5d7810857f36ca228ff400c9fce41b7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

GLAUCOMA CONFERENCE STANDARD AUTOMATED PERIMETRY Pf. 안명덕/R 3 정윤혜
Basic Principles Traquair “ an island of vision surrounded by a sea of blindness” 시야의 경계 상측 60º, 비측 60º, 하측 70 -75º, 이측 100 -110º Visual field test 중심부와 주변부의 망막의 감도 및 시 야의 경계를 측정하는 검사 ‘시력의 섬’이 정상으로부터 전반적으 로 혹은 국소적으로 변화한 정도

Basic Principles Light intensity Units of luminance : apostilbs Light sensitivity Logarithmic unit : decibels(d. B) Background illumination Standard target : white disc 31. 5 apostilbs(photopic)-Humphrey, Goldmann Stimuli size Spatial summation 지름을 2배 하는 것은 강도를 5 d. B 증가시키는 효과 Exposure time Temporal summation(~0. 1 s) Humphrey Field Analyzer : 0. 2 sec ->Prevent movement of patient’s gaze

Physiologic factors that influence VF Age reduction of retinal threshold sensitivity : pph and sup. area neuronal loss SAP protocols compensate for the effect of age by using age-bracketed databases Pupil size Significant miosis : depress central and pph threshold sensitivities and exaggerate field defects Mydriasis : less influence recommend : >3 mm Clarity of ocular media cataract : central or pph field defects nuclear cataract : central > pph nonnuclear : central sensitivity for small targets, peripheral sensitivity for large targets corneal disturbance, PCO, vitreous opacities : affect VF Applanation tonometry before perimetry : no effect on VF

Physiologic factors that influence VF Refractive error and retinal blur refractive error : influence central VF correction myopia (-3 D~) hyperopia Astigmatism (0~-1 D: SE, -1 D~: cylinder lens) Aphakic and highly myopic : CL Physiologic factors patient’s understanding, alertness, concentration, fixation, cooperation learning effect fatigue effect
Kinetic vs Static Perimetry Threshold: theoretically, just bright enough to be seen 50% of the time Kinetic perimetry moving the test object from a nonseeing(subthreshold) to a seeing(suprathreshold) area, recording the point at which it is first seen 2 -4 degree per sec, 15 degree interval isopters (boundaries or contour lines) depends on the stimulus value of the test object
Kinetic vs Static perimetry : stationary test objects suprathreshold : on-off technique against presumed stimulus 예상 역치보다 높은 빛에 대한 반응유무 screening test, 암점의 깊이나 모양을 알아내기에는 부적당 threshold : relative intensity thresholds increasing vs decreasing method Static perimetry: more sensitive than kinetic perimetry in detecting glaucomatous field loss.
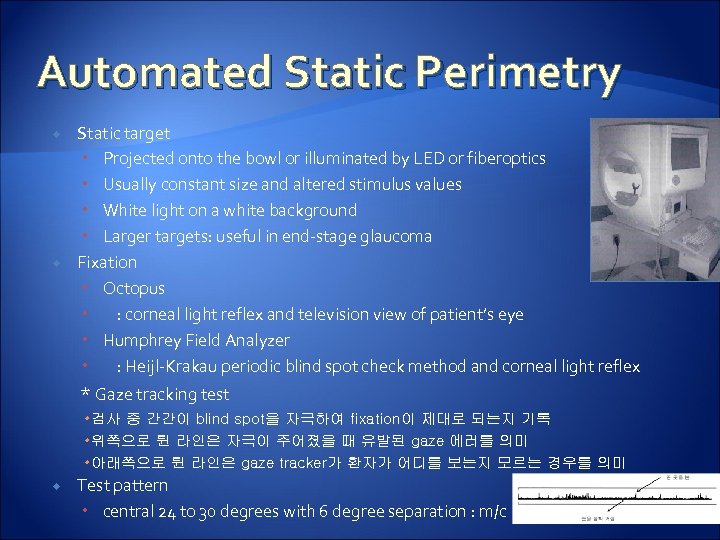
Automated Static Perimetry Static target Projected onto the bowl or illuminated by LED or fiberoptics Usually constant size and altered stimulus values White light on a white background Larger targets: useful in end-stage glaucoma Fixation Octopus : corneal light reflex and television view of patient’s eye Humphrey Field Analyzer : Heijl-Krakau periodic blind spot check method and corneal light reflex * Gaze tracking test 검사 중 간간이 blind spot을 자극하여 fixation이 제대로 되는지 기록 위쪽으로 튄 라인은 자극이 주어졌을 때 유발된 gaze 에러를 의미 아래쪽으로 튄 라인은 gaze tracker가 환자가 어디를 보는지 모르는 경우를 의미 Test pattern central 24 to 30 degrees with 6 degree separation : m/c
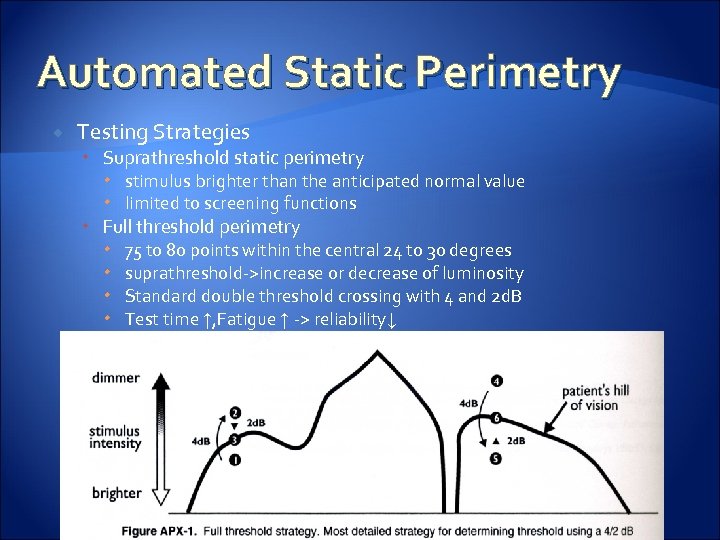
Automated Static Perimetry Testing Strategies Suprathreshold static perimetry stimulus brighter than the anticipated normal value limited to screening functions Full threshold perimetry 75 to 80 points within the central 24 to 30 degrees suprathreshold->increase or decrease of luminosity Standard double threshold crossing with 4 and 2 d. B Test time ↑, Fatigue ↑ -> reliability↓
Automated Static Perimetry Other threshold testing algorithms FASTPAC single crossing in 3 d. B increments, test time ↓ -> reliability and accuracy↓ Swedish Interactive Threshold Algorithm(SITA) Stops the test at the location being examined when threshold reaches a preselected level, more individual adjustment to patient response time, recalculation of false positive and negative rates => More time efficient SITA Standard (50% time reduction) and SITA Fast (70% time reduction) Accuracy and specificity : Full threshold = SITA Standard > SITA Fast SF : old, children, mental or physical limitation Tendency oriented perimetry(TOP) New Octopus perimeters- fast strategy algorithm mean testing time was more than 2. 5 minutes compared to SITA Fast(4 mintues) cannot spatially localize defect and accurately estimate sensitivity of visual field defect

Choice of Test Program (1) 30 -2 : standard program (2) 24 -2 : eliminates the peripheral test location of 30 -2 except for the most nasal portion : clinically useful (3) 10 -2 : useful in patients with very advanced field loss

Interpreting the results and analyzing progression Determining test reliability Short-term fluctuation Full thresholding programs Difference between the responses at the same location during the same session Glaucomatous VF > normal Increased around physiologic and glaucomatous scotomas Increased among older patients Long-term fluctuation Difference in threshold values in the same location between separate sessions Stable glaucoma=normal Increased among older patients 녹내장 환자의 장기기복이 정상인보다 크므로 시야장애 변화 확인 위해서 는 적어도 3회 이상의 검사가 필요, 2회 시야 검사의 평균 감도가 5 d. B 이 상 차이가 있을 경우 반복 측정 필요

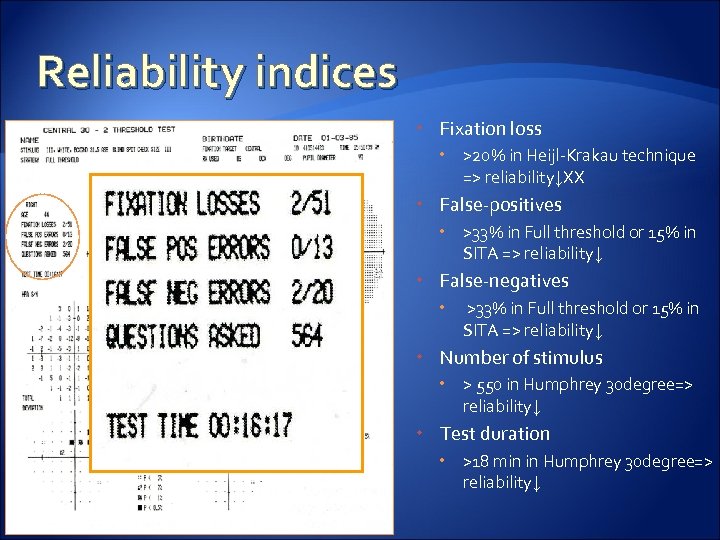
Reliability indices Fixation loss >20% in Heijl-Krakau technique => reliability↓XX False-positives >33% in Full threshold or 15% in SITA => reliability↓ False-negatives >33% in Full threshold or 15% in SITA => reliability↓ Number of stimulus > 550 in Humphrey 30 degree=> reliability↓ Test duration >18 min in Humphrey 30 degree=> reliability↓
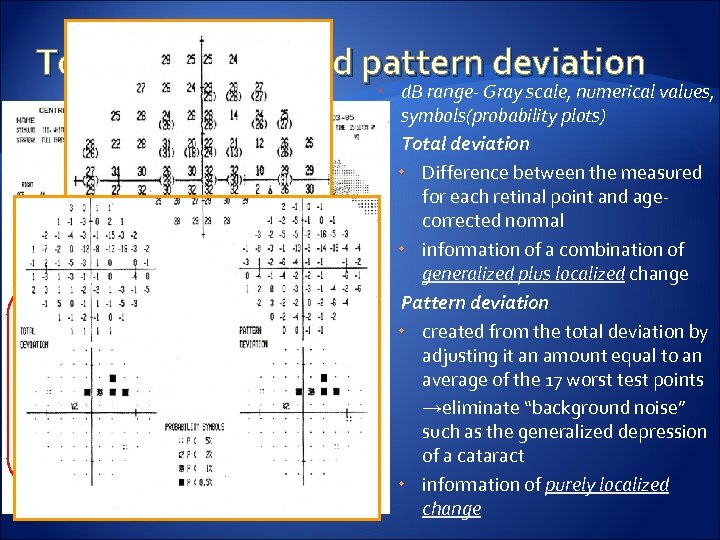
Total deviation and pattern deviation Probability symbols d. B range- Gray scale, numerical values, symbols(probability plots) Total deviation Difference between the measured for each retinal point and agecorrected normal information of a combination of generalized plus localized change Pattern deviation created from the total deviation by adjusting it an amount equal to an average of the 17 worst test points →eliminate “background noise” such as the generalized depression of a cataract information of purely localized change
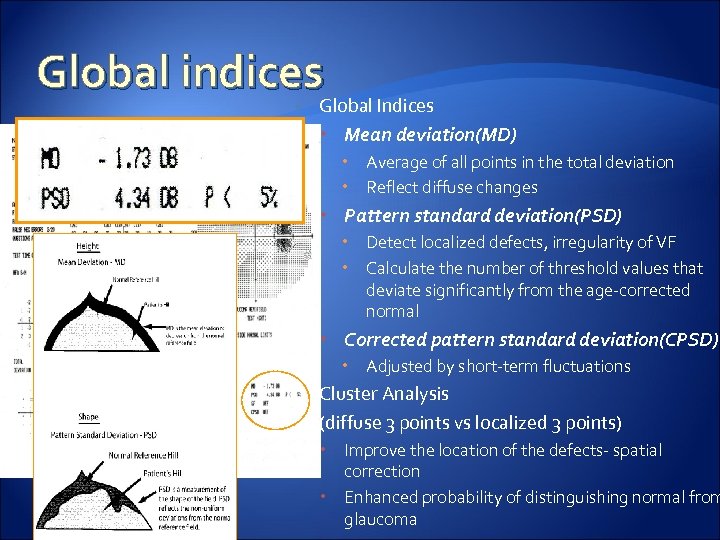
Global indices Global Indices Mean deviation(MD) Average of all points in the total deviation Reflect diffuse changes Pattern standard deviation(PSD) Detect localized defects, irregularity of VF Calculate the number of threshold values that deviate significantly from the age-corrected normal Corrected pattern standard deviation(CPSD) Adjusted by short-term fluctuations Cluster Analysis (diffuse 3 points vs localized 3 points) Improve the location of the defects- spatial correction Enhanced probability of distinguishing normal from glaucoma
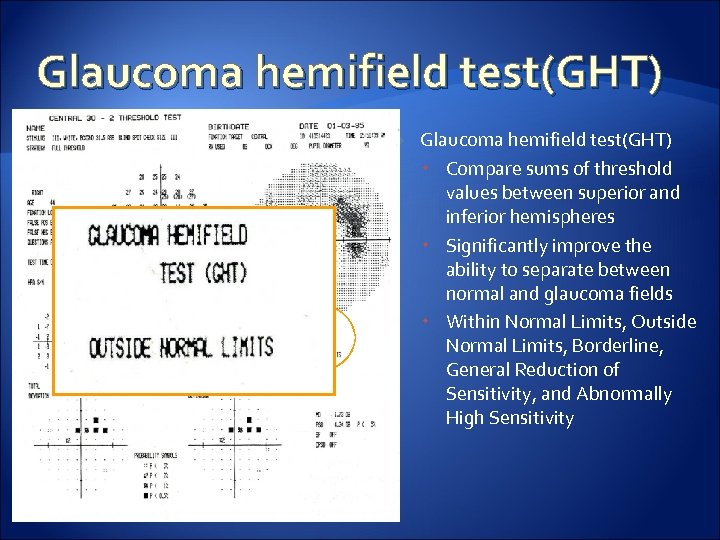
Glaucoma hemifield test(GHT) Compare sums of threshold values between superior and inferior hemispheres Significantly improve the ability to separate between normal and glaucoma fields Within Normal Limits, Outside Normal Limits, Borderline, General Reduction of Sensitivity, and Abnormally High Sensitivity

Glaucomatous visual field defect Minimal criteris for glaucomatous damage(Anderson’s criteria) : one of the following defects on Humphrey visual field test Cluster of three or more none-edge points(Pattern Deviation) : all at p<5% and one of which at p<1% in expected location on HVF 24 Glaucoma hemifield test : outside normal limits on at least two consecutive occasions CPSD : <5% ★ should be confirmed on a second test
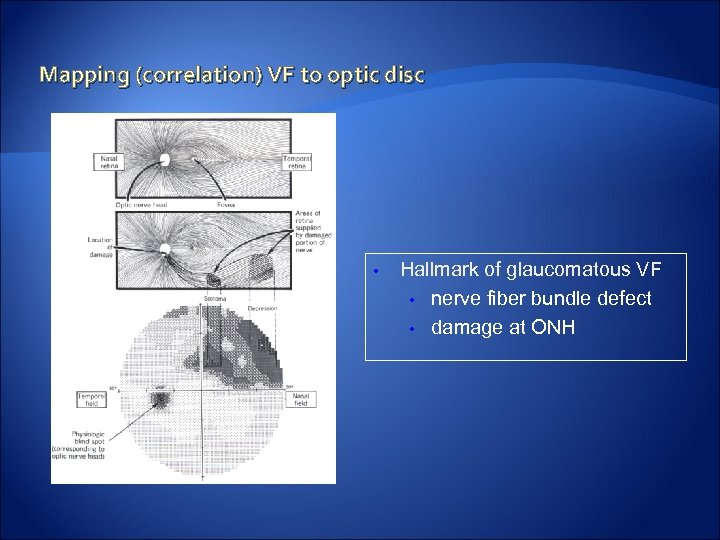
Mapping (correlation) VF to optic disc • Hallmark of glaucomatous VF • nerve fiber bundle defect • damage at ONH
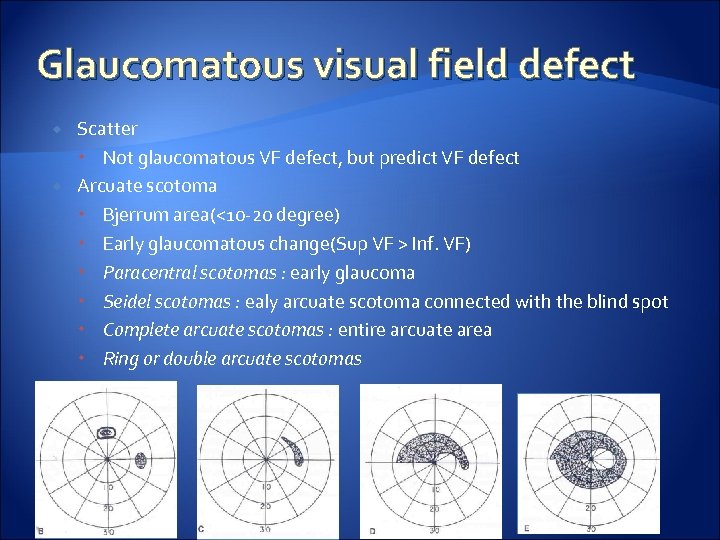
Glaucomatous visual field defect Scatter Not glaucomatous VF defect, but predict VF defect Arcuate scotoma Bjerrum area(<10 -20 degree) Early glaucomatous change(Sup VF > Inf. VF) Paracentral scotomas : early glaucoma Seidel scotomas : ealy arcuate scotoma connected with the blind spot Complete arcuate scotomas : entire arcuate area Ring or double arcuate scotomas
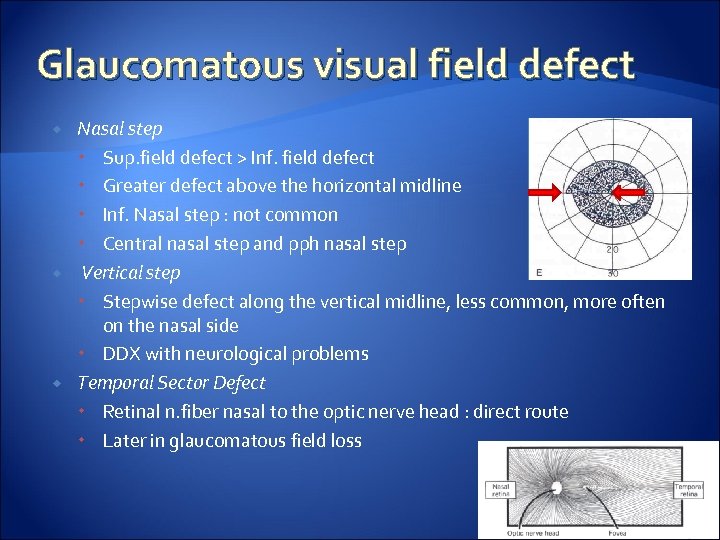
Glaucomatous visual field defect Nasal step Sup. field defect > Inf. field defect Greater defect above the horizontal midline Inf. Nasal step : not common Central nasal step and pph nasal step Vertical step Stepwise defect along the vertical midline, less common, more often on the nasal side DDX with neurological problems Temporal Sector Defect Retinal n. fiber nasal to the optic nerve head : direct route Later in glaucomatous field loss
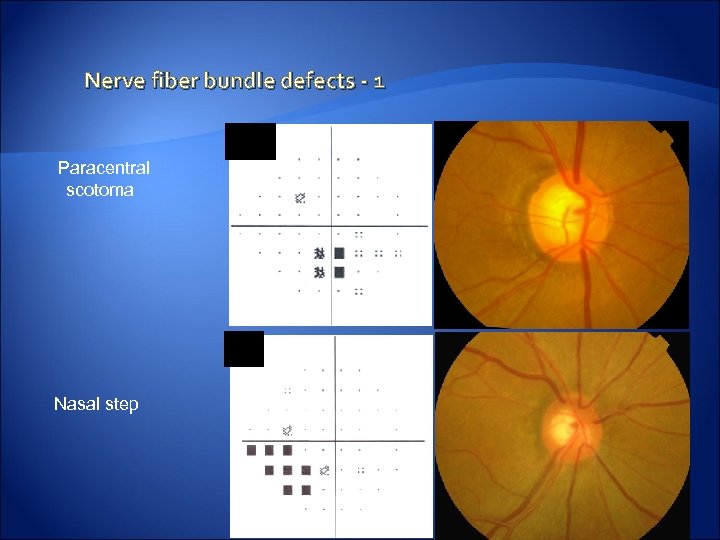
Nerve fiber bundle defects - 1 Paracentral scotoma Nasal step
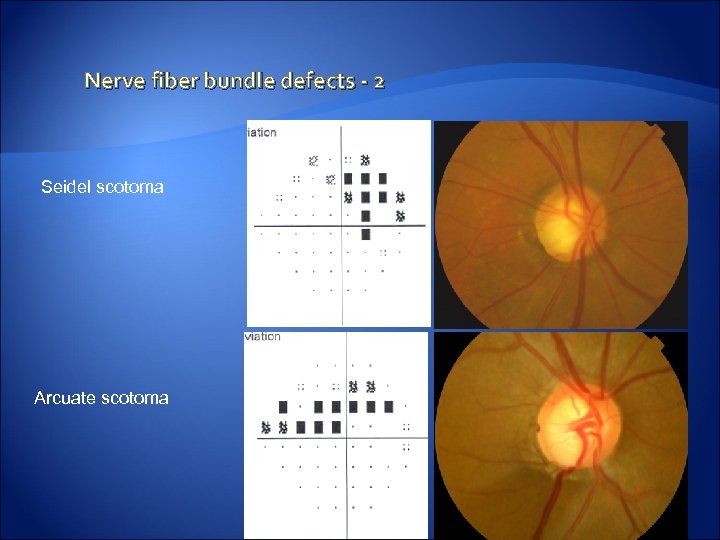
Nerve fiber bundle defects - 2 Seidel scotoma Arcuate scotoma
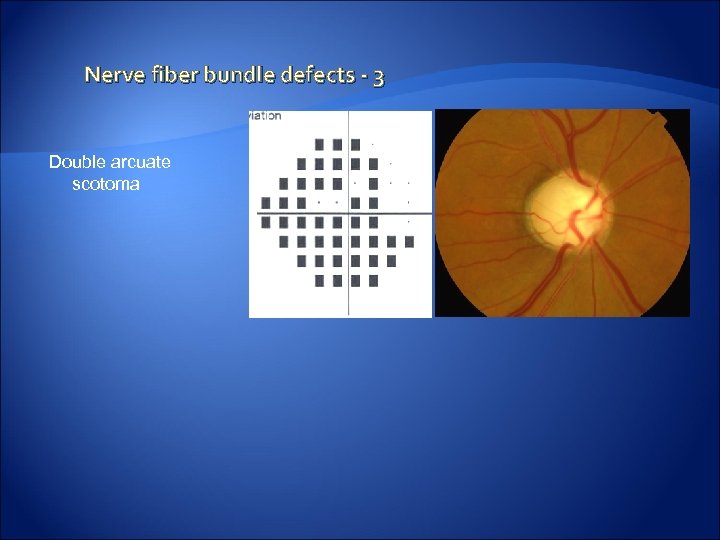
Nerve fiber bundle defects - 3 Double arcuate scotoma

감사합니다.

Other types of perimetry Short Wavelength Automated Perimetry (Blue-yellow perimetry) 밝은 빛의 yellow 배경 조명에 Goldmann size V의 blue 자극을 사용 Red와 green cone반응을 저하시켜 blue cone system에 의해 자극이 감지되도록 함. “White-on-white”보다 조기에 녹내장성 시야 손상을 감지하는 것으 로 밝혀짐. Frequency doubling technology(FDT) Large diameter ganglion cells(M ganglion cell, magnocellular visual pathway) Sensitive to motion and contrast, More vulnerable to glaucomatous damage Higher detection rate for early glaucoma than SAP->Useful screening device Contrast and motion sensitivity High –Pass Resolution Perimetry Random Dot Motion Automated Perimetry

Other types of perimetry Manual perimetry Tangent screens Arc and Bowl perimeters Specific techniques for manual perimetry Screening Techniques In-Depth Techniques
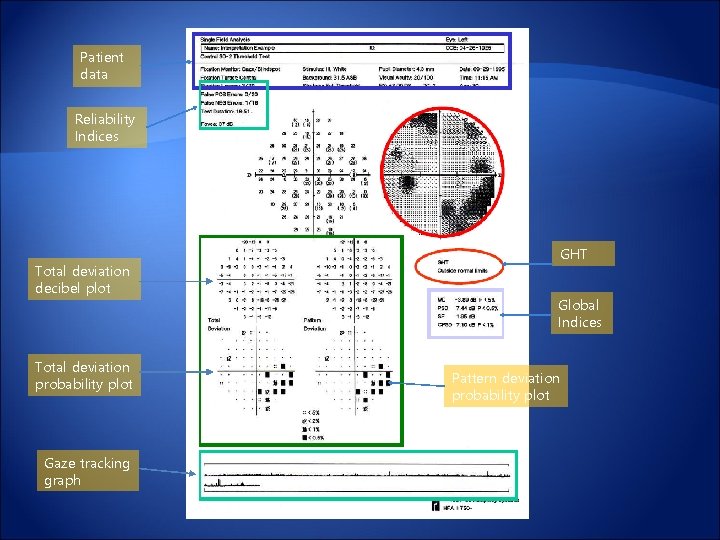
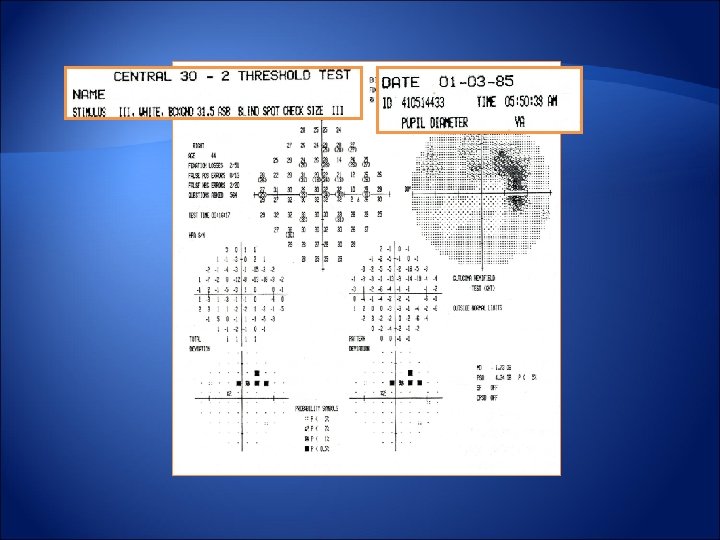
Patient data Reliability Indices Total deviation decibel plot Total deviation probability plot Gaze tracking graph GHT Global Indices Pattern deviation probability plot
5d7810857f36ca228ff400c9fce41b7b.ppt