2d2fca4c856bd336681eaf8b99e36c68.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Globalization Trade Routes in the Middle East and the relationship to US gas prices…
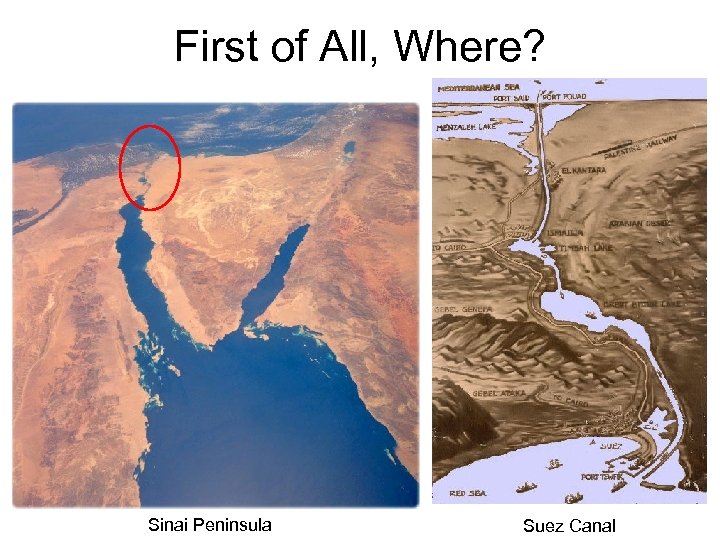
First of All, Where? Sinai Peninsula Suez Canal
A Little History First, YAY! • At least as early as 1300 B. C. the Egyptians built a navigational canal linking the Red Sea with the Nile River, and indirectly with the Mediterranean Sea. It was used off and on for more than 2, 000 years before being permanently abandoned in the eighth century A. D. After 1500, Europeans revived the idea of an Egyptian canal as a means of eliminating the long voyage around Africa. Nothing was done, however, until the early 19 th century when surveys were made.

Key Players Gamal Abdel Nasser

Suez Canal War of 1956 How it Began… • The canal represents the only direct means of travel from the Mediterranean to the Indian Ocean, making it vital to the flow of trade between Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and the U. S. Normally, free passage was granted to all who used the canal, but Britain and France desired control of it, not only for commercial shipping, but also for colonial interests. The Egyptian government had just been taken over by Gamal Abdel Nasser, who felt the canal should be under Egyptian control. The United States and Britain had promised to give aid to Egypt in the construction, this aid was retracted however, and in retaliation Nasser nationalized the canal. He intended to use the funds raised from the operation of the canal to pay for the Dam.

This Didn’t Go Over Well… • War broke out… – Angry British and French politicians joined forces with Israel, a long time enemy of Egypt, in an attack against Nasser. – Israel and Egypt were enemies because of beliefs, land, political policies…
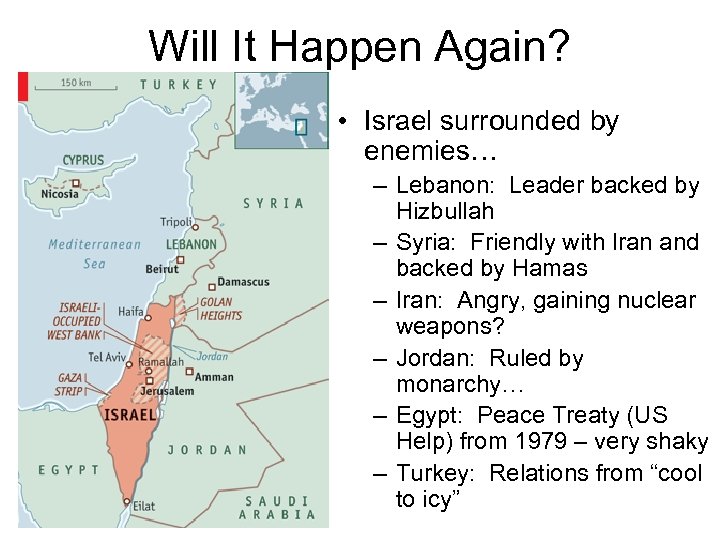
Will It Happen Again? • Israel surrounded by enemies… – Lebanon: Leader backed by Hizbullah – Syria: Friendly with Iran and backed by Hamas – Iran: Angry, gaining nuclear weapons? – Jordan: Ruled by monarchy… – Egypt: Peace Treaty (US Help) from 1979 – very shaky – Turkey: Relations from “cool to icy”
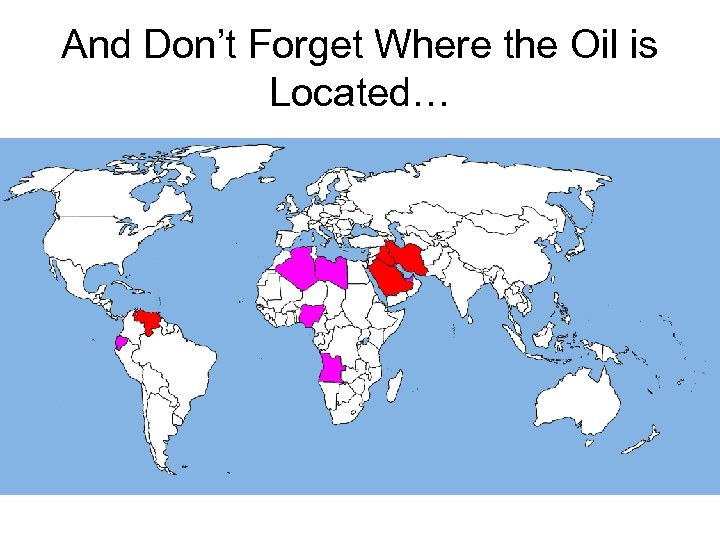
And Don’t Forget Where the Oil is Located…

Suez Canal 2011 • Israel closely watch the movement of Iranian warships were reported to cross the Suez Canal, Egypt, to Syria through the Mediterranean Sea. This situation makes the world crude oil price increases because of market participants worry over the potential conflict in the Suez Canal, which is one of the strategic distribution channels.



Suez Canal 2011 • CNN news station reported, the price of crude oil for March in the distribution of transactions in New York trading Wednesday afternoon local time rose 1. 2 percent to U. S. $ 85. 95 per barrel. In the UK stock exchange, Brent crude oil price rose 2. 1 percent to U. S. $ 103. 31 per barrel. • Andrew Lebow, analyst at MF Global, urged the traders to remain vigilant due to developments in the Suez Canal is still unclear.

The Strait of Hormuz – What? • The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow, strategically important waterway between the Gulf of Oman in the southeast and the Persian Gulf. • It is the only sea passage to the open ocean for large areas of the petroleum-exporting Persian Gulf. About 15 tankers carrying 16. 5 to 17 million barrels of crude oil pass through the strait on an average day, making it one of the world's most strategically important choke points. This represents 40% of the world's seaborne oil shipments, and 20% of all world oil shipments.
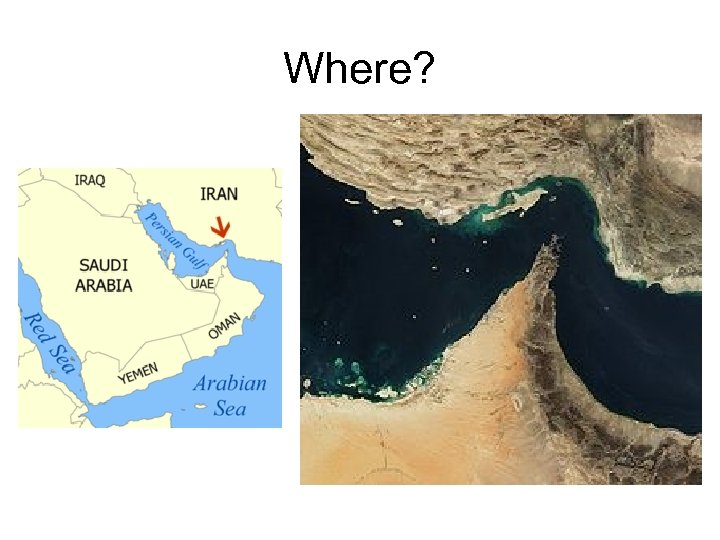
Where?

Conflicts… • April 1988 – Operation Praying Mantis • July 1988 – Downing of Iran Air Flight 655 – Still controversy • December 2007 – January 2008 – Iran harasses and provokes US Naval ships? • June 2008 – Iran threatens to seal off Strait of Hormuz if US or Israel attacks… – Conflict to re-open • July 2008 – Operation Brimstone (prep for war) • August 2008 – 5 battle groups show up (Ready for a Rumble…)

Straight of Gibraltar

Morocco – US Relations • “We are delighted with our strategic partnership with the United States of America…and we are particularly keen to consolidate and diversify our partnership relations. ” H. E. King Mohammed VI, “Throne Day” Speech, 30 July 2004

2004 US – Morocco Free Trade Agreement • The most recent of many official measures that have helped to cement the longstanding and always cordial relationship between the United States and the Royal Kingdom of Morocco. President George W. Bush talks with His Majesty King Mohammed VI of Morocco in the Oval Office Tuesday, April 23. "Today, I've informed His Majesty that our government will work to enact a free trade agreement with Morocco, " said the President to the media. "Trade is an important part of good foreign policy, it's an important part of making sure Americans can find jobs. " White House photo by Eric Draper.

Allies • When Morocco finally gained independence on March 2, 1956, President Dwight Eisenhower sent a congratulatory message to King Mohammed V: “My government renews it wishes for the peace and prosperity of Morocco, and expresses its gratification that Morocco has freely chosen, as a sovereign nation, to continue in the path of its traditional friendships. ”

Allies Continued • In the 21 st century, both countries have become close allies in the global war on terror. After the September 11, 2001 attacks, Morocco shared valuable information with the United States about al Qaeda. Conversely, when Casablanca was the victim of terrorist bombings on May 16, 2003, the U. S. government offered Morocco – one of it oldest allies -- the full resources of its military and intelligence community.
2d2fca4c856bd336681eaf8b99e36c68.ppt