0aef9e92fed6d10783aa582a4021a956.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

GIT Distributed Version Control System (we like it and you should too)

Turinys • • Asmeninė patirtis Kilmė Distributed / centralized Vidinė struktūra Metadata Terminologija Darbas lokaliai: nauda, komandos: init, checkout, branch, merge, reset, stash, gui, gitk

Turinys • • • Darbas remote: clone, remote, fetch, push Serverio pusė: gitosis Online servisai CVS / SVN integracija Git on Windows Summa summarum

Truputis asmeniškumų • • Vartojau CVS. Pabėgau į SVN valdė! Kol neprireikė sumergint. Bet buvo galima gyventi. Ilgai spyriojaus prieš GIT. Perėjau. Nesigailiu.

Kilmė • Sukurta valdyti Linux branduoliui, po to, kai Bit. Keeper tapo mokamas. • Linus manė, jog centralizuotos sistemos “čiulpia”. Citata: “if you’re using SVN you’re stupid”. Ar kažkas panašaus • CVS – puikus pavyzdys ko nedaryti. • Daryti sistemą paskirstytą, greitą ir atsparią duomenų išgadinimui.

Ką reiškia paskirstyta (distributed)? • Pilna repozitorija laikoma visuose PC. • Nėra centrinio serverio, visi lygūs. • Jeigu kažkas dingo “centriniame” serveryje – ne bėda, visi, kas dirba su projektu, turi pilną repozitorijos kopiją.
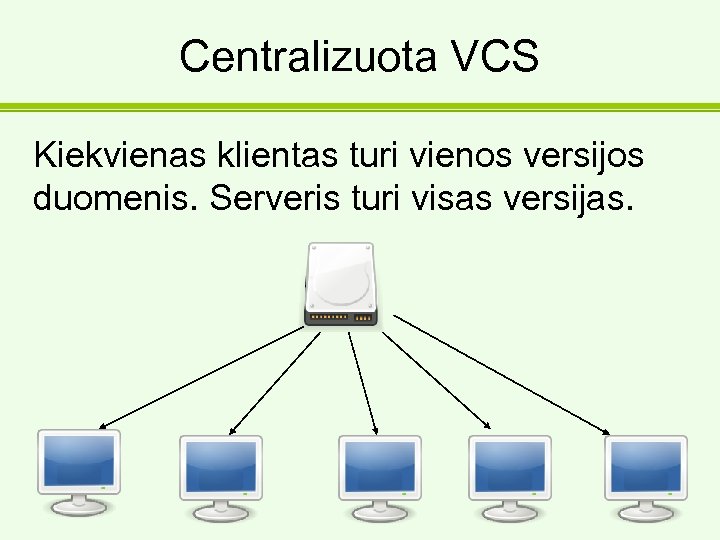
Centralizuota VCS Kiekvienas klientas turi vienos versijos duomenis. Serveris turi visas versijas.
Centralizuota VCS – kas blogai? O kas, jeigu. .
Centralizuota VCS – kas blogai? O kas, jeigu. .
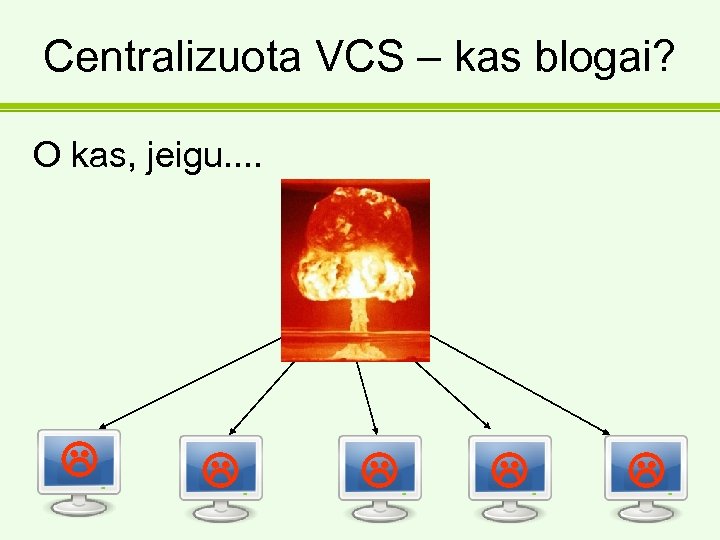
Centralizuota VCS – kas blogai? O kas, jeigu. .

Centralizuota VCS – kas blogai? Repozitorijos info, kaip branchai, tagai ir senesnės revizijos – prarasta.
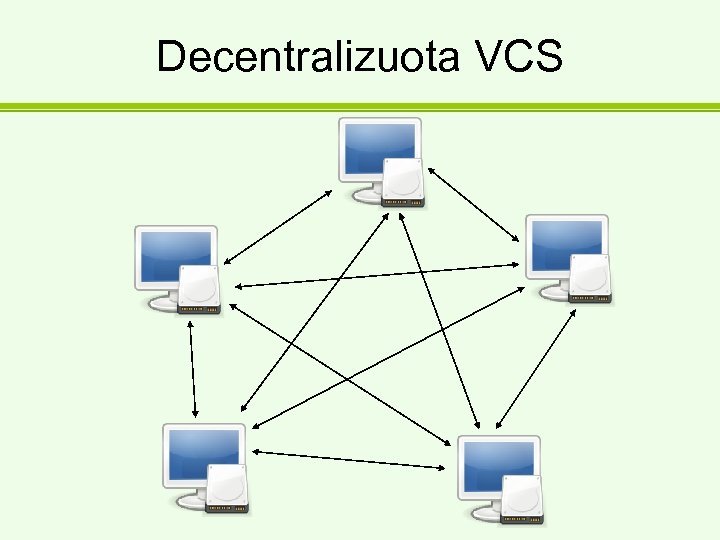
Decentralizuota VCS
Decentralizuota VCS
Decentralizuota VCS
Decentralizuota VCS
Decentralizuota VCS

Decentralizuota VCS

Be visa ko. . . • GIT yra greitas! Commit’as trunka kokius 0. 01 sekundės. • Duomenų nusiuntimas į kitą serverį trunka 0. 2 sekundės + kokia jūsų interneto sparta. • Fun fact: GIT visa repozitorija užima mažiau vietos, negu vienas SVN checkoutas • Let’s try it out.

Vidinė struktūra • Git has two data structures, a mutable index that caches information about the working directory and the next revision to be committed, and an immutable, append-only object database containing four types of objects: – A blob object is the content of a file. Blob objects have no names, timestamps, or other metadata. – A tree object is the equivalent of a directory: it contains a list of filenames, each with some type bits and the name of a blob or tree object that is that file, symbolic link, or directory's contents. This object describes a snapshot of the source tree. – A commit object links tree objects together into a history. It contains the name of a tree object (of the top-level source directory), a timestamp, a log message, and the names of zero or more parent commit objects. – A tag object is a container that contains reference to another object and can hold additional meta-data related to another object. Most commonly it is used to store a digital signature of a commit object corresponding to a particular release of the data being tracked by Git. • Jeigu kam įdomu detaliau: http: //excess. org/article/2008/07/ogre-gittutorial/ • Realiai dirbant – nereikia žinoti.

GIT metadata • find -name. svn -exec rm -rfv {} ; • Matyta? • Git, skirtingai nuo CVS ar SVN, savo metadata laiko vienoje direktorijoje: PROJECT_ROOT/. git • Yra keli papildomi failai: . gitignore, . gitmodules

Truputį teorijos/terminologijos • • Commit Branch Tracking branch Tag
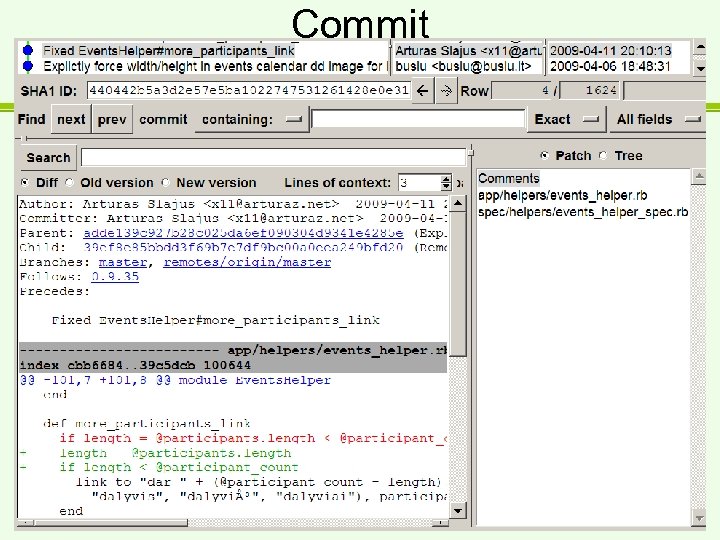
Commit

Branch/Tracking branch/Tag Pagrindinė šaka: master

Dirbti su GIT nereikia interneto! • Lokalios repozitorijos sukūrimas: git init • Su lokalia repo galima daryti viską, ką ir centralizuotoje su nutolusia: commit, checkout, branch, merge ir t. t. • Kam to reikia?

Situacija I • Deployinama per FTP. Dirbama ant kažkokios feature, išlindo kritinis bugas versijoje, kuri padeployinta. • Be VCS: – Kopijuojam stable kodą pas save, modifikuojam, uploadinam. – Kaip sumerginti? Tikrinti failų skirtumus ranktėmis?

Situacija I • Su VCS: – git checkout stable – Darom pakeitimus – git commit – Uploadinam – git checkout feature – Baigiame feature. – git checkout stable – git merge feature

Situacija II • Dirbama su kolega, repozitorija prieinama per shared diską, daromi keli featurai vienu metu. Padarei feature A, gali pradėti daryti feature B, tačiau iki deploymento reikia, kad kolega padarytu feature A (tarkim sudizainintu). • Be VCS: – Jei pradėsi B – kaip sumerginti? – Jei nepradėsi – ką veiksi?

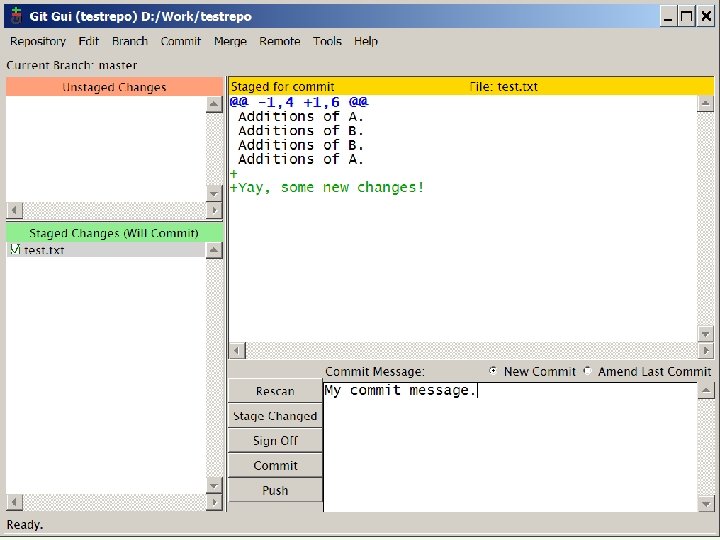
Git dažniausiai lokaliai naudojamos komandos • • git init – inicializuoją naują repozitoriją git gui gitk --all git checkout [-b] – persijungimas [ir sukūrimas] į šaką git branch – įvairios šakų operacijos git merge git reset --hard git stash
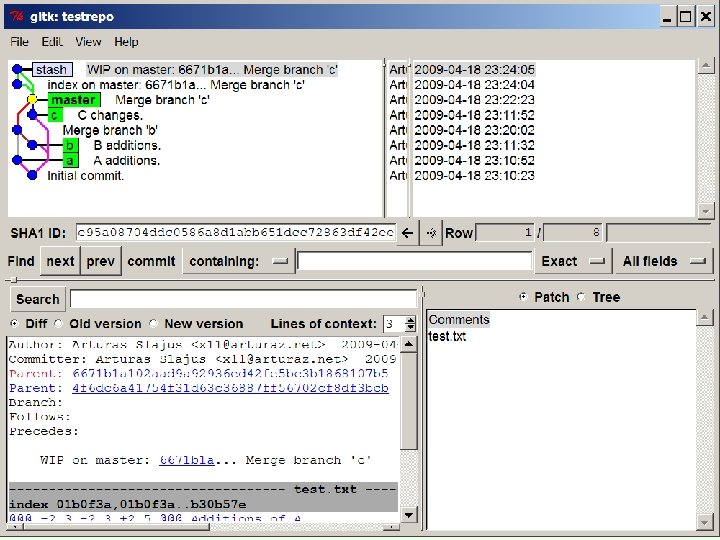
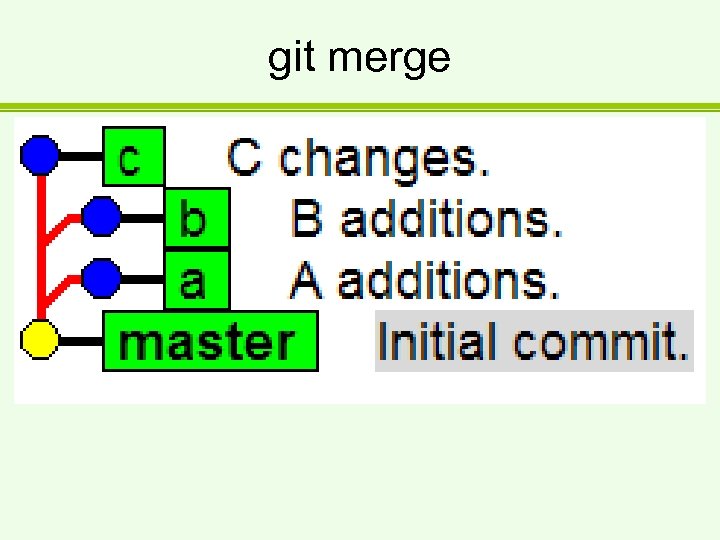
git merge

git merge D: Worktestrepo>git merge a b c Trying simple merge with d 40 f 0 de 23 c 714 dd 2007 ccf 0 a 11753 ffe 2516 c 20 b Trying simple merge with eca 4 a 1 aac 1 ae 8 b 71 fd 65743 e 72 aac 9 b 2 f 225093 f Simple merge did not work, trying automatic merge. Auto-merging test. txt ERROR: Merge conflict in test. txt fatal: merge program failed Automated merge did not work. Should not be doing an Octopus. Merge with strategy octopus failed.

Duomenų failo turinys Additions of A. Initial data. <<<<<<<. merge_file_a 00956 Additions of A. =======Additions of B. >>>>>>>. merge_file_a 02220 What a wonderfull mess!
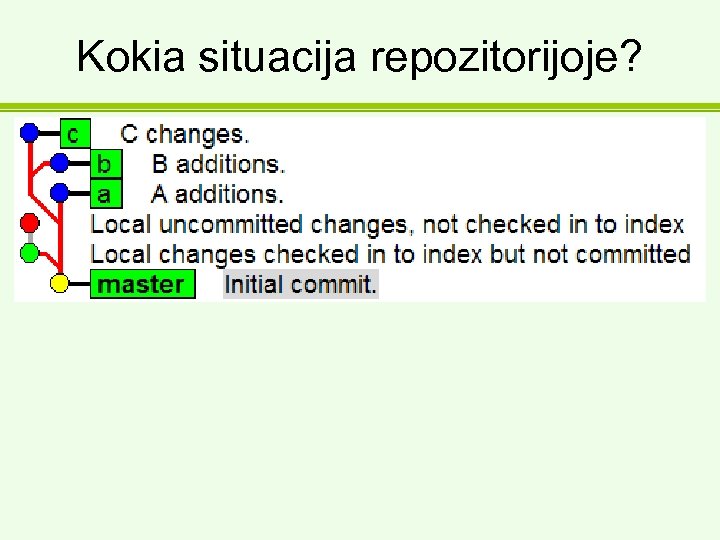
Kokia situacija repozitorijoje?

git reset --hard • Numeta HEAD ir failų sistemą į tam tikrą commit. D: Worktestrepo>git reset --hard master HEAD is now at 38 f 45 f 0 Initial commit.

Pabandom kitaip D: Worktestrepo>git merge a Updating 38 f 45 f 0. . d 40 f 0 de Fast forward test. txt | 2 ++ 1 files changed, 2 insertions(+), 0 deletions( -) D: Worktestrepo>git merge b Auto-merging test. txt CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in test. txt Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.

Turinys Additions of A. Initial data. <<<<<<< HEAD: test. txt. Additions of A. =======Additions of B. >>>>>>> b: test. txt Pataisom rankutėmis
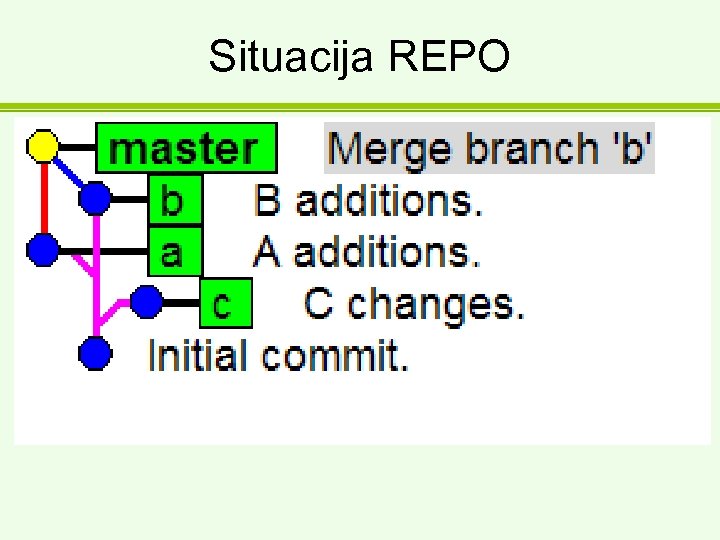
Situacija REPO
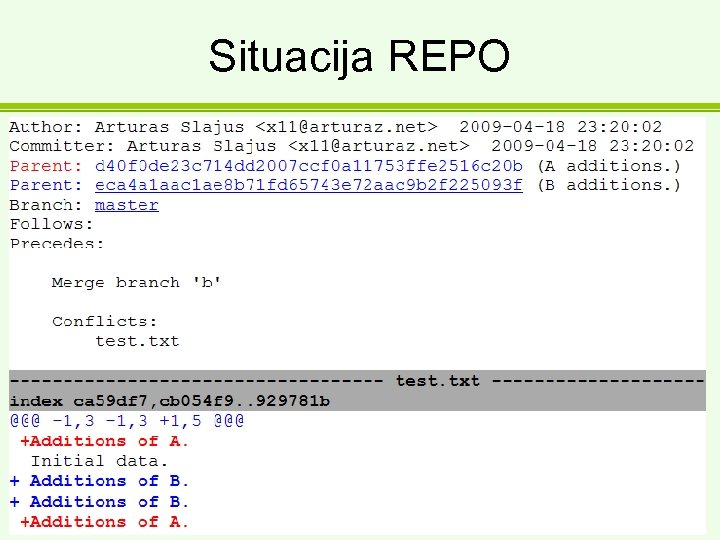
Situacija REPO
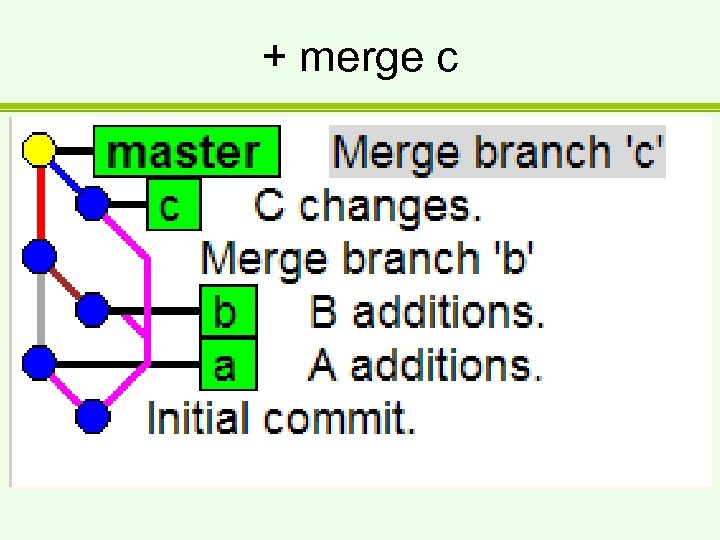
+ merge c

git stash • Ne taip dažnai naudojama, bet kartais naudinga.

Darbas su remote • Nors visi lygūs, vienas dažniausiai būna lygesnis už kitus - pristatome jums serverį. • Priėjimas per git protokolą, HTTP arba ssh. • • git clone - nusiklonuoja repozitoriją git remote - nutolusių serverių sąrašas git fetch git push remote_name branches
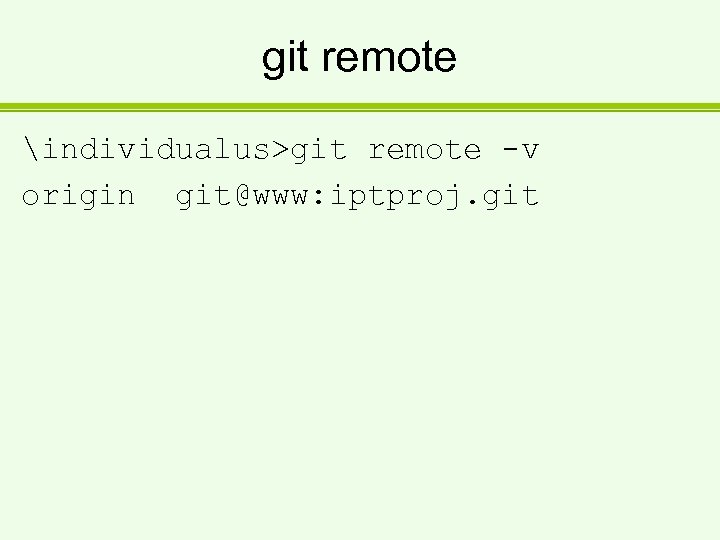
git remote individualus>git remote -v origin git@www: iptproj. git

git fetch individualus>git fetch From git@www: iptproj + 6 baa 748. . . 16 e 25 c 4 Jho (forced update) -> origin/Jho

git fetch
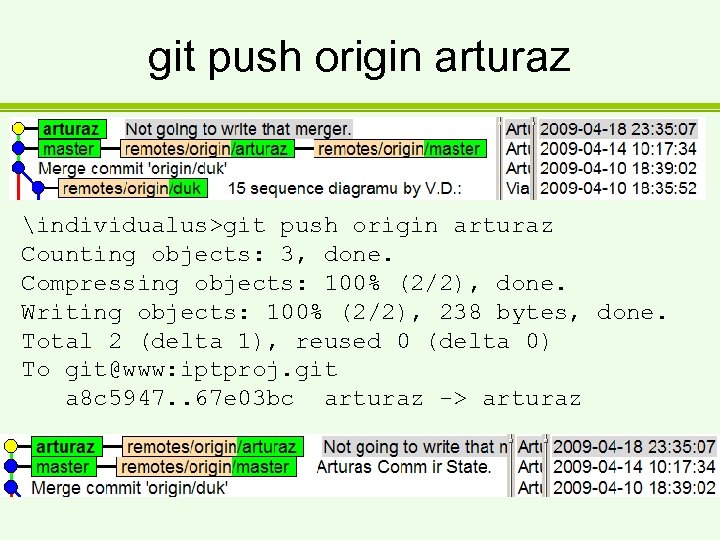
git push origin arturaz individualus>git push origin arturaz Counting objects: 3, done. Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (2/2), 238 bytes, done. Total 2 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@www: iptproj. git a 8 c 5947. . 67 e 03 bc arturaz -> arturaz

Serverio pusė • gitosis - GIT hook’ų krūva, kuri tvarko priėjimą per SSH. • Autentifikacija - SSH raktais. • Priėjimas prie projektų - gitosis. conf • Viskas per vieną SSH vartotoją, niekas neturi shell’o, saugu!

Online servisai • github. com - OSS projektams - nemokamai, kitiems - mokėjimo planai. • repo. or. cz • google: git hosting

Integracija su CVS/SVN • git cvs ir git svn • Leidžia klonuoti, sinchronizuoti repozitorijas. • Gali naudoti git net jeigu visa komanda naudoja SVN! • Tiesa, ne visai idealu

Git on Windows • Git - *NIX sistemų vaikas ir ten jam smagiausia. • msysgit - http: //code. google. com/p/msysgit/ portas į Windows. • Autentifikacijai - Pu. TTY suite: putty, plink, pageant. • Veikia, naudojuosi, patenkintas.

Summa summarum • Greita, decentralizuota, saugi, patogi. • Galima dirbti nors ir traukinyje ; ) • Pabandykite, gal patiks. Jei ne - Bazaar, Bit. Keeper, Mercurial ir kitos. • Jeigu labai nepatinka decentralizuotos - tada pabūsiu liberalesnis už Linus: naudokite kad ir SVN • Bet IMHO tikrai neverta. . . Never looked back.
![This one for ENC. ] This one for ENC. ]](https://present5.com/presentation/0aef9e92fed6d10783aa582a4021a956/image-52.jpg)
This one for ENC. ]
0aef9e92fed6d10783aa582a4021a956.ppt