0830b902fb7c763001a58b073a600941.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Global Business Environment Session 4 : Assessment of Business Environment & CRA and PRA Faculty: Dr. Bibek Ray Chaudhuri Session Date: 22. 1. 2012

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Pre-Work Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Read the article on Macroeconomics and Well-timed Business Strategy by Peter Navarro given as readings for this session • Read Business Strategy and Political Risk

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Session Plan Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • • Macroeconomics and Business (…Contd. ) Economic Environment of Countries Country Risk Analysis Political Risk Analysis

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Key Considerations while assessing Business Environment Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Countries Classified by Income Groups (2007) Ø Ø Low Income (GNI per capita $935 or lower) Lower Middle Income (GNI per capita $936 to $3, 705) Higher Middle Income (GNI per capita $3, 706 to $11, 455) Higher Income ($11, 456 or more) • Countries Classified by Economic Systems Ø Command Economies Ø Market Economies Ø Mixed Economies

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Key Considerations while assessing Business Environment Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Economic Growth Ø Past trends in GDP Growth Ø Stability of the economy • Inflation Ø Ø Interest rate Exchange Rate Cost of living General Confidence in a Country’s Economic System • Surpluses & Deficits Ø BOP Ø External Debt Ø Internal Debt & Privatization

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Making sense of the Information: Country Risk Analysis Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Performance • Strategy Ø Goals: Autonomy, Productivity & Equity Ø Policies: Fiscal, Monetary, Industrial etc. • Context: are given for a country (constraints & resources) Ø Ø Ø Political Institutional Ideological Physical International • Evaluation Ø Diagnosing the causes Ø Evaluating the Future

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Firm Strategy Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Given the CRA the firm should understand how its interests are affected by alternative scenarios • Self Reading: Ø Case of Japan (for diagnosing the causes) Ø Case of China (for scenario generation)

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Firms performing CRA Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • • • Standard & Poor’s Moody’s Economist Intelligence Unit Political Risk Services Business Environmental Risk Intelligence

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Components of CRA Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Country History Ø in order to identify aspects that could interfere in the country´s future behavior reducing the ability or willingness to payback any external commitment Ø The structure of the government and its features like political and administrative organization Ø Social aspects and their key-indicators like HDI, population growth rate, infant mortality rate

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 COUNTRY RISK AS A CORPORATE RISK Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Dependency Level: Whether dependent on a narrow range of goods • State of Finances: How much dependent on external sources of funding • Whether trading with few countries • Whether too dependent on imports

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Indicators which are important for Assessment Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Domestic Ø GDP Ø Ø Ø Ø GDP Growth rate GDP per capita Gini Index Unemployment rate Internal Savings/GDP ratio Investment to GDP ratio Gross Domestic Savings/Gross Domestic Fixed Investment
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Domestic (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Fiscal Policy Ø Budget Deficit/GDP ratio Ø Internal Debt/GDP ratio • Monetary Policy Ø Inflation rate Ø Money Supply Growth Ø Real Rate of Interest rate

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 External Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • • • Growth rate of Exports Variance of Exports Growth rate of imports Necessary imports Export/Import ratio Trade Balance Current account/GDP ratio International Reserves (International Reserves-Gold)/Imports External Debt/GDP ratio Short term debt/Reserves(minus gold)

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 External (continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 Ø External Debt Services/Exports Ø Capital Inflows Ø Exchange currency rate • Risk Management Practices • Conjectural Aspects Ø What’s in store for the future? v Vision of leaders v Projected cash flow on the basis of BOP

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 CRA (continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • How the nation is seen by the World: mainly in terms of capital inflows • Ability and Willingness to pay back
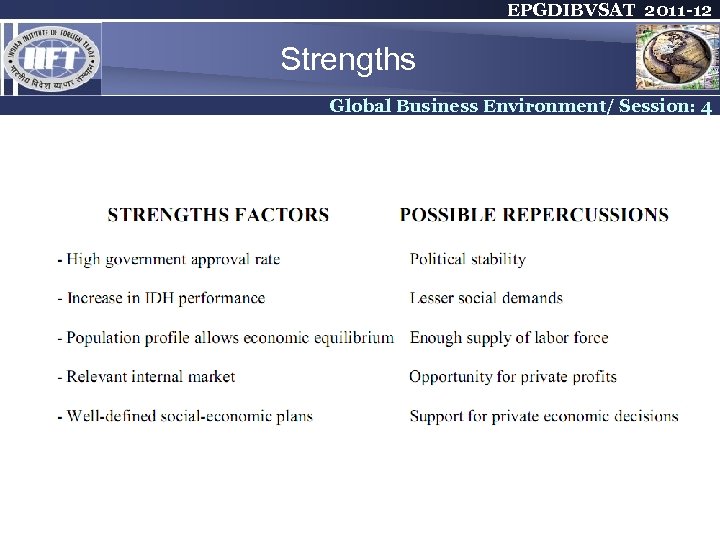
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Strengths Global Business Environment/ Session: 4

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Weaknesses Global Business Environment/ Session: 4

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 CRA (continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Risk levels and Exposure Limit • Pricing System • Follow up

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Post Work Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Group activity choose a country and perform a CRA the assignment should be submitted as PPTs by March 31 st , 2012

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 POLITICAL RISK ANALYSIS

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Introduction Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Definition of Political Risk § Possibility of an unexpected politicallymotivated event affecting the outcome of an investment § Instability vs. risk § • • • Classified based on - actor responsible - nature of effect - breadth (micro vs. macro)
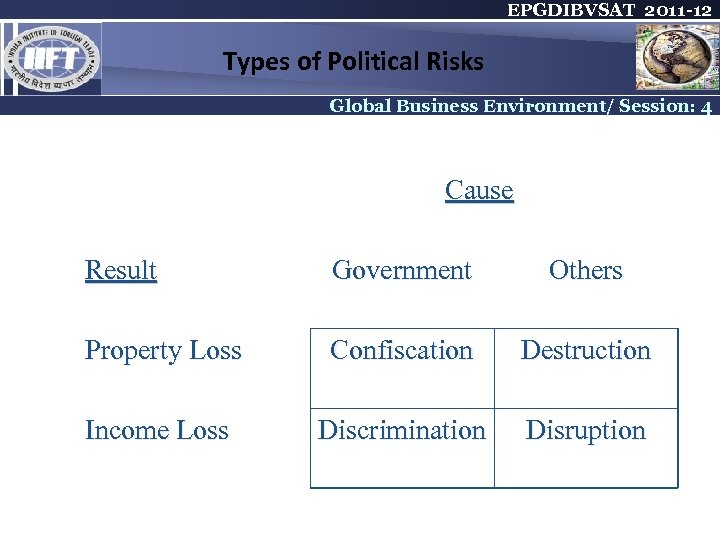
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Types of Political Risks Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 Cause Result Government Others Property Loss Confiscation Destruction Income Loss Discrimination Disruption
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 a) § § § Expropriation “Forced divestment of equity ownership of a foreign direct investor” (Minor 1994) Peaked in the mid-70 s; almost nil now Mostly Africa till 1980, then Latin America Declined since: - Key sectors already nationalized - Economic need = > privatization - Regulate rather than expropriate Many hosts have joined MIGA (Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency) Some controversy over future: - is free enterprise here to stay, or will there be a backlash when privatization, etc. fails to provide widespread benefits?
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 b) Terrorism § – – § § c) § § Terrorist acts infrequent, but spectacular - L. America #1 esp. kidnappings - U. S. – owned corps. Esp. targets, U. S. public institutions - China, India, Turley, Israel etc. -sept 11, Iraq Little research-seems to be primarily groups denied a voice in legitimate channels Symbolism particularly important (Mac. Donalds, etc. ) Selective Intervention Most risks are less dramatic changes in the rules of the game. Some areas of government policy affect foreign-owned companies more than most domestic ones

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 – § § Restrictions on Cross-Border Transfer of Resources Tariffs, NTBs inhibit sourcing, exporting FX controls limit repatriation Capital controls Labour regs – § § Taxation Concerns Restrictions on transfer pricing Unitary taxation policies Withholding taxes Availability of tax holidays and other incentives
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 – § § § Investment Restrictions Sectoral restrictions Requirements for JVs, local ownership Transparency of licensing procedures Requirements for disclosure of technology Requirements forced divestiture – § § § Operating Restrictions limits on expansion, ownership of land, etc. Discriminatory access to labour, inputs Restrictions on local market access Performance requirements (e. g. employment & export levels, etc. ) Unequal access to government procurement

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 – § § Non-Neutrality of the Legal Environment Judges or other arbiters insulated from political pressure International and regional conventions International conventions re compensation Guarantees of national treatment – § Regulations with Differential Effects on Foreigners Some may be much harder foreign companies to comply with

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Main Types of Political Risks (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 d) § – – – “Crossfire” Problems Activities may lead to international or home country sanctions or consumer boycotts against the country or firms that deal there - human rights abuses (e. g. imprisonment, torture or murder of political opponents; use of prison labor; persecution of minority groups; not abiding by election results) - conflicts with neighboring countries - lack of concern for the environment, endangered species, etc. - disregard for international agreements (e. g. re nuclear nonproliferation) - the misuse of social issues as means of protectionism What kind of cross-fire problems associated with Iraq wine-makers in the Bordeaux region faced?

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Techniques of PRA Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Observational Data Techniques : Based on historical data of destabilizing events and level of economic deprivation forecasts are generated • Expert-Based Techniques: Ø Unstructured/Unsystematic: based on discretion of the analyst with no explicit procedure Ø Unstructured/Systematic: parameters are specified but degree of usage and how inference is drawn is not explicit Ø Structured/Unsystematic: Rating of experts are considered but the basis of these ratings are not available (BERI Index) Ø Structured/Systematic: consistent panel of experts rate on a specific set of issues for different groups (WPRF)
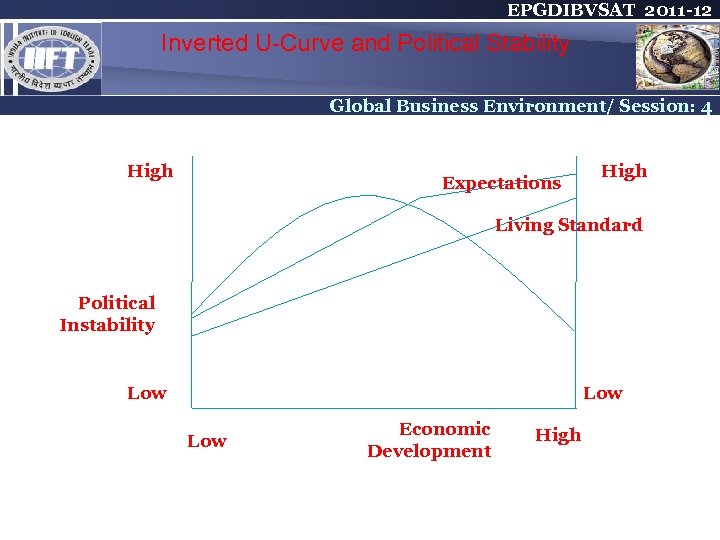
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Inverted U-Curve and Political Stability Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 High Expectations High Living Standard Political Instability Low Low Economic Development High

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Political Risk Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Empirical Relationship § Most studies examine correlates of expropriation § Minor (1993): no link with stability § • • Positive correlations (more risk) - extractive, service and key sectors - JVs with the host government - host countries with pervasive governments (“hands-on”) - medium-technology - need for scapegoats - “obsolescing bargains”

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Empirical Relationship (Continued) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 § Negative correlations (less risk) - integrated subsidiaries that depend on rest of network - low/high tech - lobbying § Makhija (1993): information indicating convergence of MNC actions and government economic objectives
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 The Economist Method Political Risk Service (PRS) -- 100 points Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • • • 33 points economic factors: falling GDP/per capita high inflation capital flight decline in productivity raw materials as percentage of exports 50 points politics: bad neighbours authoritarianism staleness illegitimacy generals in power war/armed insurrection

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 The Economist Method Political Risk Service (PRS) -- 100 points Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • • • 17 points society: urbanization Race Religious fundamentalism corruption ethnic tension

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Managing Political Risk (counter moves) Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 § Insurance from EDC, etc. § JVs with local or foreign partners § Local stakeholders § Structural dependency § Lobbying § Planned divestiture with s/t profits § Integrate with strategy § Security for expatriates § General rule: make the costs to the government of an undesirable move to the firm very costly. Provide “incentives” for appropriate government regulations and policies.

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 MNE Evaluation by Countries Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Concern of Governments Ø Independence: Whether the presence of MNE will affect sovereignty of the host country Ø Impact on Domestic firms Ø Hidden Value: Undervaluation of assets, non-transfer of technology etc. Ø Responsibility: Long-term or short run commitment
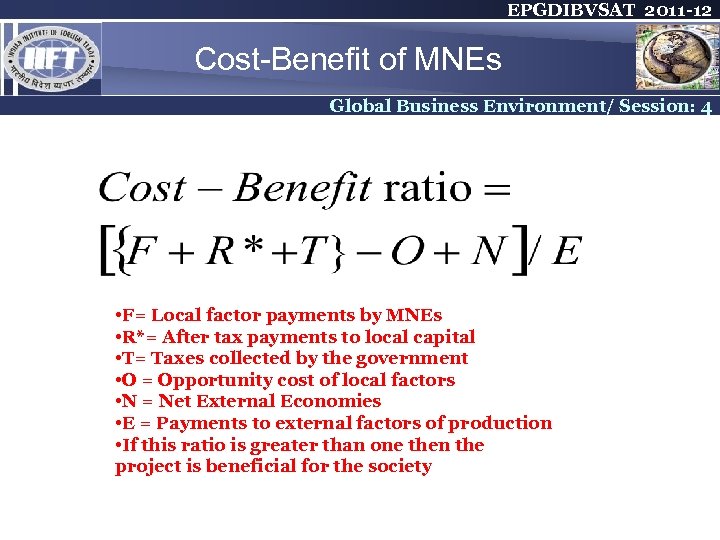
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Cost-Benefit of MNEs Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • F= Local factor payments by MNEs • R*= After tax payments to local capital • T= Taxes collected by the government • O = Opportunity cost of local factors • N = Net External Economies • E = Payments to external factors of production • If this ratio is greater than one then the project is beneficial for the society

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Other Methods Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Present Value of Costs and Benefits • Shadow price adjustments • Shifting perceptions over time
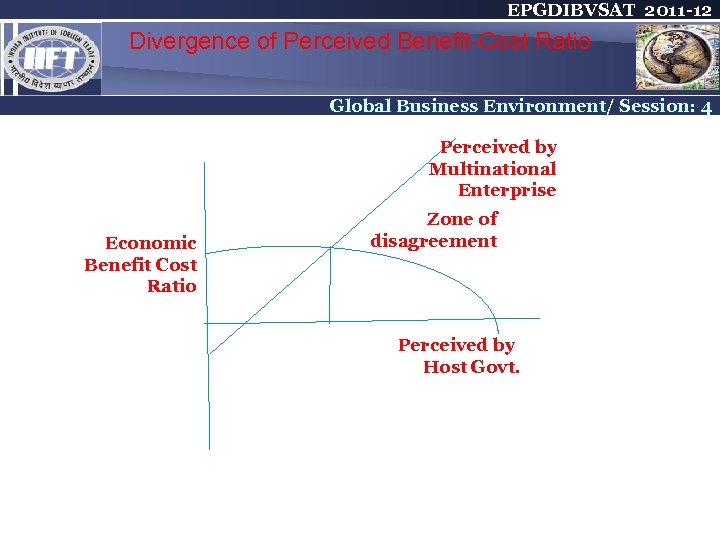
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Divergence of Perceived Benefit-Cost Ratio Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 Perceived by Multinational Enterprise Economic Benefit Cost Ratio Zone of disagreement Perceived by Host Govt.
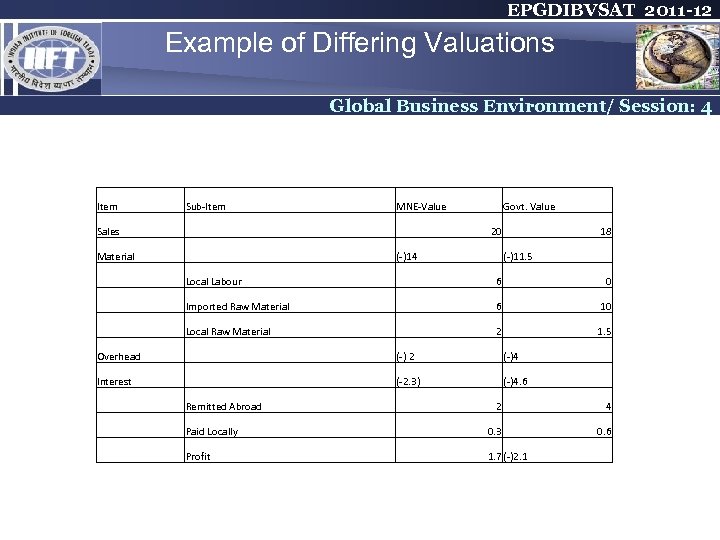
EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Example of Differing Valuations Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 Item Sub-Item MNE-Value Govt. Value Sales Material Local Labour 6 0 Imported Raw Material 6 10 Local Raw Material 2 1. 5 Overhead (-) 2 (-)4 Interest (-2. 3) (-)4. 6 Remitted Abroad 20 (-)14 18 (-)11. 5 2 4 Paid Locally 0. 3 0. 6 Profit 1. 7 (-)2. 1

EPGDIBVSAT 2011 -12 Post-Work-Session 5 Global Business Environment/ Session: 4 • Group Assignment • Perform a Political Risk Analysis of your chosen country considering any of the following sectors Ø Oil Ø FMCG Ø Automobiles Ø Steel • Assignment must be submitted by 31 st March, 2012 in PPT format
0830b902fb7c763001a58b073a600941.ppt