df02261f4aae0df848007db19de49400.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Global Sensor Networks A Platform for the Internet of Things Ali Salehi, Prof. Karl Aberer 1
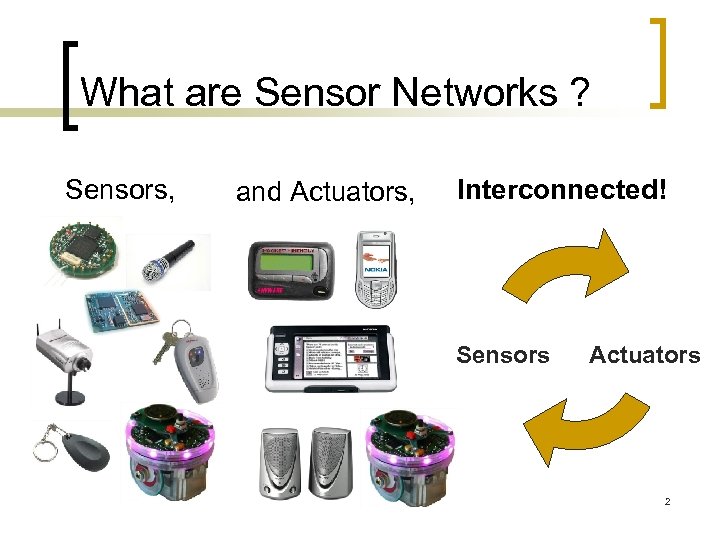
What are Sensor Networks ? Sensors, and Actuators, Interconnected! Sensors Actuators 2
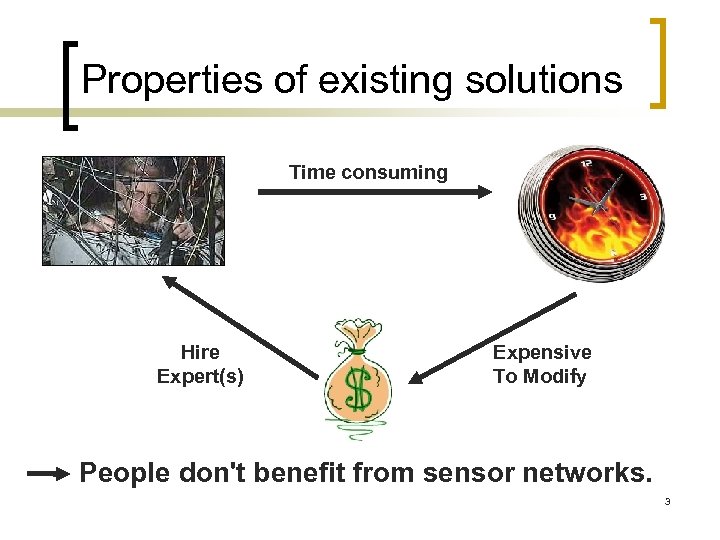
Properties of existing solutions Time consuming Hire Expert(s) Expensive To Modify People don't benefit from sensor networks. 3
Motivation, ? ? 4

Question : What is common ? 1. Stream of Data. 2. Structure can be defined. 3. Common Requirements. Virtual Sensor 5

WHAT DOES ALL THIS MEAN Internet of Things. 6

Solution, A Software : Hardware independent, any new hardware (sensors and actuators) should be integratable. Application independent. Light & Scalable (internet scale ; peer to peer) Modifications MUST be very cheap and simple. Modifications MUST be applied while system is running. Restarting the internet ? !!! 7
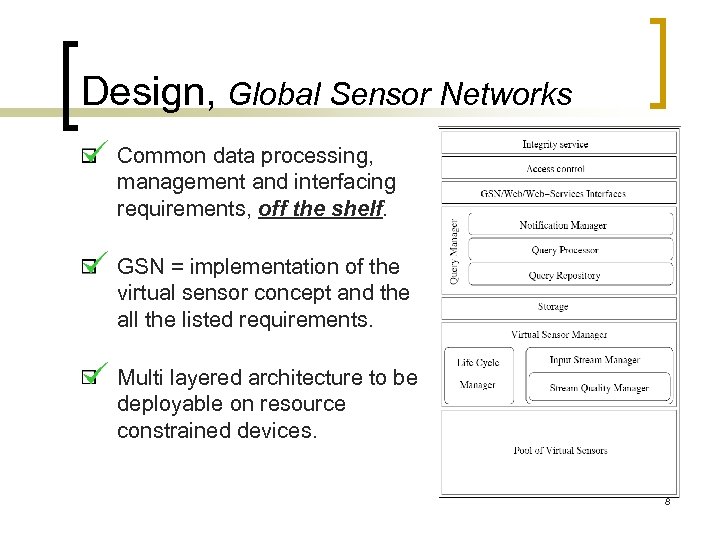
Design, Global Sensor Networks Common data processing, management and interfacing requirements, off the shelf. GSN = implementation of the virtual sensor concept and the all the listed requirements. Multi layered architecture to be deployable on resource constrained devices. 8
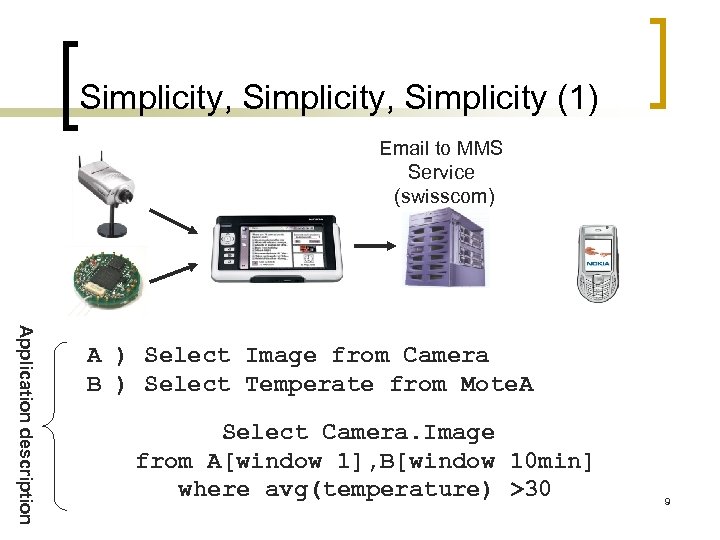
Simplicity, Simplicity (1) Email to MMS Service (swisscom) Application description A ) Select Image from Camera B ) Select Temperate from Mote. A Select Camera. Image from A[window 1], B[window 10 min] where avg(temperature) >30 9
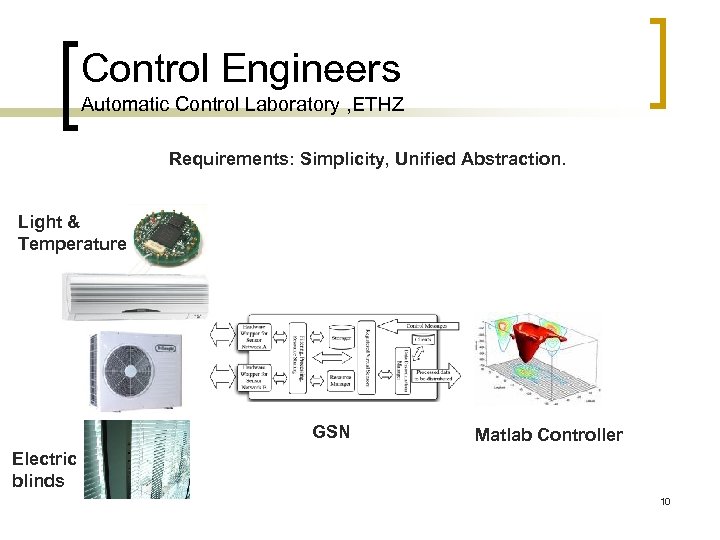
Control Engineers Automatic Control Laboratory , ETHZ Requirements: Simplicity, Unified Abstraction. Light & Temperature GSN Matlab Controller Electric blinds 10
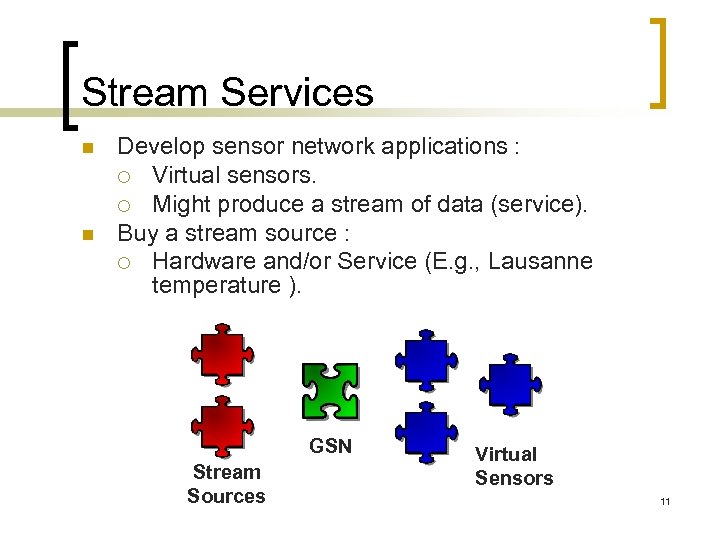
Stream Services n n Develop sensor network applications : ¡ Virtual sensors. ¡ Might produce a stream of data (service). Buy a stream source : ¡ Hardware and/or Service (E. g. , Lausanne temperature ). GSN Stream Sources Virtual Sensors 11
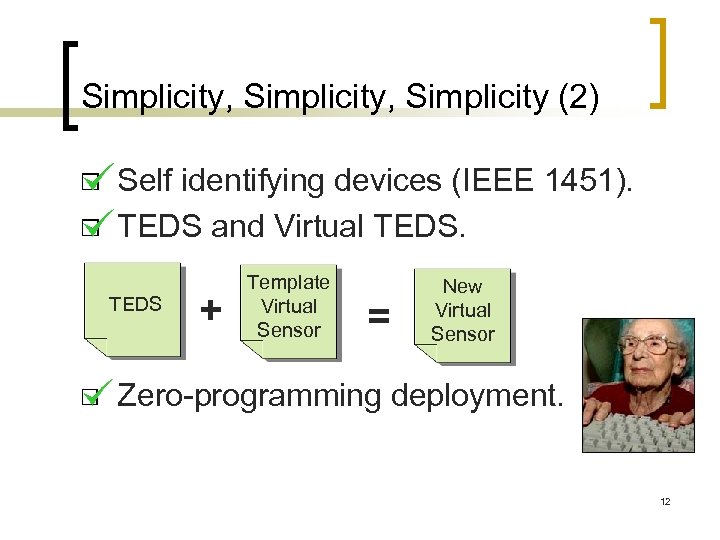
Simplicity, Simplicity (2) Self identifying devices (IEEE 1451). TEDS and Virtual TEDS + Template Virtual Sensor = New Virtual Sensor Zero-programming deployment. 12
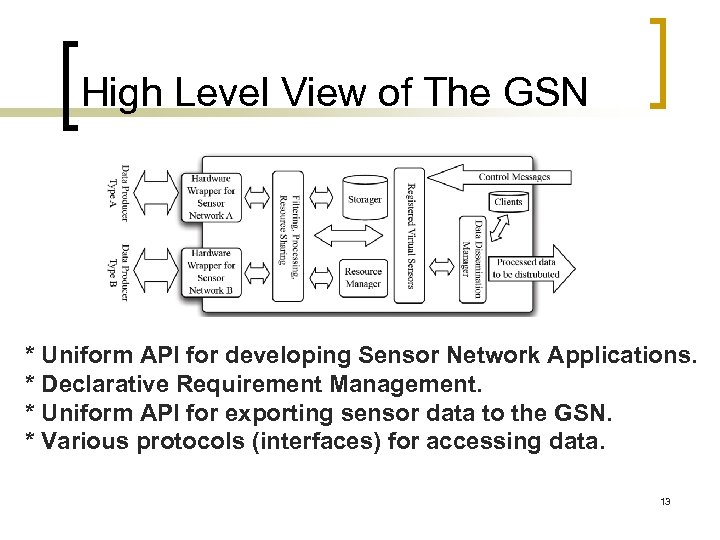
High Level View of The GSN * Uniform API for developing Sensor Network Applications. * Declarative Requirement Management. * Uniform API for exporting sensor data to the GSN. * Various protocols (interfaces) for accessing data. 13
Resource Discovery Addressing the virtual sensors : Static (e. g. , socket address). Dynamic using a set of predicates : Using a Directory Service: <predicate key=“GPS. Latitude”>46. 3423</predicate> <predicate key=“Type”>temperature</predicate> Distributed Directory Service (DDS)*: Based on P-Grid infrastructure. Each node acts as a peer in DDS. * Not implemented yet. 14
Resource Constrained Devices Resources are allocated on demand. Resource sharing as much as possible. 20 virtual sensors, 10% > CPU, 64 MB RAM, 500 Mhz. Requirements (e. g. , Nokia 770), ¡ ¡ ¡ 32 -bit processor. 64 MB Memory and/or Swap Option. 25 MB Storage. 15
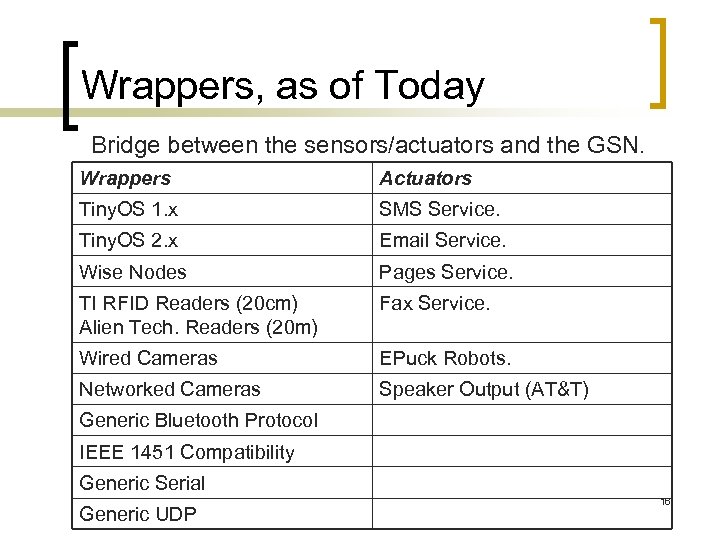
Wrappers, as of Today Bridge between the sensors/actuators and the GSN. Wrappers Actuators Tiny. OS 1. x SMS Service. Tiny. OS 2. x Email Service. Wise Nodes Pages Service. TI RFID Readers (20 cm) Alien Tech. Readers (20 m) Fax Service. Wired Cameras EPuck Robots. Networked Cameras Speaker Output (AT&T) Generic Bluetooth Protocol IEEE 1451 Compatibility Generic Serial Generic UDP 16

Outcome as of today. Successful Open Source Project. More than 20 sensors/actuators supported. 7 Releases of the engine (Stable). 30 K visitors, 600 downloads. Users Community GNU GPL License 17

WHAT DOES ALL THIS MEAN GSN, Middleware for Internet of Things. Q/A 18
df02261f4aae0df848007db19de49400.ppt