f2dd3ccc4290046a5aecf135fad12c3f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Global Marketing Management, 4 e Chapter 9 Global Market Entry Strategies 글로벌 시장진입 전략 Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1

Chapter Overview 1. Target Market Selection(목표시장선정) 2. Choosing the Mode of Entry(진입유형선택) 3. Exporting(수출) 4. Licensing(라이센싱) 5. Franchising(프랜차이징) 6. Contract Manufacturing(계약생산, 아웃소싱) 7. Joint Ventures(합작투자) 8. Wholly Owned Subsidiaries(100% 자회사) 9. Strategic Alliances(전략적 제휴) 10. Timing of Entry(진입시점) 11. Exit Strategies(철수전략) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2

Introduction § The need for a solid market entry decision(신중한 시장진입 결정) is an integral part of a global market entry strategy. § Entry decisions will heavily influence the firm’s other marketing-mix decisions. § Global marketers have to make a multitude of decisions regarding the entry mode which may include: – – – (1) the target product/market(목표 제품/시장) (2) the goals of the target markets(목표시장 목적) (3) the mode of entry(진입유형) (4) The time of entry(진입시점) (5) A marketing-mix plan(마케팅 믹스 계획) (6) A control system to check the performance in the entered markets(진출시장에서 성과평가를 위한 통제시스템) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 3

1. Selecting the Target Market § A crucial step in developing a global expansion strategy is the selection of potential target markets (see Exhibit 9 -1 for the entry decision process). § A four-step procedure for the initial screening process(목표시장선정 4대 절차): 1. Select indicators and collect data(지표선정 및 자료수집) 2. Determine importance of country indicators(지표별 가중치 결정) 3. Rate the countries in the pool on each indicator(지표별 국가의 점수 평가) 4. Compute overall score for each country(국가별 총점 계산) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 4
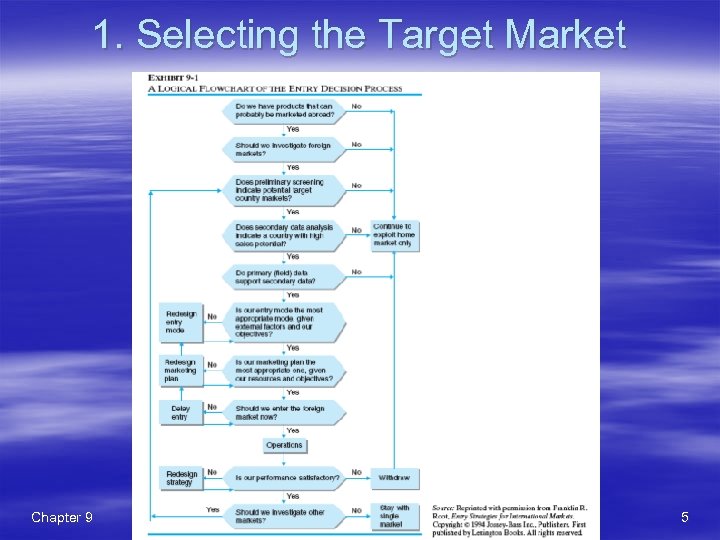
1. Selecting the Target Market Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5

2. Choosing the Mode of Entry § Decision Criteria for Mode of Entry(진입유형결정 기준): – Market Size and Growth(시장규모 및 성장) – Risk(위험) – Government Regulations(정부규제) – Competitive Environment/Cultural Distance(경쟁 환경/문화차이) – Local Infrastructure(현지 인프라) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 6
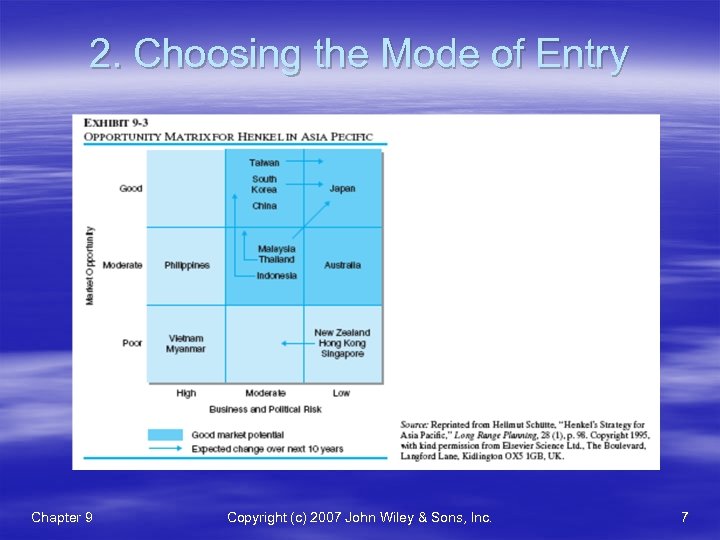
2. Choosing the Mode of Entry Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 7
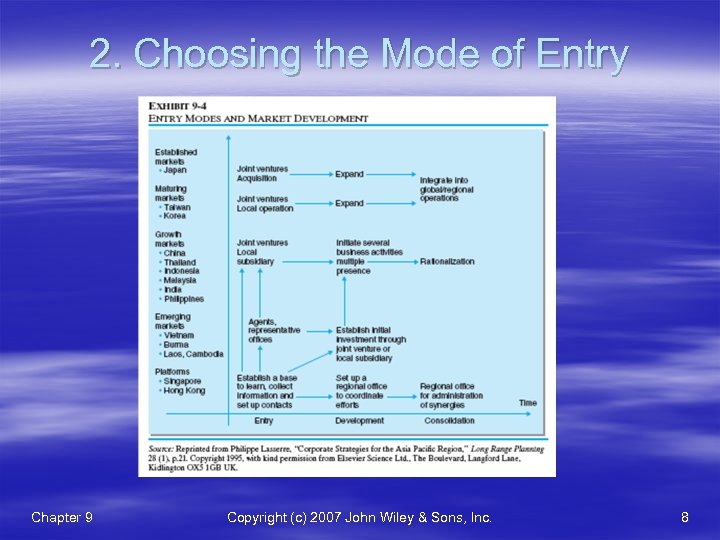
2. Choosing the Mode of Entry Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 8

2. Choosing the Mode of Entry § Classification of Markets(시장분류): – Platform Countries 거점(Singapore & Hong Kong) – Emerging Countries 신흥 (Vietnam & the Philippines) – Growth Countries 성장 (China & India) – Maturing and established countries 성숙 (examples: South Korea, Taiwan & Japan) – – – Company Objectives(기업 목적) Need for Control(통제 필요) Internal Resources, Assets and Capabilities(내부 자원, 자산 및 역량 – Flexibility(유연성) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 9

2. Choosing the Mode of Entry § Mode of Entry Choice: A Transaction Cost Explanation(거래비용이론) – Regarding entry modes, companies normally face a tradeoff between the benefits of increased control and the costs of resource commitment and risk(진입유형과 관련, 기업은 통제가 증가할 수록 투입되는 자원 비용과 위험 이 증대하는 상쇄관계에 직면함). – Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA) perspective – Transaction-Specific Assets(거래특유자산: 매우 좁은 적용범위에서만 가치가 있는 자산) (assets valuable for a very narrow range of applications) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 10

3. Exporting § Indirect Exporting(간접수출) – Export merchants(수출상, 무역상) – Export agents(수출대리인, 대리상) – Export management companies (EMC, 미국 수 출대행업체) § Cooperative Exporting(협력수출) – Piggyback Exporting § Direct Exporting(직접수출) – Firms set up their own exporting departments Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 11

4. Licensing § Licensor and the licensee(라이센서와 라이센시) § Benefits: – Appealing to small companies that lack resources – Faster access to the market(신속한 시장진출) – Rapid penetration of the global markets(신속한 시장침투 ) § Caveats: – Other entry mode choices may be affected – Licensee may not be committed(라이센시의 소극성) – Lack of enthusiasm on the part of a licensee – Biggest danger is the risk of opportunism(기회주의 위험) – Licensee may become a future competitor(라이센시가 미 Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John 12 래의 경쟁자가 될 수 있음) Wiley & Sons, Inc.

4. Licensing § How to seek a good licensing agreement (see Global Perspective 9 -1): – Seek patent or trademark protection(특허권 및 상표권 보호방안 모색) – Thorough profitability analysis(철저한 수익성 분 석) – Careful selection of prospective licensees(잠재 라이센시에 대한 신중한 선정) – Contract parameter 계약조항 점검(technology package, use conditions, compensation, and provisions for the settlement of disputes) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 13

5. Franchising § Franchisor and the franchisee(프랜차이저와 프 §Caveats: 랜차이지) – Revenues may not be adequate § Master franchising – Availability of a master (마스터프랜차이지) § Benefits: – Overseas expansion with a minimum investment – Franchisees’ profits tied to their efforts – Availability of local franchisees’ knowledge Chapter 9 franchisee – Limited franchising opportunities overseas – Lack of control over the franchisees’ operations – Problem in performance standards – Cultural problems – Physical proximity Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 14
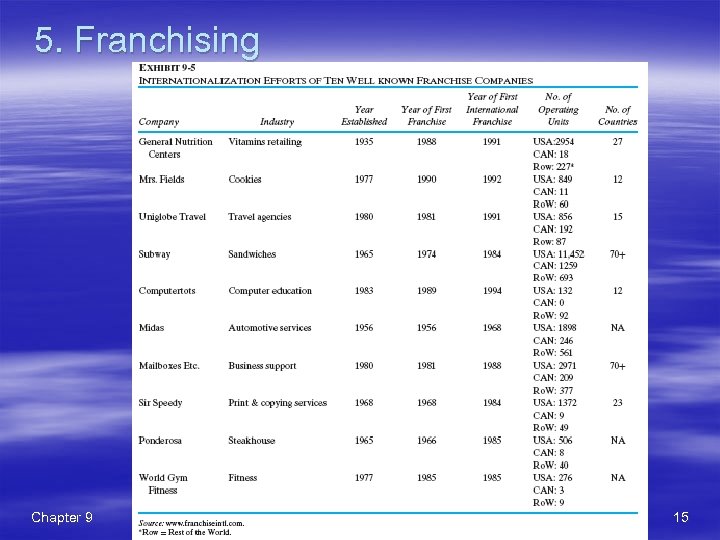
5. Franchising Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 15

6. Contract Manufacturing (Outsourcing) 계약생산(아웃소싱) § Benefits: – Labor cost advantages – Savings via taxation, lower energy costs, raw materials, and overheads(조세, 에너지비용, 원재료 및 기타 고정비 등의 절 약을 통해서 비용절감) – Lower political and economic risk – Quicker access to markets § Caveats: – – – Contract manufacturer may become a future competitor Lower productivity standards Backlash from the company’s home-market employees regarding HR and labor issues(본국 종업원의 반발) – Issues of quality and production standards Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 16

6. Contract Manufacturing (Outsourcing) Qualities of an ideal subcontractor(이상적인 하청 기업의 요건): – Flexible/geared toward just-in-time delivery(적시 납품에 대한 유연성 및 연동성) – Able to meet quality standards – Solid financial footings(건실한 재무건전성) – Able to integrate with company’s business(본 사 업과 통합가능성) – Must have contingency plans(돌발상황 대응계 획) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17

7. Expanding through Joint Ventures § Cooperative joint venture(협력사업) § Equity joint venture(합작투자) § Benefits: – Higher rate of return and more control over the operations(높은 투자수익 및 사업에 대한 통제) – Creation of synergy(시너지 창출) – Sharing of resources(자원의 공유) – Access to distribution network(유통네트워크 접근) – Contact with local suppliers and government officials(현 지 공급자 및 정부관리 접근) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 18

7. Expanding through Joint Ventures § Caveats: – Lack of control(통제결여) – Lack of trust(신뢰결여) – Conflicts arising over matters such as strategies, resource allocation, transfer pricing, ownership of critical assets like technologies and brand names(전략, 자원배분, 이전가격, 기술 및 브랜 드 등과 같은 핵심자산에 대한 소유권 등의 문제 에 대해서 갈등이 발생할 소지가 높음) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 19

7. Expanding through Joint Ventures § Drivers Behind Successful International Joint Ventures(성 공적인 국제합작투자의 요건) : – – Pick the right partner(적절한 파트너 선정) Establish clear objectives from the beginning(초기부터 명백 한 목표설정) Bridge cultural gaps(문화적 차이 해소) Gain top managerial commitment and respect(최고경영진의 전적인 관심과 배려 확보) Use incremental approach(점증적 접근 필요) Create a launch team during the launch phase(추진팀 구성): – – (1) Build and maintain strategic alignment(전략적 협력의 형성 및 유지) (2) Create a governance system(지배구조의 합의 및 도출) (3) Manage the economic interdependencies(경제적 상호의존성 관리) (4) Build the organization for the joint venture(JV를 위한 조직 구성) – – Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 20

8. Entering New Markets through Wholly Owned Subsidiaries § Acquisitions(인수합병형 투자) § Greenfield Operations(그린필드형 투자) § Benefits: – Greater control and higher profits(보다 많은 통제와 높은 이익) – Strong commitment to the local market on the part of companies – Allows the investor to manage and control marketing, production, and sourcing decisions(투자 자가 직접 마케팅, 생산 및 조달관련 결정을 관리하 고 통제) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 21

8. Entering New Markets through Wholly Owned Subsidiaries § Caveats: – Risks of full ownership(100% 지분의 위험) – Developing a foreign presence without the support of a third part – Risk of nationalization(국유화 위험) – Issues of cultural and economic sovereignty of the host country(현지국의 문화적 및 경제적 주 권 등과 관련된 이슈) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 22

8. Entering New Markets through Wholly Owned Subsidiaries § Acquisitions and Mergers(M&A형 투자) – Quick access to the local market – Good way to get access to the local brands § Greenfield Operations(그린필드형 투자) – Offer the company more flexibility than acquisitions in the areas of human resources, suppliers, logistics, plant layout, and manufacturing technology(인사, 공급자, 물류, 공장배치 및 제조기 술 등과 관련 M&A보다 유연성 확보 가능). Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 23

9. Creating Strategic Alliances § Types of Strategic Alliances(전략적 제휴의 유형) – Simple licensing agreements between two partners(단순 라이센싱 계약) – Market-based alliances (시장기반 제휴) – Operations and logistics alliances(운영 및 물류 제휴) – Operations-based alliances(운영기반 제휴) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 24

9. Creating Strategic Alliances § The Logic Behind Strategic Alliances (전략적 제휴 의 논리적 배경) – Defend(방어) – Catch-Up (추격) – Remain(잔류) – Restructure(구조조정) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 25

9. Creating Strategic Alliances Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 26

9. Creating Strategic Alliances § Cross-Border Alliances that Succeed(성공적인 국 제 전략적 제휴): – Alliances between strong and weak partners seldom work(강력한 파트너와 약한 파트너간 제 휴는 성공가능성 희박). – Autonomy and flexibility(자유성과 유연성) – Equal ownership(동등 지분참여) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 27

9. Creating Strategic Alliances – Other factors(기타 요인): § Commitment and support of the top of the partners’ organizations § Strong alliance managers are the key § Alliances between partners that are related in terms of products, technologies, and markets § Have similar cultures, assets sizes and venturing experience § Tend to start on a narrow basis and broaden over time § A shared vision on goals and mutual benefits Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 28

10. Timing of Entry § International market entry decisions should also cover the following timing-of-entry issues(진입시기 관련 검토사항): – When should the firm enter a foreign market? – Other important factors include: level of international experience, firm size – Also, the broader the scope of products and services – Mode of entry issues, market knowledge, various economic attractiveness variables, etc. Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 29

10. Timing of Entry § Reasons for exit(철수이유): – Sustained losses(손실지속) – Volatility(변동성) – Premature entry(성급한 진출) – Ethical reasons(윤리적 이유) – Intense competition(경쟁격화) – Resource reallocation (자원재배치) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 30

11. Exit Strategies § Risks of exit(철수위험): – – Fixed costs of exit(철수 고정비용) Disposition of assets(자산처분) Signal to other markets(다른 시장에 부정적 신호) Long-term opportunities(장기기회 상실) § Guidelines: – Contemplate and assess all options to salvage the foreign business(해외사업을 살리기 위한 모든 옵 션을 상정하고 평가) – Incremental exit(점진적 철수) – Migrate customers(고객이동) Chapter 9 Copyright (c) 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 31
f2dd3ccc4290046a5aecf135fad12c3f.ppt