577ce5caf69ad8d1002ad85f5035d922.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 80

Global History Final Exam Review Part 2 Wait! Do you remember the Paleolithic or the Gupta? Go back to the Final Exam Review Part ONE; the final exam will cover everything we have done since September of 2013!

The Middle Ages 476 – 15 th century • After the fall of the Roman Empire in Western Europe (476 CE), Europe entered the Middle Ages. Because there was no strong, centralized government, there was chaos, illiteracy and an increased reliance on the Christian Church. • The eastern half of the Roman Empire became the Byzantine Empire.
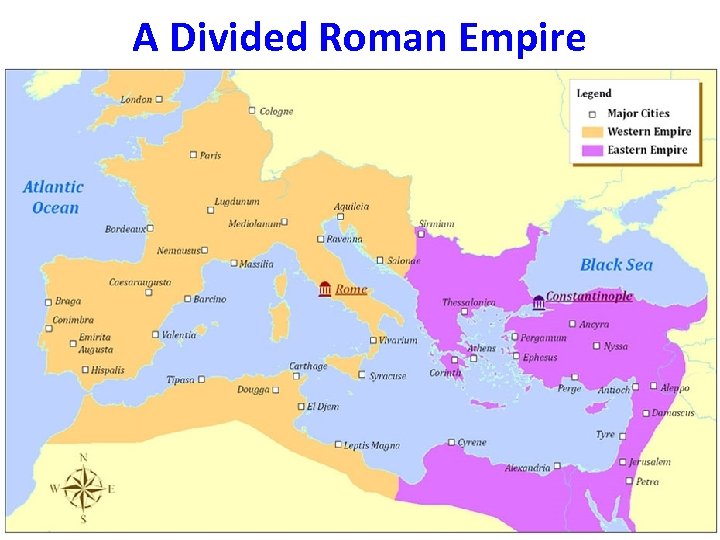
A Divided Roman Empire

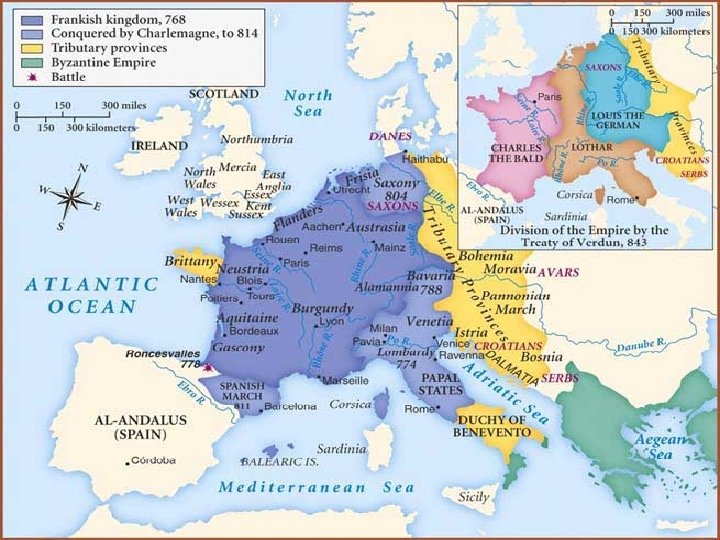
Charlemagne • Charlemagne was a leader of the Franks, a barbarian tribe. He tried to rebuild the Roman Empire. • He was crowned Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope in 800 CE. • He did create the strongest government since Rome; he built schools and conquered what is today France and Germany. After he died in 814, his empire began to decline. In 843, his grandsons signed the Treaty of Verdun that divided up his empire.

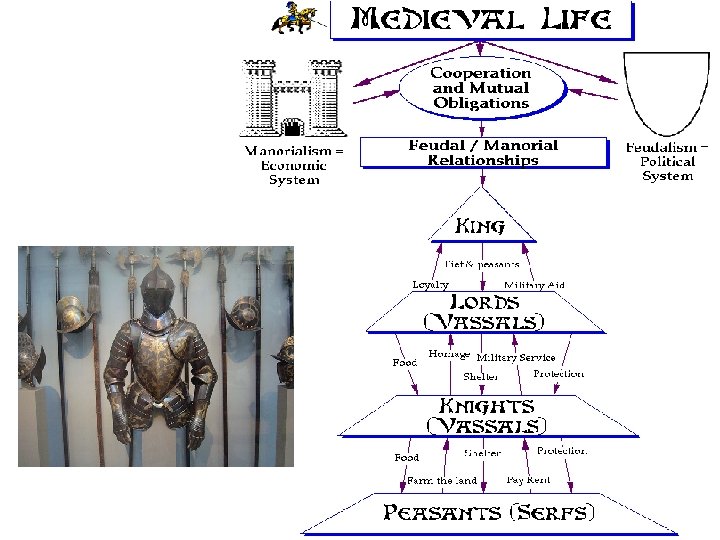
Feudalism • During the Middle Ages, most of Western Europe had a feudal government. • Kings or lords would offer land in exchange for loyalty and service (this exchange was called a fief). • Feudalism also provided a social hierarchy for medieval society. • Anyone who owed loyalty to someone of a higher social status was known as a vassal. • Knights were mounted soldiers who served and protected their lords. They had to take an oath of chivalry (code of honor); they had to be brave, loyal and honorable. • The majority of people under feudalism were serfs. They were farmers who could not leave the land due to debt to their lord.

Medieval Castles Not only were castles a home for medieval nobility, but it also served as a fortress for protection.

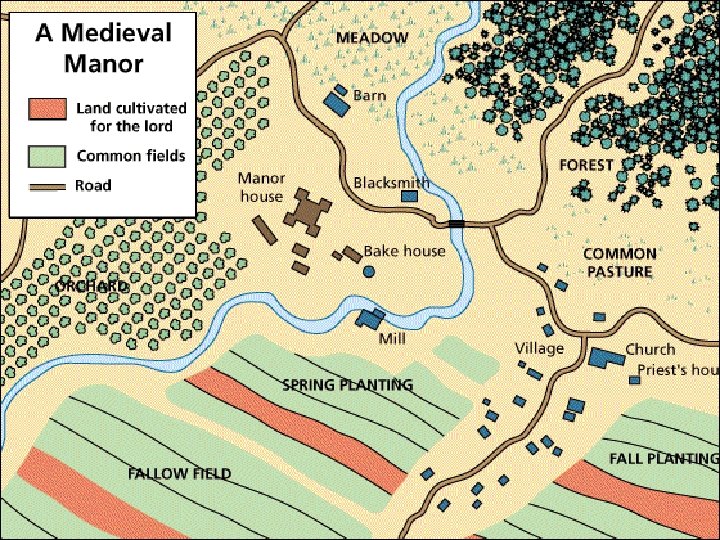
Manorialism was a medieval economic system, that was used throughout most of Western Europe. It was based around the manor (a large farm estate). Serfs (peasant farmers) worked the land in exchange for the lord’s protection and permission to live on the land. In order to maximize the amount of crops produced, serfs used crop rotation. In the two field system, the serfs would plant one field and leave the other fallow (unplanted) so the soil could regain its nutrients. By the later middle ages, more serfs were using the three field system. The serfs would plant two fields, and leave third fallow. (This produced more crops than the two field system).

Medieval Church • In the Byzantine Empire in Eastern Europe, the Eastern Orthodox Church dominated. • In Western Medieval Europe, the Roman Catholic Church was the main stabilizing force. The Pope headed the Church from the Vatican in Rome. The Pope often competed with kings for power. • The Catholic Church was the largest landowner in all of Western Europe! • Everyone had to pay a tithe, or 10% of their income to the Church. • Almost no one except for the clergy (people who worked in the Church) were educated.

Early Medieval Churches were Romanesque. Shorter & heavier with Roman style arches and vaulted ceilings.

Later Medieval Churches were Gothic style. Taller & lighter with more detail.

Monks and nuns lived in monasteries (isolated communities). They dedicated their lives to g-d, were not allowed to marry or have sex. Monks created illuminated manuscripts; they copied ancient texts by hand added illustrations.

The Crusades • In the 1050 s, the Seljuk Turks (Muslims) took control of Jerusalem. • 1095 the Byzantine emperor asked the Pope for help. • 1095 Pope Urban II called for Christian Knights to travel to the Holy Land rescue it from the Turks. - He promised forgiveness of sins - Many went for wealth & adventure
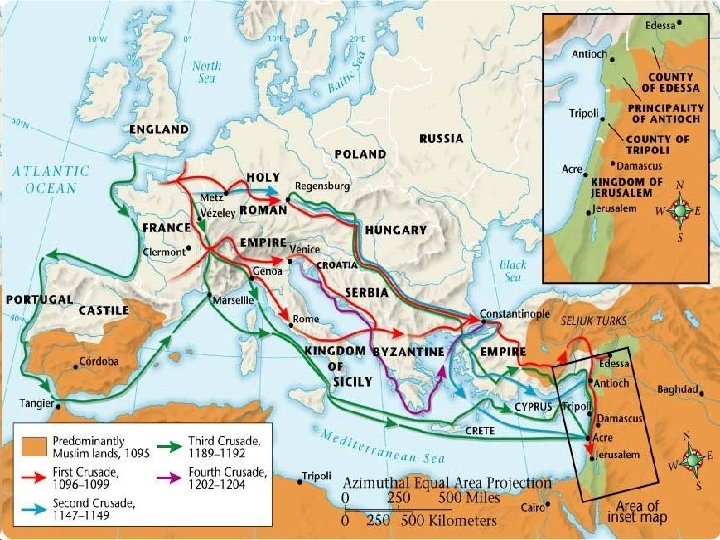

• During the First Crusade, in 1099 the Christians conquered Jerusalem and established a Christian feudal kingdom. • However, the Muslims were able to gain back some of the land they lost. This led to more crusades. • During the 12 th century, Saladin was a very strong Muslim leader. He recaptured Jerusalem but allowed the crusaders to leave safely.

Consequences of the Crusades Negatives • After 9 long Crusades and several smaller ones, the crusaders failed to recapture Jerusalem. • Millions died and were injured. • Many knights killed Jews on the way to Jerusalem. • Trade in Europe increased after returning knights brought back luxuries from the east. • Europeans had seen how the Muslims had preserved ancient Greek & Roman texts, as well as having universities. This led to an increased desire for education and learning. • Kings became more powerful due to the wealth they gained. Feudalism began to decline as a result.

The Inquisition The Church began the inquisition to find and stop heresy (actions that went against the Church), as well as blasphemy (speech or writing that went against the Church). Church officials would ask questions to prove if you were truly Catholic. If they believed you not to be a true Catholic and you did not confess, they would torture you, often until death.

The Black Death CAUSES: The Black Death was a deadly disease spread by fleas on rats. It began in Asia in the 1340 s and spread along trade routes to Africa, the Middle East and Europe. Symptoms included black swellings, pain and death within days. Medieval doctors often wore masks to protect themselves. They would bleed their patients (often making it worse).
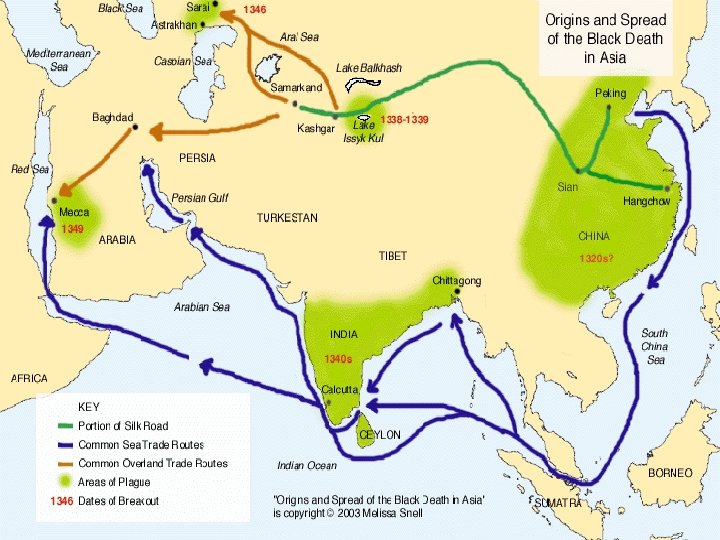
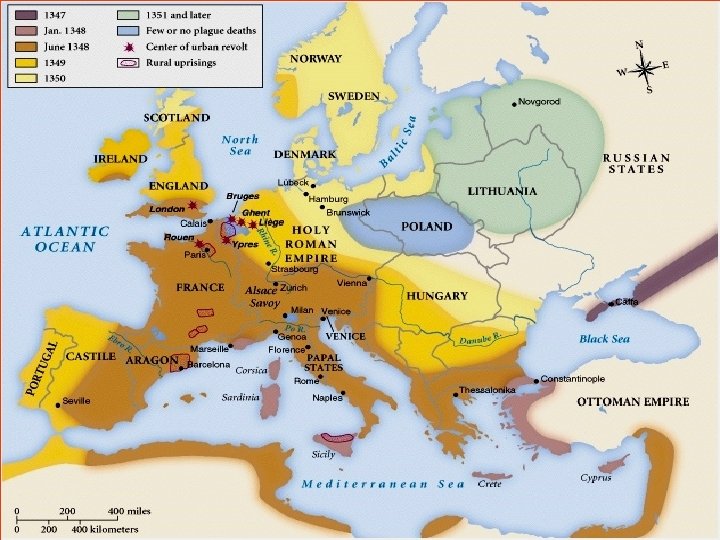

Flagellants travelled town to town, whipping themselves. They believed G-d was punishing them. Many Europeans also blamed the Jews; it led to increased anti-Semitism. CONSEQUENCES: 1/3 of Europeans died. Approximately 75 million died worldwide. Due to less serfs, many lords switched from farming to raising sheep. Serfs began to move to towns and cities.

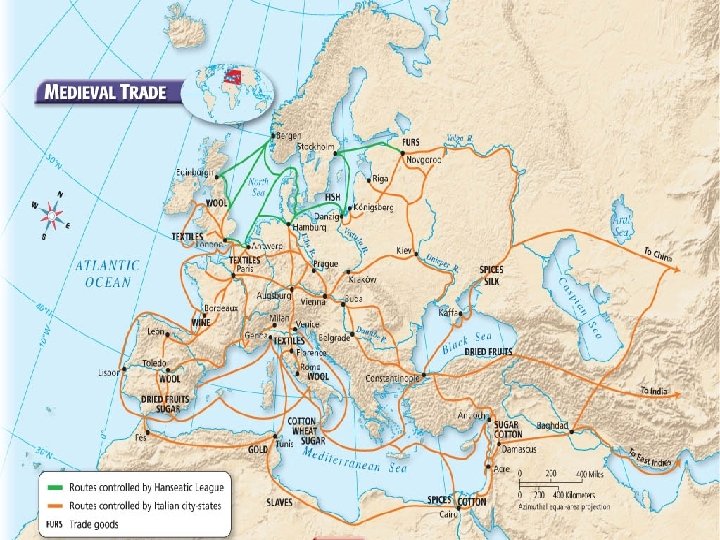
Growth of Medieval Towns The agricultural revolution (switch from a wooden to an iron plow, switch from the 2 field to the 3 field system) increased crops, leading to an increase in Europe’s population. This helped lead to the growth of towns and cities. The commercial revolution allowed people to go to banks for loans, insurance, and to buy stocks in businesses. This led to a new economic system of capitalism.

• Merchants would set up temporary shops along busy trade routes. Over time, these became trade fairs, and eventually towns. • Many lords allowed their serfs to move to towns for a fee.

Late Medieval Trade • The Hanseatic League dominated medieval trade in northern Europe. • Venice dominated medieval trade in southern Europe. • Both built lighthouses, policed piracy and controlled the trade routes.

Guilds • Because Europe still was under feudalism, business was not regulated. Merchants and craftspeople formed guilds so they could regulate themselves. Typically guilds: - Made sure the quality of the goods/service stayed high - Provided social services for its members, such as hospitals - Controlled hours of work and prices of goods • To join a craft guild (such as the bakers or iron smiths), you had to become an apprentice to a master. After years of training you became a journeyman, and possibly if the guild accepts you, a master.

William the Conqueror 1066 William of Normandy (northern France) sailed to England to compete for the throne against Harold, a cousin of the recently dead king. William won the Battle of Hastings. Harold was struck in the eye with an arrow! The events were recorded in the Bayeux Tapestry (wall hanging).
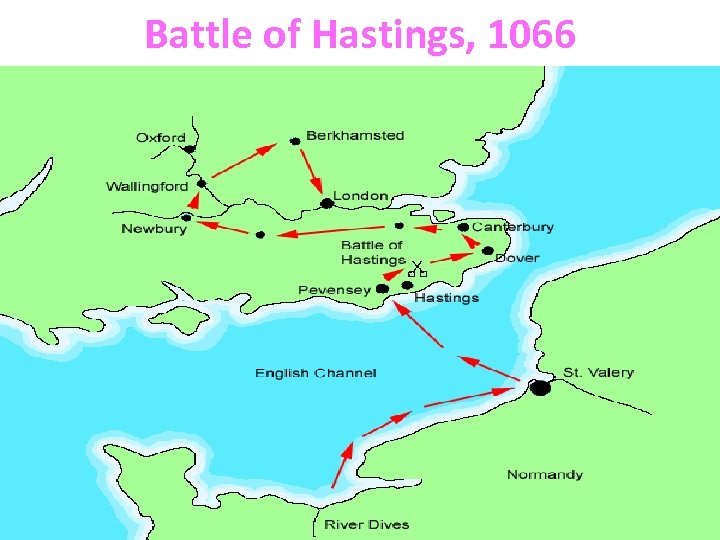
Battle of Hastings, 1066

• William the Conqueror divided England up into shires (districts) and sent government officials to count people and their animals. This information was recorded in the Domesday Book, and was used for tax purposes. (Similar to our census) • In 1297, King John of England was forced by his nobles to sign the Magna Carta (Great Charter). This document limited the power of the king, and guaranteed certain rights to the nobility. • By 1400, England’s parliament had 2 houses (Lords & Commons). Parliament checked the power of the king.
100 Years War • The 100 Years War (1337 1453) was fought between England France. Because William the Conqueror was from France, England claimed France as theirs… and because William the Conqueror became king of England, France claimed England as theirs.

• In the beginning of the war, England was winning due to their new weapon, the long bow. (It shot arrows at a longer range and more accurately than the French’s cross bow). • Joan of Arc was a young peasant girl. She heard a heavenly voice that told her to lead the French to victory in 1429. • Joan did turn the tide of the war; the French were now winning. However, Joan was captured and sold to the British who put her on trial for witchcraft. She was burned at the stake in 1431.

Europe by the End of the Middle Ages • Population, trade and education increased • Feudalism and manorialism decreased • Local kingdoms became more powerful, forming the first real European nations. - After the 100 Years War, England France became very nationalistic (to have pride for your nation). • The Catholic Church was still the most powerful institution in Europe.

Medieval Achievements • Architecture: Romanesque and Gothic Cathedrals, castles • Art: Medieval art was deeply religious, flat and abstract, tapestries • Literature: By the late Middle Ages, books began to be written in the vernacular (every day language). - Chaucer: Canterbury Tales - Dante: The Divine Comedy • Philosophy: Peter Abelard and Thomas Aquinas combined their knowledge of ancient Greek philosophy (logic and reason) with Christian beliefs • Commerce and trade: guilds, banks • Science and technology: three field system, iron plow
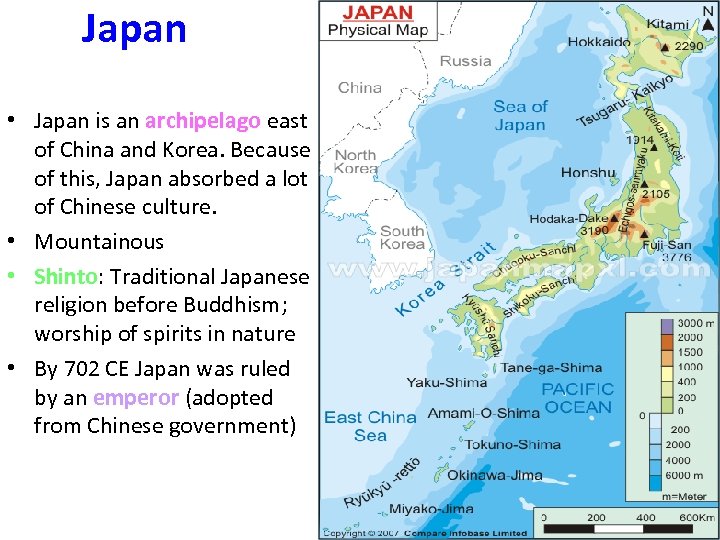
Japan • Japan is an archipelago east of China and Korea. Because of this, Japan absorbed a lot of Chinese culture. • Mountainous • Shinto: Traditional Japanese religion before Buddhism; worship of spirits in nature • By 702 CE Japan was ruled by an emperor (adopted from Chinese government)
Japanese Feudalism • By the 9 th century, the power of the emperor declined. Japan became a feudal government with the emperor remaining as a figurehead (someone with little to no real power). • The shogun had the most power. • Just like in European feudalism, people below the shogun owed loyalty and service to the person above him in exchange for land protection. • The samurai were Japanese warriors. They lived by the code of Bushido (similar to European chivalry). Bushido was a code of honor; a samurai had to be brave, loyal and honorable. If he lost a battle, he had to commit seppuku (ritual suicide).
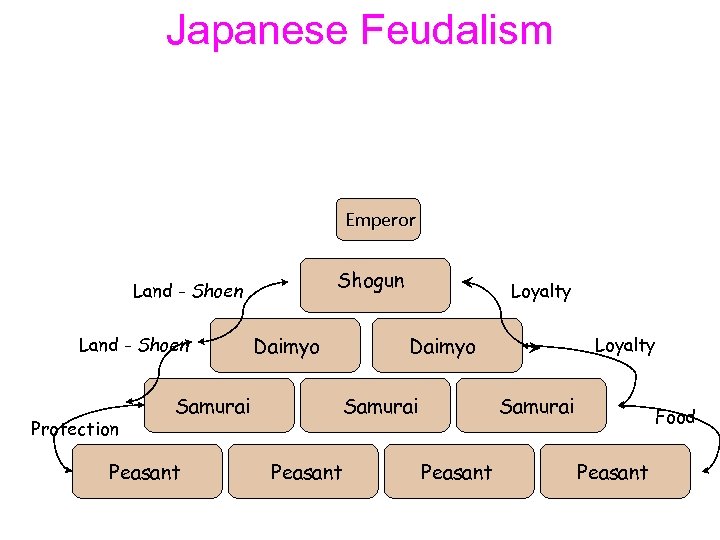
Japanese Feudalism Emperor Shogun Land - Shoen Protection Daimyo Samurai Peasant Loyalty Samurai Peasant Food Peasant

Japanese Culture • Zen Buddhism: A Japanese form of Buddhism from China. Focus on simplicity and beauty in nature. Led to the creation of Zen gardens and rock gardens (for meditation). • Tea Ceremony: A ceremony that developed from Zen Buddhism. Focus on the beauty in the preparation of tea. • Haiku: A short but simple poem (5, 7 and 5 syllables).

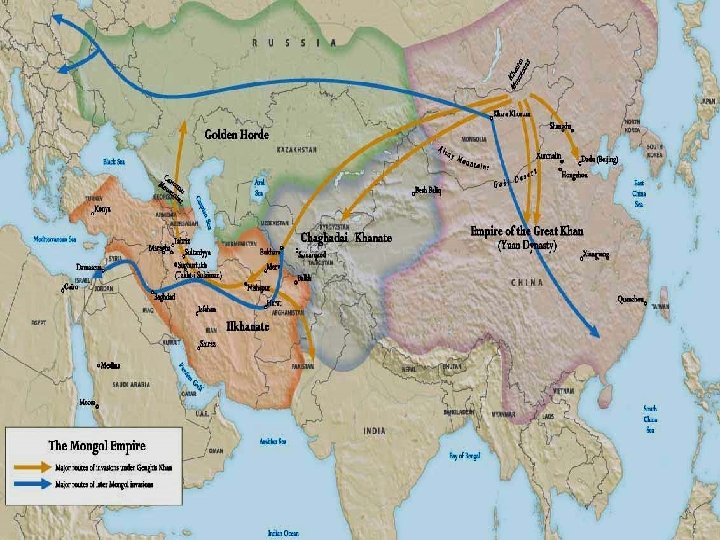
Mongols • The Mongols were nomadic, mounted warriors who lived north of China. They traveled easily around the Mongolian steppe and Gobi desert. • They were known as the Golden Horde due to the color of their tents. • Genghis Khan conquered most of Asia in the 12 th century. • His grandson, Batu, conquered Russia and eastern Europe. Russia was cut off from Western Europe for centuries. • 1279 another grandson, Kublai Khan, conquered China and began the Yuan Dynasty. He gave the best jobs in the government to Mongols, but he kept Chinese culture. *This led to the Pax Mongolia: a period of stability, including safe passage along the Silk Road.

• 1368 peasants rebelled against Mongol rule and began the Ming Dynasty. • The Ming brought back the Civil Service Exam (a test one had to take to work in the government, based on Confucianism). • The Forbidden City was built • Early 15 th century, Zheng He established trade links with southeast Asia and eastern Africa. *His ships were larger than those of Colombus! • After Zheng He’s death, the emperor banned more voyages of exploration. This may have been due to China’s belief that it was the Middle Kingdom, or center of the world. Ming Dynasty
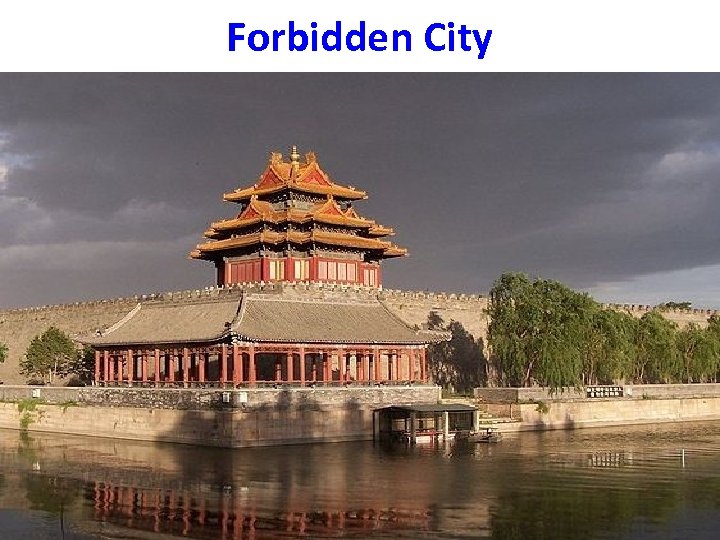

Forbidden City

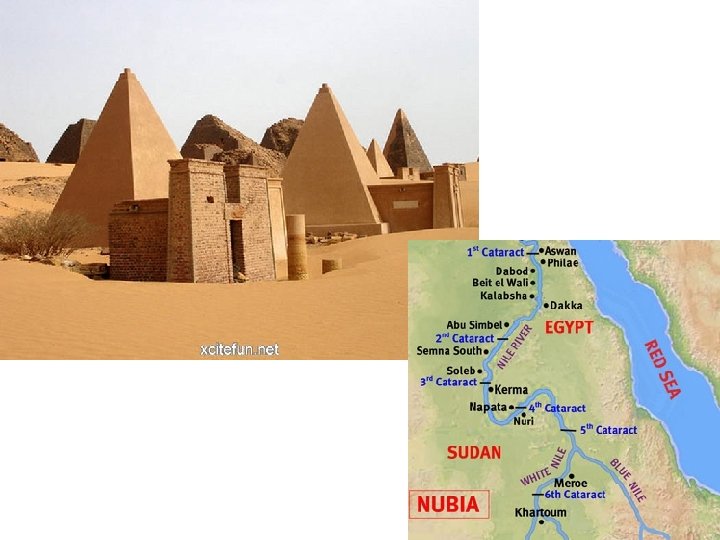
Eastern African Civilizations Nubia (3000 BCE – 400 BCE) Axum (400 BCE – 7 th century CE) Swahili States (began 7 th century CE) Co-existed along the Nile with Ancient Egypt. Lived in Upper Egypt. Axum conquered Nubia. Arab and Persian merchants built cities along Africa’s eastern coast. Was controlled by Egypt for much of its history, but Nubia took control of Nubia for a short time! Due to its location on the Red Sea, it had a thriving trade network linking the Mediterranean, Africa and India. Cultural diffusion led to a new language and culture, Swahili (a mix of Arabic and Bantu). Built pyramids and tombs similar to Egyptian ones, but on a smaller scale. Cultural diffusion between Jews, Christians and Muslims.
Ethiopian Church in Axum
Western African Civilizations Ghana (800 – 1000 CE) Maili (1200 – 1450 CE) Songhai (1450 – 1600 CE) Controlled the gold-salt trade in West Africa. Mali conquered Ghana and took over the gold-salt trade. Songhai conquered Mali and took over the gold-salt trade. Women worked in business and government Mansa Musa was a Muslim Emperor of Mali. He went on a hajj to Mecca, distributing his wealth on the way. Set up a Muslim dynasty. Had Muslim advisors. Timbuktu became a great city of a great center of learning; had a trade. university.

Origins of Renaissance • The Renaissance was the rebirth of Western Europe after the Middle Ages (14 -15 th centuries) • Began in Florence due to - Italian city-states never stopped trading in the Middle Ages - Ancient ruins were a reminder of Ancient Roman and Greek civilizations - Medici family (wealthy bankers) funded paintings, sculptures and new building projects - Invention of the printing press by Gutenberg spread Renaissance ideas

Humanism • During the Renaissance, Europeans developed a new way of thinking, called humanism. • During the Middle Ages, thinkers focused on religion and life after death. Renaissance humanists instead were curious about life in the present. • Humanists looked back to classical civilizations and their achievements (Greece & Rome). • Believed the individual is important, and that every human is capable of great achievements.

Renaissance Art Example of Medieval Art • Medieval art was flat, abstract and based on religion. • Renaissance art was realistic due to the use of perspective (making distant objects smaller). Renaissance artists often did have religious themes, but used Greek or Roman backgrounds. • Portraits (paintings of individuals) became popular in the Renaissance.
Renaissance Artists Michelangelo Leonardo da Vinci Raphael Vermeer Jan van Eyk Brunelleschi Sistine Chapel Mona Lisa School of Athens Girl with a Pearl Earring The Arnolfini Wedding Brunelleschi's Dome in Florence David (Statue) The Last Supper Virgin and Child Girl with a Water Jug St. Peter’s Basilica Vetruvian Man Brunelleschi's Dome, Florence, Italy

Leonardo da Vinci

Michelangelo

Renaissance Writers • Machiavelli (from Italy) wrote The Prince; a guide on how to rule. He believed it is better to be feared than loved if one cannot have both, and that a good ruler will always be prepared. • Shakespeare (from England) wrote timeless plays such as Hamlet, Romeo & Juliet and Macbeth.

Protestant Reformation • 1517 Martin Luther wrote the 95 Theses (arguments) protesting abuses by the Catholic Church. This included the selling of indulgences (the promise of salvation in heaven in exchange for money). • Johan Tetzel, the Catholic priest who Luther complained to, excommunicated him. This led Luther to break away from the Catholic Church, beginning the Protestant Church.

Catholic Church • Pope is the highest authority under G-d • Priests cannot marry • Prayer to saints • Confession • Elaborate ceremonies • Latin is the official Church language Protestant Church • Pope is NOT the highest authority under G-d • Everyone should read the Bible for themselves in the vernacular (everyday language) • Church officials CAN marry • Elaborate ceremonies are not necessary • No saints • Christians can only reach salvation by faith in G-d Other Protestant Churches that Evolved as a Result of the Protestant Reformation: Anglican Church: began by King Henry VIII of England when he could not get a divorce in the Catholic Church Calvinism: Began by John Calvin. Believed like Luther that you can only reach salvation through faith in G-d. However, he also believed in predestination (those who will be saved were chosen before they were born)

Counter Reformation The Catholic Church had its own reformation to fight back against the Protestant movement. - Council of Trent: Began 1545. Church officials met for 20 years to decide how to fight Protestantism. Agreed to ban indulgences, build more schools, but to keep most Catholic traditions. Created the Index of Forbidden Books; anything that was found to be blasphemous to the church was burned. - Jesuits: Ignatius Loyala founded the Society of Jesus (Jesuits), specially trained missionaries who were sent around the world to spread Catholicism. - Increase of the inquisition. Effects of the Counter Reformation: Religious wars broke out (including the 30 Years War). Anti-Semitism increased. Witch hunts increased. Many Protestants fled to new lands (including the Americas. )

Scientific Revolution • In the Middle Ages, Europeans believed in the geocentric model of the universe (the sun and other planets revolve around the earth). The scientific method was not used, and the Bible was seen as the only source of truth. • In the 16 th century, Copernicus used math and observation of the skies to create the heliocentric model of the universe (the planets revolve around the sun). • Early 17 th century, Galileo Galilei designed an improved telescope. He saw mountains on our moon and moons revolving around Jupiter. This proved Copernicus was correct. Galileo was arrested for heresy and blasphemy (going against the church). He was forced to deny his findings. • Isaac Newton used math to prove in the existence of gravity, a force that keeps the planets in orbit around the sun. He believed that nature follows uniform laws (laws that exist the same in any part of the universe.
• By the 17 th century, scientists were using the scientific method. Scientific facts now had to be proven through observation and experimentation. • Rene Descartes believed in the power of human reason. The ideas of Descartes and other thinkers of the Scientific Revolution led to the Enlightenment, the period in the 18 th century when people looked for natural laws that govern human behavior.
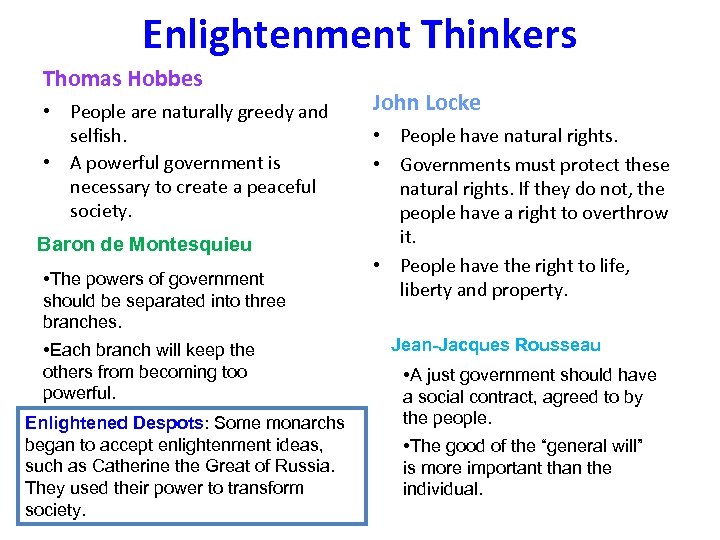
Enlightenment Thinkers Thomas Hobbes • People are naturally greedy and selfish. • A powerful government is necessary to create a peaceful society. Baron de Montesquieu • The powers of government should be separated into three branches. • Each branch will keep the others from becoming too powerful. Enlightened Despots: Some monarchs began to accept enlightenment ideas, such as Catherine the Great of Russia. They used their power to transform society. John Locke • People have natural rights. • Governments must protect these natural rights. If they do not, the people have a right to overthrow it. • People have the right to life, liberty and property. Jean-Jacques Rousseau • A just government should have a social contract, agreed to by the people. • The good of the “general will” is more important than the individual.

Age of Exploration Reasons for European Exploration • Ottoman Turks took control of the Silk Road. Europeans needed an alternative route to the Indies. • Increased demand for spices. European Explorers New Technologies Allowed for Exploration • Portolan maps (showed compass points) • Improved magnetic compass • Caravel ships (larger than previous ships, could sail in bad weather and go against the current). • Prince Phillip II of Portugal created a naval school and began exploring the west coast of Africa. • 1488 Bartholomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa. • 1498 Vasco de Gama followed Dias’s route to go all the way around Africa to India. • Magellan tried to sail around the world. He was killed on the way, but one of his ships made it back to Europe.
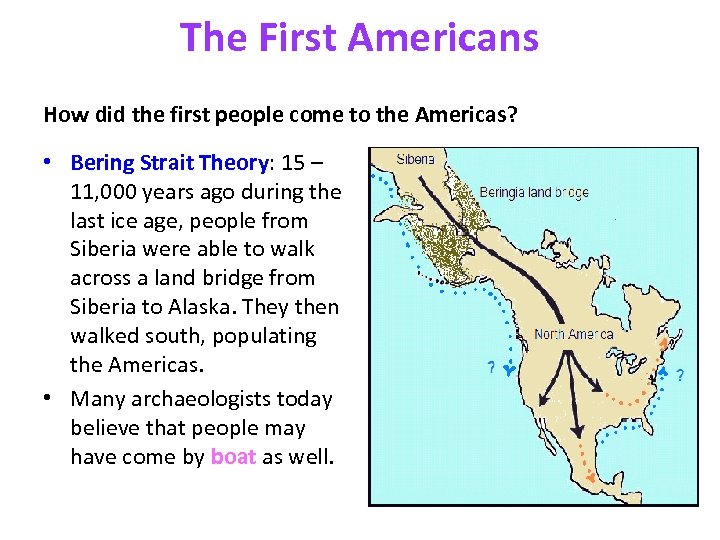
The First Americans How did the first people come to the Americas? • Bering Strait Theory: 15 – 11, 000 years ago during the last ice age, people from Siberia were able to walk across a land bridge from Siberia to Alaska. They then walked south, populating the Americas. • Many archaeologists today believe that people may have come by boat as well.
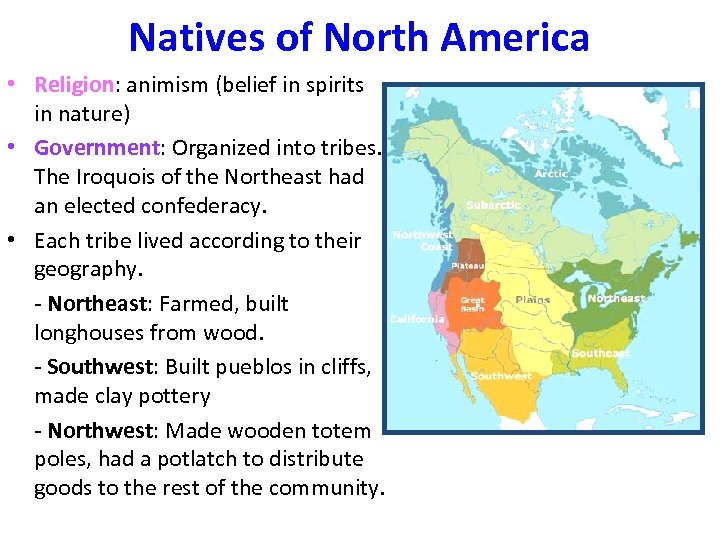
Natives of North America • Religion: animism (belief in spirits in nature) • Government: Organized into tribes. The Iroquois of the Northeast had an elected confederacy. • Each tribe lived according to their geography. - Northeast: Farmed, built longhouses from wood. - Southwest: Built pueblos in cliffs, made clay pottery - Northwest: Made wooden totem poles, had a potlatch to distribute goods to the rest of the community.
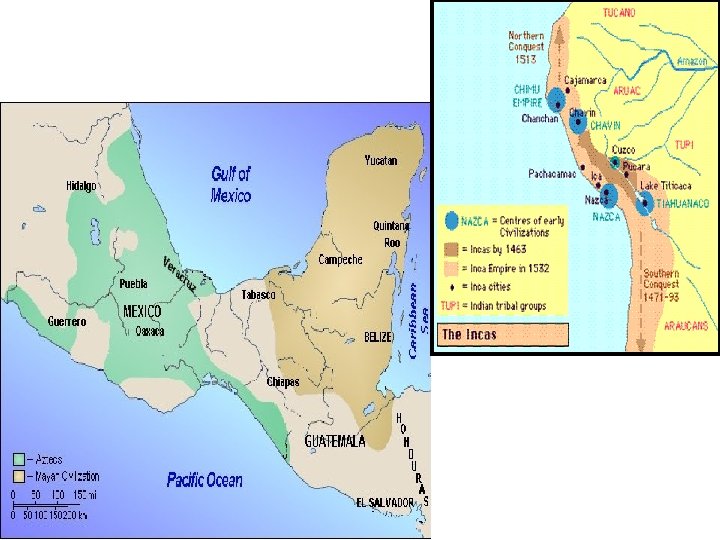
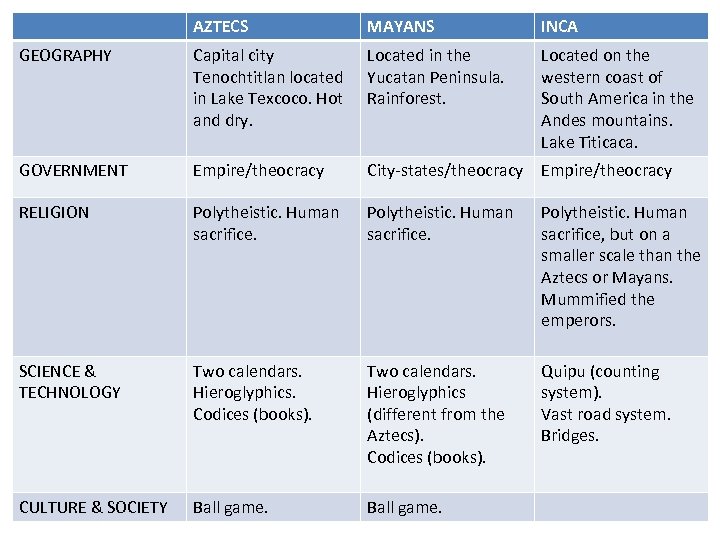
AZTECS MAYANS INCA GEOGRAPHY Capital city Tenochtitlan located in Lake Texcoco. Hot and dry. Located in the Yucatan Peninsula. Rainforest. Located on the western coast of South America in the Andes mountains. Lake Titicaca. GOVERNMENT Empire/theocracy City-states/theocracy Empire/theocracy RELIGION Polytheistic. Human sacrifice, but on a smaller scale than the Aztecs or Mayans. Mummified the emperors. SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Two calendars. Hieroglyphics. Codices (books). Two calendars. Hieroglyphics (different from the Aztecs). Codices (books). Quipu (counting system). Vast road system. Bridges. CULTURE & SOCIETY Ball game.
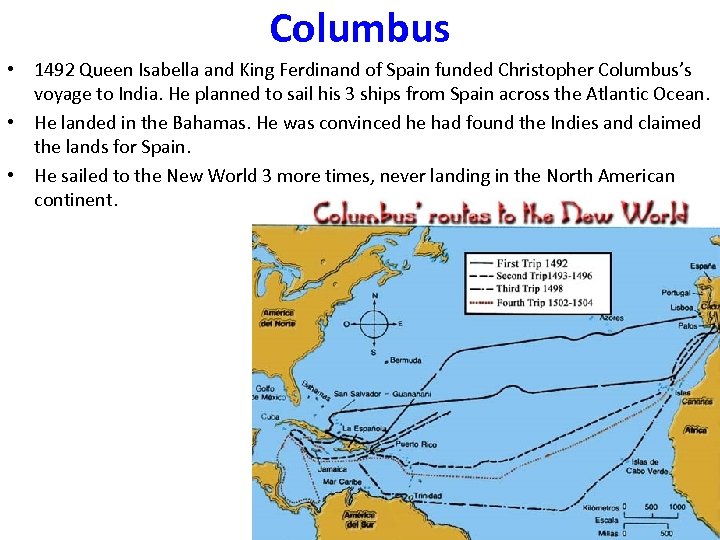
Columbus • 1492 Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand of Spain funded Christopher Columbus’s voyage to India. He planned to sail his 3 ships from Spain across the Atlantic Ocean. • He landed in the Bahamas. He was convinced he had found the Indies and claimed the lands for Spain. • He sailed to the New World 3 more times, never landing in the North American continent.
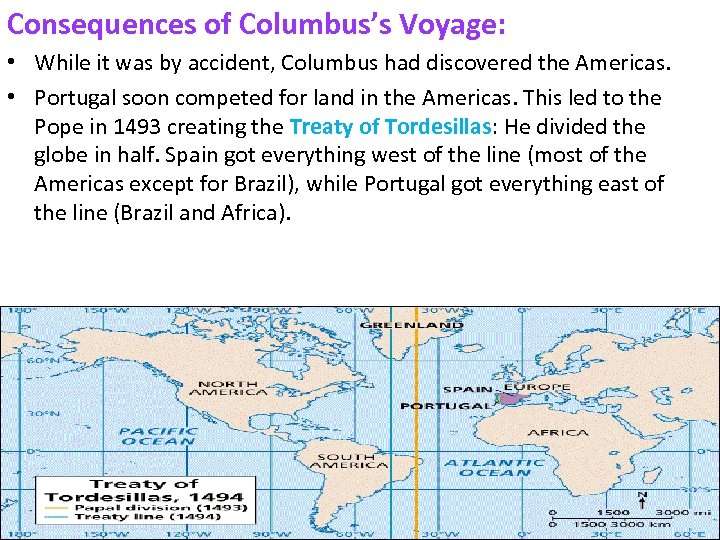
Consequences of Columbus’s Voyage: • While it was by accident, Columbus had discovered the Americas. • Portugal soon competed for land in the Americas. This led to the Pope in 1493 creating the Treaty of Tordesillas: He divided the globe in half. Spain got everything west of the line (most of the Americas except for Brazil), while Portugal got everything east of the line (Brazil and Africa).
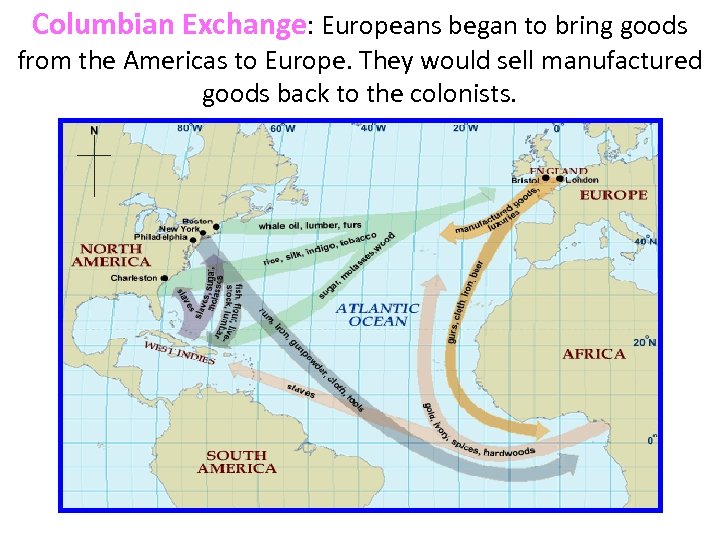
Columbian Exchange: Europeans began to bring goods from the Americas to Europe. They would sell manufactured goods back to the colonists.

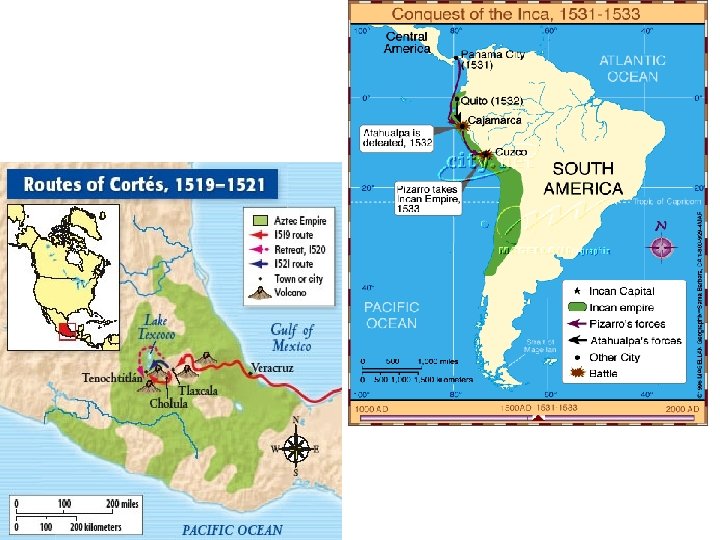
Fall of Aztecs and Inca • 1519 Hernan Cortes, a Spanish conquistador, conquered the Aztec Empire in less than 2 years. • 1532 Francisco Pizarro conquered the Inca Empire in less than 3 years. DUE TO: • Superior technology (guns, cannons, larger ships) • Diseases that the natives were not immune to • Possible belief that the Spanish were Gods
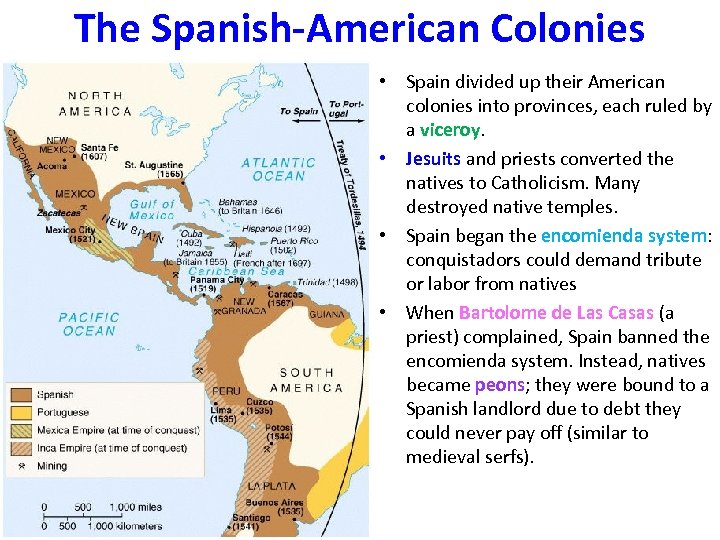
The Spanish-American Colonies • Spain divided up their American colonies into provinces, each ruled by a viceroy. • Jesuits and priests converted the natives to Catholicism. Many destroyed native temples. • Spain began the encomienda system: conquistadors could demand tribute or labor from natives • When Bartolome de Las Casas (a priest) complained, Spain banned the encomienda system. Instead, natives became peons; they were bound to a Spanish landlord due to debt they could never pay off (similar to medieval serfs).

The Spanish colonies developed a new social class system.

The Global Slave Trade • Slavery has existed for thousands of years, including Ancient Egypt, Rome and Greece. The word “slave” comes from the Slavs, who were slaves in Ancient Rome. At this time, slavery was based on war and debt, not racism. • Starting with Portugal, Europeans in the 15 th century began to trade manufactured goods for slaves in Africa. Europeans built slave forts on the West African coast. Africans would kidnap people from rival tribes and bring them to the coastal forts. • The African slaves were then put on slave trips. Their journey across the Atlantic Ocean was called the Middle Passage. The conditions were horrific and many would not survive. • Once in the Americas, the slaves would be cleaned and sold for auction. • African slaves at this time were seen as property that could be bought and sold. Racism evolved to justify this practice.
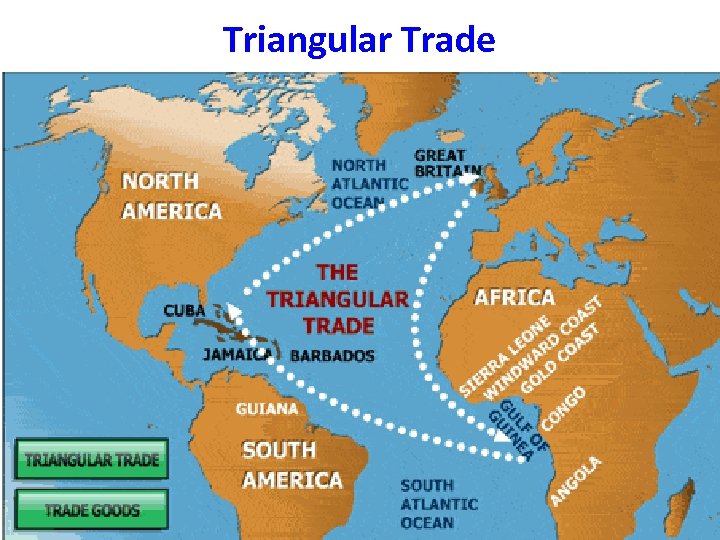
Triangular Trade
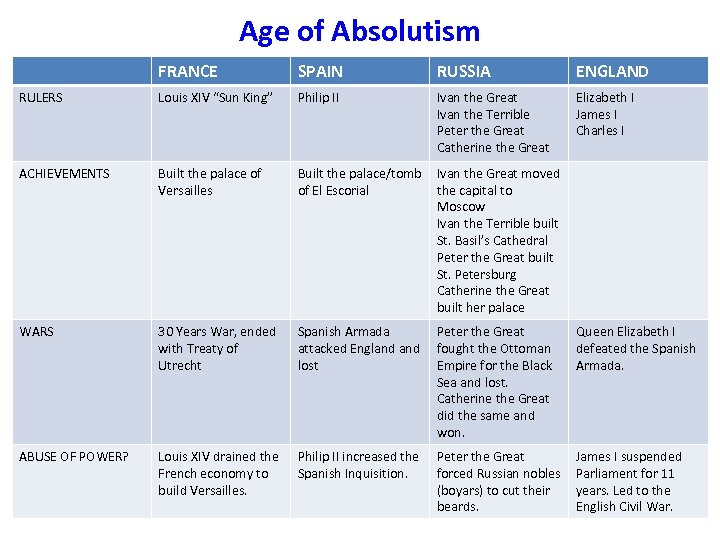
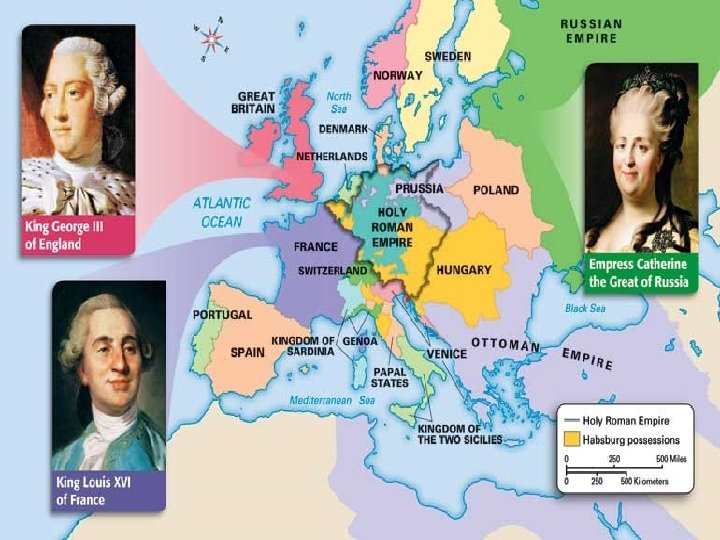
Age of Absolutism FRANCE SPAIN RUSSIA ENGLAND RULERS Louis XIV “Sun King” Philip II Ivan the Great Ivan the Terrible Peter the Great Catherine the Great Elizabeth I James I Charles I ACHIEVEMENTS Built the palace of Versailles Built the palace/tomb of El Escorial Ivan the Great moved the capital to Moscow Ivan the Terrible built St. Basil’s Cathedral Peter the Great built St. Petersburg Catherine the Great built her palace WARS 30 Years War, ended with Treaty of Utrecht Spanish Armada attacked England lost Peter the Great fought the Ottoman Empire for the Black Sea and lost. Catherine the Great did the same and won. Queen Elizabeth I defeated the Spanish Armada. ABUSE OF POWER? Louis XIV drained the French economy to build Versailles. Philip II increased the Spanish Inquisition. Peter the Great forced Russian nobles (boyars) to cut their beards. James I suspended Parliament for 11 years. Led to the English Civil War.

English Civil War • The first Stuart King of England, James I, sought to increase his power, using divine right as his justification. He even suspended Parliament! He also angered the Puritans, who wanted to “purify” the Anglican Church of Catholic practices. • When James’ son Charles I took power and suspended Parliament (except when he needed money), it led to a civil war. - Cavaliers supported Charles - Roundheads supported Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell • The Roundheads won the war. Charles I was the first English monarch ever to be executed. Oliver Cromwell became “Lord Protector” of England (NOT a king). England became a commonwealth; he gave more power to Parliament. • When England was a commonwealth, Cromwell and most of Parliament were Puritans. (A strict form of Protestantism) They imposed new laws banning most forms of entertainment.

• After Cromwell’s death, 1660 Parliament invited Charles I’s son Charles II to return to England. This marked the restoration of the Stuart monarchy. • 1685, his brother, James II took the throne. He was openly Catholic. Parliament became worried and asked Mary Stuart and her husband, William (both Protestants) to take throne instead. When they arrived in England, James II fled to France. This bloodless transfer of power was known as the Glorious Revolution. • Before they could take power, William and Mary were forced to accept the English Bill of Rights, a set of acts passed by Parliament to ensure its superiority over the monarchy. It stated: - King must regularly work with Parliament King must give the House of Commons financial control Abolished excessive fines and cruel or unusual punishment Affirmed habeus corpus, meaning no person could be held in jail without first being charged with a crime *The English Bill of Rights influenced the American Constitution!

Do NOT Think You are Done Yet! • Go to regentsprep. org to take practice multiple choice questions. • Reread your notes. You will need a lot of detail for your essay. • Break up your studying. Do NOT wait until the last minute. Good luck!
577ce5caf69ad8d1002ad85f5035d922.ppt