8349f264e2e94cfc6dc7188926c3a15e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Globalization indicators The Import Content Of Export The case of the Netherlands Marjolijn Jaarsma Statistics Netherlands April 27 th 2004

Agenda Globalization Definitions, causes and characteristics OECD introduction ‘globalization’ indicators Monitoring globalization with new indicator Import content of export Internationalization of production processes Problems in case of the Netherlands Re-exports New model

Economic globalization New phase in international economic transactions, characterized by increasing economic interaction and integration among countries Trade in goods and services increasingly matched by international investment and multinational activity International framework has changed Standard (trade) indicators become less telling New indicators needed, capable of looking beyond surface FT and FDI

How to ‘capture’ globalization Globalization indicator(s) developed by OECD Focused on internationalization of production processes rather than international trade and investment ‘Import Content Of Export’ The necessity to import in order to be able to export Fraction import in an average unit of export Relative integration with and dependence on foreign production A high import content of export not necessarily bad

Internationalization of production Analysis of (internationalization of) production processes Input-output tables (Netherlands) Supply consists of intermediate deliveries and deliveries to final demand (e + r) Use consists of intermediate deliveries, import and primary inputs f Total Uses input-output tables OECD Olisnet (40*40 sectors) Intermediate deliveries e m r

Input-output analysis (1) Sector output depends on final demand intermediate demand (which depends on. . . ) Output cycle How much output must each sector produce? Leontieff inverse : total amount of final demand : unity matrix : matrix of technical coefficients Amount of output each sector needs to produce in order to satisfy final and intermediate demand
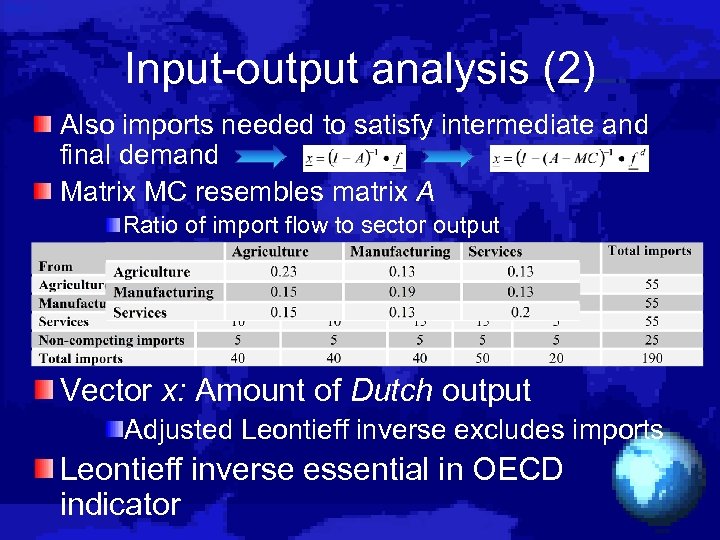
Input-output analysis (2) Also imports needed to satisfy intermediate and final demand Matrix MC resembles matrix A Ratio of import flow to sector output Vector x: Amount of Dutch output Adjusted Leontieff inverse excludes imports Leontieff inverse essential in OECD indicator

Import content of export ‘Manual of economic globalization indicators’ Import Content of Export indicator : share of import per sector of sector output : Leontieff inverse (adjusted!) : share of export per sector in total sectoral export Yields a single figure for whole economy Requires the use of Total Uses input-output tables and Import Flows tables (OECD Olisnet)

Import content of Dutch exports ICOE risen from 33. 6% in 1995 to 34. 7% in 1997 Decline also found in FT – picked up after 1998

Problems Differences classification FT data: commodity flows Input-output tables: economic activity Re-exports Focusing on m and e/E yields structurally lower ICOE Important activity for Netherlands Extracted from trade data and represented separately Re-exports not reported separately for many other OECD countries; somehow assigned to sectoral exports Different interpretation ICOE indicator between countries Indicator might not be ready for cross-country comparison
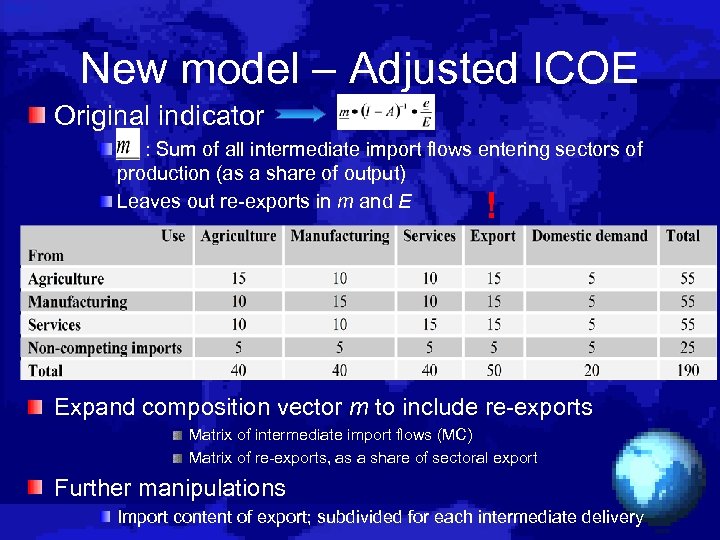
New model – Adjusted ICOE Original indicator : Sum of all intermediate import flows entering sectors of production (as a share of output) Leaves out re-exports in m and E ! Expand composition vector m to include re-exports Matrix of intermediate import flows (MC) Matrix of re-exports, as a share of sectoral export Further manipulations Import content of export; subdivided for each intermediate delivery
ICOE Input-output tables 40*40 9*9

Import content of export per delivery To deliver 1 unit of export, sector j needs intermediate deliveries from sector i, which consist for x% of imports Intermediate deliveries sector 5 (ICT) receives from sector 5, consist for 67. 86% of imports Useful for detailed analysis of internationalization production

Adjusted ICOE Objective indicator Monitoring globalization (1 figure) cross-country Import content Dutch exports Whole economy, including re-exports

Conclusion Initial indicator overlooks part of Dutch trade Adjusted calculations lead to higher import content of Dutch exports On aggregate basis, cross-country comparison possible Disaggregated suitable for in depth analysis The fraction imports in an average export unit approximately 40% Further questions mjra@cbs. nl
8349f264e2e94cfc6dc7188926c3a15e.ppt