graduate Research Fellow, Multidisciplinary Science Ph. D. Program
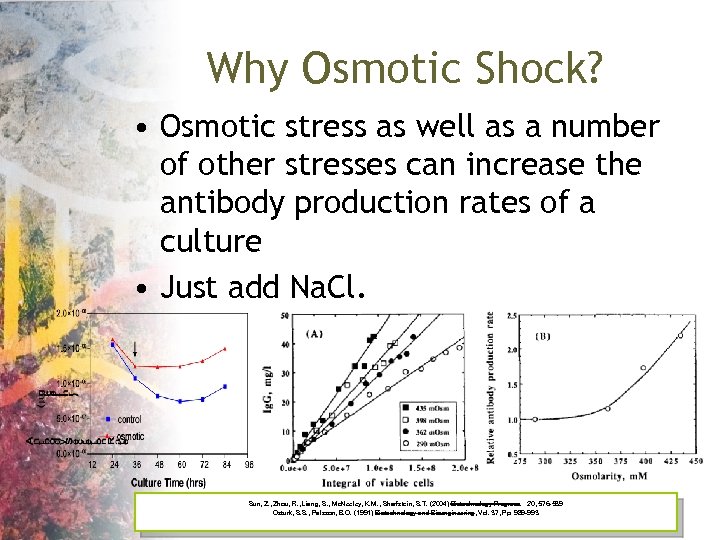
Why Osmotic Shock? • Osmotic stress as well as a number of other stresses can increase the antibody production rates of a culture • Just add Na. Cl. Sun, Z. , Zhou, R. , Liang, S. , Mc. Neeley, K. M. , Sharfstein, S. T. (2004) Biotechnology Progress. 20, 576 -589 Ozturk, S. S. , Palsson, B. O. (1991) Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 37, Pp. 989 -993
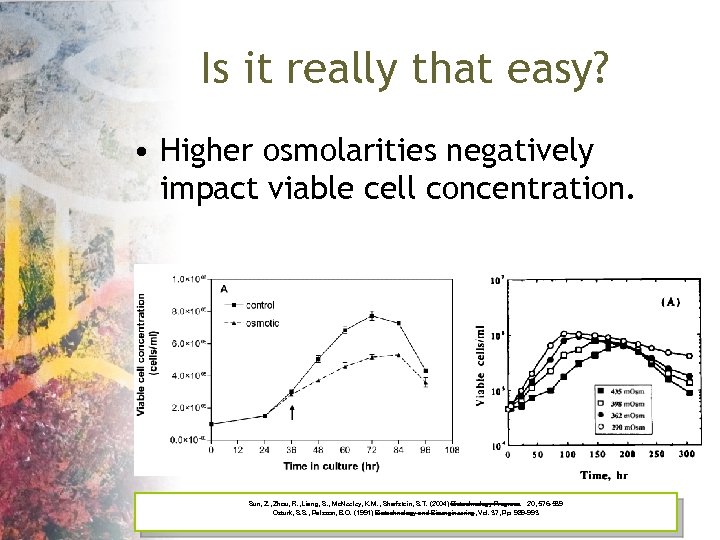
Is it really that easy? • Higher osmolarities negatively impact viable cell concentration. Sun, Z. , Zhou, R. , Liang, S. , Mc. Neeley, K. M. , Sharfstein, S. T. (2004) Biotechnology Progress. 20, 576 -589 Ozturk, S. S. , Palsson, B. O. (1991) Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 37, Pp. 989 -993

So, just shock them a little. Right? • In fed-batch cultures osmolarity becomes problematic both due to the addition of nutrients as well as the production of waste products, primarily lactic acid. • Lactic acidifies the culture, necessitating the addition of base to control the p. H. • Over the course of a fed-batch culture the osmolarity can increase from ~290 m. Osm/kg to 500 m. Osm/kg (Zhu 2005). • Viability can be reduced by as much as 50% (Kurano 1990).

Systems Biology of Osmotic Shock in Antibody Producing Cell Lines Candidacy Proposal Thomas R. Kiehl NSF Graduate Research Fellow, Multidisciplinary Science Ph. D. Program

Systems Biology “I am a Biologist, and I work on systems. I guess that makes me a Systems Biologist. ” -Howard Berg, ICSB 2005
Systems Biology “To understand biology at the system level, we must examine the structure and dynamics of cellular and organismal function, rather than the characteristics of isolated parts of a cell or organism. Properties of systems, such as robustness, emerge as central issues, and understanding these properties may have an impact on the future of medicine. ” – Hiroaki Kitano, H. (2002), Systems Biology: a brief overview, Science, 295: 1662 -1664

3 C’s of Systems Biology • Complexity • Computation • Cross-Disciplinary Cooperation

Systems Biology Lab Experiment(s) Refine model In-Silico Experiment(s)

Systems Biology of Osmotic Shock in Antibody Producing Cell Lines Candidacy Proposal Thomas R. Kiehl NSF Graduate Research Fellow, Multidisciplinary Science Ph. D. Program

Objective • Engineer mammalian cells for optimal recombinant protein production. – To build a model of the cellular response to osmotic shock. • Characterize the response in terms of some specific components.

Overview • • • Mammalian Pathway Yeast Model Scope Sample Model Ton. EBP/NFAT 5/OREBP • Experimental Plan & Preliminary Results • Related Efforts – – Batch Culture Model Microarrays Co. EPr. A Evolutionary Computing
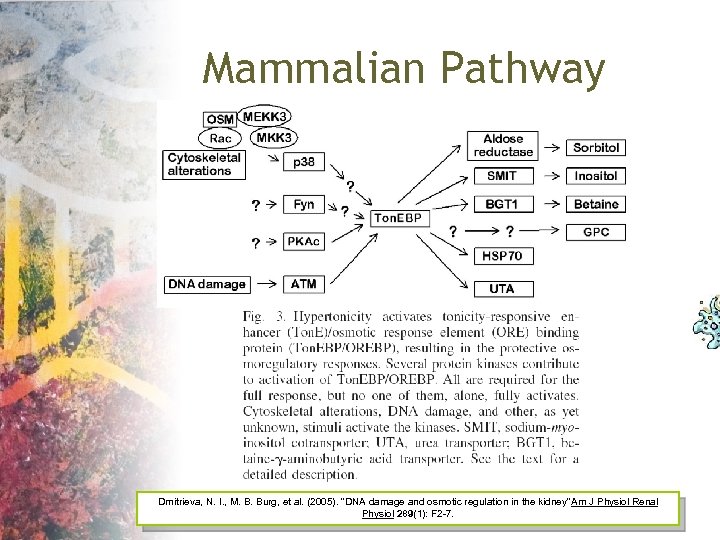
Mammalian Pathway Dmitrieva, N. I. , M. B. Burg, et al. (2005). "DNA damage and osmotic regulation in the kidney" m J Physiol Renal A Physiol 289(1): F 2 -7.
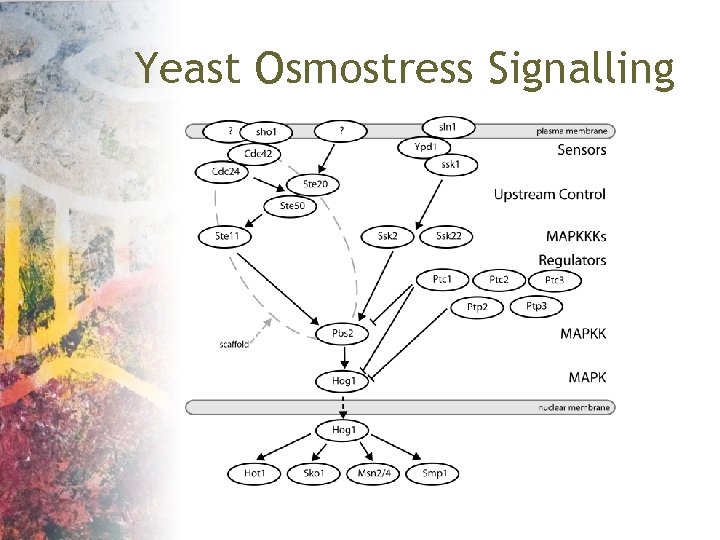
Yeast Osmostress Signalling
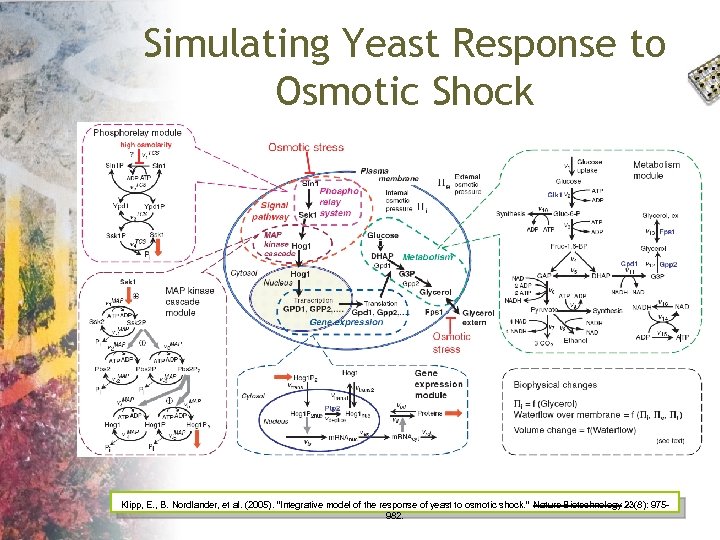
Simulating Yeast Response to Osmotic Shock Klipp, E. , B. Nordlander, et al. (2005). "Integrative model of the response of yeast to osmotic shock. " Nature Biotechnology 23(8): 975982.
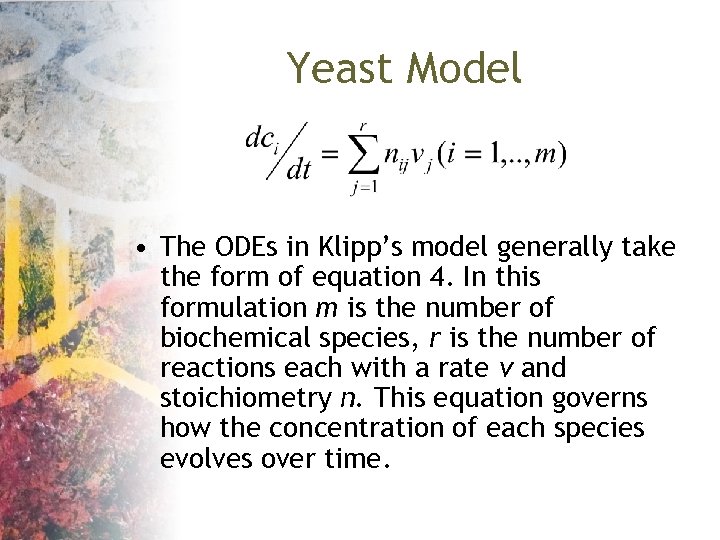
Yeast Model • The ODEs in Klipp’s model generally take the form of equation 4. In this formulation m is the number of biochemical species, r is the number of reactions each with a rate v and stoichiometry n. This equation governs how the concentration of each species evolves over time.
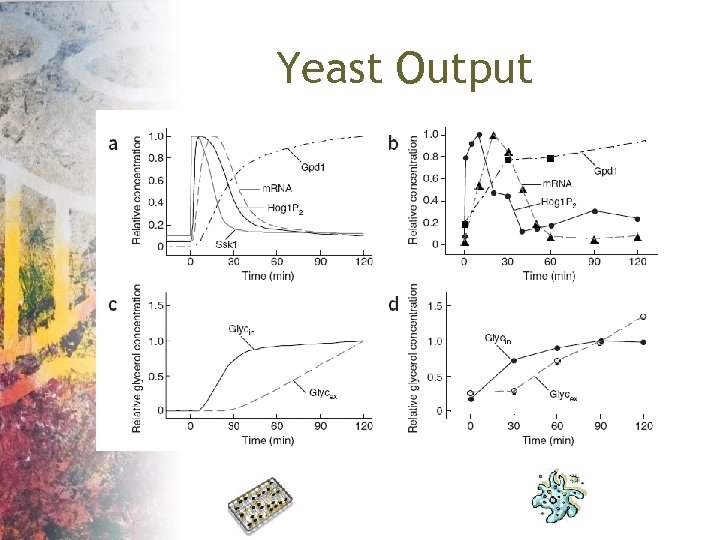
Yeast Output
Yeast Model • Klipp showed that the pathway can be activated again by an additional shock. • They also showed that this reactivation would not be possible if the pathway were structured such that the phosphatases provided the primary feedback control. • They demonstrated that the gene transcripts for phosphatases should not increase by more than two-fold.
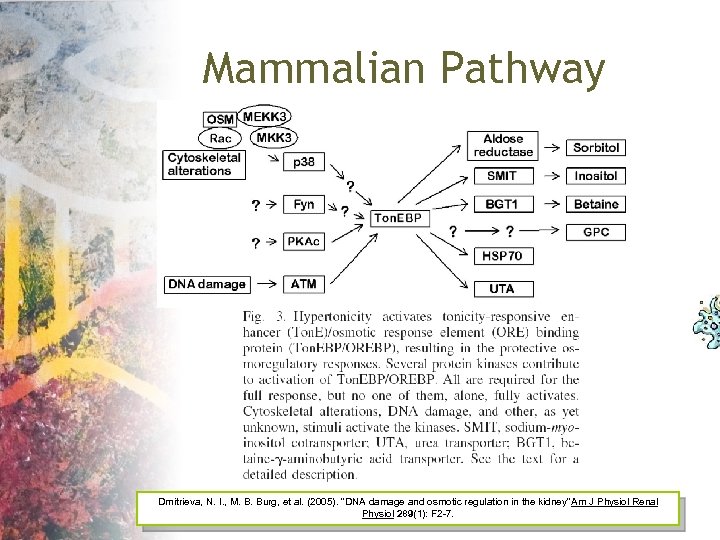
Mammalian Pathway Dmitrieva, N. I. , M. B. Burg, et al. (2005). "DNA damage and osmotic regulation in the kidney" m J Physiol Renal A Physiol 289(1): F 2 -7.
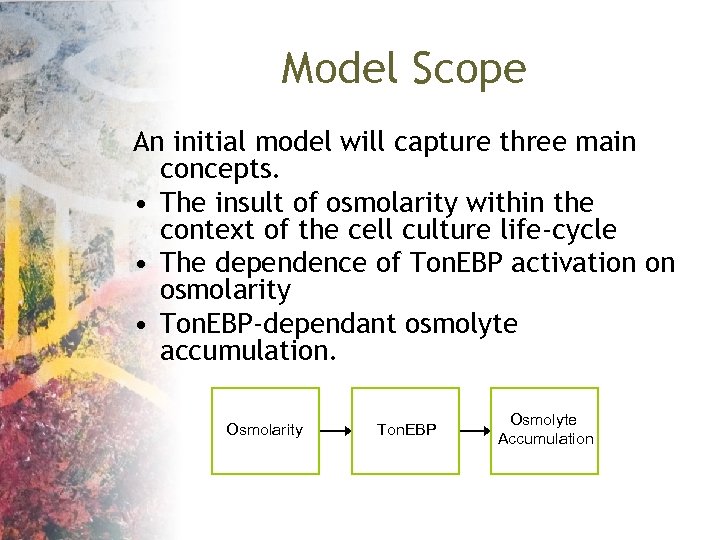
Model Scope An initial model will capture three main concepts. • The insult of osmolarity within the context of the cell culture life-cycle • The dependence of Ton. EBP activation on osmolarity • Ton. EBP-dependant osmolyte accumulation. Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation
Refined Objective • Experimentally demonstrate the central role of NFAT 5 in our cell lines the cellular osmotic response. • Build a model to characterize that role – What portion of the osmotic response can be accounted for solely by Ton. EBP? – Are other factors or feedback loops required to explain observed dynamics?
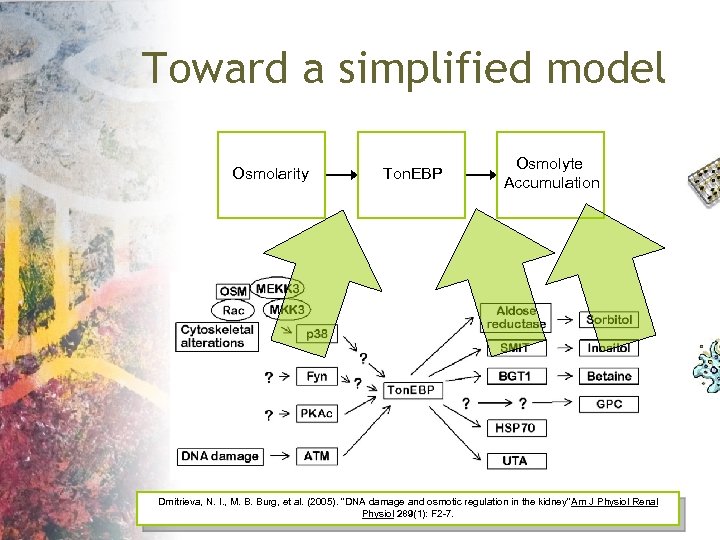
Toward a simplified model Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation Dmitrieva, N. I. , M. B. Burg, et al. (2005). "DNA damage and osmotic regulation in the kidney" m J Physiol Renal A Physiol 289(1): F 2 -7.
Osmolarity • This is the primary independent variable in the system – Could be modeled in terms of a rapidly decreasing osmotic gradient – Could be kept at a constant – Could be modeled as a slowly increasing quantity. Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation
Ton. EBP • First dependant variable, primarily dependant on the osmolarity – Goal is to fit this quantity to experimental data Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation

Osmolyte Accumulation • We presume that osmolyte accumulation is dependant on Ton. EBP activation • We’ll use a proxy of cell volume initially. Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation
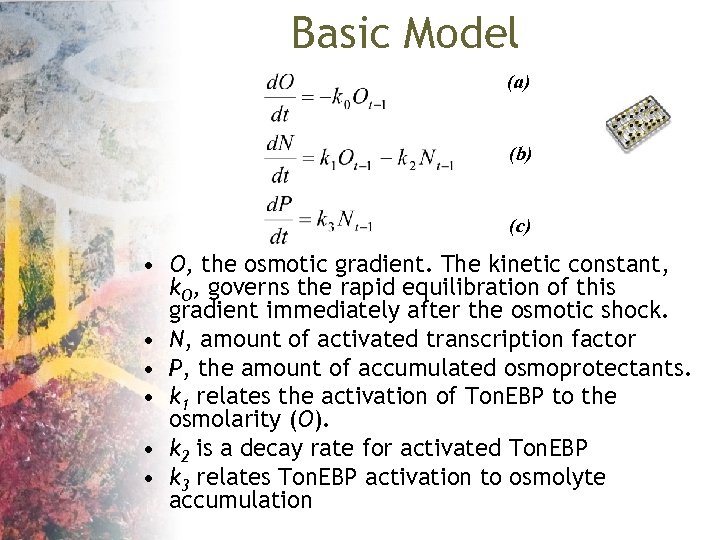
Basic Model (a) (b) (c) • O, the osmotic gradient. The kinetic constant, k. O, governs the rapid equilibration of this gradient immediately after the osmotic shock. • N, amount of activated transcription factor • P, the amount of accumulated osmoprotectants. • k 1 relates the activation of Ton. EBP to the osmolarity (O). • k 2 is a decay rate for activated Ton. EBP • k 3 relates Ton. EBP activation to osmolyte accumulation
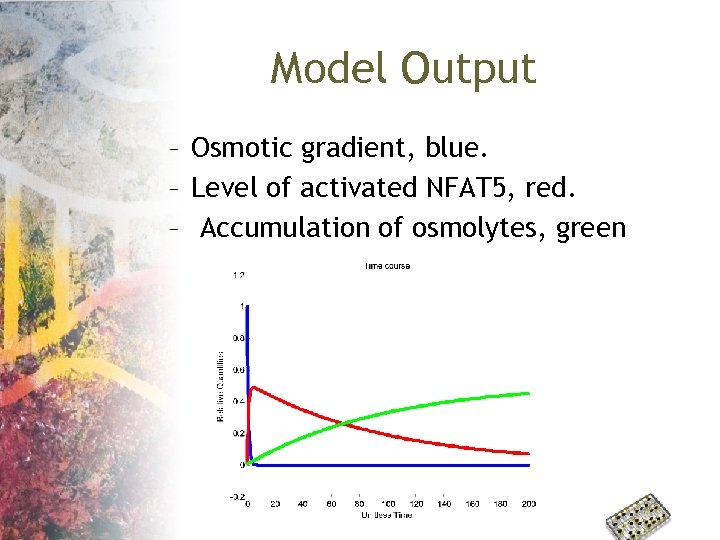
Model Output – Osmotic gradient, blue. – Level of activated NFAT 5, red. – Accumulation of osmolytes, green
Iterate on the model • Generally fits with what we expect • Missing some important features • Must relate the model to actual data. Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation

Experimental Plans, Initial Data • • Osmotic stress protocol Quantify Ton. EBP Quantify Cell Volume Other experimental possibilities

Osmostress Experiment • Stress cells with 100 m. Osm increase • Sample Cells at – Pre-stress Control – Post-stress 5, 10, 15, 30, 60 & 120 min • For western blot: – Lyse in SDS and shear DNA – Use lysate in chemoluminescent or fluorescent western blot.
![NFAT 5 DNA Binding • Consensus Sequence – TGGAAANN(C/T) [1] • N = any NFAT 5 DNA Binding • Consensus Sequence – TGGAAANN(C/T) [1] • N = any](https://present5.com/presentation/e4ad2710a524112a800fa963b7bb7af3/image-39.jpg)
NFAT 5 DNA Binding • Consensus Sequence – TGGAAANN(C/T) [1] • N = any nucleotide • C/T = any pyrimidine • NFAT Family, but similar to an NF-k. B 1) Miyakawa H, Woo S K, Dahl S C, Handler J S, Kwon H M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999; 96: 2538– 2542. [Pub. Med] 2) <image> James C. Stroud et al Nature Structural Biology 9, 90 - 94 (2002)
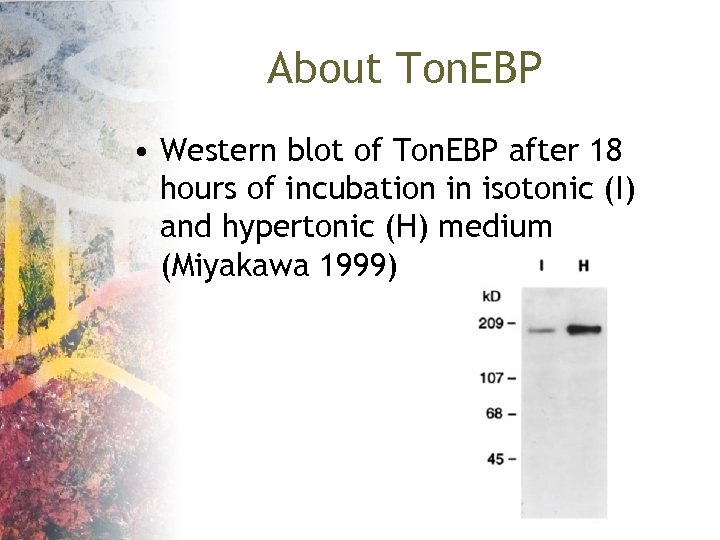
About Ton. EBP • Western blot of Ton. EBP after 18 hours of incubation in isotonic (I) and hypertonic (H) medium (Miyakawa 1999)
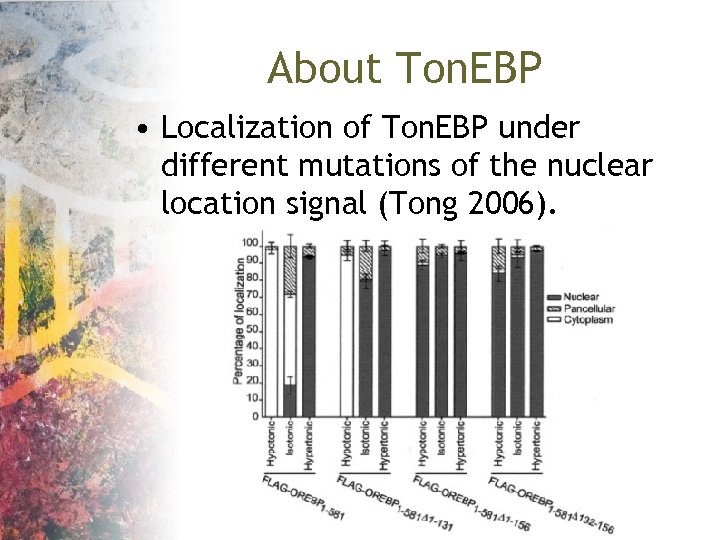
About Ton. EBP • Localization of Ton. EBP under different mutations of the nuclear location signal (Tong 2006).
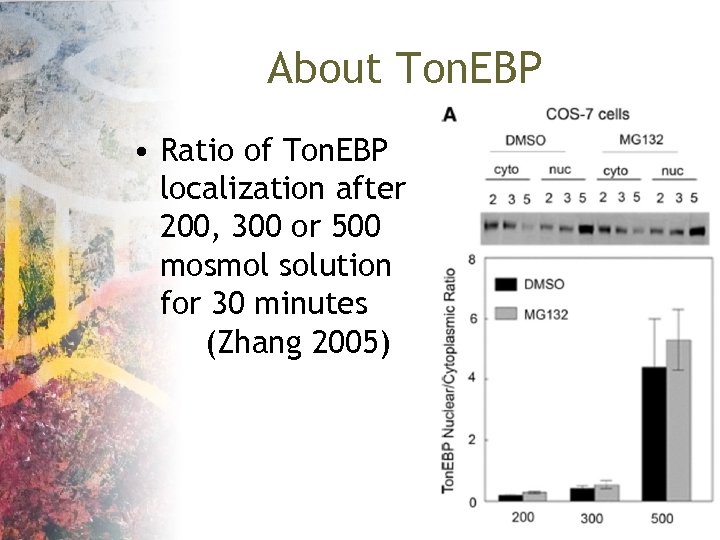
About Ton. EBP • Ratio of Ton. EBP localization after 200, 300 or 500 mosmol solution for 30 minutes (Zhang 2005)
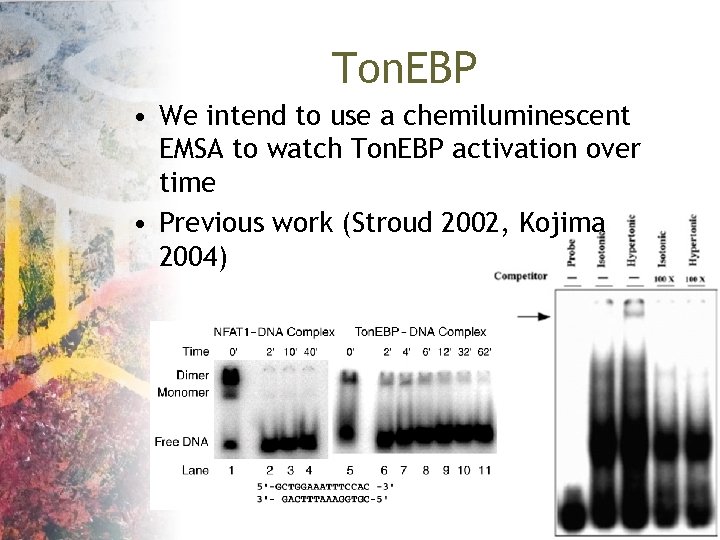
Ton. EBP • We intend to use a chemiluminescent EMSA to watch Ton. EBP activation over time • Previous work (Stroud 2002, Kojima 2004)
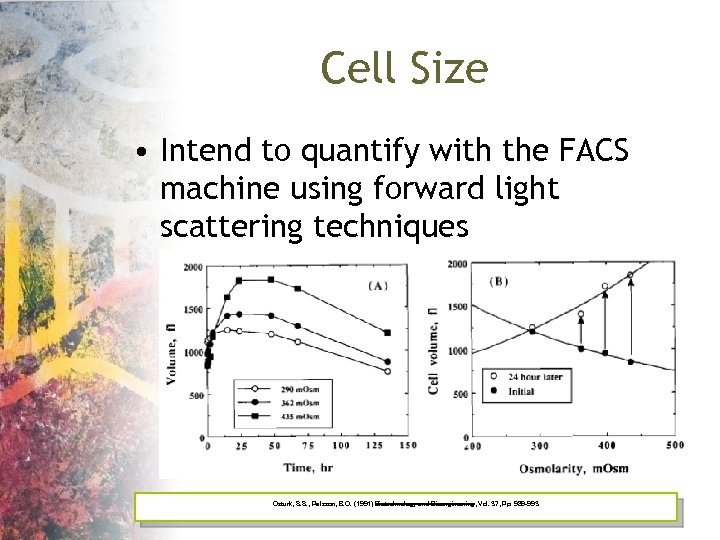
Cell Size • Intend to quantify with the FACS machine using forward light scattering techniques Ozturk, S. S. , Palsson, B. O. (1991) Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 37, Pp. 989 -993

Other measurements • As time allows – Upstream signaling components – Specific osmolyte accumulation – Lactic acid production
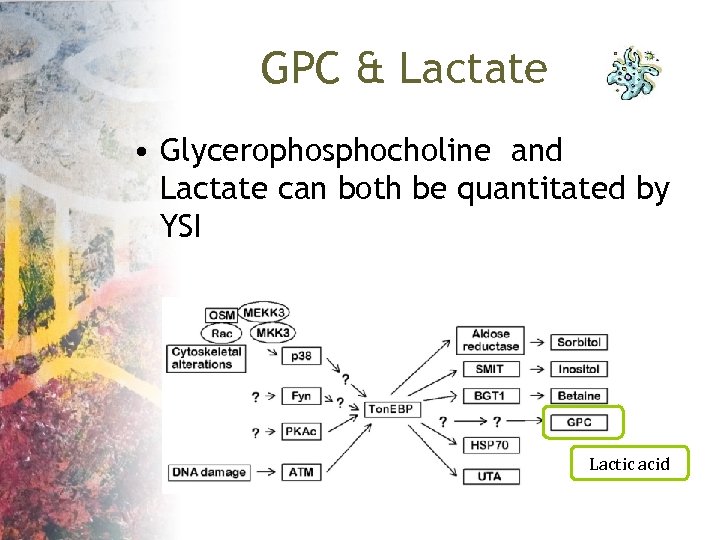
GPC & Lactate • Glycerophosphocholine and Lactate can both be quantitated by YSI Lactic acid
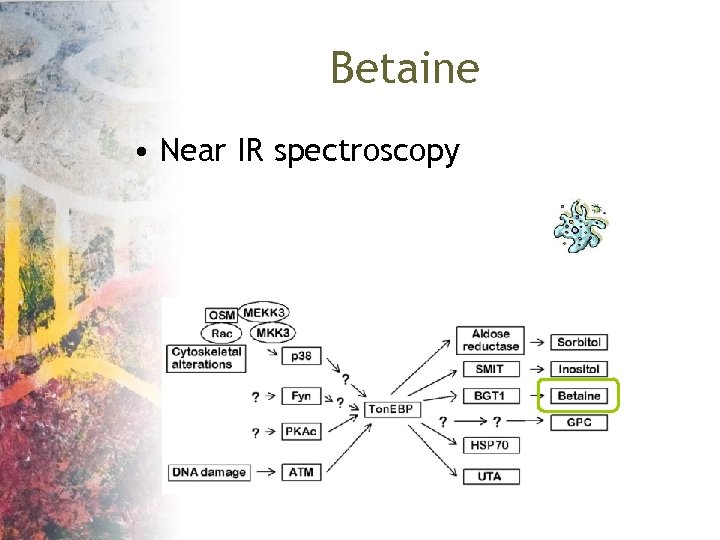
Betaine • Near IR spectroscopy
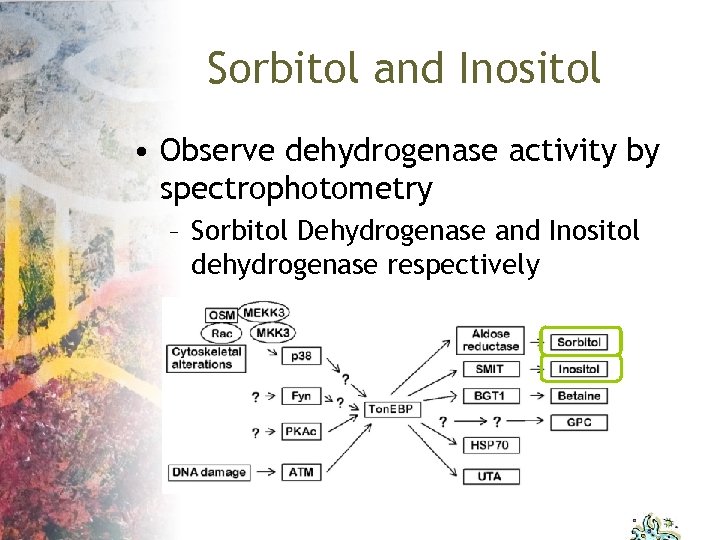
Sorbitol and Inositol • Observe dehydrogenase activity by spectrophotometry – Sorbitol Dehydrogenase and Inositol dehydrogenase respectively
Aldose Reductase Activity • Spectrophotometry, absorbtion at 340 (Bagnasco et al. , PNAS 84: 1718) (JBC 1965 page 877)
PKA & Fyn • PKA by ELISA, from Stressgen Bioreagents (already attempted with a kit from Omnia, need to further optimize) • Fyn immuniprecipitation following Ko et. al from JBC vol 273 pp 46083
P 38 MAPK • Chemiluminescent Western from Cell Signaling Technologies
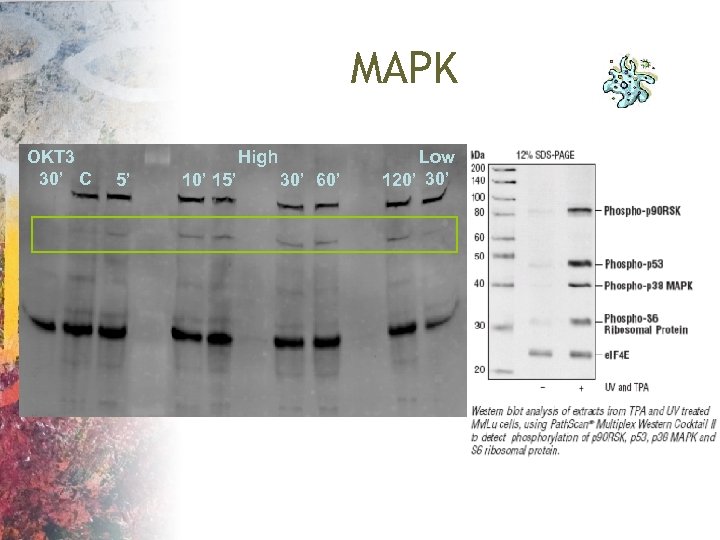
MAPK OKT 3 30’ C High 5’ 10’ 15’ 30’ 60’ Low 120’ 30’
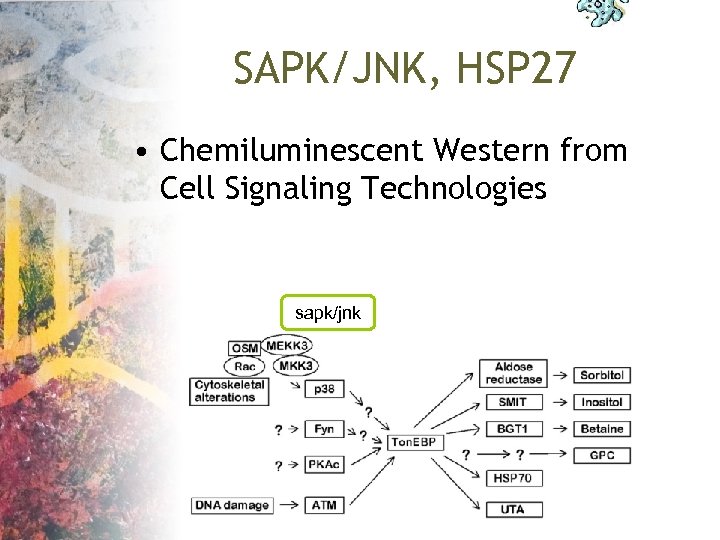
SAPK/JNK, HSP 27 • Chemiluminescent Western from Cell Signaling Technologies sapk/jnk
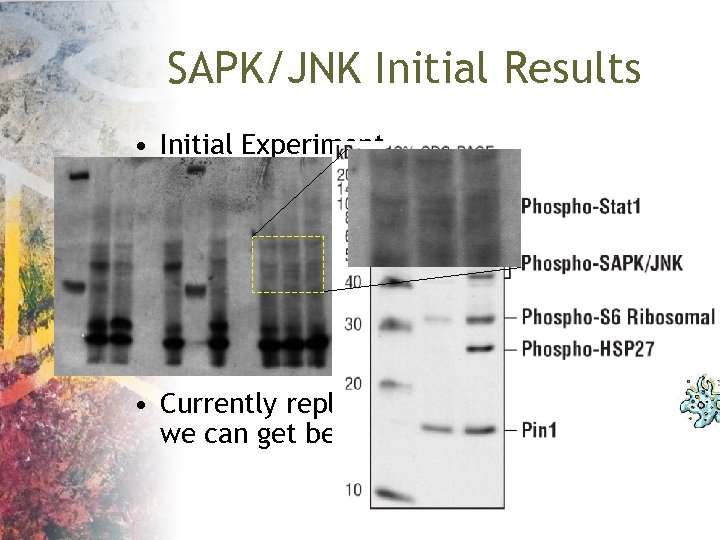
SAPK/JNK Initial Results • Initial Experiment • Currently replicating this work to see if we can get better resolution
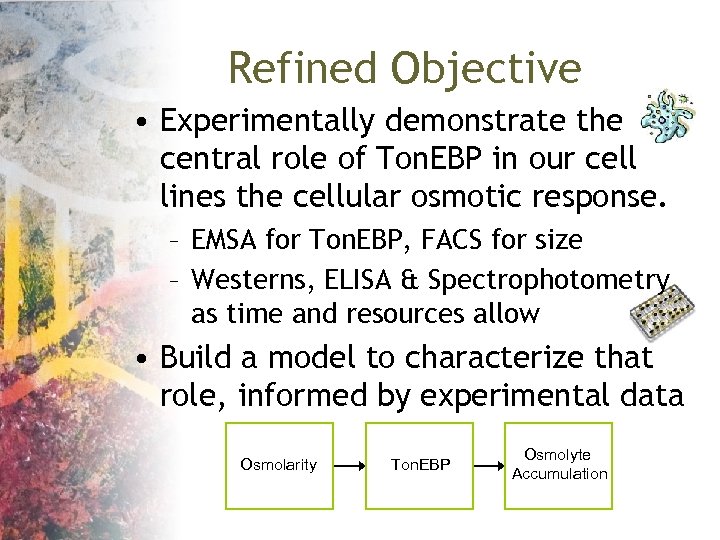
Refined Objective • Experimentally demonstrate the central role of Ton. EBP in our cell lines the cellular osmotic response. – EMSA for Ton. EBP, FACS for size – Westerns, ELISA & Spectrophotometry as time and resources allow • Build a model to characterize that role, informed by experimental data Osmolarity Ton. EBP Osmolyte Accumulation


Other Efforts • • Microarray Analysis Batch Culture Model Co. EPr. A Evolving Bifurcating Networks
Microarray Analysis • Looking at network component analysis (NCA) • Conceptualized some other SVM related approaches with Prof. Embrects (DSES)
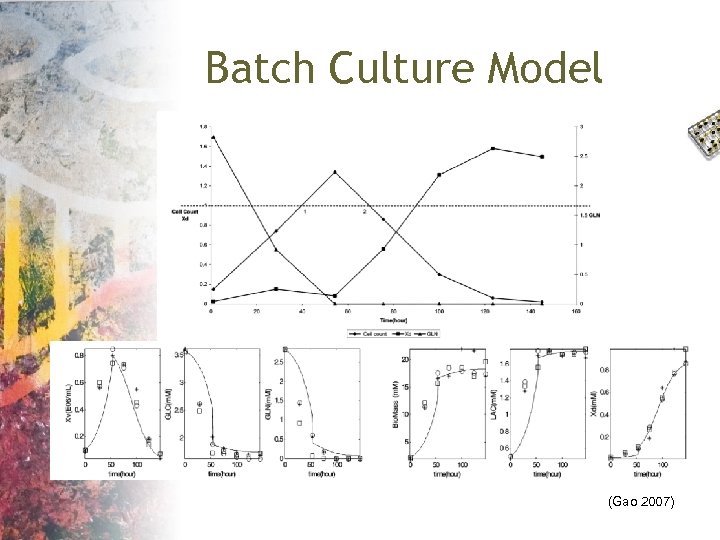
Batch Culture Model (Gao 2007)

Co. EPr. A Comparative Evaluation of Prediction Algorithms • “Primitive” Linear Algebra approach Placed 8 th out of 16 participants on a classification task. • Paper submission invited. • Task was to classify short peptides (8 -9 amino acids) so as to predict activity. http: //www. coepra. org

Method • Our method utilized a simple mechanism of computing distances between LOGO’s generated for each sequence and each class of sequences (Crooks 2004). • We used a random search algorithm to identify active nonapeptides in the prediction set. • Random subsets of the joint calibrationprediction superset were compared with the active calibration subset. The retained loss function is the Frobenius matrix norm of the difference between the logos. • One thousand runs were completed and results were pooled together to make the final prediction.
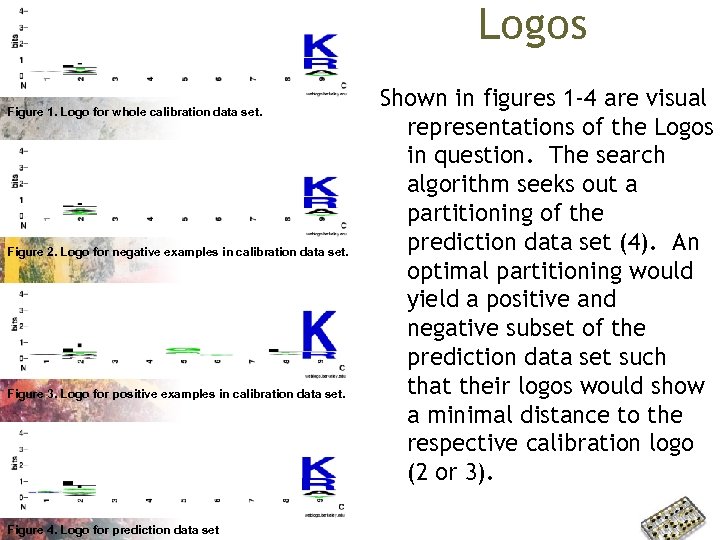
Logos Figure 1. Logo for whole calibration data set. Figure 2. Logo for negative examples in calibration data set. Figure 3. Logo for positive examples in calibration data set. Figure 4. Logo for prediction data set Shown in figures 1 -4 are visual representations of the Logos in question. The search algorithm seeks out a partitioning of the prediction data set (4). An optimal partitioning would yield a positive and negative subset of the prediction data set such that their logos would show a minimal distance to the respective calibration logo (2 or 3).
Evolving Bifurcating Networks • A good body of literature has started to form in the area of Evolving Biochemical Reaction Networks. • Looking to build on previous work to create networks with specific distributions of outputs
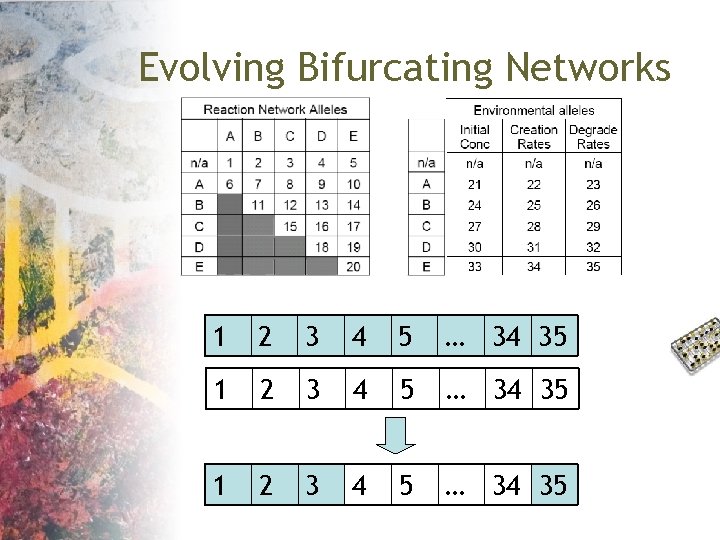
Evolving Bifurcating Networks 1 2 3 4 5 … 34 35
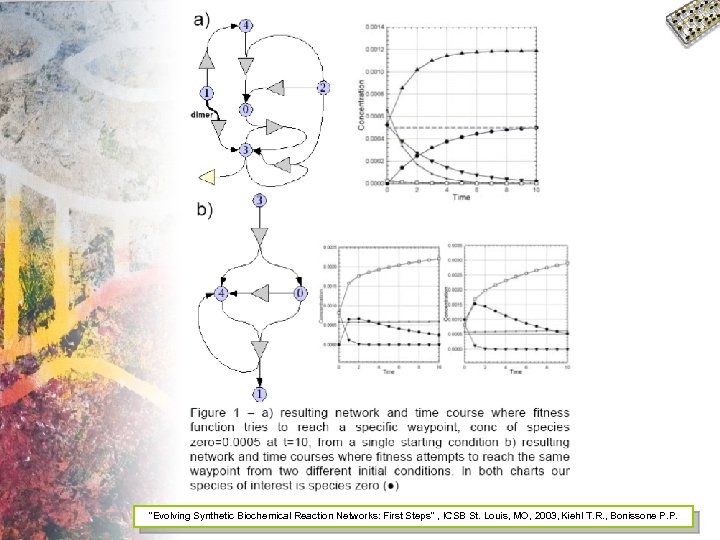
"Evolving Synthetic Biochemical Reaction Networks: First Steps" , ICSB St. Louis, MO, 2003, Kiehl T. R. , Bonissone P. P.
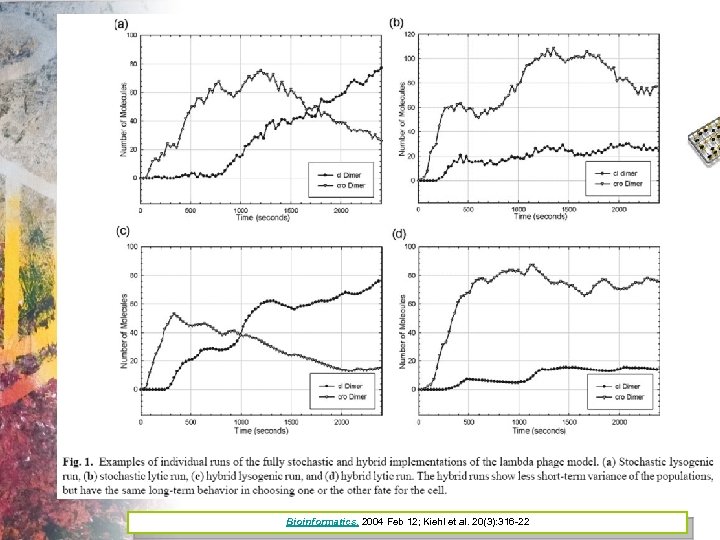
Bioinformatics. 2004 Feb 12; Kiehl et al. 20(3): 316 -22

Thanks. • • • NSF GRF Susan Sharfstein Lealon Martin Sam Wait David Isaacson Joyce Diwan Mark Embrechts Numerous folks @ GE Charles Bergeron Duan Shen Family & Friends

Ongoing work the end

the end

Osmotic Shock
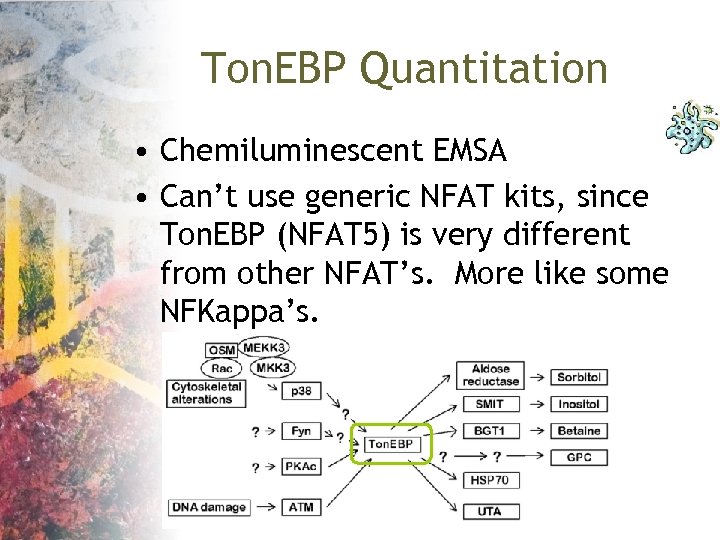
Ton. EBP Quantitation • Chemiluminescent EMSA • Can’t use generic NFAT kits, since Ton. EBP (NFAT 5) is very different from other NFAT’s. More like some NFKappa’s.

Antibody Production • How does one stimulate production and maintain cell viability, thereby increasing specific productivity? • Various types of stress are used to stimulate production, including Osmotic stress. • What mechanisms are responsible for this response?
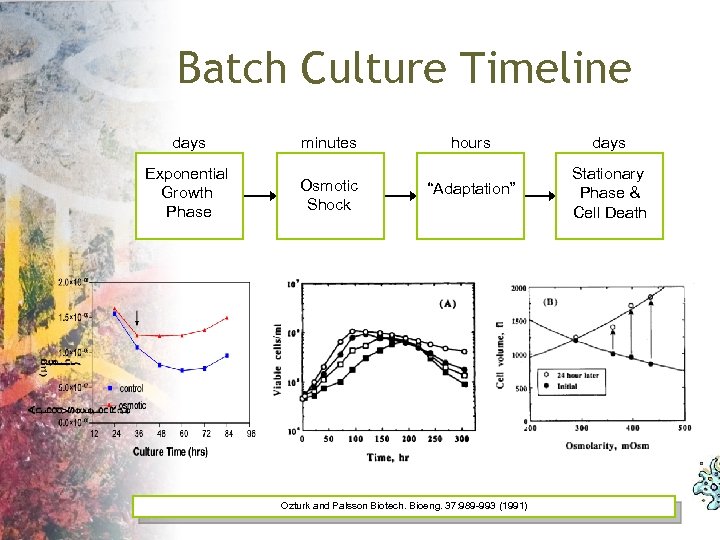
Batch Culture Timeline days minutes Exponential Growth Phase Osmotic Shock hours days “Adaptation” Stationary Phase & Cell Death Ozturk and Palsson Biotech. Bioeng. 37: 989 -993 (1991)

Modelling Response to Osmotic Shock • Incorporate the acquired data, along with data from literature to into a computational model • Following Klipp et al in their yeast model
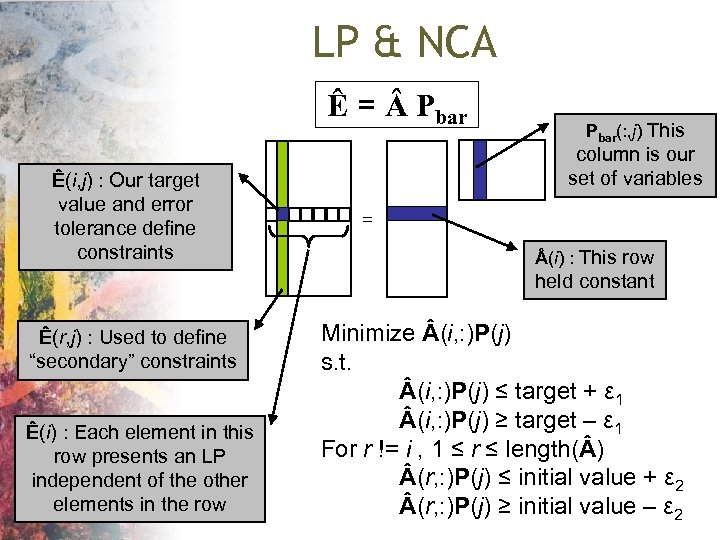
LP & NCA Ê = Pbar Ê(i, j) : Our target value and error tolerance define constraints Pbar(: , j) This column is our set of variables = (i) : This row held constant Ê(r, j) : Used to define “secondary” constraints Ê(i) : Each element in this row presents an LP independent of the other elements in the row Minimize (i, : )P(j) s. t. (i, : )P(j) ≤ target + ε 1 (i, : )P(j) ≥ target – ε 1 For r != i , 1 ≤ r ≤ length( ) (r, : )P(j) ≤ initial value + ε 2 (r, : )P(j) ≥ initial value – ε 2

PCA → NCA With Prof. Martin: • Relative acid concentrations in grape varieties. • Can NCA be applied to get more information out of the data?

Questions asked • Where to publish? – Sys bio journals, bioinformatics, ieee – Probably multiple, some more bio focused, some more computationally focused. • Have you thought about the model? – Two main pieces, the structure and the numbers.
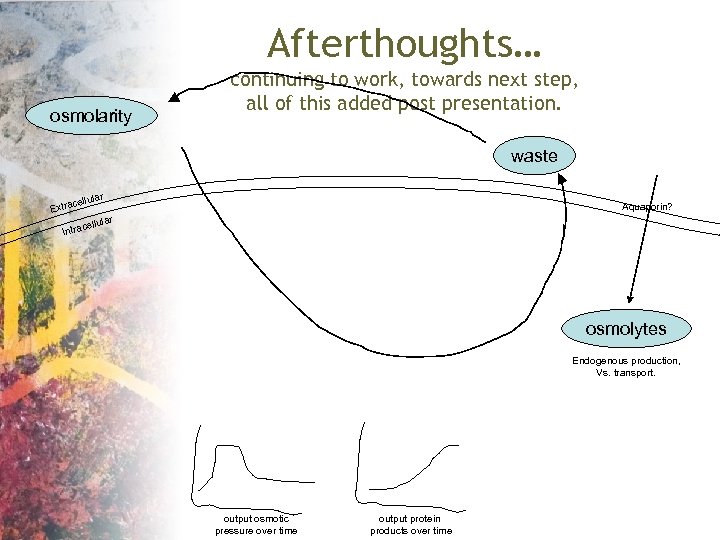
Afterthoughts… osmolarity continuing to work, towards next step, all of this added post presentation. waste r ellula xtrac E lar cellu Intra Aquaporin? osmolytes Endogenous production, Vs. transport. output osmotic pressure over time output protein products over time

Calculation of osmotic pressure • Osmotic pressure in atmospheres – π = MRT • M is the molar concentration of dissolved species (units of mol/L). • R is the ideal gas constant (0. 08206 L atm mol-1 K-1, or other values depending on the pressure units). • T is the temperature on the Kelvin scale. molarity * R * temp(kelvin) • Quantitating amounts of osmolytes prior to stress should give us an idea of: – Baseline pressure – Initial maximum pressure • Quantitating during stress should give us a time course of osmotic pressure.

Random questions • Osmolarity in our cultures vs. industry relevent cultures vs. in vivo renal medullary conditions – Qi Cai et al 2004 cite different responses for linear increases in osmolarity vs. step incresases

Market reports… … are numerous. • This is a very simplistic measure of the importance of this market • Google: monoclonal antibody market • See how much money you could spend just buying reports on the market.

(ROUGH) Candidacy Practice Biological blablah. Computational Experiments and blah Analysis Toward theblah Signaling blah Elucidation of Signaling and Gene Expression Responses to blah Osmotic Shock Gene Expression blah Osmotic Shock and blah blah Antibody Resultant Osmolyte Accumulation in Producing Cell Lines blah Spring 2007 Tom Kiehl

YSI Analyzer Can provide quick measurements of the following analytes: – – – D-Glucose (Dextrose) L-Lactate Sucrose Lactose Ethanol L-Glutamate Choline L-Glutamine Methanol Galactose* Hydrogen Peroxide*
e4ad2710a524112a800fa963b7bb7af3.ppt