e1674d8e9fddc7b5f8552c28cee7d881.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Global Education Market Presentation To World Education Market Lisbon 2003 Ronald Perkinson International Finance Corporation (World Bank Group) www. ifc. org / www. ifc. org/edinvest

The Global Market • $2. 2 trillion+ total – one third of market in USA – approx 15% only in the developing world • Teachers – 5% of global labor force • Primary & Secondary Education – 83% of students in developing countries • Tertiary & Adult Education – 90 million tertiary students worldwide, or less than 20% of all 18 to 25 yr olds Sources: Merrill Lynch 2000; OECD 2000/ 01; UNESCO 2000/01; IFC

The Second Millennium Development Goal Achieving Universal Primary Education – ‘Education For All’ The EFA commitment undertakes by 2015 to: § Ensure universal primary education § Eliminate gender disparities in primary and secondary education § Improve early childhood care and education § Ensure equitable access to “life skills” programs § Achieve a 50 percent increase in adult literacy § Improve all aspects of the quality of education
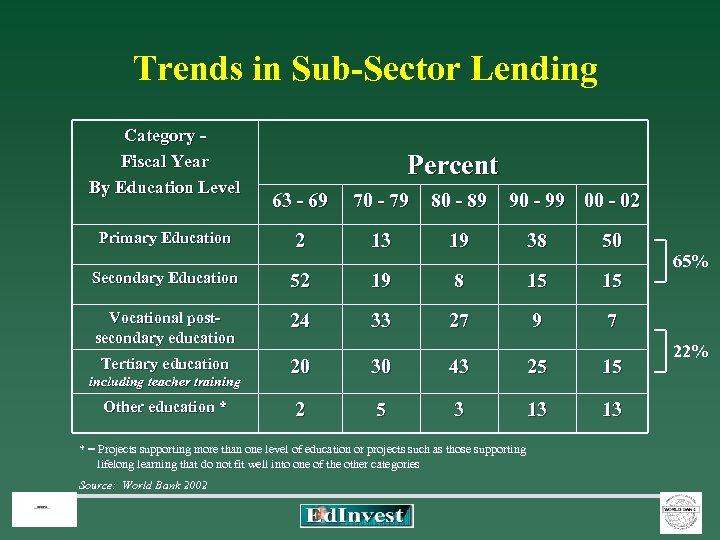
Trends in Sub-Sector Lending Category - Fiscal Year By Education Level Percent 63 - 69 70 - 79 80 - 89 2 13 19 38 50 Secondary Education 52 19 8 15 15 Vocational postsecondary education 24 33 27 9 7 Tertiary education 20 30 43 25 15 2 5 3 13 13 Primary Education including teacher training Other education * 90 - 99 00 - 02 * = Projects supporting more than one level of education or projects such as those supporting lifelong learning that do not fit well into one of the other categories Source: World Bank 2002 65% 22%
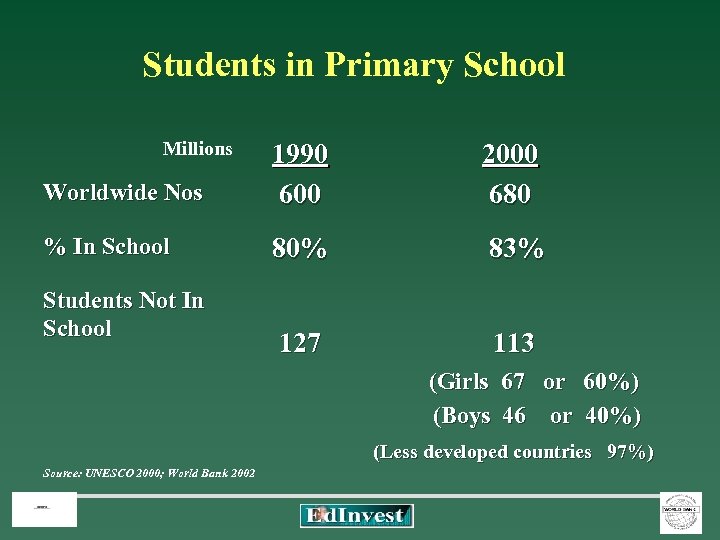
Students in Primary School Millions Worldwide Nos 1990 600 2000 680 % In School 80% 83% 127 113 Students Not In School (Girls 67 or 60%) (Boys 46 or 40%) (Less developed countries 97%) Source: UNESCO 2000; World Bank 2002

HIV/AIDS! • By EO 2001, over 40 million people with HIV / AIDS • Teachers – the most infected profession in SADC – (32% in Kwa Zulu; 30% in Malawi & Botswana) • Africa – 10% of world’s population – but has 90% of new HIV cases • Also spreading in India, China, Eastern Europe and Russia • AIDS orphans = 15. 6 million – most in Sub Saharan Africa Sources: World Bank 2002; Christian Aid 2001

World Population Growth Year Population Time Per Billion Yr 1 250 m – 1800 1 b 1800 yrs 1930 2 b 130 yrs 1960 3 b 30 yrs 1975 4 b 15 yrs 1988 5 b 13 yrs 2001 6 b 13 yrs Source: “ 6 Billion Human Beings: ” - Musée de l'Homme Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris –France

Balancing Education Sector Needs. . . . With Fiscal Realities • Markets do not solve problems of equity / fairness – need for the public sector to address • Economic decline – available resources for education shrink • Governments reconciling education fiscal realities and demographic trends • ‘Supplementary’ costs – shifting to parents and students – and increasing annually • 1% annual change – global public and private financing Sources: World Bank & IFC; OECD 2000; Statistics Canada 2002
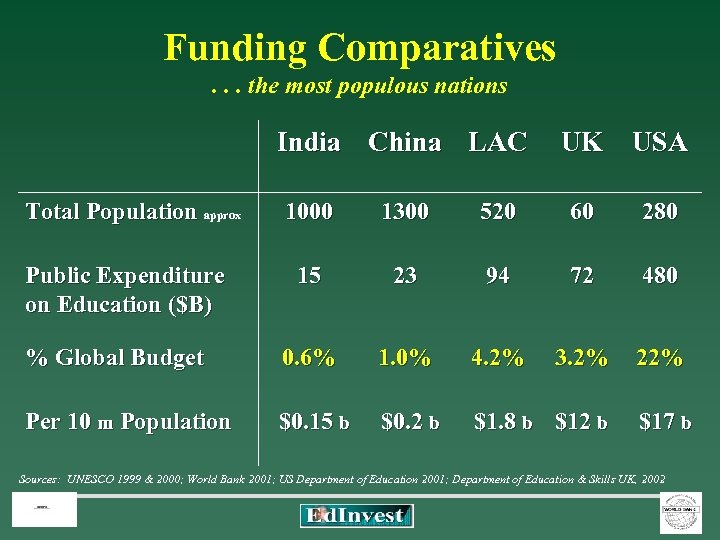
Funding Comparatives . . . the most populous nations India China LAC UK USA Total Population approx 1000 1300 520 60 280 Public Expenditure on Education ($B) 15 23 94 72 480 0. 6% 1. 0% 4. 2% 3. 2% 22% % Global Budget Per 10 m Population $0. 15 b $0. 2 b $1. 8 b $12 b $17 b Sources: UNESCO 1999 & 2000; World Bank 2001; US Department of Education 2001; Department of Education & Skills UK, 2002

Global Giants – Lack of Supply in the world’s most populous countries China: – 10 to 11% gross enrollment – Yr 2001 – 7. 2 m students enrolled – admitted 2. 2 m new students in Yr 2002 – 26 m students currently in high school – 15 m students to enroll over next 4 years India: – 5 to 6% gross enrollment – 10, 900 HEI’s (includes 237 Deemed Universities) – over 8 m students enrolled – some programs - 6000 applicants per place Sources: Unesco 2000; India Planning Commission Report 2002; China Dept of Statistics 2002

Higher Education . . . the five converging forces of change Five major converging forces on higher education • The increasing importance of knowledge • The further impact of globalization • The impact of increasing competition • Continuing Information & Communications Technologies revolution • Decline in public financing – sourcing alternative financing • Source: ‘World Bank ‘Constructing Knowledge Economies” 2002; The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002; IFC

Higher Education . . . other important trends • Unmet demand & supply – demographic pressures • Public financing declining – burden shifting from the State to Higher Education Institutions • Pressures on governance – global market paradigm – increased competition – rising costs – funding uncertainty • Systems shift towards education and training – equipping learners with different ‘higher-order skills’ • Importance of general / liberal education more pronounced • Impact of use of technologies and Internet

Globalization, Accreditation, Internationalization. . & GATS Globalization – global market – cross-border competition – GATS Accreditation – in over 80 countries – setting quality standards & compliance Internationalization – cross-border exchange of curriculum, faculty and students Source: ‘The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002; World Bank & IFC 2003; AUCC – Association of Universities & Colleges In Canada - 2002

Students Studying Abroad • Over 1. 6 million international tertiary students abroad in OECD countries (est $30 billion market) • Over 580, 000 in USA – approx 35% of world total (6. 4% inc from Yr 2000) – 6740 in top 20 US business schools • Other significant share of global market include – UK (14%) Other significant share of global market include – – Germany ( 12% ) – Australia ( 9% ) – France ( 8% ) • UK in 2001, students from China increased by 67% from previous year – 31% increase from India • New Zealand 300% growth between 1999 and 2002 Sources: Chronicle 2003; OECD; IFC Staff Research

Lifelong Learning Changing Student Profiles • Adults with tertiary qualifications – increased from 22% to over 40% today in OECD countries • Over 40% of undergraduates in US & 30% of Canada’s undergraduate students are over 25 yrs • Yr 2000 – over 20% of first year university students were over 27 yrs – in Australia, NZ, Denmark, Norway & Sweden • Lifelong learning attracting new learners – more diversified – older and part time students Sources: OECD 2000; ‘The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002;

Student Financing • Over 60 countries have student loans – mostly public schemes • Governments must see loan schemes important – can improve access and opportunity • Many barriers exist for private sector banks • Future government underwriting of risk is crucial – for mobilizing private banks

Faculty – Looming Issues • By 2010 student demographics increase – growing competition looming for Scholars – increasing global pressure on staffing • Canada – 33% of faculty over 55 yrs – 50% are 40 to 54 yrs • In US, 30% are over 55 years – and 27% are 40 to 54 yrs • Concern ‘brain drain’ will occur – higher salary incentives • Private sector – lures scholars with higher salaries Source: ‘The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002;

Distance Education – High Growth • Tertiary distance ed. – world’s fastest growing sub-sector • Canada – 500, 000 students – many on-line • Asia has 3. 5 m students (2000) – China Central Radio and TV University has 1. 5 million – enrolls over 100, 000 each year • 30% of all tertiary courses in Russia are distance – 26% in Turkey – 37% in Thailand – LAC has over 1 million tertiary distance education students – Europe approx 900, 000 • UK Open University – produces approx 9% of undergraduates in Britain with 5% of the national university operating budget Source: ‘The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002; World Bank & IFC;
On-Line Education – steady growth • African Virtual University – EO Yr 2001, 24000 students since 1997, from 17 countries – Yr 2003 restructured – shared site by 34 universities – RMIT Melbourne latest program provider • Tengtu China – 12, 000 schools connected early 2003 – networking 6 million students • Yr 2002, 19% of corporate training in US was on-line • Over 2000 United States HEI’s offer courses today • Globally – a $150 billion industry by 2025 Sources: Merril Lynch 2000; World Bank, WBI & IFC 2003
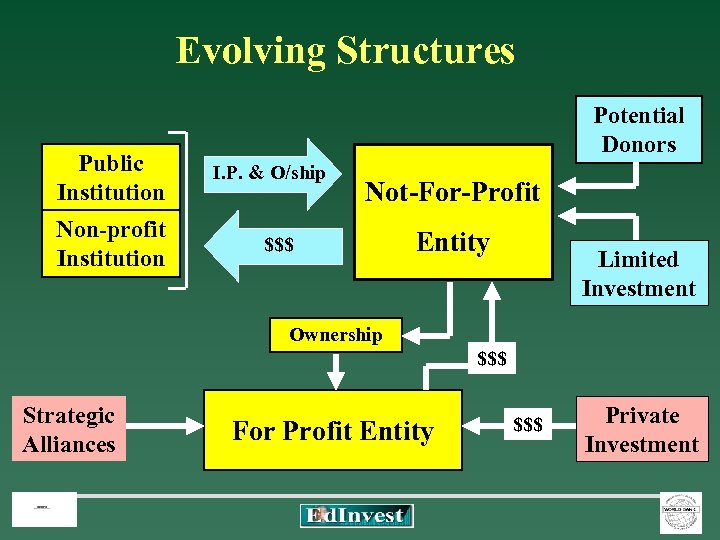
Evolving Structures Public Institution Non-profit Institution Potential Donors I. P. & O/ship Not-For-Profit Entity $$$ Limited Investment Ownership $$$ Strategic Alliances For Profit Entity $$$ Private Investment

The Parallel Training Universe • Global I. T. companies / I. T. training providers – operate outside certified higher ed credentials and accreditation. • In Yr 2000, global I. T. companies ‘certified’ 1. 6 million students worldwide with 2. 4 million certificates in Information Technologies. • Corporate & government training – one third of the US for-profit industry – but no threat competitively. • China – this sub-sector is worth US$1 billion annually Source: ‘The Changing Enterprise’ – ACE 2002; Rothstein, Economic Policy Institute 2003

Future Outlook • Financing of education will tighten – demographics outweigh fiscal realities – growth in non-public financing • Millennium goals – continued emphasis to 2015 • Knowledge societies and lifelong learning – important for economic development – new systems for education and trg • Globalization and internationalization – changing the future landscape of higher education, national and cross-border • ICT’s and the Internet – optimizing use of new technologies – models advancing quality-based mass education delivery
e1674d8e9fddc7b5f8552c28cee7d881.ppt