139ee2e860dedd1f63ce6dfbf3122d30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 + GMOs Friend or Foe? Social Studies 11 – Human Geography May 12, 2014
+ GMOs Friend or Foe? Social Studies 11 – Human Geography May 12, 2014
 + What are genetically modified foods? n Also called genetically modified organisms (GMO), or GE foods (Genetically engineered). n Genetically Modified Organism: an organism that contains genes that have been put into it by processes that do not occur in nature (biotechnology) n Created by inserting DNA from one organism into another OR modifying an organism’s DNA to attain a desirable trait. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ What are genetically modified foods? n Also called genetically modified organisms (GMO), or GE foods (Genetically engineered). n Genetically Modified Organism: an organism that contains genes that have been put into it by processes that do not occur in nature (biotechnology) n Created by inserting DNA from one organism into another OR modifying an organism’s DNA to attain a desirable trait. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 + Examples of GMO’s n Golden rice – enriched rice containing betacarotene (Vitamin A). This vitamin is not found in normal rice. n Bt corn – corn containing a chemical normally found in bacteria (Bacillus thuringiensis). This is toxic to insects, not humans. Insects try to eat the plant and die. n Herbicide resistant plants (roundup ready corn). These plants are immune to a certain herbicide, so they live while all the other plants in the field are killed. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ Examples of GMO’s n Golden rice – enriched rice containing betacarotene (Vitamin A). This vitamin is not found in normal rice. n Bt corn – corn containing a chemical normally found in bacteria (Bacillus thuringiensis). This is toxic to insects, not humans. Insects try to eat the plant and die. n Herbicide resistant plants (roundup ready corn). These plants are immune to a certain herbicide, so they live while all the other plants in the field are killed. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 + GMO foods…are common According to Greenpeace, up to 70% of processed foods in Canada contain GM ingredients. Most common are corn, soy, canola and cotton. Image credit: http: //www. usda. gov: US Dept of Agriculture
+ GMO foods…are common According to Greenpeace, up to 70% of processed foods in Canada contain GM ingredients. Most common are corn, soy, canola and cotton. Image credit: http: //www. usda. gov: US Dept of Agriculture
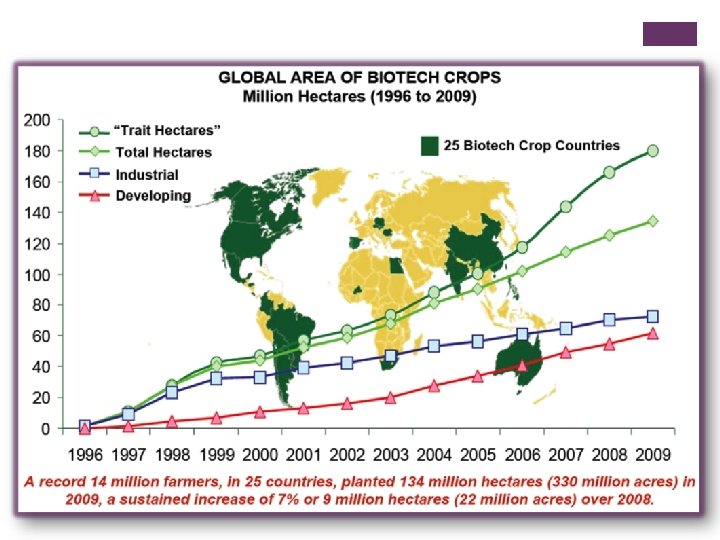
 + What is grown globally? n In 2001 the area of genetically modified crops grown globally was 52. 6 million hectares. That is an area the size of France or Spain. This includes food and non-food crops (I. e. cotton) n 4 countries produced 99% of the world's genetically modified crops. These are: n n USA (68%) Argentina (22%) Canada (6%) China (3%) n More than 80% of canola grown in Canada and a high proportion of the country’s soybean and corn crops are genetically modified. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ What is grown globally? n In 2001 the area of genetically modified crops grown globally was 52. 6 million hectares. That is an area the size of France or Spain. This includes food and non-food crops (I. e. cotton) n 4 countries produced 99% of the world's genetically modified crops. These are: n n USA (68%) Argentina (22%) Canada (6%) China (3%) n More than 80% of canola grown in Canada and a high proportion of the country’s soybean and corn crops are genetically modified. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 From ( U. S. Dept. Agriculture 2001)
From ( U. S. Dept. Agriculture 2001)
 + foods in Canada GM Health Canada groups GM foods into a category called “Novel Foods”. Foods • Foods that have been modified by genetic manipulation, also known as genetically modified (GM) foods, genetically engineered foods or biotechnology-derived foods 70 novel foods have been approved for sale in Canada. Potatoes Canola Corn Tomatoes Squash Soybeans Flax Sugarbeets Are all examples!! These crops are processed into the goods in grocery stores…. • Fries, cakes, oils, sugars, sauces • Animals that feed on GMOs… And more… all without mandatory labeling.
+ foods in Canada GM Health Canada groups GM foods into a category called “Novel Foods”. Foods • Foods that have been modified by genetic manipulation, also known as genetically modified (GM) foods, genetically engineered foods or biotechnology-derived foods 70 novel foods have been approved for sale in Canada. Potatoes Canola Corn Tomatoes Squash Soybeans Flax Sugarbeets Are all examples!! These crops are processed into the goods in grocery stores…. • Fries, cakes, oils, sugars, sauces • Animals that feed on GMOs… And more… all without mandatory labeling.
 + Benefit #1 n. Increased crop productivity n. This includes herbicide tolerance, npest and disease resistance n. E. g. “Roundup ready” crops, and BT corn. n. Could mean using less harmful pesticide spray Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
+ Benefit #1 n. Increased crop productivity n. This includes herbicide tolerance, npest and disease resistance n. E. g. “Roundup ready” crops, and BT corn. n. Could mean using less harmful pesticide spray Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
 + Benefit #2 n. Environmental Tolerance n Cold tolerance n plants developed to tolerate cold temperatures n & withstand unexpected frost n could destroy seedlings n Drought & salinity tolerance n currently inhospitable regions can now be cultivated Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/
+ Benefit #2 n. Environmental Tolerance n Cold tolerance n plants developed to tolerate cold temperatures n & withstand unexpected frost n could destroy seedlings n Drought & salinity tolerance n currently inhospitable regions can now be cultivated Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/
 + Benefit #3 n. Improved nutrition ncrops like rice are a staple in developing countries n nutritionally inadequate! n. GM "golden rice" is high in beta -carotene (vitamin A) n Reduces eye-related problems like blindness due to malnutrition Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
+ Benefit #3 n. Improved nutrition ncrops like rice are a staple in developing countries n nutritionally inadequate! n. GM "golden rice" is high in beta -carotene (vitamin A) n Reduces eye-related problems like blindness due to malnutrition Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
 + Benefit #4 n Future benefits: benefits n food without allergens; (I. e. anyone could eat nuts) n grains, fruit & vegetables with improved nutrition (multi-vitamin potatoes=healthy fast food french fries!) n longer shelf life and better taste (reduced food waste due to spoilage) n rice enhanced with iron (prevent anemia) n foods used as vaccines (bye-bye needles) n Many more possibilities Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ Benefit #4 n Future benefits: benefits n food without allergens; (I. e. anyone could eat nuts) n grains, fruit & vegetables with improved nutrition (multi-vitamin potatoes=healthy fast food french fries!) n longer shelf life and better taste (reduced food waste due to spoilage) n rice enhanced with iron (prevent anemia) n foods used as vaccines (bye-bye needles) n Many more possibilities Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 + Challenge #1 n Environmental – possibility of unintended harm to other organisms: n potential risk of harm to non-target organisms, e. g. a pest resistant crop that produces toxins that may harm both crop-damaging and non cropdamaging insects n E. g. The pollen of BT corn on milkweed is thought to affect (slow or kill) the larvae of Monarch butterflies. Further studies are underway. Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
+ Challenge #1 n Environmental – possibility of unintended harm to other organisms: n potential risk of harm to non-target organisms, e. g. a pest resistant crop that produces toxins that may harm both crop-damaging and non cropdamaging insects n E. g. The pollen of BT corn on milkweed is thought to affect (slow or kill) the larvae of Monarch butterflies. Further studies are underway. Image credit: http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ & Microsoft clipart
 + Challenges #2 n“Superweeds” n gene transfer to non-target species where herbicide tolerant plants crossbreed with weeds potentially creating herbicide resistant weeds. n Some Western Canadian farmers are calling Monsanto’s round-up ready canola a superweed. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ Challenges #2 n“Superweeds” n gene transfer to non-target species where herbicide tolerant plants crossbreed with weeds potentially creating herbicide resistant weeds. n Some Western Canadian farmers are calling Monsanto’s round-up ready canola a superweed. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 + Challenges #3 n. Human health risks n n introducing a gene into a plant may create a new allergen or cause an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals For example, inserting genes from a nut into another plant could be dangerous for people who are allergic to nuts Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ Challenges #3 n. Human health risks n n introducing a gene into a plant may create a new allergen or cause an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals For example, inserting genes from a nut into another plant could be dangerous for people who are allergic to nuts Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 + Challenges #4 n. Economic Hazards n Elimination n GM seeds are patented (must buy each year) n n of competition This presents problems for poor farmers in both the developed and developing worlds. Large companies like Monsanto have resorted to suing small farmers found to be using their seed without paying. n Suicide seeds Plants with sterile seeds that are infertile are created n Farmers are forced to buy seeds every year n n However, some companies have reduced costs or donated GM seeds to impoverished nations. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ Challenges #4 n. Economic Hazards n Elimination n GM seeds are patented (must buy each year) n n of competition This presents problems for poor farmers in both the developed and developing worlds. Large companies like Monsanto have resorted to suing small farmers found to be using their seed without paying. n Suicide seeds Plants with sterile seeds that are infertile are created n Farmers are forced to buy seeds every year n n However, some companies have reduced costs or donated GM seeds to impoverished nations. Image credit: Microsoft clipart
 Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
 Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
 Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
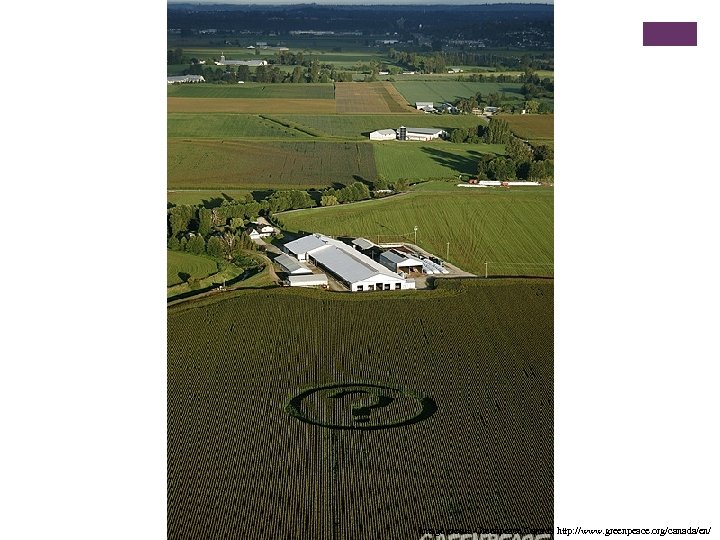 Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
 + About the previous picture…. . n Greenpeace activists have created a 61 -metre crop circle in a corn field in Abbotsford, British Columbia. The field contains Monsanto’s NK 603 genetically engineered (GE) corn, which scientists recently linked with liver and kidney toxicity in rats. Greenpeace is calling for mandatory labelling of GE foods across Canada. n Canada grows over 5. 8 million hectares of GE crops, including 820, 000 hectares of GE corn. That’s an area of GE crops more than twice the size of Vancouver Island. We are one of the top producers of GE worldwide along with USA, Argentina, and Brazil. Forty countries around the world already have mandatory GE labelling in place. Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
+ About the previous picture…. . n Greenpeace activists have created a 61 -metre crop circle in a corn field in Abbotsford, British Columbia. The field contains Monsanto’s NK 603 genetically engineered (GE) corn, which scientists recently linked with liver and kidney toxicity in rats. Greenpeace is calling for mandatory labelling of GE foods across Canada. n Canada grows over 5. 8 million hectares of GE crops, including 820, 000 hectares of GE corn. That’s an area of GE crops more than twice the size of Vancouver Island. We are one of the top producers of GE worldwide along with USA, Argentina, and Brazil. Forty countries around the world already have mandatory GE labelling in place. Image credit: Greenpeace Canada http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/
 + References n Information: n http: //www. cpma. ca/en_gov_biotech_factsheet. asp n http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/campaigns/big-question-marks-on-genetica n http: //www. hc-sc. gc. ca/sr-sr/biotech/food-aliment/index_e. html n http: //www. bionetonline. org n http: //www. uoguelph. ca/news/2006/11/runaway_gm_crop. html n http: //www. exploratorium. edu/theworld/gm/test. html n n Pictures from: Greenpeace Canada (verbal permission via phone conversation June 2008) http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/ n www. microsoft. com n http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ n http: //www. usda. gov Image credit: Microsoft clipart
+ References n Information: n http: //www. cpma. ca/en_gov_biotech_factsheet. asp n http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/campaigns/big-question-marks-on-genetica n http: //www. hc-sc. gc. ca/sr-sr/biotech/food-aliment/index_e. html n http: //www. bionetonline. org n http: //www. uoguelph. ca/news/2006/11/runaway_gm_crop. html n http: //www. exploratorium. edu/theworld/gm/test. html n n Pictures from: Greenpeace Canada (verbal permission via phone conversation June 2008) http: //www. greenpeace. org/canada/en/ n www. microsoft. com n http: //www. public-domain-photos. com/ n http: //www. usda. gov Image credit: Microsoft clipart


