Glimpses on English history and literature. From the











11656-the_beginning.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Glimpses on English history and literature. From the beginning
Glimpses on English history and literature. From the beginning
 Early Britain (5 century BC) The beginning of the Iron Age coincided with the arrival of new people from the continent, mainly from France. They were the Celts. Archaeologists have discovered at least three Celtic groups, whom they call А, В and С people. The С people, the last and most advanced group, were the people known to the Romans as the Belgae (they did indeed come from area of Belgium). They were not 'pure' Celts, having some German blood.
Early Britain (5 century BC) The beginning of the Iron Age coincided with the arrival of new people from the continent, mainly from France. They were the Celts. Archaeologists have discovered at least three Celtic groups, whom they call А, В and С people. The С people, the last and most advanced group, were the people known to the Romans as the Belgae (they did indeed come from area of Belgium). They were not 'pure' Celts, having some German blood.
 Celtic language in geographical names. Dun/dum= down (Dumbarton, Dunscore) Avon= river (Stratford upon Avon) Kil= wood (Kilbrook) Loch= lake Others: to curse - проклинать, javelin - дротик, pibroch - военная песня, tory- разбойник, clan - племя, whisky – водка.
Celtic language in geographical names. Dun/dum= down (Dumbarton, Dunscore) Avon= river (Stratford upon Avon) Kil= wood (Kilbrook) Loch= lake Others: to curse - проклинать, javelin - дротик, pibroch - военная песня, tory- разбойник, clan - племя, whisky – водка.
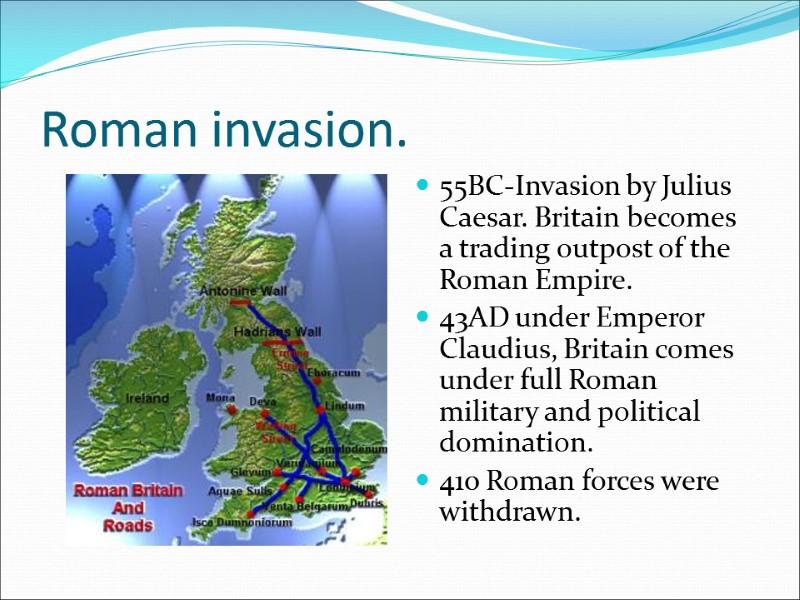
 Roman invasion. 55BC-Invasion by Julius Caesar. Britain becomes a trading outpost of the Roman Empire. 43AD under Emperor Claudius, Britain comes under full Roman military and political domination. 410 Roman forces were withdrawn.
Roman invasion. 55BC-Invasion by Julius Caesar. Britain becomes a trading outpost of the Roman Empire. 43AD under Emperor Claudius, Britain comes under full Roman military and political domination. 410 Roman forces were withdrawn.
 Roman borrowings. street — от лат. strata via ‘прямая, мощёная дорога’, wall — от лат. vallum, стена Chester, Gloucester, Lancaster — от лат. castrum ‘военный лагерь’, или Lincoln, Colches — от лат. colonia ‘колония’, Port-Smouth, Devonport — от лат. portus ‘гавань’; wine — от лат. vinum ‘вино’, butter — греко-латинское butyrum ‘масло’, cheese — лат. caseus ‘сыр’, pear — лат. pirum ‘груша’, peach — лат. persica ‘персик’, pall — лат. pallium ‘плащ’.
Roman borrowings. street — от лат. strata via ‘прямая, мощёная дорога’, wall — от лат. vallum, стена Chester, Gloucester, Lancaster — от лат. castrum ‘военный лагерь’, или Lincoln, Colches — от лат. colonia ‘колония’, Port-Smouth, Devonport — от лат. portus ‘гавань’; wine — от лат. vinum ‘вино’, butter — греко-латинское butyrum ‘масло’, cheese — лат. caseus ‘сыр’, pear — лат. pirum ‘груша’, peach — лат. persica ‘персик’, pall — лат. pallium ‘плащ’.
 449- Angles, Saxons, Jutes. Anglo-Saxon England settled into a pattern of 7 kingdoms. The three largest, Northumbria, Mercia and Wessex eventually came to dominate the country, each at different times. Borrowings- elementary notions (family, body, animals, nature, seasons) Runes. (telling fortune) “Beowulf”
449- Angles, Saxons, Jutes. Anglo-Saxon England settled into a pattern of 7 kingdoms. The three largest, Northumbria, Mercia and Wessex eventually came to dominate the country, each at different times. Borrowings- elementary notions (family, body, animals, nature, seasons) Runes. (telling fortune) “Beowulf”
 The second period of Roman borrowings (Christianization-597) episcopus - еписко = bishop presbyter - священник = priest monachus - монах = monk candela - свеча = candle monasterium - монастырь mynster (minster) (Westminster - Западный монастырь) + others: schola, magister, leo, palma, rosa, chorus, notarius.
The second period of Roman borrowings (Christianization-597) episcopus - еписко = bishop presbyter - священник = priest monachus - монах = monk candela - свеча = candle monasterium - монастырь mynster (minster) (Westminster - Западный монастырь) + others: schola, magister, leo, palma, rosa, chorus, notarius.
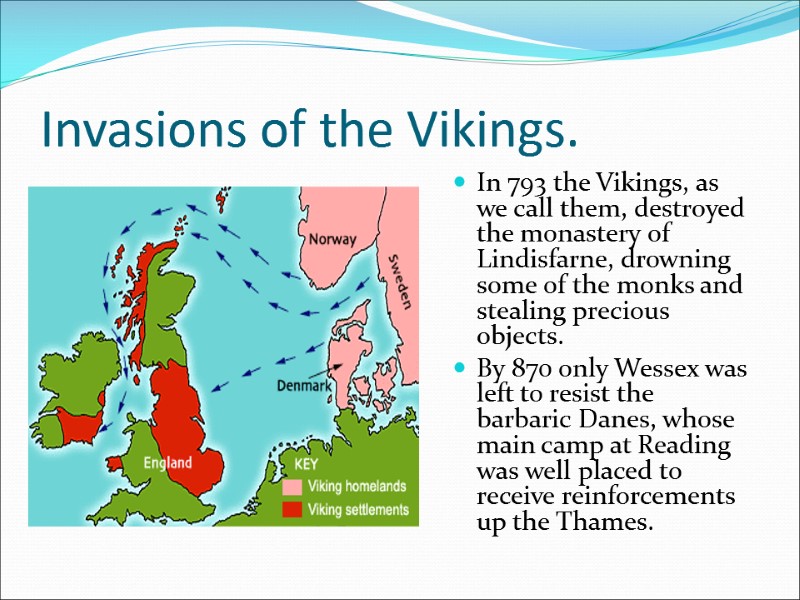
 Invasions of the Vikings. In 793 the Vikings, as we call them, destroyed the monastery of Lindisfarne, drowning some of the monks and stealing precious objects. By 870 only Wessex was left to resist the barbaric Danes, whose main camp at Reading was well placed to receive reinforcements up the Thames.
Invasions of the Vikings. In 793 the Vikings, as we call them, destroyed the monastery of Lindisfarne, drowning some of the monks and stealing precious objects. By 870 only Wessex was left to resist the barbaric Danes, whose main camp at Reading was well placed to receive reinforcements up the Thames.
 Scandinavian borrowings. they, them instead of hie, hem; take, cut, get instead of nim, snide, werth; are, fellow, ill, happen, law, happy, husband, kick, leg, low, scalp, skill, skin, skip, tight, ugly, wrong .
Scandinavian borrowings. they, them instead of hie, hem; take, cut, get instead of nim, snide, werth; are, fellow, ill, happen, law, happy, husband, kick, leg, low, scalp, skill, skin, skip, tight, ugly, wrong .
 Alfred the Great (849 – 26.10.899) He is the only English king who has earned that title. What made Alfred a great man was not just his military victories but his statesmanship. After years and years of bloody conflict, he saw the futility of trying to destroy the Danes by force. He signed peace treaty with them and was determined to reach friendly agreement . His treaty with Guthrum gave the Danes a large part of eastern England, where Alfred hoped they would settle down as peaceful farmers.
Alfred the Great (849 – 26.10.899) He is the only English king who has earned that title. What made Alfred a great man was not just his military victories but his statesmanship. After years and years of bloody conflict, he saw the futility of trying to destroy the Danes by force. He signed peace treaty with them and was determined to reach friendly agreement . His treaty with Guthrum gave the Danes a large part of eastern England, where Alfred hoped they would settle down as peaceful farmers.
 Anglo- Saxon literature. (7 -10 cent.) Oral works Written works “Beowulf” Characteristic features: It was composed in the 7th century, written in the 10th. It was worked up by Christian scribes (no pagan gods). It consists of 2 parts. It contains synonyms, metaphors, alliteration (a sound effect –there should be 3 stressed syllables in each line). Religious literature was written in Latin and Greek (the first church was built in Canterbury). Many English writers imitated Latin books (stories about saints). Numerous popular songs were written in English. First prose in English appeared.
Anglo- Saxon literature. (7 -10 cent.) Oral works Written works “Beowulf” Characteristic features: It was composed in the 7th century, written in the 10th. It was worked up by Christian scribes (no pagan gods). It consists of 2 parts. It contains synonyms, metaphors, alliteration (a sound effect –there should be 3 stressed syllables in each line). Religious literature was written in Latin and Greek (the first church was built in Canterbury). Many English writers imitated Latin books (stories about saints). Numerous popular songs were written in English. First prose in English appeared.
 Anglo- Saxon literature. (7 -10 cent.) Cynewulf -a poet (in Latin). Description of nature, sea, women`s characters “Elene”, “Juliana”. Caedmon –a poet (in Anglo-Saxon). 2 types of poetry (popular songs and religious poetry). “Paraphrase”-retelling of some parts of the Bible-story. Bede- a writer (in Latin)- scientific books. “The History of the English Church”. Alfred the Great- a writer (the first prose in English). Translations of Bede, a code of laws. “Anglo-Saxon Chronicles”-the history of the early Britons.
Anglo- Saxon literature. (7 -10 cent.) Cynewulf -a poet (in Latin). Description of nature, sea, women`s characters “Elene”, “Juliana”. Caedmon –a poet (in Anglo-Saxon). 2 types of poetry (popular songs and religious poetry). “Paraphrase”-retelling of some parts of the Bible-story. Bede- a writer (in Latin)- scientific books. “The History of the English Church”. Alfred the Great- a writer (the first prose in English). Translations of Bede, a code of laws. “Anglo-Saxon Chronicles”-the history of the early Britons.

