5985303648c82661f458535ee26f7920.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

GLOBAL COMPETITIVENESS OF INDIAN AGRICULTURE Technologies – Policies - Strategies Presentation made to Ms. Isabel Guerrero, Country Director World Bank, India By P. Chengal Reddy, Secretary General, CIFA, “Trade increases the wealth and glory of a country: But its real strength and stamina are to be looked for among the cultivators of the land” - Lord Chatham Hyderabad Address: Delhi Address: Flat # 209, Vijaya Towers, Shanthi Nagar, 8/32, South Patel Nagar, New Delhi -110 008 Hyderabad - 500 028, A. P. India Tel : 011 39484754, 25842111 Tel: 91 -40 -23319643, 66665191, 23378046 Fax : 011 – 25842123 E-mail : Chengal_ifia@yahoo. com P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, 1 E-mail : cifa_delhi@yahoo. com chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in Website: www. indianfarmers. org
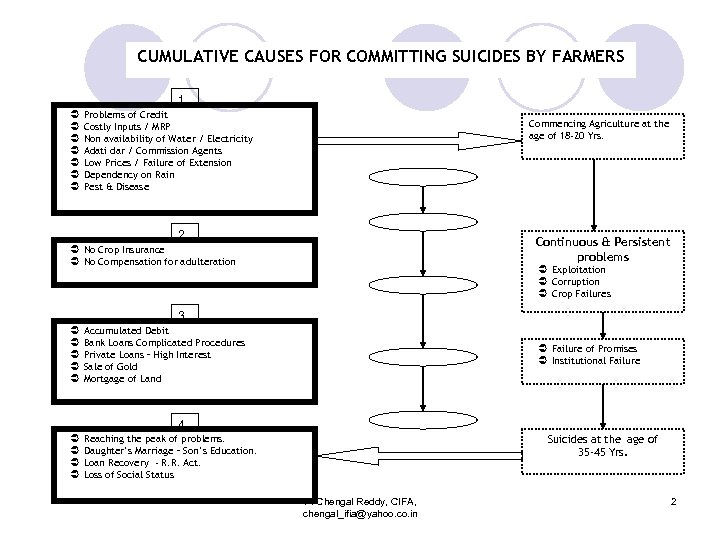
CUMULATIVE CAUSES FOR COMMITTING SUICIDES BY FARMERS 1 Ü Ü Ü Ü Problems of Credit Costly Inputs / MRP Non availability of Water / Electricity Adati dar / Commission Agents Low Prices / Failure of Extension Dependency on Rain Pest & Disease Commencing Agriculture at the age of 18 -20 Yrs. 2 Continuous & Persistent problems Ü No Crop Insurance Ü No Compensation for adulteration Ü Exploitation Ü Corruption Ü Crop Failures 3 Ü Ü Ü Accumulated Debit Bank Loans Complicated Procedures Private Loans – High Interest Sale of Gold Mortgage of Land Ü Ü Reaching the peak of problems. Daughter’s Marriage – Son’s Education. Loan Recovery - R. R. Act. Loss of Social Status Ü Failure of Promises Ü Institutional Failure 4 Suicides at the age of 35 -45 Yrs. P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 2
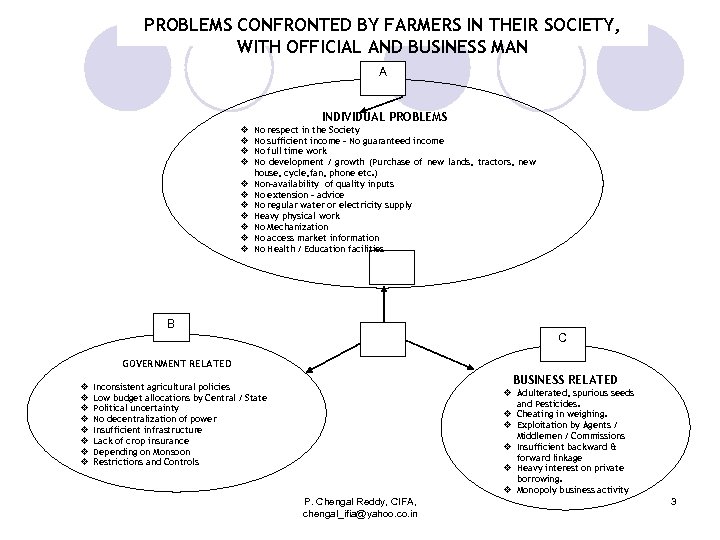
PROBLEMS CONFRONTED BY FARMERS IN THEIR SOCIETY, WITH OFFICIAL AND BUSINESS MAN A INDIVIDUAL PROBLEMS v v v No respect in the Society No sufficient income – No guaranteed income No full time work No development / growth (Purchase of new lands, tractors, new house, cycle, fan, phone etc. ) Non-availability of quality inputs No extension – advice No regular water or electricity supply Heavy physical work No Mechanization No access market information No Health / Education facilities B C GOVERNMENT RELATED v v v v BUSINESS RELATED Inconsistent agricultural policies Low budget allocations by Central / State Political uncertainty No decentralization of power Insufficient infrastructure Lack of crop insurance Depending on Monsoon Restrictions and Controls v Adulterated, spurious seeds and Pesticides. v Cheating in weighing. v Exploitation by Agents / Middlemen / Commissions v Insufficient backward & forward linkage v Heavy interest on private borrowing. v Monopoly business activity P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 3
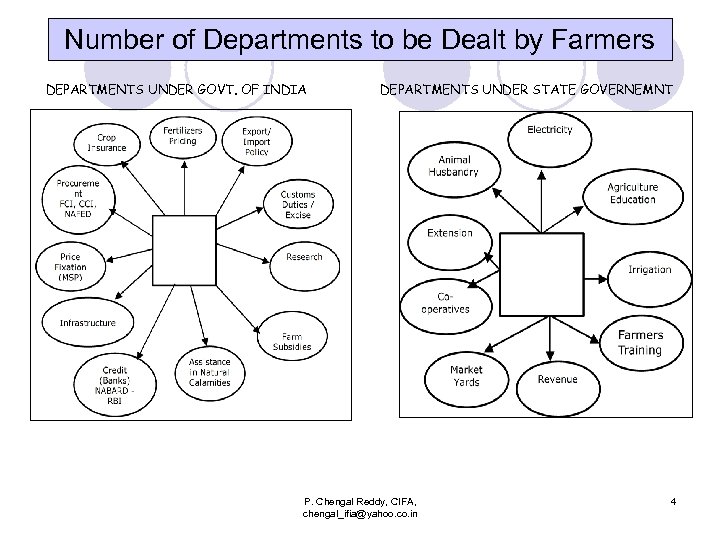
Number of Departments to be Dealt by Farmers DEPARTMENTS UNDER GOVT. OF INDIA DEPARTMENTS UNDER STATE GOVERNEMNT P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 4
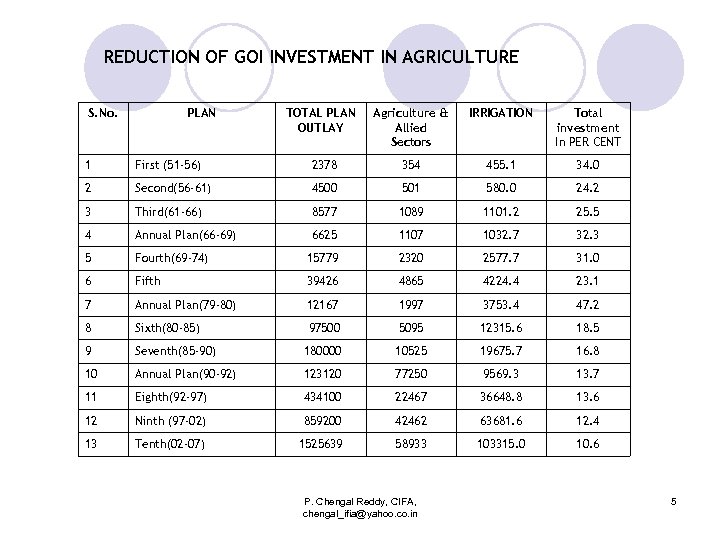
REDUCTION OF GOI INVESTMENT IN AGRICULTURE S. No. PLAN TOTAL PLAN OUTLAY Agriculture & Allied Sectors IRRIGATION Total investment In PER CENT 1 First (51 -56) 2378 354 455. 1 34. 0 2 Second(56 -61) 4500 501 580. 0 24. 2 3 Third(61 -66) 8577 1089 1101. 2 25. 5 4 Annual Plan(66 -69) 6625 1107 1032. 7 32. 3 5 Fourth(69 -74) 15779 2320 2577. 7 31. 0 6 Fifth 39426 4865 4224. 4 23. 1 7 Annual Plan(79 -80) 12167 1997 3753. 4 47. 2 8 Sixth(80 -85) 97500 5095 12315. 6 18. 5 9 Seventh(85 -90) 180000 10525 19675. 7 16. 8 10 Annual Plan(90 -92) 123120 77250 9569. 3 13. 7 11 Eighth(92 -97) 434100 22467 36648. 8 13. 6 12 Ninth (97 -02) 859200 42462 63681. 6 12. 4 13 Tenth(02 -07) 1525639 58933 103315. 0 10. 6 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 5
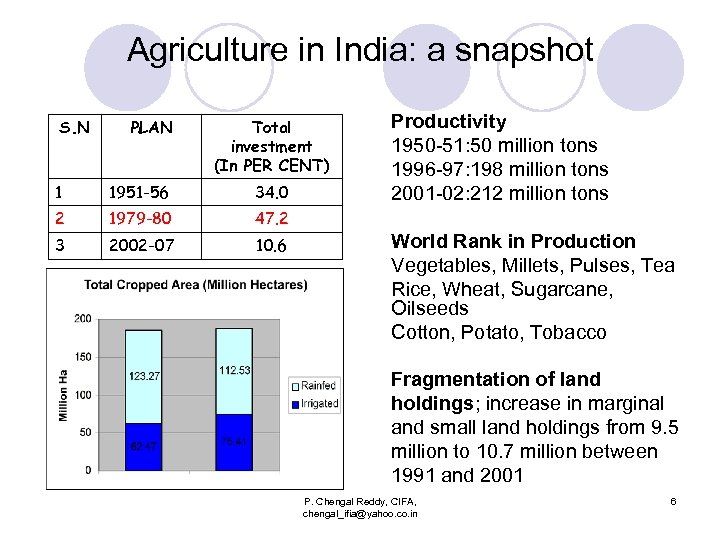
Agriculture in India: a snapshot S. N PLAN Total investment (In PER CENT) 1 1951 -56 34. 0 2 1979 -80 47. 2 3 2002 -07 10. 6 Productivity 1950 -51: 50 million tons 1996 -97: 198 million tons 2001 -02: 212 million tons World Rank in Production Vegetables, Millets, Pulses, Tea Rice, Wheat, Sugarcane, Oilseeds Cotton, Potato, Tobacco Fragmentation of land holdings; increase in marginal and small land holdings from 9. 5 million to 10. 7 million between 1991 and 2001 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 6

Agriculture in India: the future Challenges l l l l l Limited Extension Services Inadequate Infrastructure irrigation, cold storage. post-harvest facilities Market exploitation – middle man Market based productivity Reducing physical drudgery Reducing cost of production Nuxalisam - Migration Opportunities l l l l P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in Pro-agriculture policies Huge production base Huge consumer base Cheap raw material Agro-Climatic advantages Availablity of Technologies Investment by private sector Specialised native crops (Mango) 7

GLOBAL COMPETITIVENESS OF INDIAN AGRICULTURE Technologies – Policies - Strategies There is No Culture - In -Agri-culture Technologies – IT – BT – Space - Irradiation – Mechanization Marketing – Contract Farming – Forward Trading Policies – MSP – Crop Insurance – Ethanol Blending Farmers Involvement – Panchayat Raj Empowerment Private Sector Involvment P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 8
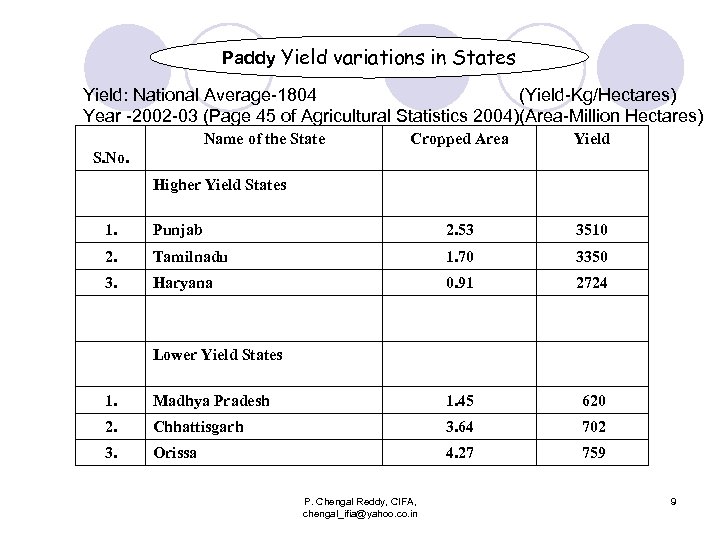
Paddy Yield variations in States Yield: National Average-1804 (Yield-Kg/Hectares) Year -2002 -03 (Page 45 of Agricultural Statistics 2004)(Area-Million Hectares) Name of the State Cropped Area Yield S. No. Higher Yield States 1. Punjab 2. 53 3510 2. Tamilnadu 1. 70 3350 3. Haryana 0. 91 2724 Lower Yield States 1. Madhya Pradesh 1. 45 620 2. Chhattisgarh 3. 64 702 3. Orissa 4. 27 759 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 9
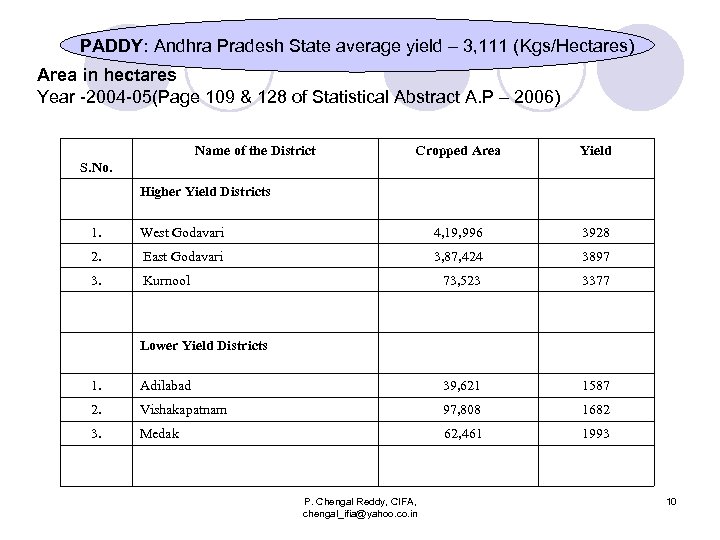
PADDY: Andhra Pradesh State average yield – 3, 111 (Kgs/Hectares) Area in hectares Year -2004 -05(Page 109 & 128 of Statistical Abstract A. P – 2006) Name of the District Cropped Area Yield S. No. Higher Yield Districts 1. West Godavari 4, 19, 996 3928 2. East Godavari 3, 87, 424 3897 3. Kurnool 73, 523 3377 Lower Yield Districts 1. Adilabad 39, 621 1587 2. Vishakapatnam 97, 808 1682 3. Medak 62, 461 1993 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 10
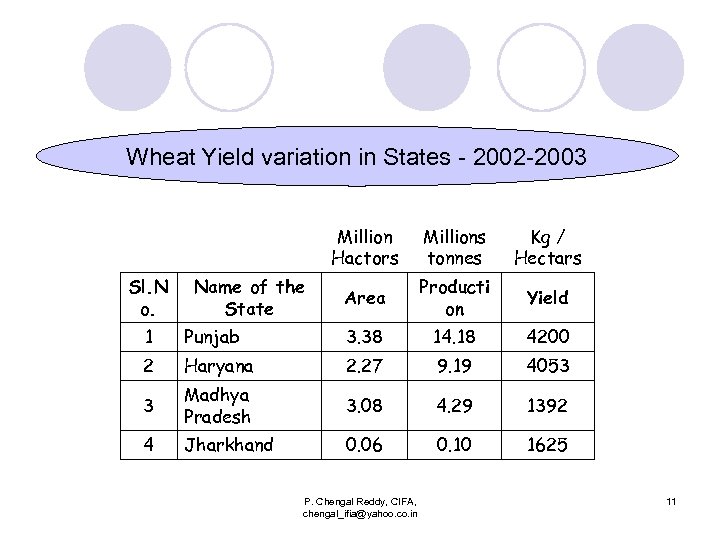
Wheat Yield variation in States - 2002 -2003 Million Hactors Sl. N o. Name of the State Millions tonnes Kg / Hectars Area Producti on Yield 1 Punjab 3. 38 14. 18 4200 2 Haryana 2. 27 9. 19 4053 3 Madhya Pradesh 3. 08 4. 29 1392 4 Jharkhand 0. 06 0. 10 1625 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 11
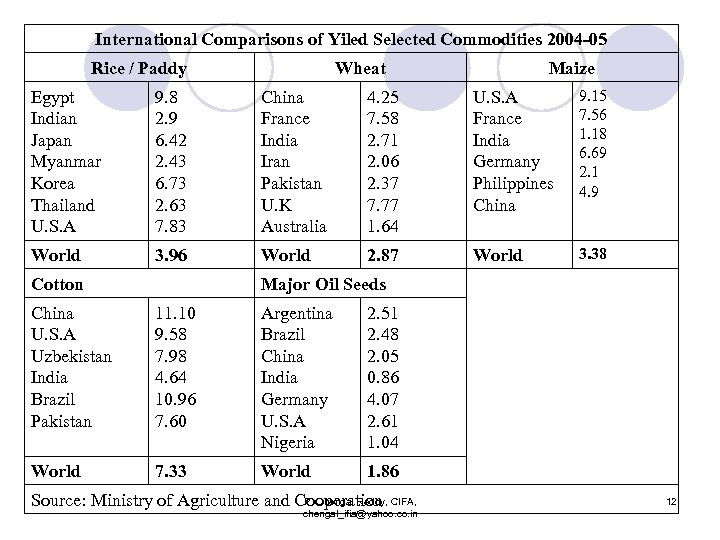
International Comparisons of Yiled Selected Commodities 2004 -05 Rice / Paddy Wheat Maize Egypt Indian Japan Myanmar Korea Thailand U. S. A 9. 8 2. 9 6. 42 2. 43 6. 73 2. 63 7. 83 China France India Iran Pakistan U. K Australia 4. 25 7. 58 2. 71 2. 06 2. 37 7. 77 1. 64 U. S. A France India Germany Philippines China 9. 15 7. 56 1. 18 6. 69 2. 1 4. 9 World 3. 96 World 2. 87 World 3. 38 Cotton Major Oil Seeds China U. S. A Uzbekistan India Brazil Pakistan 11. 10 9. 58 7. 98 4. 64 10. 96 7. 60 Argentina Brazil China India Germany U. S. A Nigeria 2. 51 2. 48 2. 05 0. 86 4. 07 2. 61 1. 04 World 7. 33 World 1. 86 P. Chengal Reddy, Source: Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperation CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 12
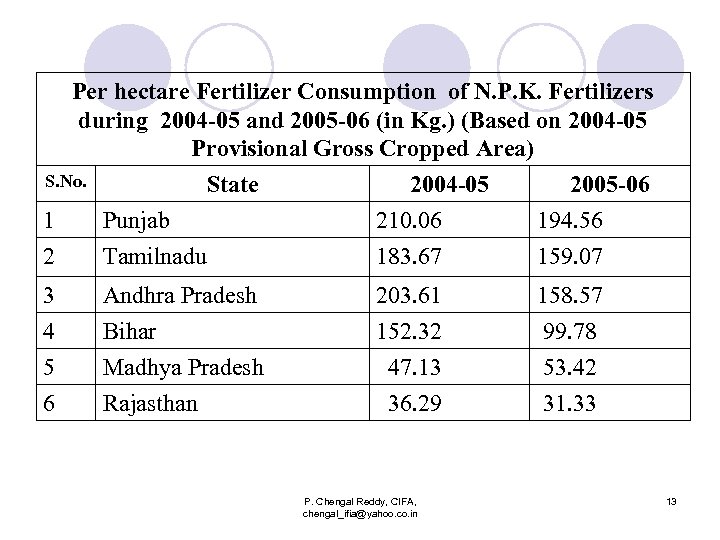
Per hectare Fertilizer Consumption of N. P. K. Fertilizers during 2004 -05 and 2005 -06 (in Kg. ) (Based on 2004 -05 Provisional Gross Cropped Area) S. No. State 2004 -05 2005 -06 1 2 Punjab Tamilnadu 210. 06 183. 67 194. 56 159. 07 3 4 5 6 Andhra Pradesh Bihar Madhya Pradesh Rajasthan 203. 61 152. 32 47. 13 36. 29 158. 57 99. 78 53. 42 31. 33 P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 13

ISSUES OF PESTS & DISEASES 1) Crop losses due to pests and diseases – 50, 000/- crores 2)Average use of pesticides. Japan 10. 70 Kg. Ha Europe 3. 00 Kg. Ha USA 4. 5 Kg. Ha India 0. 480 Kg. Ha 3) NO. of pesticides used USA 755 EU 600 Pakistan 495 India 175 4) Yield losses caused by Pest in different crops Cotton 30 -50% Rice 25 -60% Vegetables 15 -40% Pulses 20 -75% Sugarcane 15 -30% 5) 46% of farmers use pesticides in India. 6) Pesticides market in India 4300 corers. 7) Excise on pesticides 16%. P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 14

Consortium of Indian Farmers Associations (CIFA) An apex organization representing Indian farmers Goals ü Empowering farmers for effective participation in decision making. ü To reduce economic gap between farmers and other sectors. ü Develop global competitiveness of Indian Farmers. Membership on 23 States of India l It consists of State Level Farmers Federations, Cooperatives, Commodity Associations / Committees / Council, of cotton, wheat, paddy, sugarcane, Pulses, Commercial Crops and others. Essential Roles of CIFA v v Strengthening farmers’ skills through HRD training business etc. , To sharpen farmers negotiating and advocacy powers. Be able to participate in and influence policies in Parliament. Establishing backward and forward linkage with industry & research. P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 15

Thank you P. Chengal Reddy, CIFA, chengal_ifia@yahoo. co. in 16
5985303648c82661f458535ee26f7920.ppt