Globalization Grigoryan G..pptx
- Количество слайдов: 10

“ Globalisation” Executed by: Grigoryan Gevorg Group M 3 -5 Moscow 2013

• Globalisation is not a serious idea. We, the Americans invented it as means of concealing our policy of economic penetration into other nations’ J. K. Galbraith 1970

Globalisation – What Does It Mean ? Globalisation has many dimensions worth considering, because all of them influence and shape our organisations: – Socio-cultural dimensions: language, culture, value systems – Political dimensions: rules of national and international governance – Legal dimensions: international commercial law, patents, intellectual property recognition. – Financial dimensions: currency controls, financial regulations, capital flows.

Definitions are categorized to three main frames 1. The positive frame points to the potential gains and benefits of globalization. 2. The neutral frame portrays globalization as a natural, evolutionary, and largely inevitable development. This discourse, which is associated with the financial community, avoids making moral judgments. 3. The negative frame points out the increasing potential for economic crisis, the threat to the livelihoods of workers, and the growing income inequality caused by globalization. This frame also includes discourse which is primarily concerned with the negative impact of globalization in the third World.
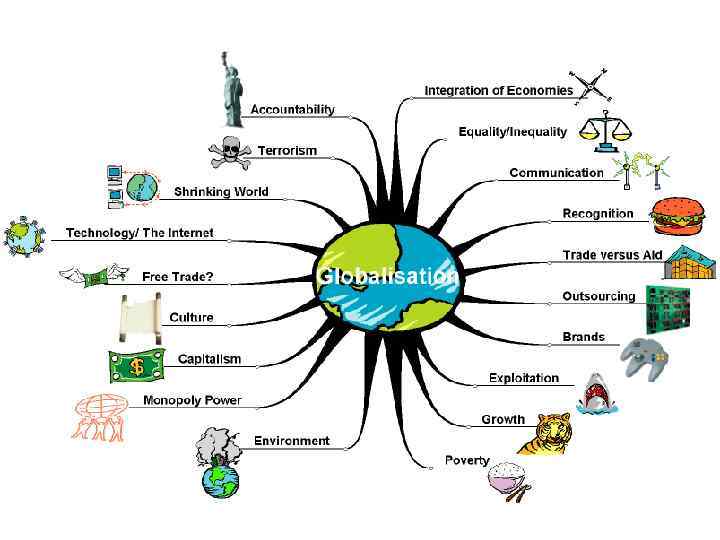

Globalisation – When did it Begin? • Some analysts view globalisation as a process beginning at the end of WWII. This period saw a significant expansion in the flow of investment capital, and the emergence of multinational corporations – looking to produce and sell in domestic markets in many countries around the world. • Those with a more immediate time horizon, see globalisation’s direct origins gaining momentum at one of the following points: 1980: Japan begins its ascendancy as host nation to a number of significant multinational corporations. – 1989: The fall of the Berlin Wall & the collapse of Communism: The apparent triumph of Western capitalism, entrepreneurship, and the concept of creative destruction. – The 1990 s: The dawning of the information age: personal computers, widespread digitisation of information, the rise of Microsoft and the ubiquity of its products. –

Politics Globalization traditionally politics has been undertaken within national political systems. National governments have been ultimately responsible for maintaining the security and economic welfare of their citizens, as well as the protection of human rights and the environment within their borders. With global ecological changes, an ever more integrated global economy, and other global trends, political activity increasingly takes place at the global level.

Factors which help the spread of globalisation • • • Political stability Low transport costs, containerisation Telecommunications Internet Low trade barriers Increasing role of TNCs

CONCLUSION Globalization is a tool that should benefit all sections of mankind. One cannot ignore its negative effects. These must be addressed for the world’s peace and prosperity.

Thank you for attention!
Globalization Grigoryan G..pptx