6201b67642a2a938a247788e21ca87d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Goal 5 Part 2 Labor Unions / Strikes

What is a union? ____– a group of laborers with a common cause: – expose the harsh conditions of jobs n 2 major types: (1) _____ (SKILLED) (2) __________ (SKILLED / UNSKILLED) n “United we stand, divided we fall”
Stats and conditions Working Conditions: 7 day workweek 12 or more hour shifts (daily) no vacation / no sick days No workman’s compensation Injured – no reimbursement ALL family members had to work to survive Children -. 27 every 14 hours Men - $498 / year Women - $267 / year Carnegie - $23 million / year Statistics: 1882 – 675 (avg. ) weekly deaths in America

Collective Bargaining n Unions form to fight for TWO things (1) ______________ (2) ______________ “Negotiation between laborers and management”

Early Labor Unions _________(NLU) 1866 – - refused African Americans as members - __________ (Trade unionism) Leader: ___________ - Lobbied _____, not the ________ MAIN LEGACY: ______(Originally pushed by Populist…later adopted by Democrats) Colored National Labor Union (CNLU) – accepted African Americans

________ n Beliefs: (1) ____ = Equal pay for equal work ***(2) ______…(women and African Americans) / “skilled AND unskilled” Leader: Terrence Powderly (3) DID NOT USE _______– refusal to work, as a LAST resort (favored non-violence) (4) Practiced ______: resolving a dispute OUTSIDE of the court system “Injury to one is the concern of all”
2 types of Unions / Craft vs. Trade 1 Craft Unionism: includes skilled workers ____________________ Leader - SAMUEL _________ - believed in “collective bargaining” - used ________________ tactic /resort (supported violence)* Complete opposite of Knights of Labor 2 Industrial Unionism / Trade Unionism: included skilled AND unskilled workers ____________________ Leader - __________ (SOCIALIST) *STRIKES WERE USED! “The Strike is the ___________” Eugene V. Debs

Eugene V. Debs – Socialist

Socialism / Industrial Workers of the World ( I. W. W. ) n n n ______ – an economic system in which the government controls ___________/ less extreme version of _______ Individuals do not work for themselves, but live in corporation of one another Purpose: Overthrow _______ Pro: total equality regardless of physical differences Con: hard workers get no support “EQUAL DISTRIBUTION OF WEALTH” __________________(IWW) ********Example of Socialist Union*********** -Mostly Unskilled workers Leader: __________ / Bill Haywood Nickname: ______ Used STRIKES…. all the time! (USED _______) * Socialist Unions – EUGENE V. DEBS!!!!

Strikes Federal Government response to Strikes / Unions: unhappy and acted with force (threat to the capitalist government – messes w/$) n Federal troops are sent in (injunction) n n n ____________of 1877 – B & O Railroad lead a strike (covered 50, 000 miles) President _________claimed they threatened *___________* - sent federal troops to end the strike!

Great Railroad Strike of 1877

INJUNCTION ________: when federal government “jumps in” and tries to fix everything Example: Great Railroad Strike of 1877 Pullman Strike (federal troops were sent in) n

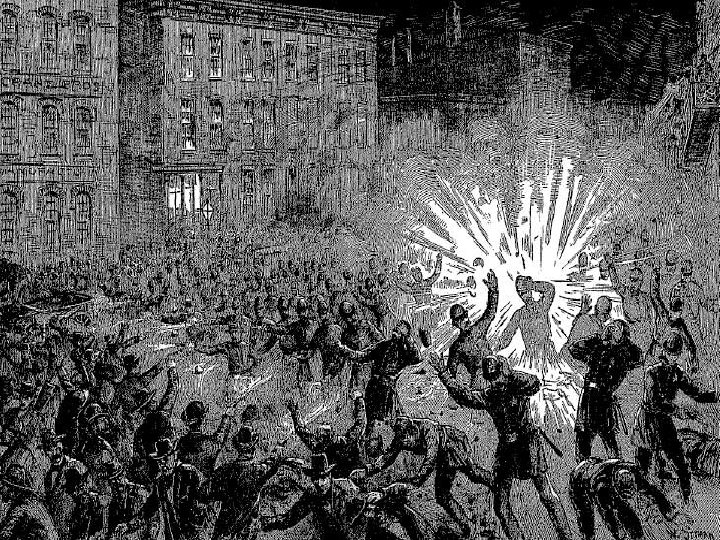
**______________** Strike in Chicago…. police show up, workers threw a bomb into police lines! n Several police officers died n MAJOR EFFECT: THE _________________________ MOVEMENT (due to violence) ______________ n


___________ n n Carnegie Steel Company (Homestead Plant in PA) – cut wages – a strike occurs! ________, Homestead Plant manager hired , _____, or strikebreakers, that continued to work, despite the strike to keep the company going

The Pullman Company Strike n n n Pullman Company laid off 3, 000 workers George Pullman hired employees and gave them housing…after lay offs, didn’t lower the rent on the house! ****George Pullman wanted to control the lives of his workers (no loitering on front porch!) George Pullman hired SCABS, strikebreakers…strikes turned violent Major effect: federal troops were sent in *** Railroads “_________” the strikers *Blacklist – a list that included people that COULD NOT work on the railroads, due to their connection to strikes

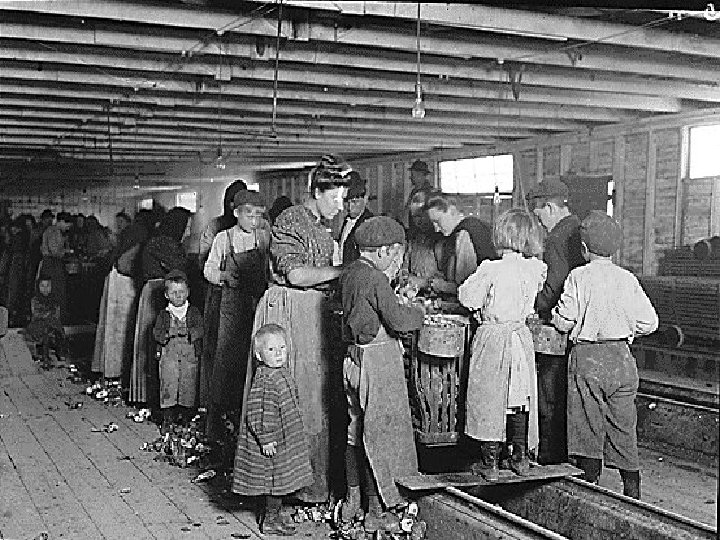
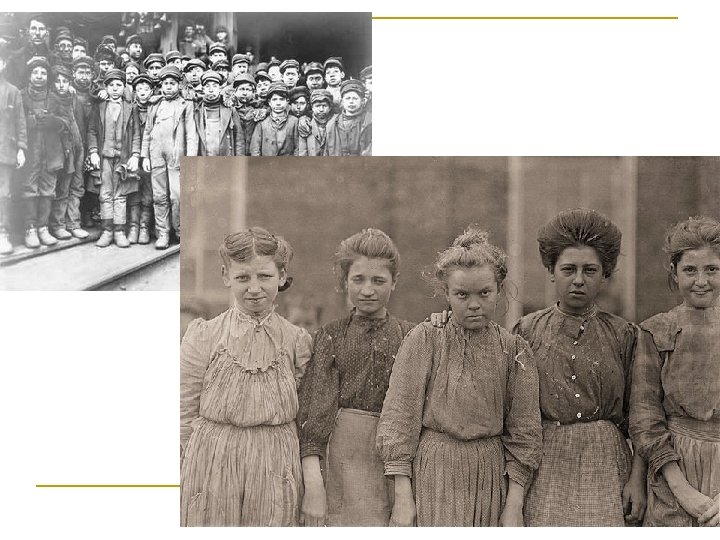
Women Organize n Fighting for: q q q Better _________ Equal pay ________ End of _________ ****MAIN LEADER: __________ (MOTHER) To expose the cruelties of child labor – Mary Harris Jones led a march of 80 mill children to home of President Teddy Roosevelt…. this crusade influenced the passage of Child Labor Laws

Child Labor / Mary Harris Jones

CHILD LABOR



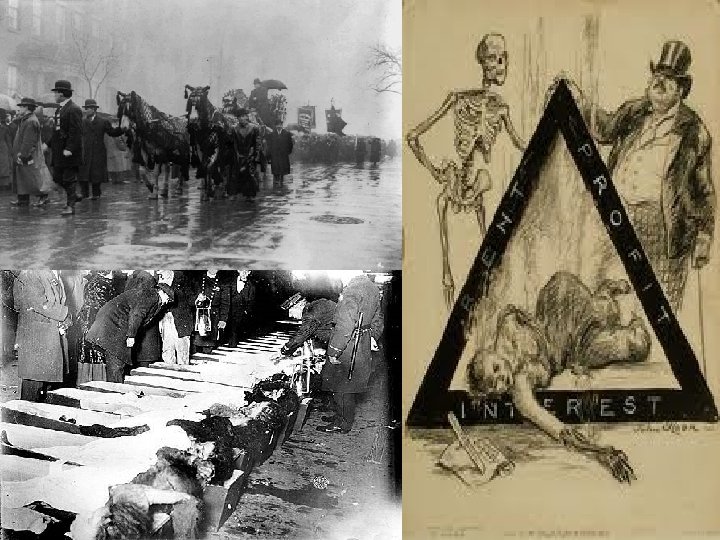
___________- Fire n n n March 25, 1911 (New York City) Oil-drenched machines caught on fire! (conditions) Company locked all of the doors *(Crime / force) 146 women died (from fire or jumping) MAJOR EFFECT/ Public Reaction: ________ to study the terrible _______ of many industries in New York * spurred the growth of improved factory conditions and safety standards

Triangle Shirtwaste Fire (1911)
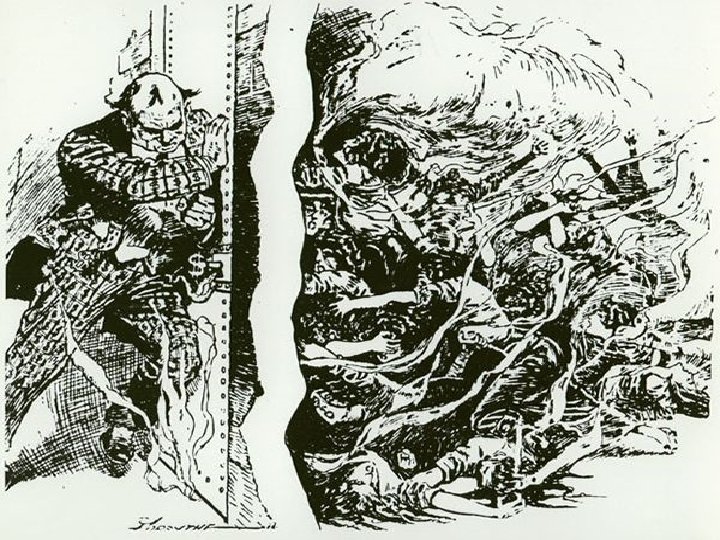

Factors that LIMIT the success of Labor Unions / Employers CONTROL ____________– swearing / oath they will NOT join a Union _________– if you are part of or leader of a union against the productivity of a business, you are placed on this list / difficult for you to get a job _________: owner tells the employees not to bother showing up until they agree to a pay cut ________: Strikebreakers (hired to continue economy of business while strikers are not working) _________: a company claims strikers are affecting interstate commerce and the federal government comes running!

* T. Q. Which statement BEST describes how the Knights of Labor differed from the American Federation of Labor (AFL)? A. Knights of Labor used strikes as a major tactic B. Knights of Labor ONLY organized skilled laborers C. Knights of Labor used strikes as a last resort D. Knights of Labor opposed equal pay for women

What event contributed MOST to the demise of the Knights of Labor? A. B. C. D. Great Chicago Fire Haymarket Square Riot Homestead Act Pullman Company Strike Why?
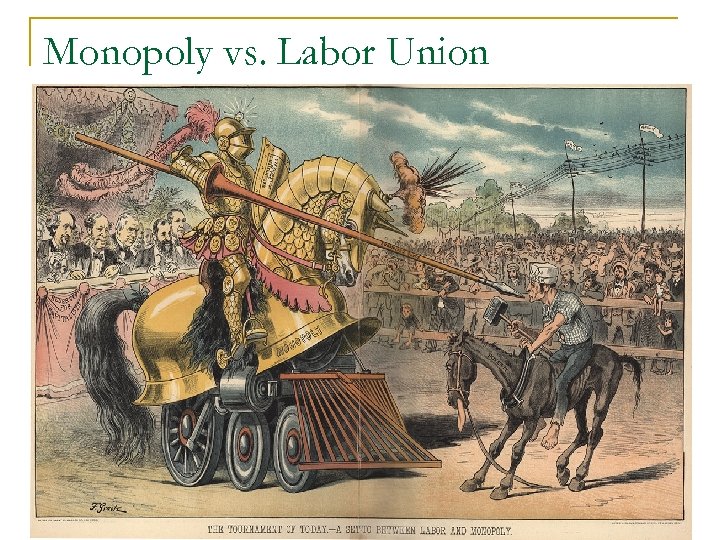
Monopoly vs. Labor Union
6201b67642a2a938a247788e21ca87d1.ppt