dd51f6629347c79b3d5cbde2d6521f8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Global Risk Management © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Presentation Plan 1 Risk Defined 1. 1 Drivers of Key Risks 1. 2 Risk Management Process 1. 3 Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques 2 Risk Management in New Product Development 3 Risk Management pertaining to the Business Environment 4 Risk Management pertaining to Data Quality Slide 2 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
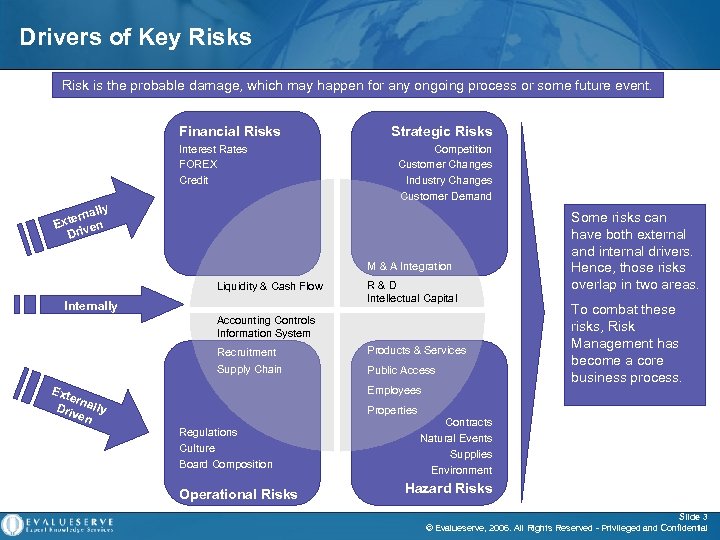
Drivers of Key Risks Risk is the probable damage, which may happen for any ongoing process or some future event. Financial Risks Interest Rates FOREX Credit y nall xter en E Driv Strategic Risks Competition Customer Changes Industry Changes Customer Demand M & A Integration Liquidity & Cash Flow Internally Driven R & D Intellectual Capital Accounting Controls Information System Recruitment Products & Services Supply Chain Public Access Ext ern Driv ally en Employees Some risks can have both external and internal drivers. Hence, those risks overlap in two areas. To combat these risks, Risk Management has become a core business process. Properties Regulations Culture Board Composition Operational Risks Contracts Natural Events Supplies Environment Hazard Risks Slide 3 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
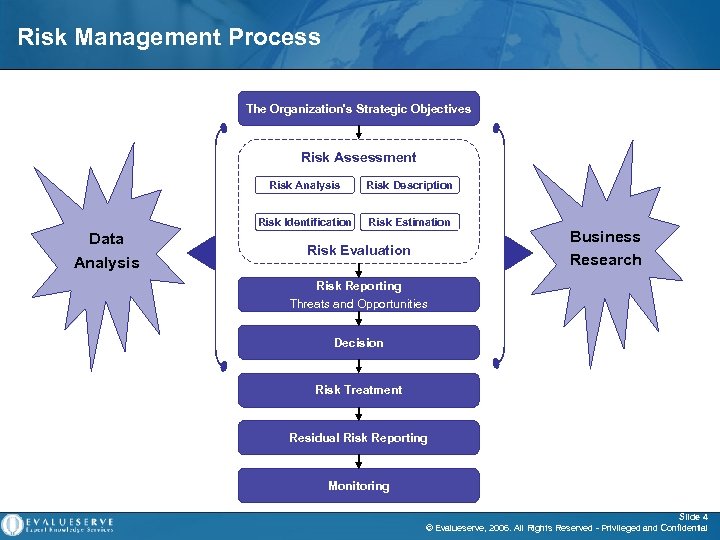
Risk Management Process The Organization's Strategic Objectives Risk Assessment Risk Analysis Risk Identification Data Analysis Risk Description Risk Estimation Risk Evaluation Business Research Risk Reporting Threats and Opportunities Decision Risk Treatment Residual Risk Reporting Monitoring Slide 4 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
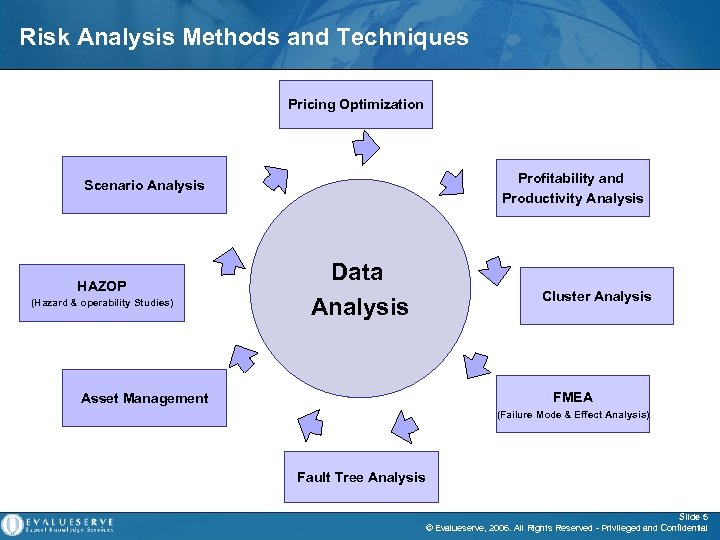
Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques Pricing Optimization Profitability and Productivity Analysis Scenario Analysis Data Analysis HAZOP (Hazard & operability Studies) Asset Management Cluster Analysis FMEA (Failure Mode & Effect Analysis) Fault Tree Analysis Slide 5 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
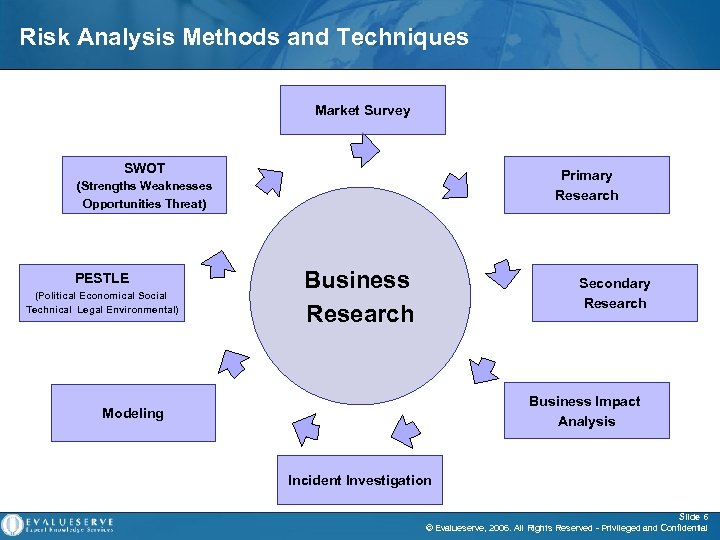
Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques Market Survey SWOT Primary Research (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threat) Business Research PESTLE (Political Economical Social Technical Legal Environmental) Modeling Secondary Research Business Impact Analysis Incident Investigation Slide 6 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Presentation Plan 1 Risk Defined 1. 1 Drivers of Key Risks 1. 2 Risk Management Process 1. 3 Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques 2 Risk Management in New Product Development 3 Risk Management pertaining to the Business Environment 4 Risk Management pertaining to Data Quality Slide 7 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
Risk Management in New Product Development Why research and analysis before new product development New product have a very high failure rates. Products fail, not because of technical shortcomings, but due to absence of market. Over 60% of new product fail before entering the market, and out of the remaining 40% that do see the ray of light, 40% fail to yield profit and are withdrawn from the market. Timely and reliable knowledge about customer preferences is most important. Such data is obtained from business research. New product development is linked with very limited historical or preliminary data. Hence, risky Risk can be in form of market, technical, or organizational issues. Risk analysis solves the problem through flexible modeling, primary and secondary research. A good strategy is a must for evaluating and dealing with the associated and unavoidable risks. Research conducted to understand customer needs and develop a new product is different from research required to launch a new product. Product development research is focused on needs of customers while launch research focuses on understanding the motivation and attitudes of early adopters. Successful targeting of early adopters builds the fountain for new product success. Slide 8 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Business Research at Kellogg’s investment in new product development resulted in strengthening its global brand. Kellogg’s carried out business/market research to understand the market 1000 consumers were questioned about the Kellogg's brands Understanding how ‘Special K’ could be extended into different variants to grow the brand, keeping the core product strong. • Effect of the market changes on the product • Effect of new technology on the business • Future market trends • Market opportunities • New categories appealing to the target market • Consumers’ view on stretching the brand into new categories • Kellogg's launched Special K Red Berries in the UK followed by Special K Peach & Apricot • Good performance with very little damage to the core brand. • Quantitative tests of product ideas across a range of products was conducted to tap further opportunities to develop “Special K” as a healthy snack. • Hence, business/market research helped the company to develop variants of Special K, resulting in a low risk project offering prospect of a good rate of return. Slide 9 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Presentation Plan 1 Risk Defined 1. 1 Drivers of Key Risks 1. 2 Risk Management Process 1. 3 Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques 2 Risk Management in New Product Development 3 Risk Management pertaining to the Business Environment 4 Risk Management pertaining to Data Quality Slide 10 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
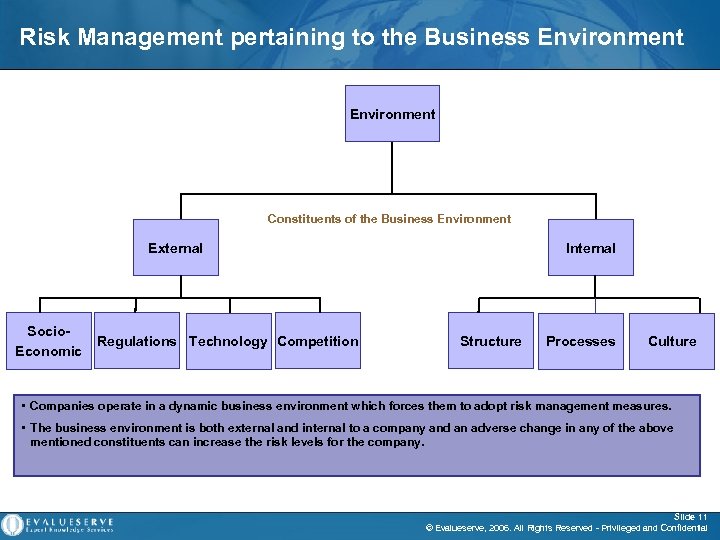
Risk Management pertaining to the Business Environment Constituents of the Business Environment External Socio. Economic Regulations Technology Competition Internal Structure Processes Culture • Companies operate in a dynamic business environment which forces them to adopt risk management measures. • The business environment is both external and internal to a company and an adverse change in any of the above mentioned constituents can increase the risk levels for the company. Slide 11 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
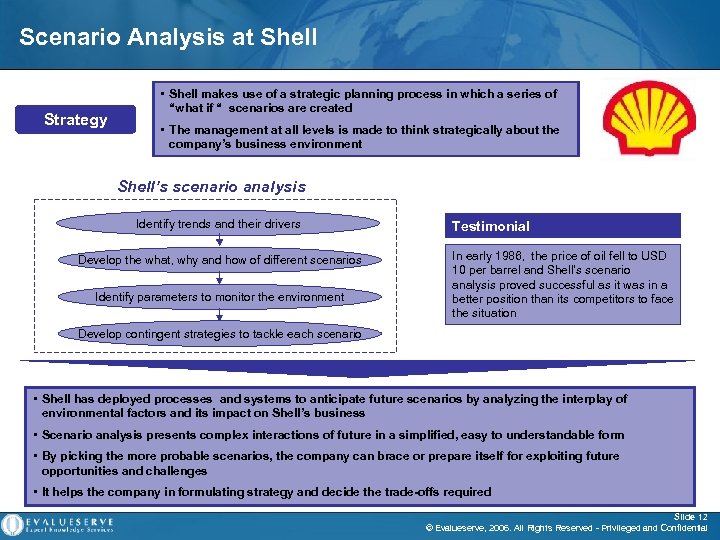
Scenario Analysis at Shell Strategy • Shell makes use of a strategic planning process in which a series of “what if “ scenarios are created • The management at all levels is made to think strategically about the company’s business environment Shell’s scenario analysis Identify trends and their drivers Develop the what, why and how of different scenarios Identify parameters to monitor the environment Testimonial In early 1986, the price of oil fell to USD 10 per barrel and Shell’s scenario analysis proved successful as it was in a better position than its competitors to face the situation Develop contingent strategies to tackle each scenario • Shell has deployed processes and systems to anticipate future scenarios by analyzing the interplay of environmental factors and its impact on Shell’s business • Scenario analysis presents complex interactions of future in a simplified, easy to understandable form • By picking the more probable scenarios, the company can brace or prepare itself for exploiting future opportunities and challenges • It helps the company in formulating strategy and decide the trade-offs required Slide 12 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Presentation Plan 1 Risk Defined 1. 1 Drivers of Key Risks 1. 2 Risk Management Process 1. 3 Risk Analysis Methods and Techniques 2 Risk Management in New Product Development 3 Risk Management pertaining to the Business Environment 4 Risk Management pertaining to Data Quality Slide 13 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
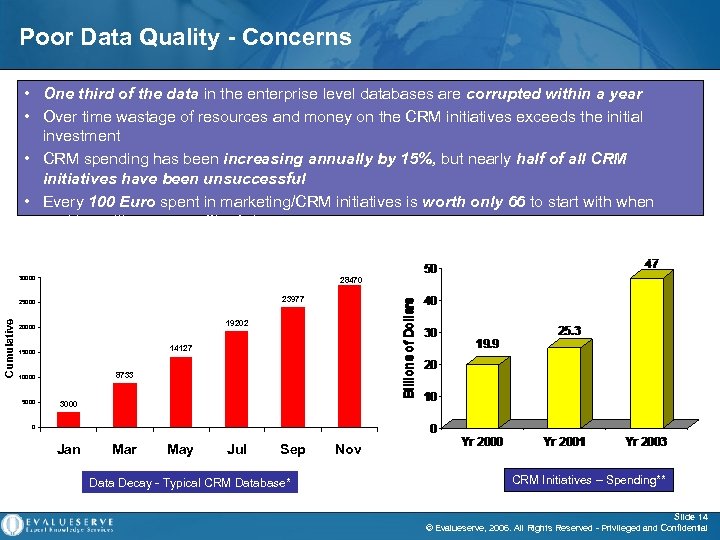
Poor Data Quality - Concerns • One third of the data in the enterprise level databases are corrupted within a year • Over time wastage of resources and money on the CRM initiatives exceeds the initial investment • CRM spending has been increasing annually by 15%, but nearly half of all CRM initiatives have been unsuccessful • Every 100 Euro spent in marketing/CRM initiatives is worth only 66 to start with when working with poor quality data 30000 28470 23977 Cumulative 25000 19202 20000 14127 15000 8733 10000 5000 3000 0 Jan Mar May Jul Sep Data Decay - Typical CRM Database* Nov CRM Initiatives – Spending** Slide 14 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
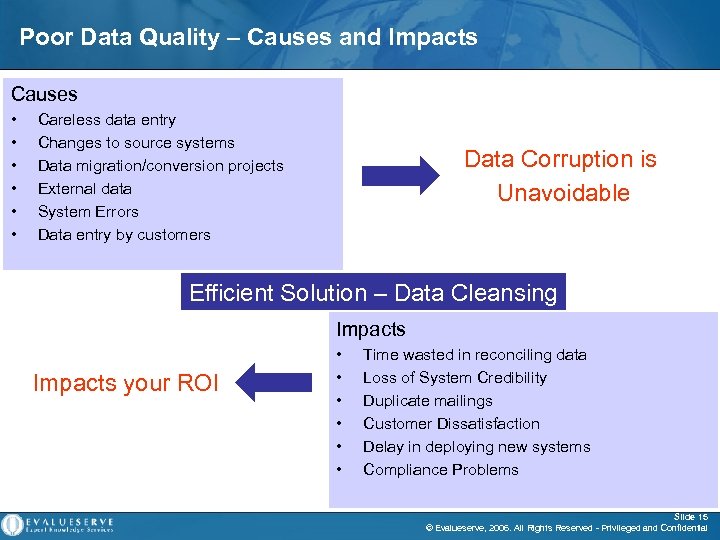
Poor Data Quality – Causes and Impacts Causes • • • Careless data entry Changes to source systems Data migration/conversion projects External data System Errors Data entry by customers Data Corruption is Unavoidable Efficient Solution – Data Cleansing Impacts your ROI • • • Time wasted in reconciling data Loss of System Credibility Duplicate mailings Customer Dissatisfaction Delay in deploying new systems Compliance Problems Slide 15 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
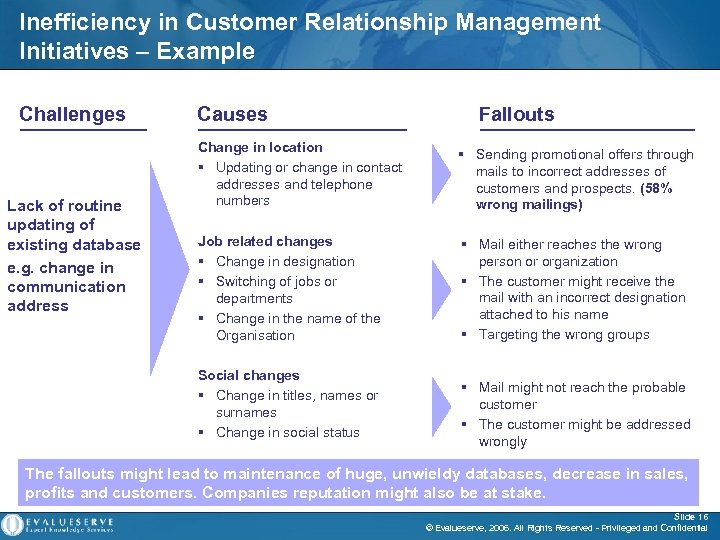
Inefficiency in Customer Relationship Management Initiatives – Example Challenges Lack of routine updating of existing database e. g. change in communication address Causes Fallouts Change in location § Updating or change in contact addresses and telephone numbers § Sending promotional offers through mails to incorrect addresses of customers and prospects. (58% wrong mailings) Job related changes § Change in designation § Switching of jobs or departments § Change in the name of the Organisation § Mail either reaches the wrong person or organization § The customer might receive the mail with an incorrect designation attached to his name § Targeting the wrong groups Social changes § Change in titles, names or surnames § Change in social status § Mail might not reach the probable customer § The customer might be addressed wrongly The fallouts might lead to maintenance of huge, unwieldy databases, decrease in sales, profits and customers. Companies reputation might also be at stake. Slide 16 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
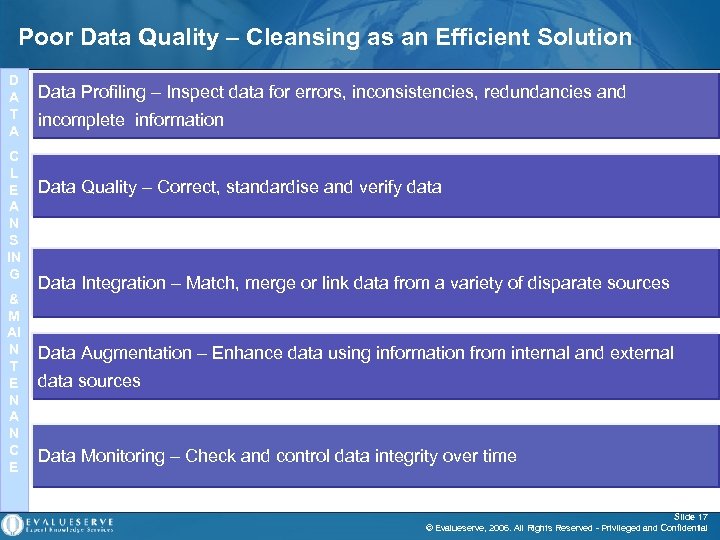
Poor Data Quality – Cleansing as an Efficient Solution D A T A C L E A N S IN G & M AI N T E N A N C E Data Profiling – Inspect data for errors, inconsistencies, redundancies and incomplete information Data Quality – Correct, standardise and verify data Data Integration – Match, merge or link data from a variety of disparate sources Data Augmentation – Enhance data using information from internal and external data sources Data Monitoring – Check and control data integrity over time Slide 17 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential

Evalueserve Disclaimer The information contained herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable. Evalueserve disclaims all warranties as to the accuracy, completeness or adequacy of such information. Evalueserve shall have no liability for errors, omissions or inadequacies in the information contained herein or for interpretations thereof. Slide 18 © Evalueserve, 2006. All Rights Reserved - Privileged and Confidential
dd51f6629347c79b3d5cbde2d6521f8a.ppt