Giovanni Landoni, MD landoni. giovanni@hsr. it Strategies for











































![February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%] February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%]](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_85.jpg)







![Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_98.jpg)













![All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_125.jpg)












1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 150
 Giovanni Landoni, MD [email protected] Strategies for reducing mortality rates in surgical interventions. The impact of cardioprotection with phosphocreatine on survival 15th Congress Of «All-Russian Non-Governmental Organization Federation Of Anesthesiologists And Reanimatologists» September 17th 2016 – Moscow, Russia Associate Professor Vita-Salute San Raffaele University , Milan, Italy Head of Research Anesthesia and Intensive Care San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy Italian Representative EACTA (European Association of Cardiothoracic Anesthesiologists)
Giovanni Landoni, MD [email protected] Strategies for reducing mortality rates in surgical interventions. The impact of cardioprotection with phosphocreatine on survival 15th Congress Of «All-Russian Non-Governmental Organization Federation Of Anesthesiologists And Reanimatologists» September 17th 2016 – Moscow, Russia Associate Professor Vita-Salute San Raffaele University , Milan, Italy Head of Research Anesthesia and Intensive Care San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy Italian Representative EACTA (European Association of Cardiothoracic Anesthesiologists)
 San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy
San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy
 ARMANI BENETTON DOLCE GABBANA FERRE’ GEOX GUCCI PRADA TOD’S TRUSSARDI VALENTINO ZEGNA 3
ARMANI BENETTON DOLCE GABBANA FERRE’ GEOX GUCCI PRADA TOD’S TRUSSARDI VALENTINO ZEGNA 3
 4
4
 CONFLICT OF INTEREST NO
CONFLICT OF INTEREST NO
 Disclosures (speaker fees, patents) Biomedical Orion Tenax Abbvie Pall Octapharma Alfa Wassermann Baxter
Disclosures (speaker fees, patents) Biomedical Orion Tenax Abbvie Pall Octapharma Alfa Wassermann Baxter
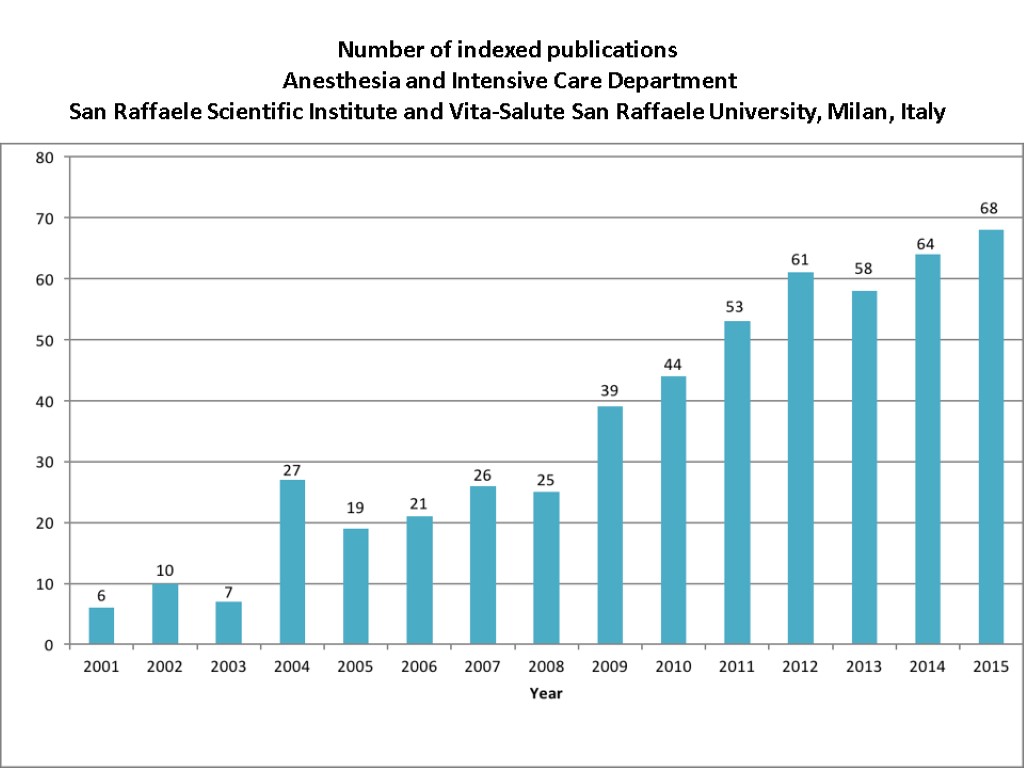
 Number of indexed publications Anesthesia and Intensive Care Department San Raffaele Scientific Institute and Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy
Number of indexed publications Anesthesia and Intensive Care Department San Raffaele Scientific Institute and Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy

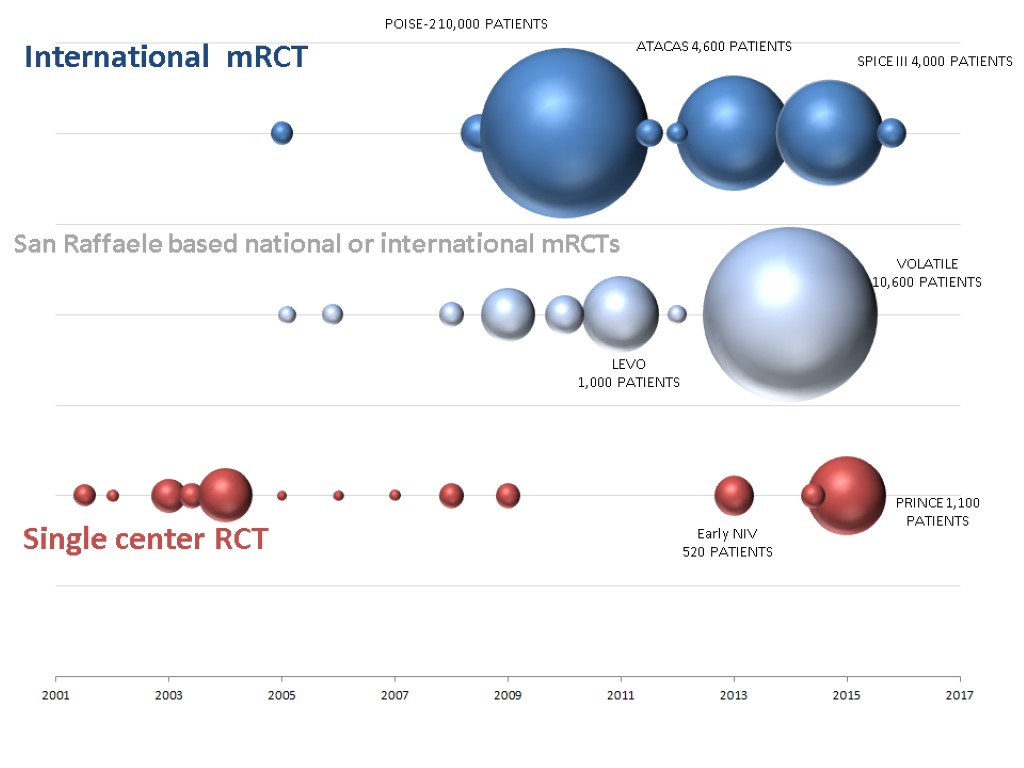
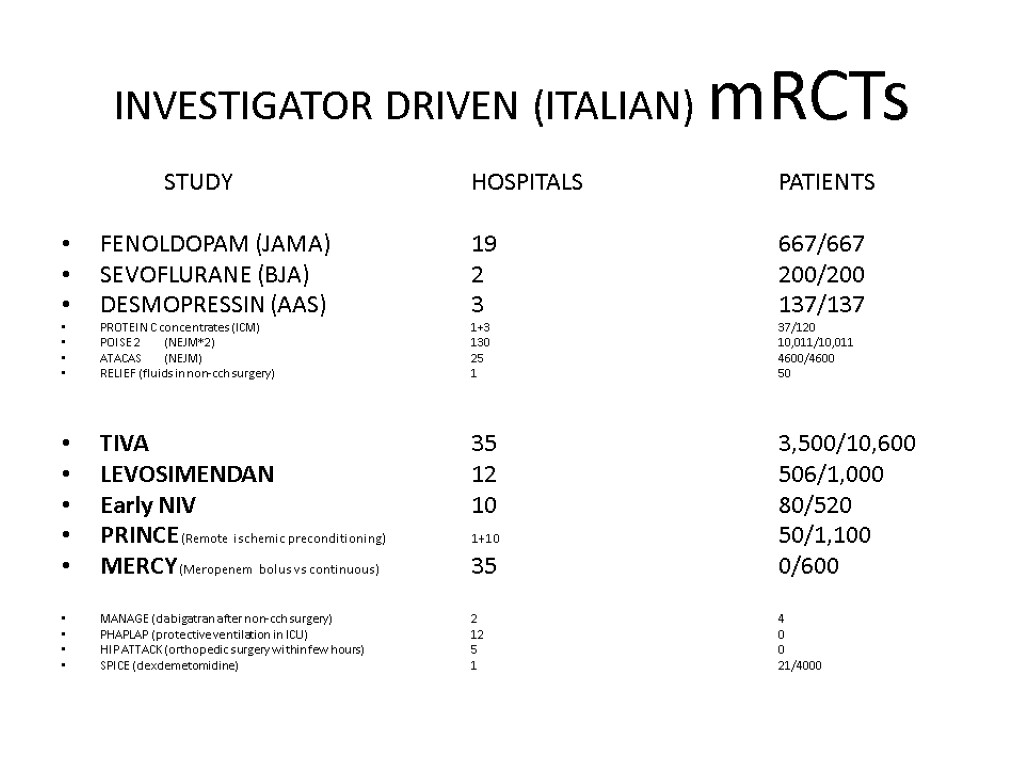
 INVESTIGATOR DRIVEN (ITALIAN) mRCTs STUDY HOSPITALS PATIENTS FENOLDOPAM (JAMA) 19 667/667 SEVOFLURANE (BJA) 2 200/200 DESMOPRESSIN (AAS) 3 137/137 PROTEIN C concentrates (ICM) 1+3 37/120 POISE 2 (NEJM*2) 130 10,011/10,011 ATACAS (NEJM) 25 4600/4600 RELIEF (fluids in non-cch surgery) 1 50 TIVA 35 3,500/10,600 LEVOSIMENDAN 12 506/1,000 Early NIV 10 80/520 PRINCE (Remote ischemic preconditioning) 1+10 50/1,100 MERCY (Meropenem bolus vs continuous) 35 0/600 MANAGE (dabigatran after non-cch surgery) 2 4 PHAPLAP (protective ventilation in ICU) 12 0 HIP ATTACK (orthopedic surgery within few hours) 5 0 SPICE (dexdemetomidine) 1 21/4000
INVESTIGATOR DRIVEN (ITALIAN) mRCTs STUDY HOSPITALS PATIENTS FENOLDOPAM (JAMA) 19 667/667 SEVOFLURANE (BJA) 2 200/200 DESMOPRESSIN (AAS) 3 137/137 PROTEIN C concentrates (ICM) 1+3 37/120 POISE 2 (NEJM*2) 130 10,011/10,011 ATACAS (NEJM) 25 4600/4600 RELIEF (fluids in non-cch surgery) 1 50 TIVA 35 3,500/10,600 LEVOSIMENDAN 12 506/1,000 Early NIV 10 80/520 PRINCE (Remote ischemic preconditioning) 1+10 50/1,100 MERCY (Meropenem bolus vs continuous) 35 0/600 MANAGE (dabigatran after non-cch surgery) 2 4 PHAPLAP (protective ventilation in ICU) 12 0 HIP ATTACK (orthopedic surgery within few hours) 5 0 SPICE (dexdemetomidine) 1 21/4000
 MAIN RESEARCH INTEREST PERIOPERATIVE ORGAN PROTECTION AND REDUCTION IN PERIOPERATIVE MORTALITY MET / NIV WEB BASED INNOVATIVE CONSENSUS CONFERENCES META-ANALYSES ECMO 26/11/2017 XXXXX 10
MAIN RESEARCH INTEREST PERIOPERATIVE ORGAN PROTECTION AND REDUCTION IN PERIOPERATIVE MORTALITY MET / NIV WEB BASED INNOVATIVE CONSENSUS CONFERENCES META-ANALYSES ECMO 26/11/2017 XXXXX 10
 WELCOME TO VISIT OUR CENTER (We had «long term» visitors from Austria, Portugal, Brasil, Russia, Costa Rica, China, Egypt) WELCOME TO PARTICIPATE TO OUR TRIALS --LEVOSIMENDAN (AFTER CARDIAC SURGERY) --TIVA VS VOLATILE (CABG) --NIV OUTSIDE THE ICU (ANY HOSPITAL WARD) 11
WELCOME TO VISIT OUR CENTER (We had «long term» visitors from Austria, Portugal, Brasil, Russia, Costa Rica, China, Egypt) WELCOME TO PARTICIPATE TO OUR TRIALS --LEVOSIMENDAN (AFTER CARDIAC SURGERY) --TIVA VS VOLATILE (CABG) --NIV OUTSIDE THE ICU (ANY HOSPITAL WARD) 11
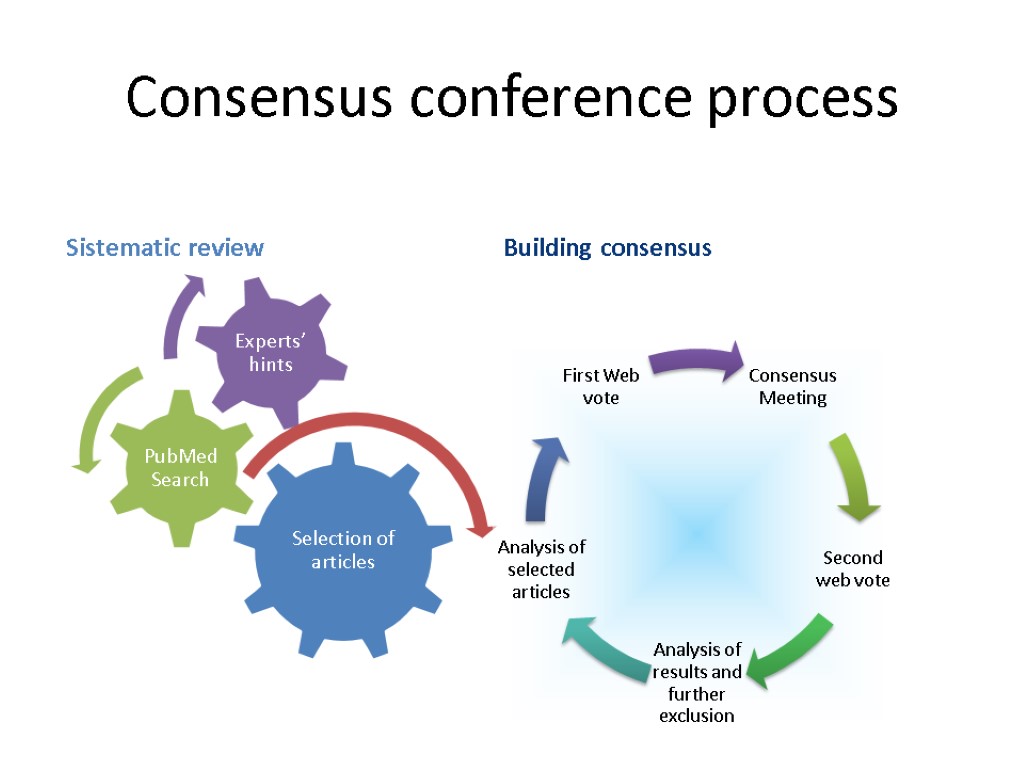
 Consensus conference process Sistematic review Building consensus 12
Consensus conference process Sistematic review Building consensus 12

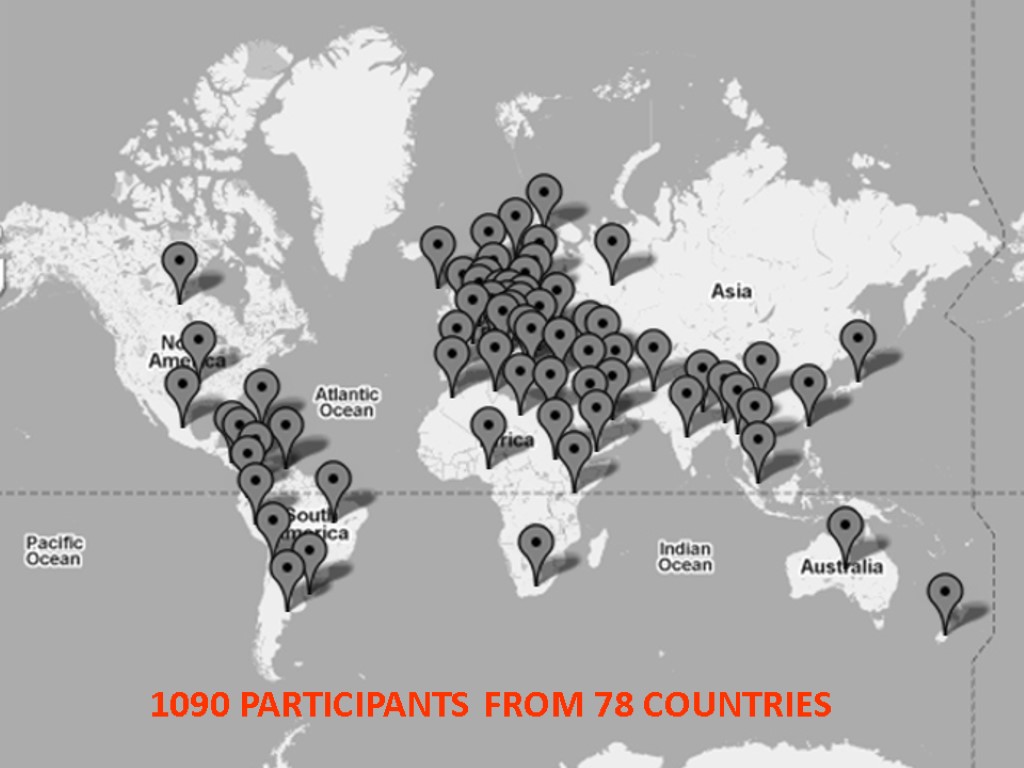
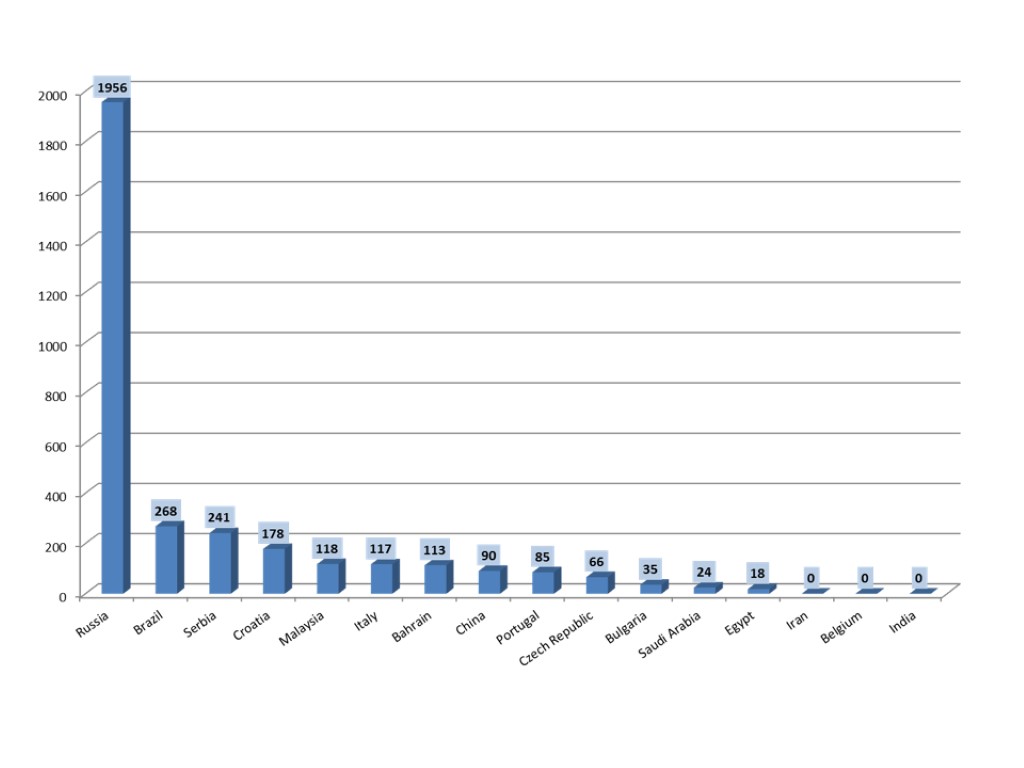
 1090 PARTICIPANTS FROM 78 COUNTRIES
1090 PARTICIPANTS FROM 78 COUNTRIES
 15
15
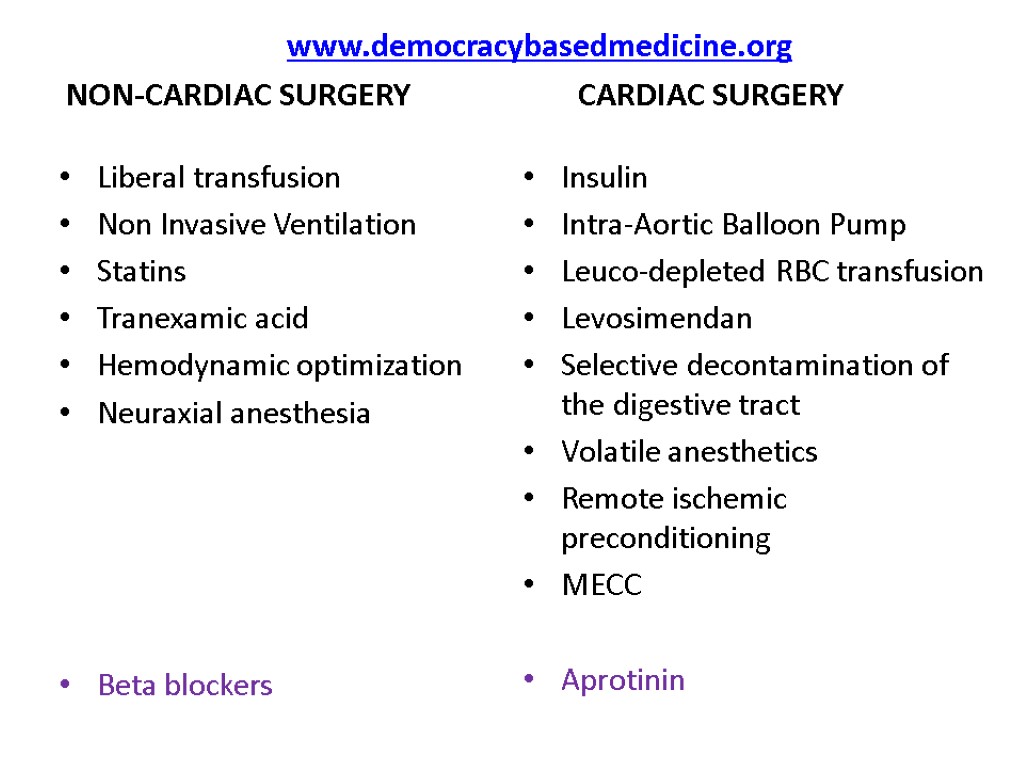
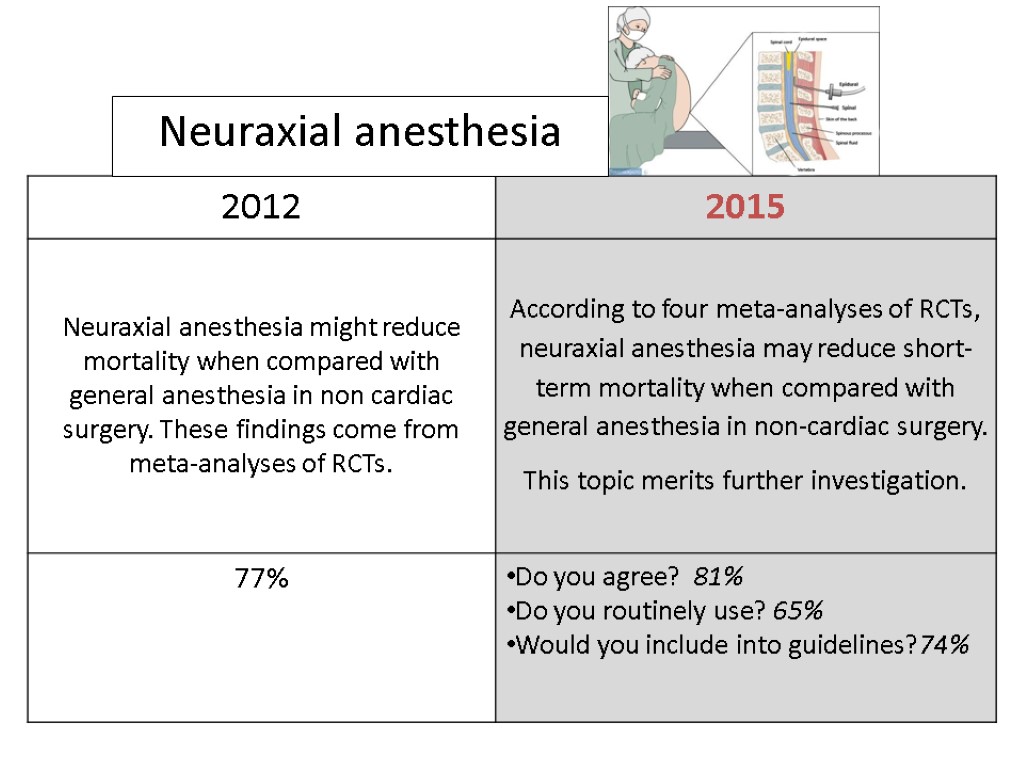
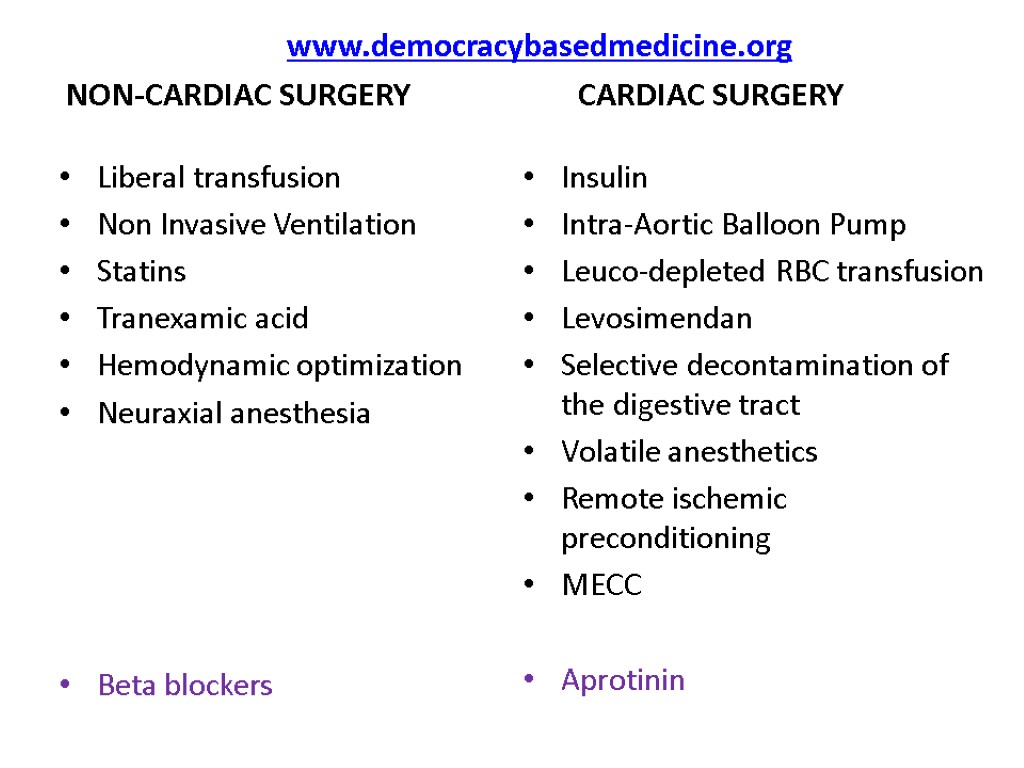
 www.democracybasedmedicine.org NON-CARDIAC SURGERY CARDIAC SURGERY Liberal transfusion Non Invasive Ventilation Statins Tranexamic acid Hemodynamic optimization Neuraxial anesthesia Beta blockers Insulin Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Leuco-depleted RBC transfusion Levosimendan Selective decontamination of the digestive tract Volatile anesthetics Remote ischemic preconditioning MECC Aprotinin
www.democracybasedmedicine.org NON-CARDIAC SURGERY CARDIAC SURGERY Liberal transfusion Non Invasive Ventilation Statins Tranexamic acid Hemodynamic optimization Neuraxial anesthesia Beta blockers Insulin Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Leuco-depleted RBC transfusion Levosimendan Selective decontamination of the digestive tract Volatile anesthetics Remote ischemic preconditioning MECC Aprotinin
 Questions Do you agree with the above sentence? Do you routinely use this intervention in your clinical practice? Would you include this intervention into future international guidelines to reduce perioperative mortality?
Questions Do you agree with the above sentence? Do you routinely use this intervention in your clinical practice? Would you include this intervention into future international guidelines to reduce perioperative mortality?
 Interventions reducing postoperative mortality Part 1
Interventions reducing postoperative mortality Part 1
 NON-CARDIAC SURGERY
NON-CARDIAC SURGERY
 Liberal transfusion strategy in the perioperative period
Liberal transfusion strategy in the perioperative period
 RESTRICTIVE Hb < 9.7 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 11.3 g/dl
RESTRICTIVE Hb < 9.7 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 11.3 g/dl
 RESTRICTIVE Hb < 7 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 9 g/dl
RESTRICTIVE Hb < 7 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 9 g/dl

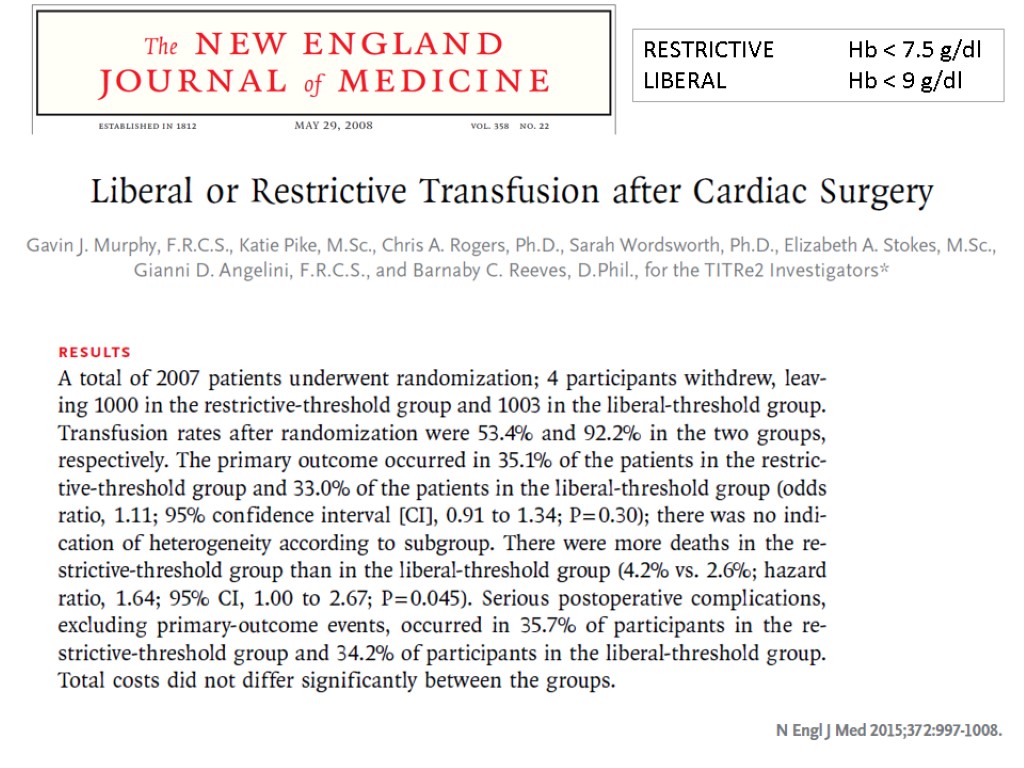
 RESTRICTIVE Hb < 7.5 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 9 g/dl
RESTRICTIVE Hb < 7.5 g/dl LIBERAL Hb < 9 g/dl

 Liberal transfusion strategy in the perioperative period
Liberal transfusion strategy in the perioperative period
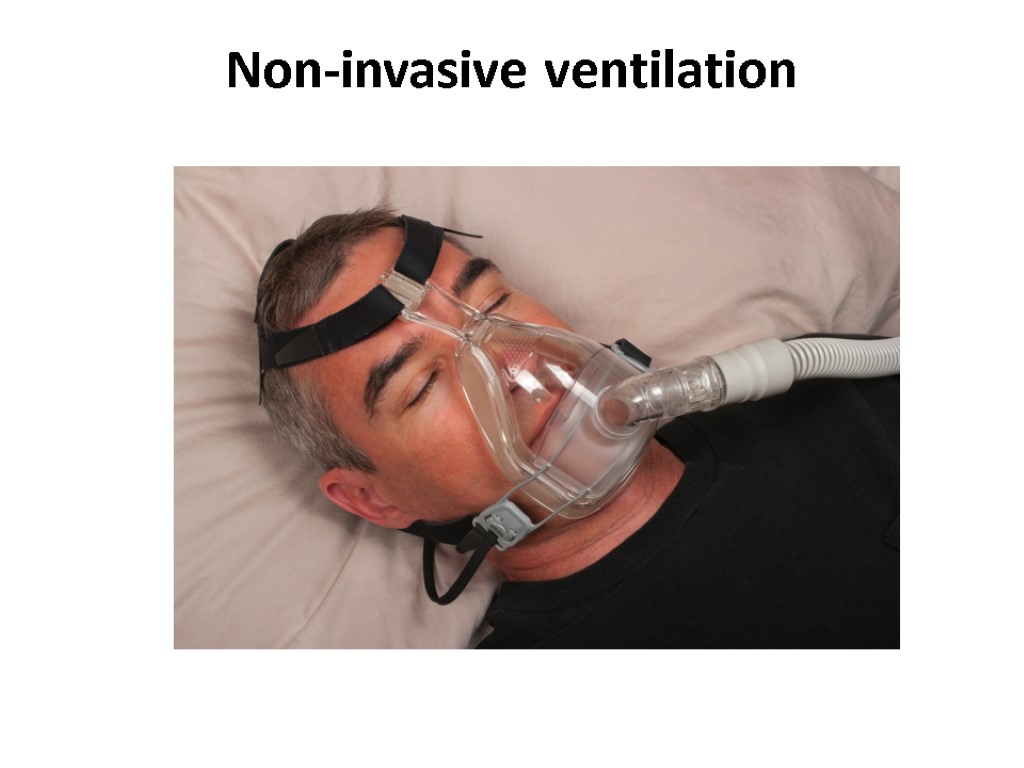
 Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation
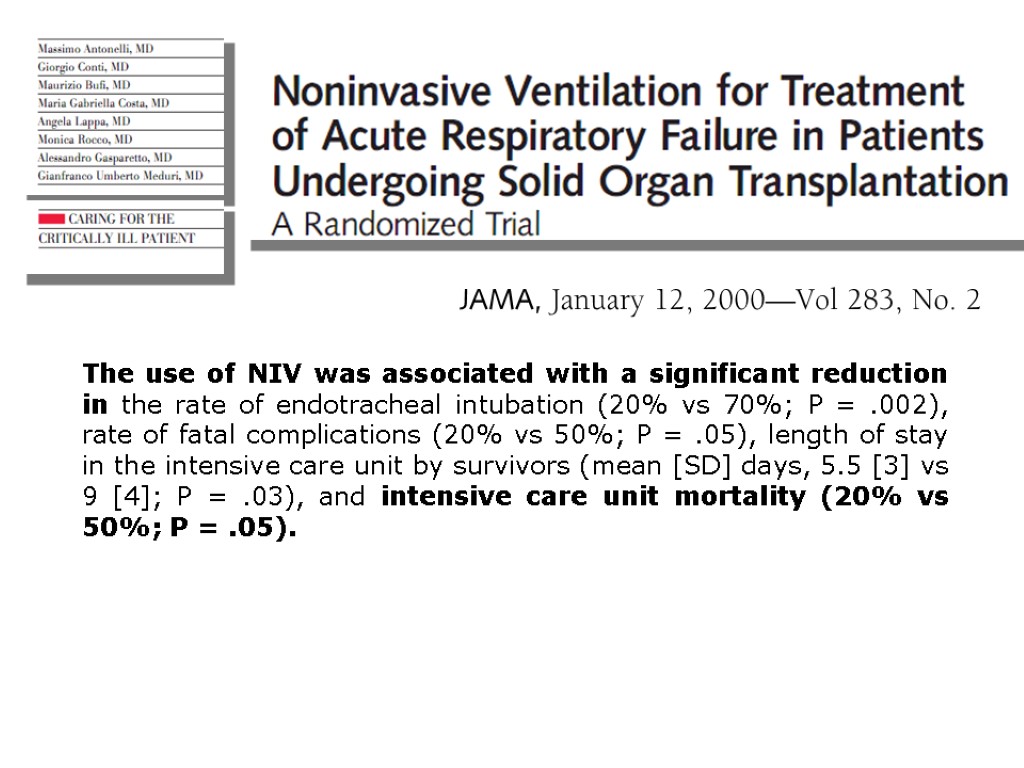
 The use of NIV was associated with a significant reduction in the rate of endotracheal intubation (20% vs 70%; P = .002), rate of fatal complications (20% vs 50%; P = .05), length of stay in the intensive care unit by survivors (mean [SD] days, 5.5 [3] vs 9 [4]; P = .03), and intensive care unit mortality (20% vs 50%; P = .05).
The use of NIV was associated with a significant reduction in the rate of endotracheal intubation (20% vs 70%; P = .002), rate of fatal complications (20% vs 50%; P = .05), length of stay in the intensive care unit by survivors (mean [SD] days, 5.5 [3] vs 9 [4]; P = .03), and intensive care unit mortality (20% vs 50%; P = .05).
 Nine patients in the no-NPPV group died (37.5%), and three (12.5 %) patients in the NPPV group died (p = 0.045).
Nine patients in the no-NPPV group died (37.5%), and three (12.5 %) patients in the NPPV group died (p = 0.045).

 Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation
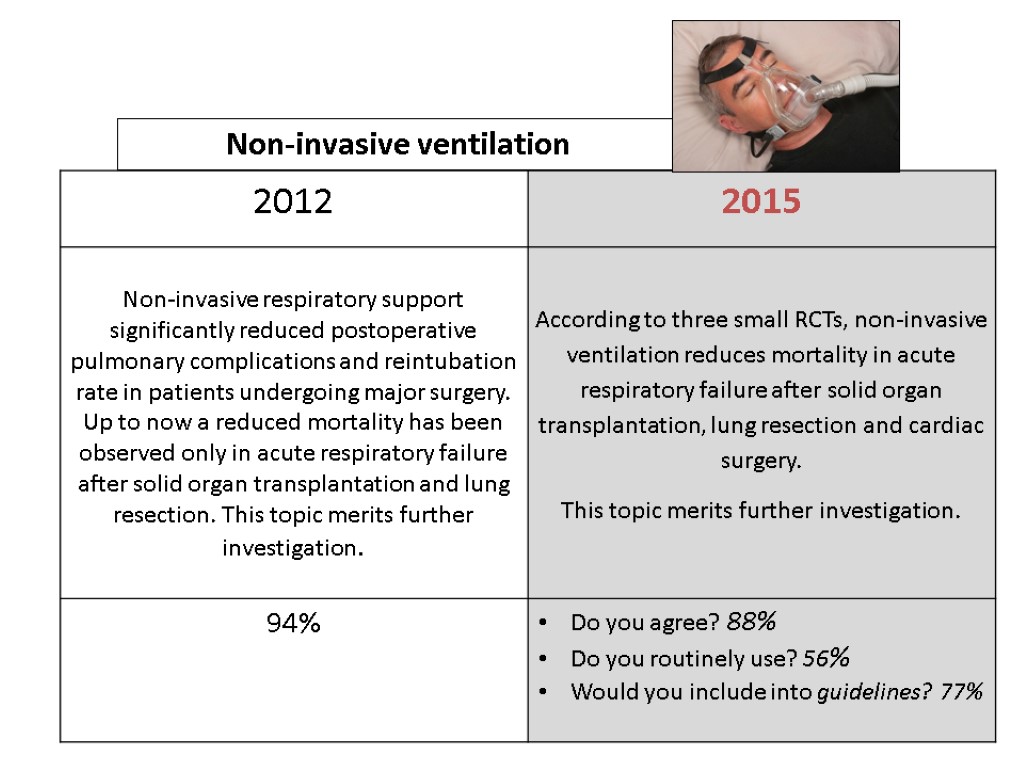
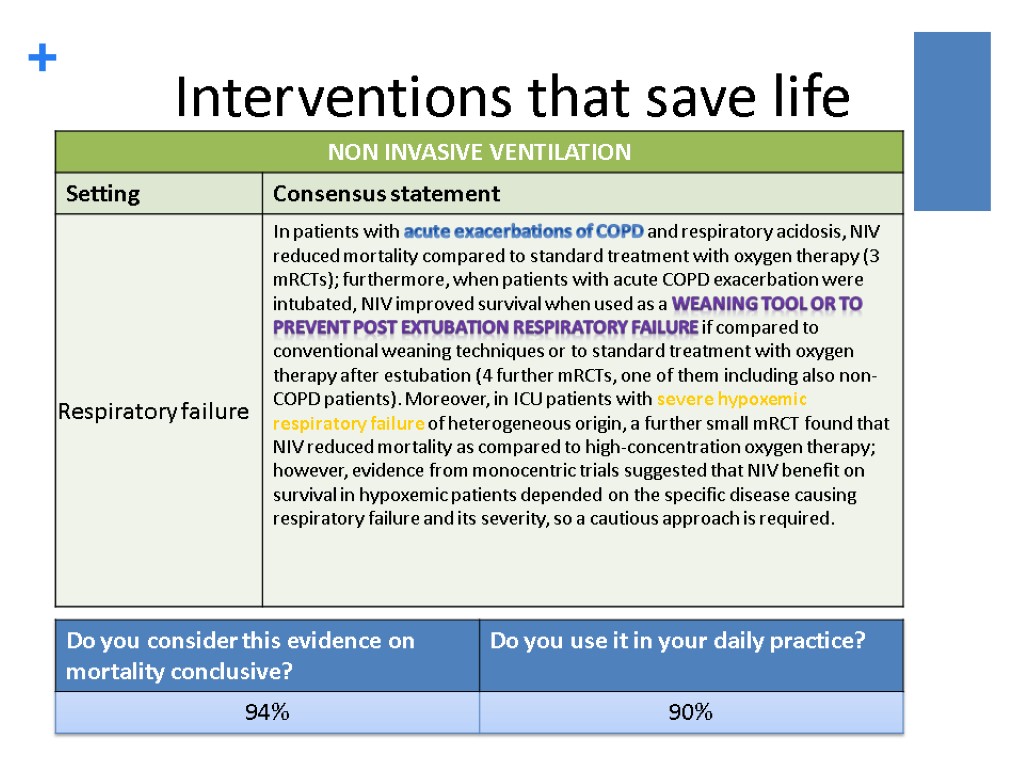
 Interventions that save life 32
Interventions that save life 32
 Ongoing RCTs (welcome to participate) «EARLY NIV» RCTs 520 PATIENTS OUTSIDE THE ICU
Ongoing RCTs (welcome to participate) «EARLY NIV» RCTs 520 PATIENTS OUTSIDE THE ICU
 34
34

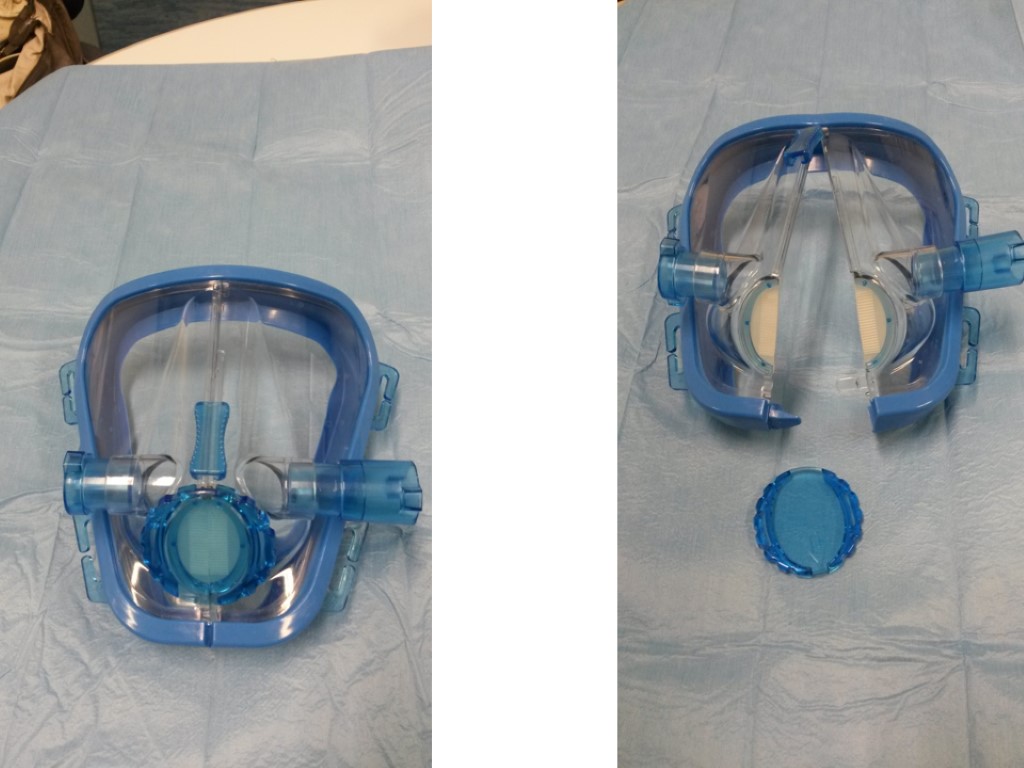
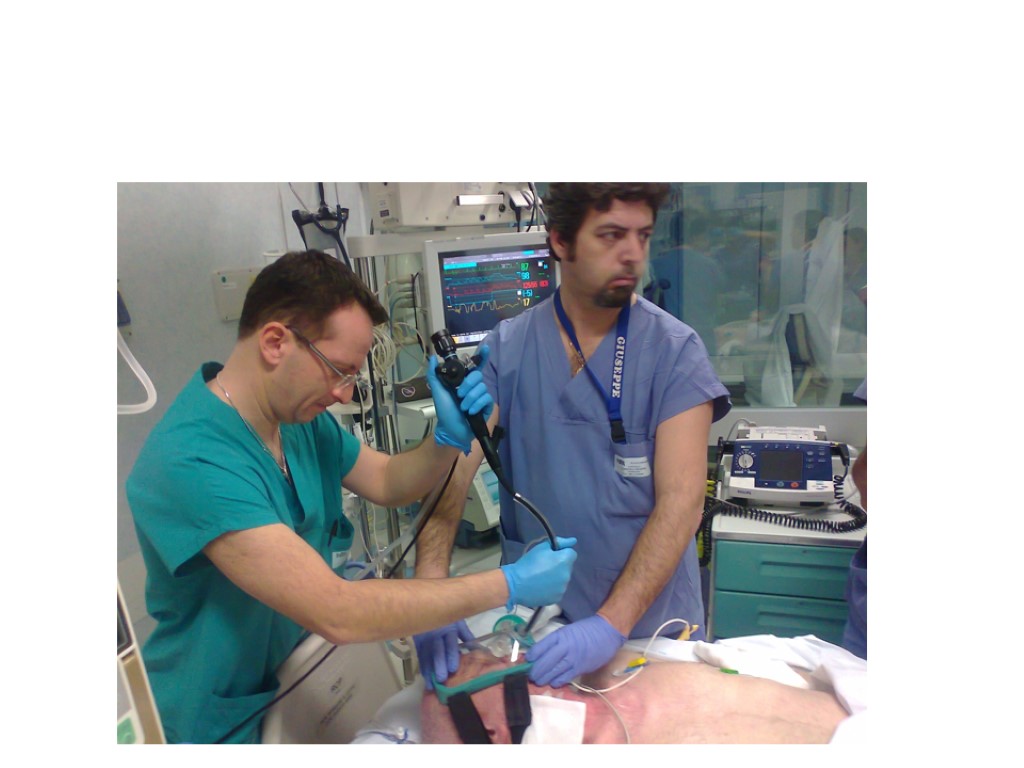
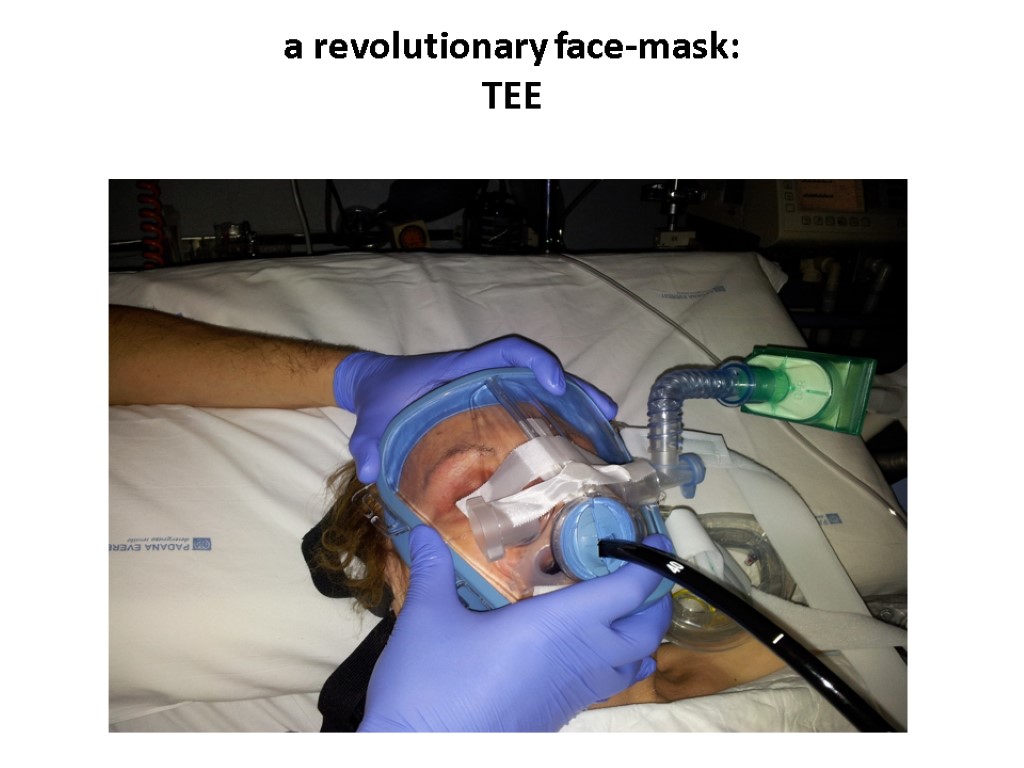
 a revolutionary face-mask: TEE
a revolutionary face-mask: TEE
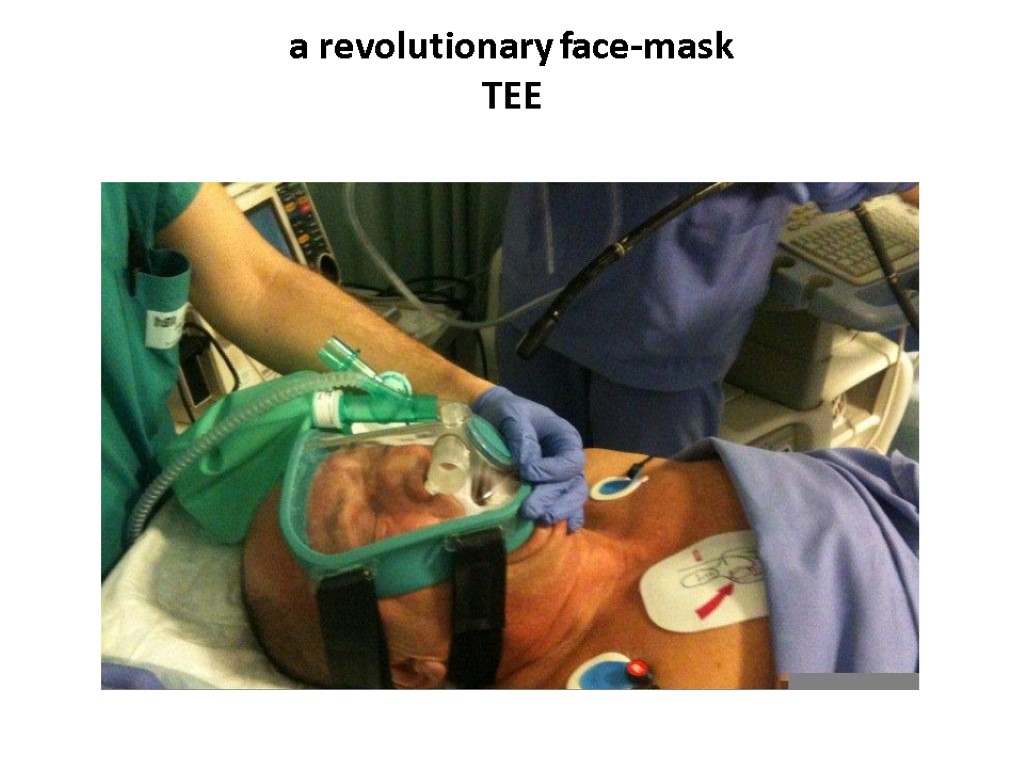
 a revolutionary face-mask TEE
a revolutionary face-mask TEE
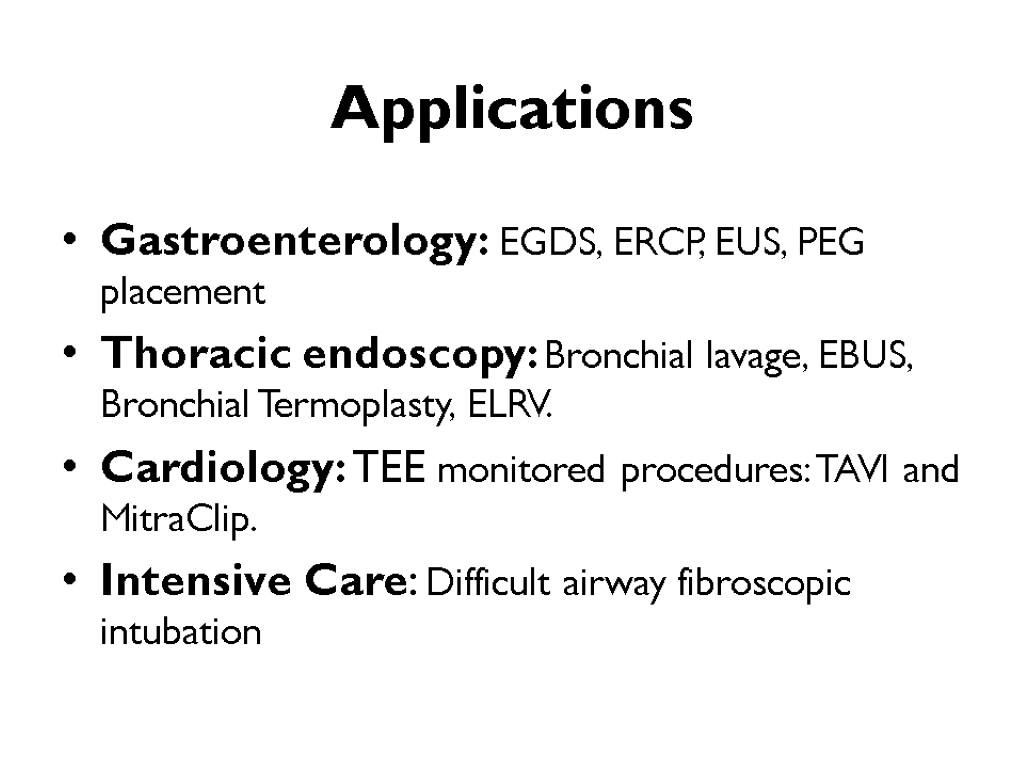
 Applications Gastroenterology: EGDS, ERCP, EUS, PEG placement Thoracic endoscopy: Bronchial lavage, EBUS, Bronchial Termoplasty, ELRV. Cardiology: TEE monitored procedures: TAVI and MitraClip. Intensive Care: Difficult airway fibroscopic intubation 38
Applications Gastroenterology: EGDS, ERCP, EUS, PEG placement Thoracic endoscopy: Bronchial lavage, EBUS, Bronchial Termoplasty, ELRV. Cardiology: TEE monitored procedures: TAVI and MitraClip. Intensive Care: Difficult airway fibroscopic intubation 38
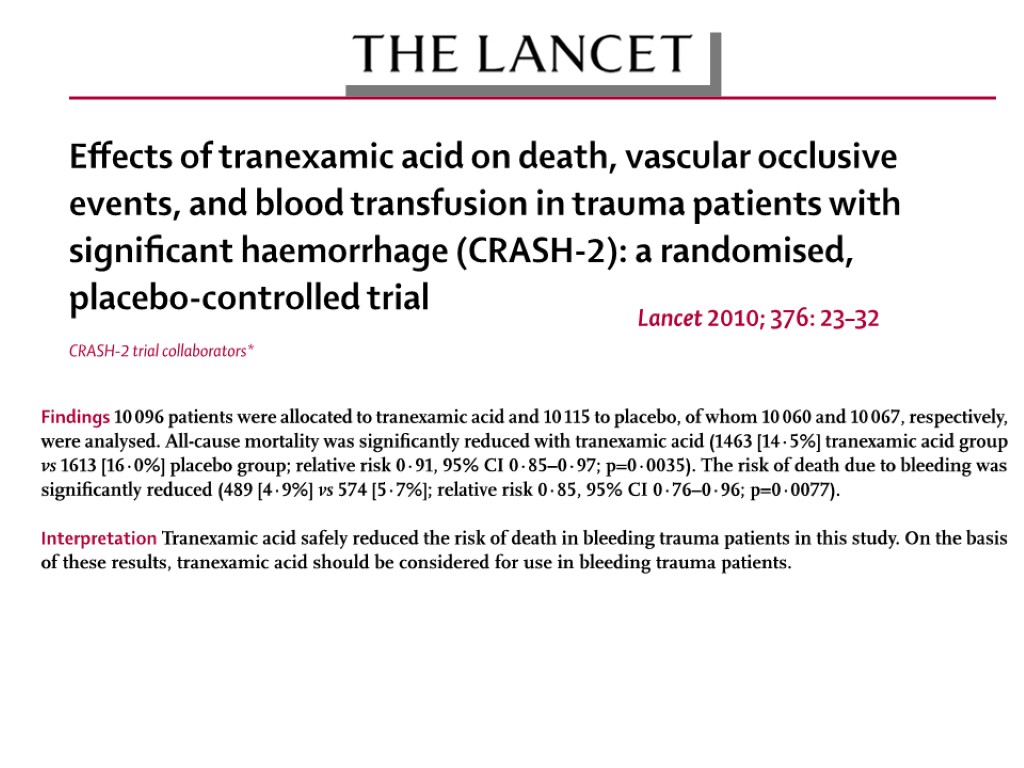
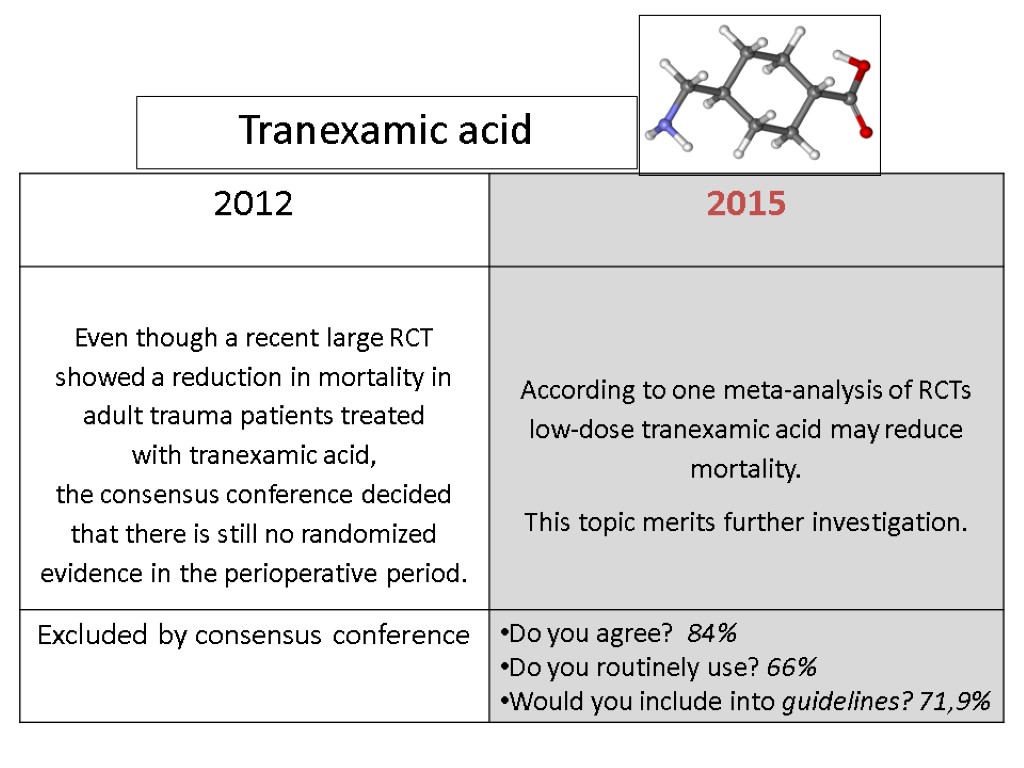
 Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid


 Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid
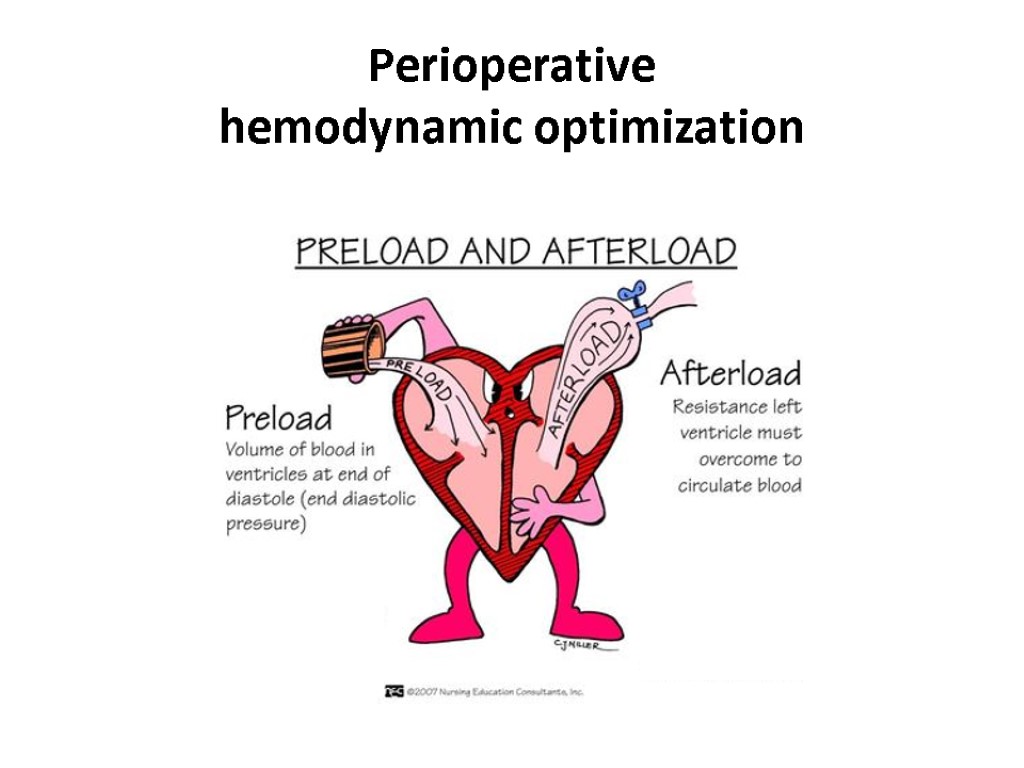
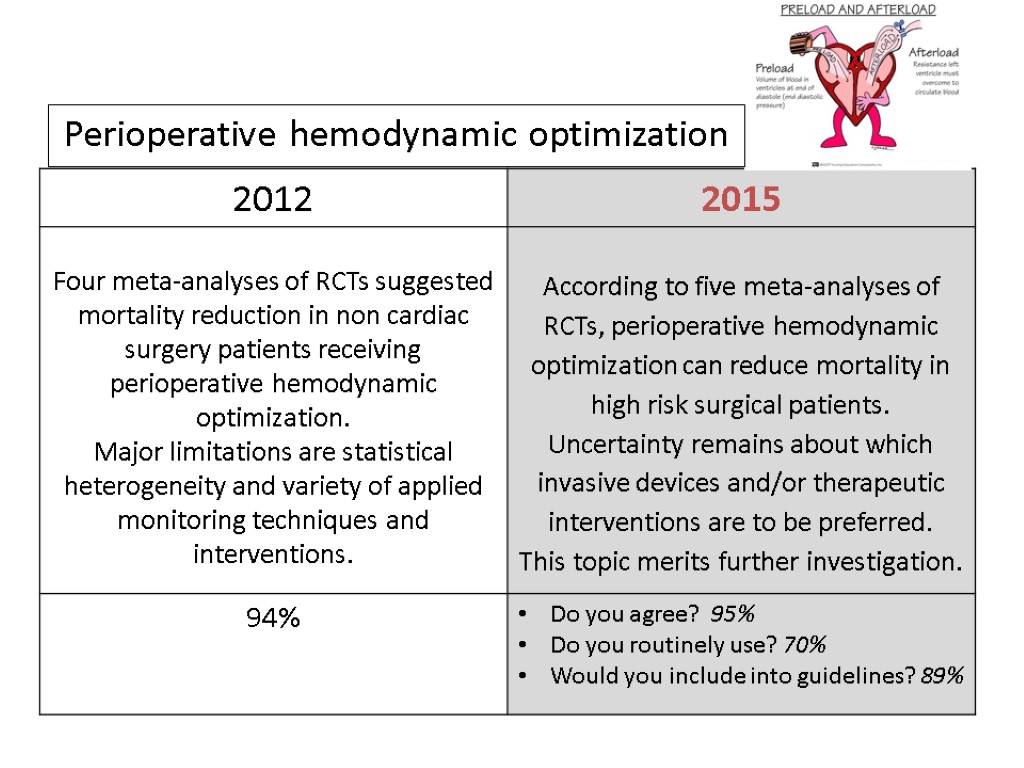
 Perioperative hemodynamic optimization
Perioperative hemodynamic optimization


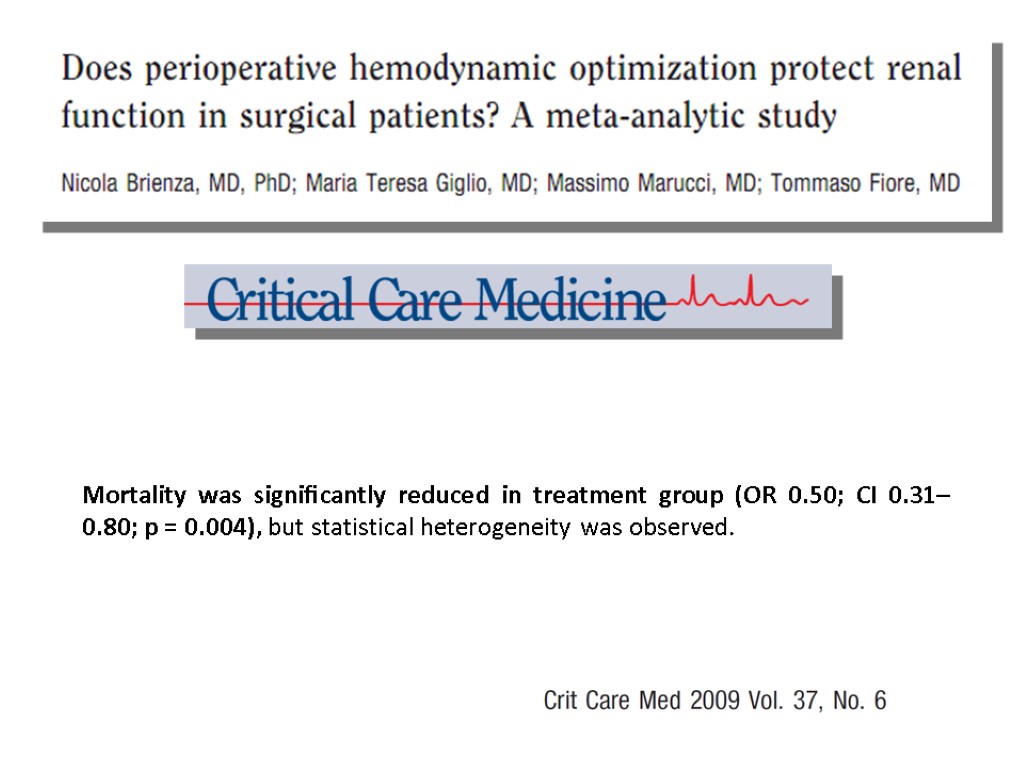
 Mortality was significantly reduced in treatment group (OR 0.50; CI 0.31– 0.80; p = 0.004), but statistical heterogeneity was observed.
Mortality was significantly reduced in treatment group (OR 0.50; CI 0.31– 0.80; p = 0.004), but statistical heterogeneity was observed.
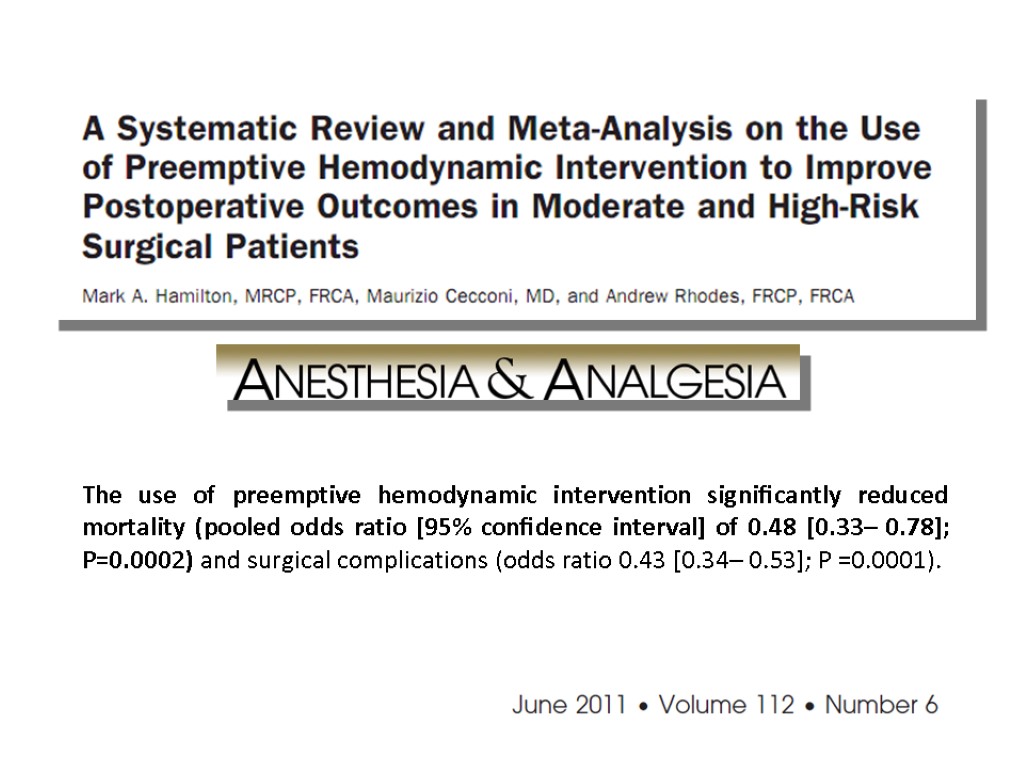
 The use of preemptive hemodynamic intervention significantly reduced mortality (pooled odds ratio [95% confidence interval] of 0.48 [0.33– 0.78]; P=0.0002) and surgical complications (odds ratio 0.43 [0.34– 0.53]; P =0.0001).
The use of preemptive hemodynamic intervention significantly reduced mortality (pooled odds ratio [95% confidence interval] of 0.48 [0.33– 0.78]; P=0.0002) and surgical complications (odds ratio 0.43 [0.34– 0.53]; P =0.0001).
 Perioperative hemodynamic optimization
Perioperative hemodynamic optimization
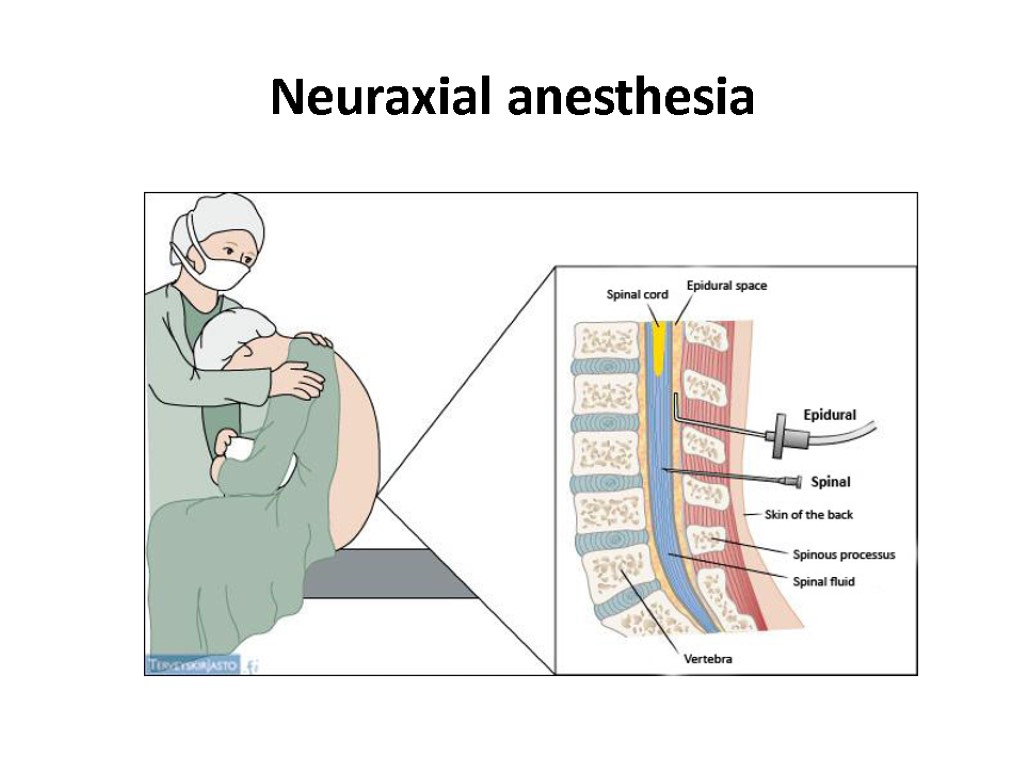
 Neuraxial anesthesia
Neuraxial anesthesia
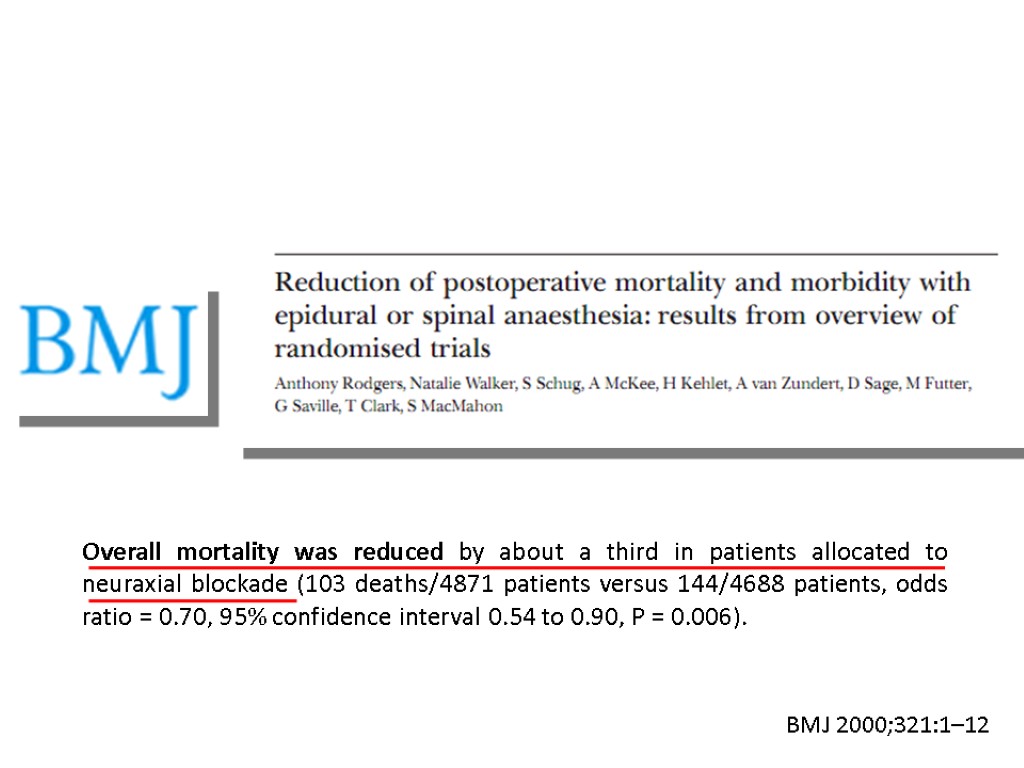
 Overall mortality was reduced by about a third in patients allocated to neuraxial blockade (103 deaths/4871 patients versus 144/4688 patients, odds ratio = 0.70, 95% confidence interval 0.54 to 0.90, P = 0.006). BMJ 2000;321:1–12
Overall mortality was reduced by about a third in patients allocated to neuraxial blockade (103 deaths/4871 patients versus 144/4688 patients, odds ratio = 0.70, 95% confidence interval 0.54 to 0.90, P = 0.006). BMJ 2000;321:1–12
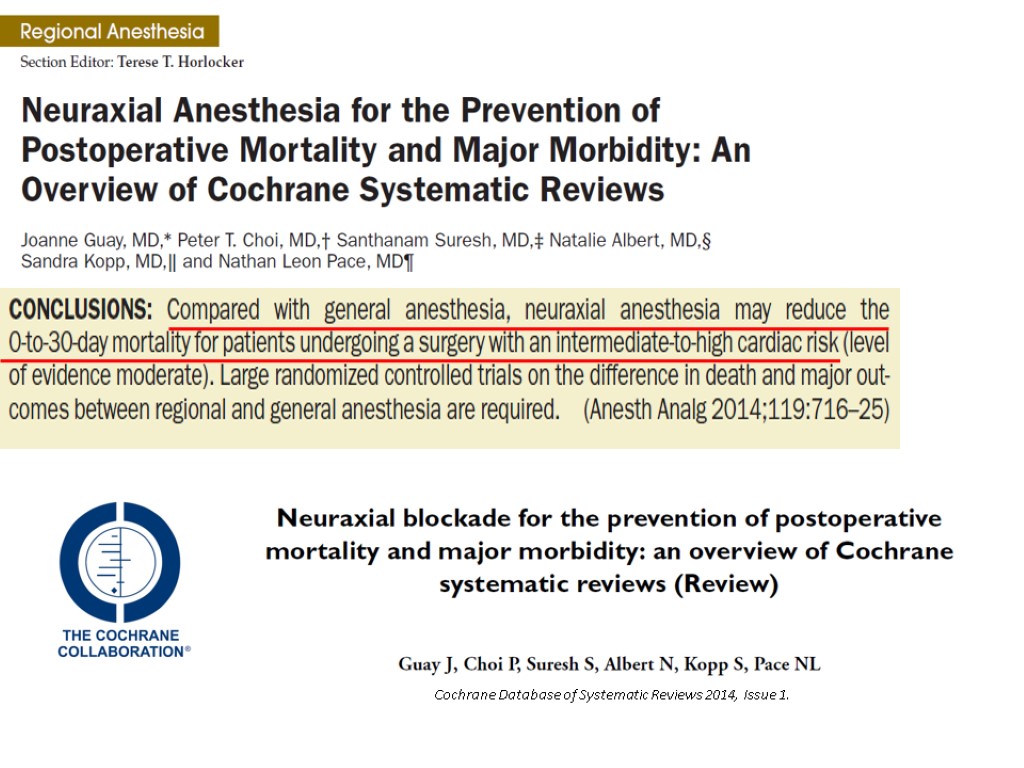
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 1.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 1.
 (Ann Surg 2014;259:1056–1067)
(Ann Surg 2014;259:1056–1067)

 Neuraxial anesthesia
Neuraxial anesthesia
 Interventions increasing postoperative mortality
Interventions increasing postoperative mortality
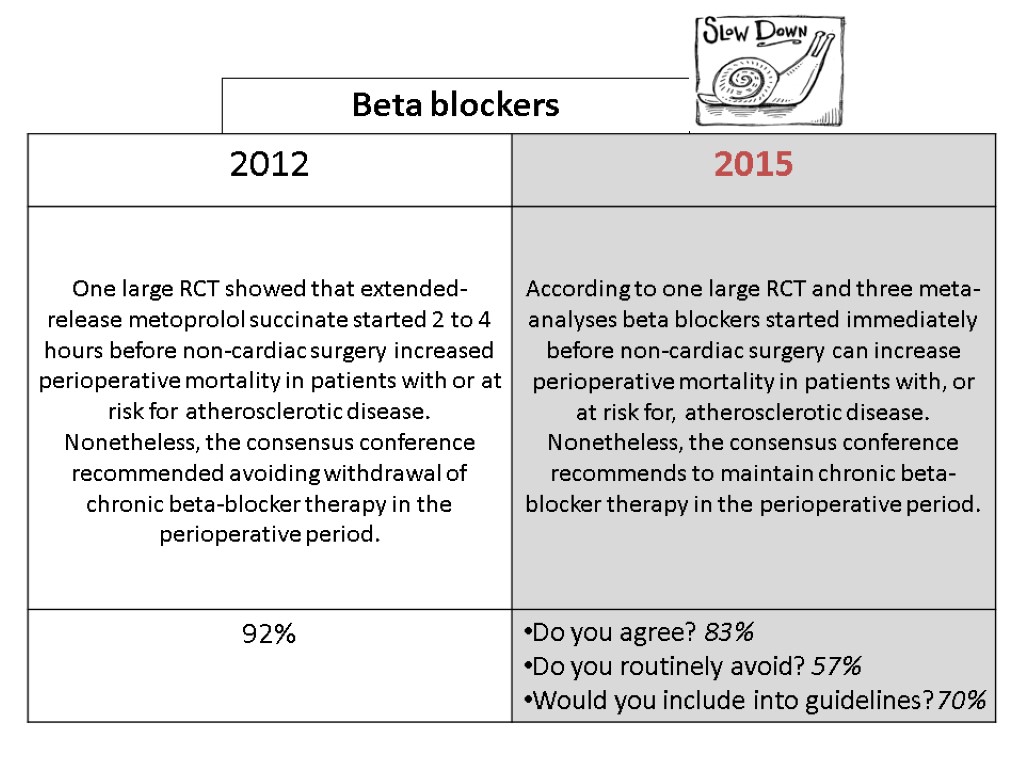
 Beta blockers
Beta blockers
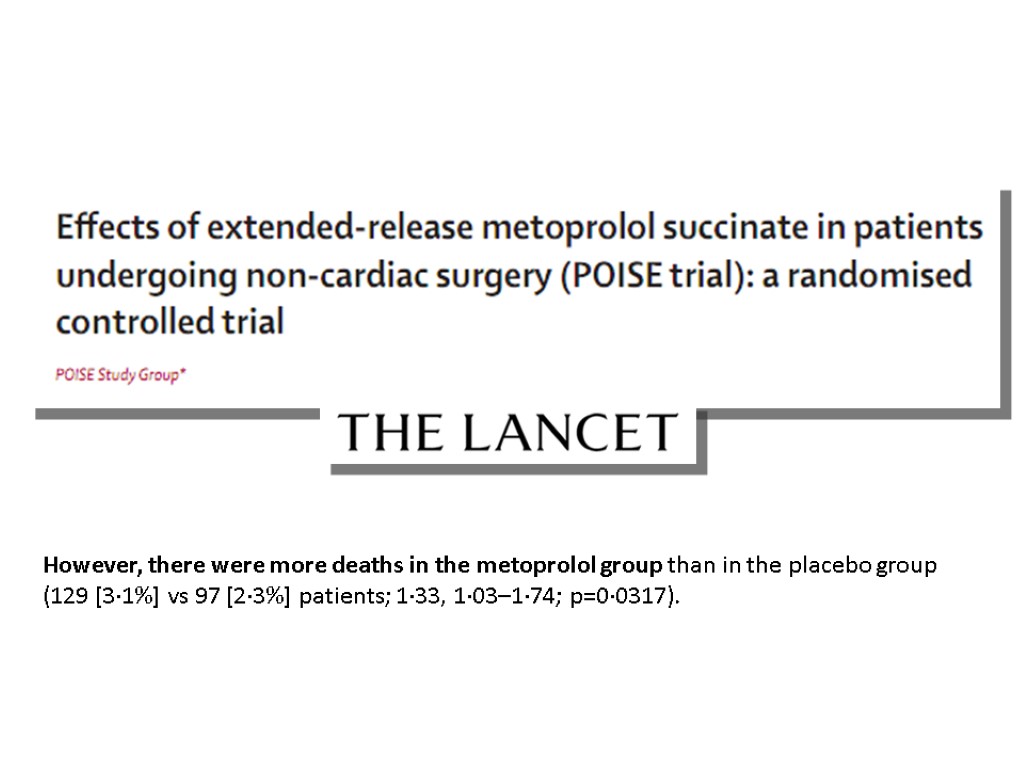
 However, there were more deaths in the metoprolol group than in the placebo group (129 [3·1%] vs 97 [2·3%] patients; 1·33, 1·03–1·74; p=0·0317).
However, there were more deaths in the metoprolol group than in the placebo group (129 [3·1%] vs 97 [2·3%] patients; 1·33, 1·03–1·74; p=0·0317).




 Beta blockers
Beta blockers
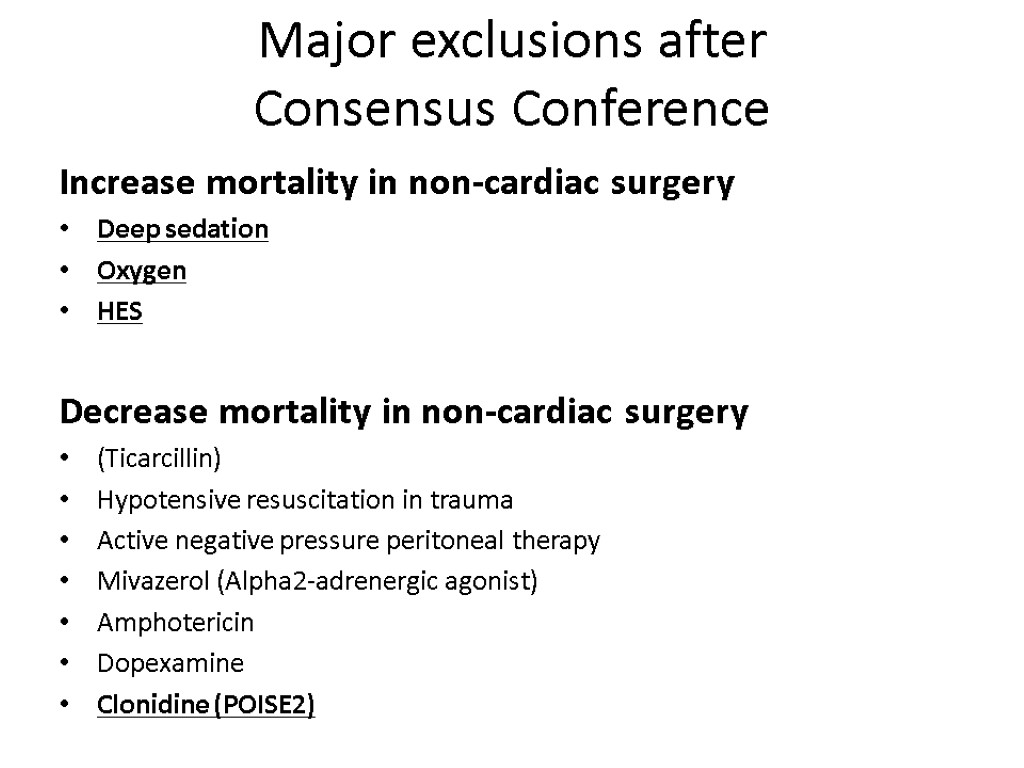
 Major exclusions after Consensus Conference Increase mortality in non-cardiac surgery Deep sedation Oxygen HES Decrease mortality in non-cardiac surgery (Ticarcillin) Hypotensive resuscitation in trauma Active negative pressure peritoneal therapy Mivazerol (Alpha2-adrenergic agonist) Amphotericin Dopexamine Clonidine (POISE2)
Major exclusions after Consensus Conference Increase mortality in non-cardiac surgery Deep sedation Oxygen HES Decrease mortality in non-cardiac surgery (Ticarcillin) Hypotensive resuscitation in trauma Active negative pressure peritoneal therapy Mivazerol (Alpha2-adrenergic agonist) Amphotericin Dopexamine Clonidine (POISE2)

 CARDIAC SURGERY
CARDIAC SURGERY
 Interventions reducing postoperative mortality Part 1
Interventions reducing postoperative mortality Part 1
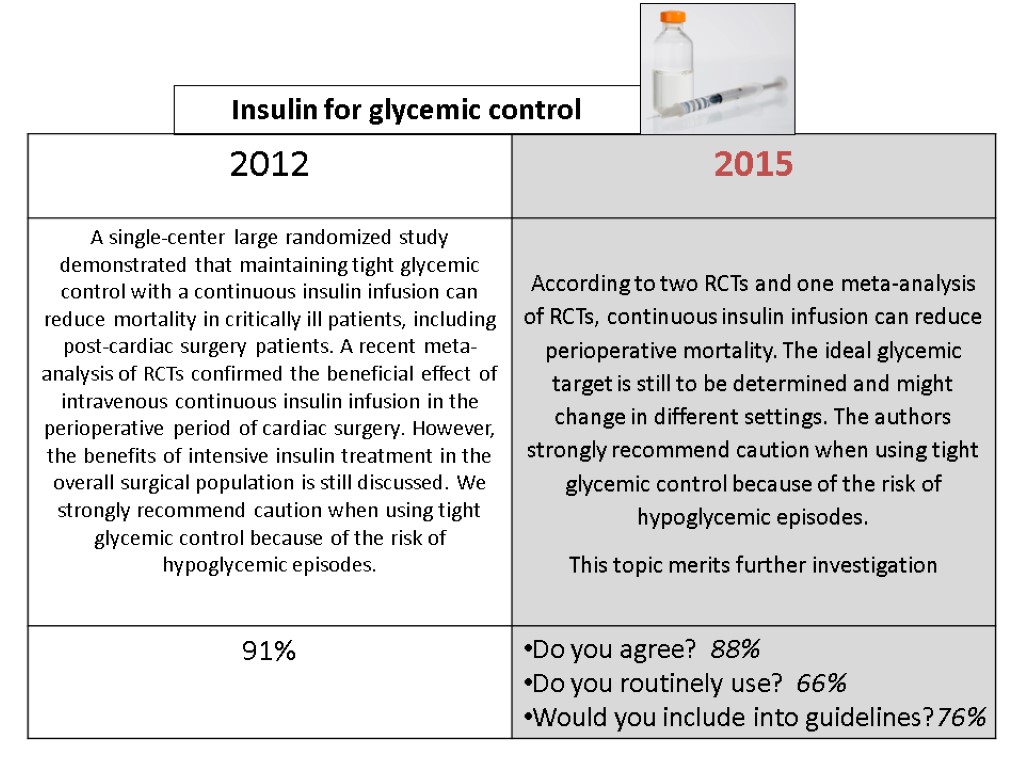
 Insulin for glycemic control
Insulin for glycemic control
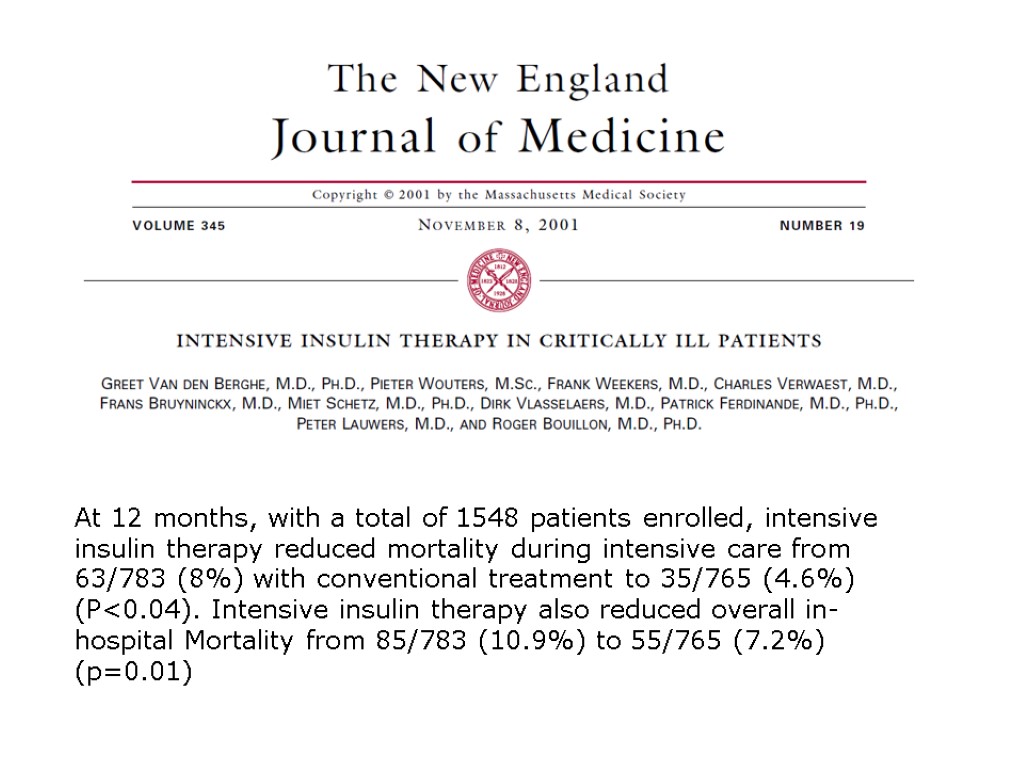
 At 12 months, with a total of 1548 patients enrolled, intensive insulin therapy reduced mortality during intensive care from 63/783 (8%) with conventional treatment to 35/765 (4.6%) (P<0.04). Intensive insulin therapy also reduced overall in-hospital Mortality from 85/783 (10.9%) to 55/765 (7.2%) (p=0.01)
At 12 months, with a total of 1548 patients enrolled, intensive insulin therapy reduced mortality during intensive care from 63/783 (8%) with conventional treatment to 35/765 (4.6%) (P<0.04). Intensive insulin therapy also reduced overall in-hospital Mortality from 85/783 (10.9%) to 55/765 (7.2%) (p=0.01)


 Insulin for glycemic control
Insulin for glycemic control
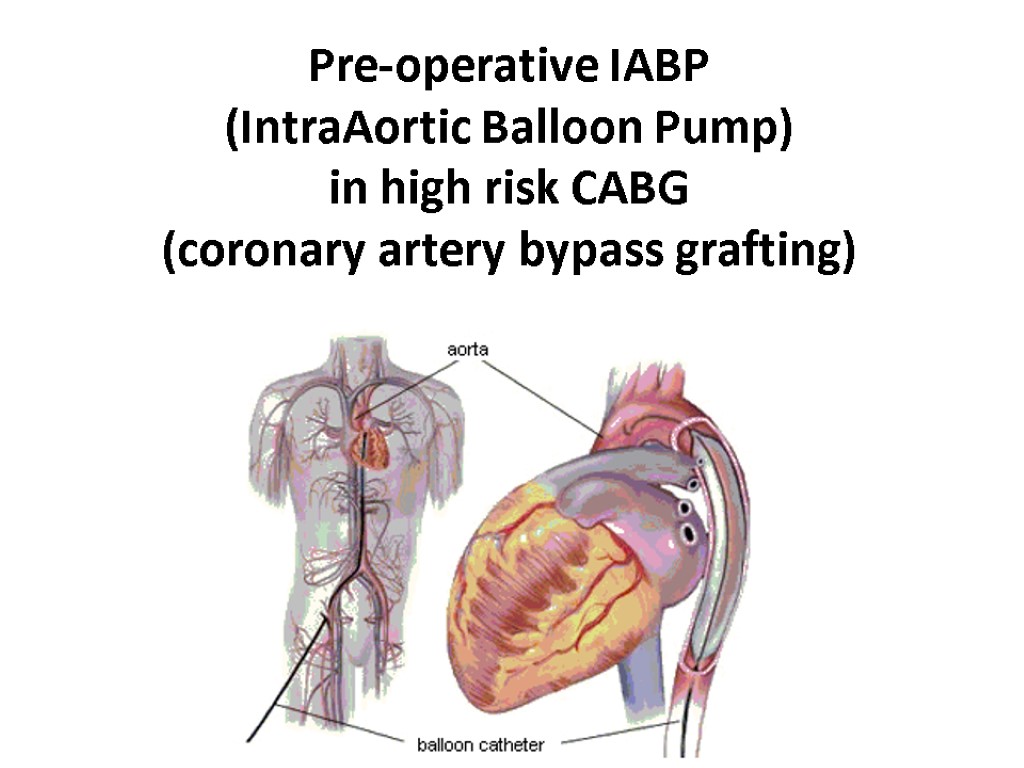
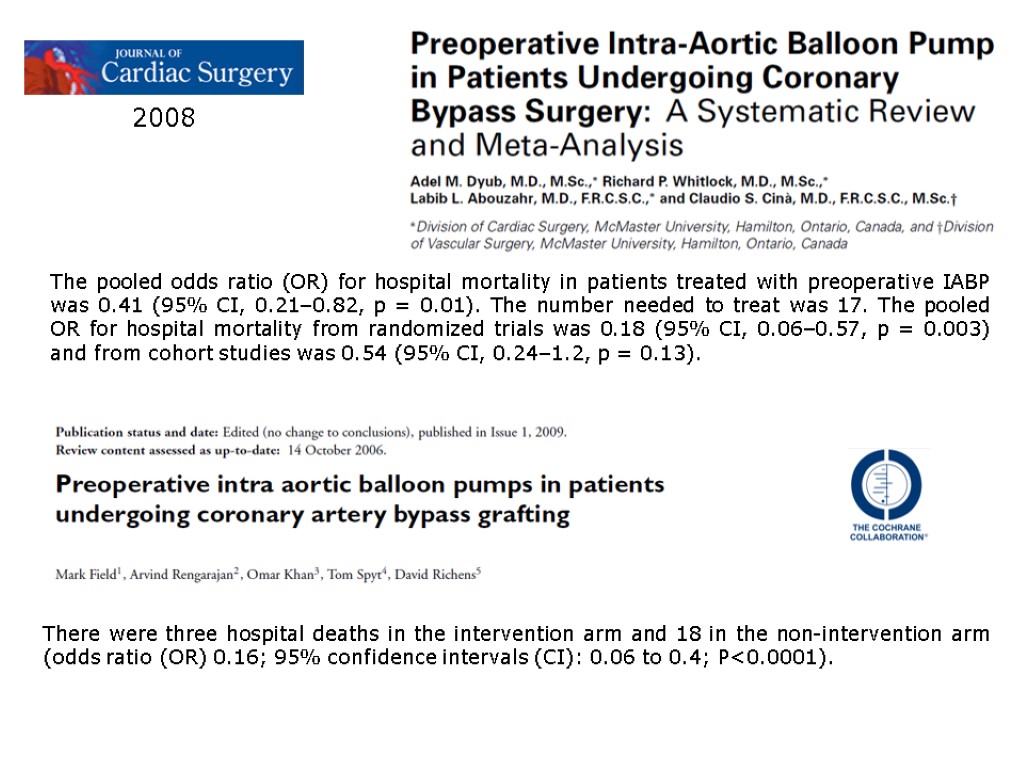
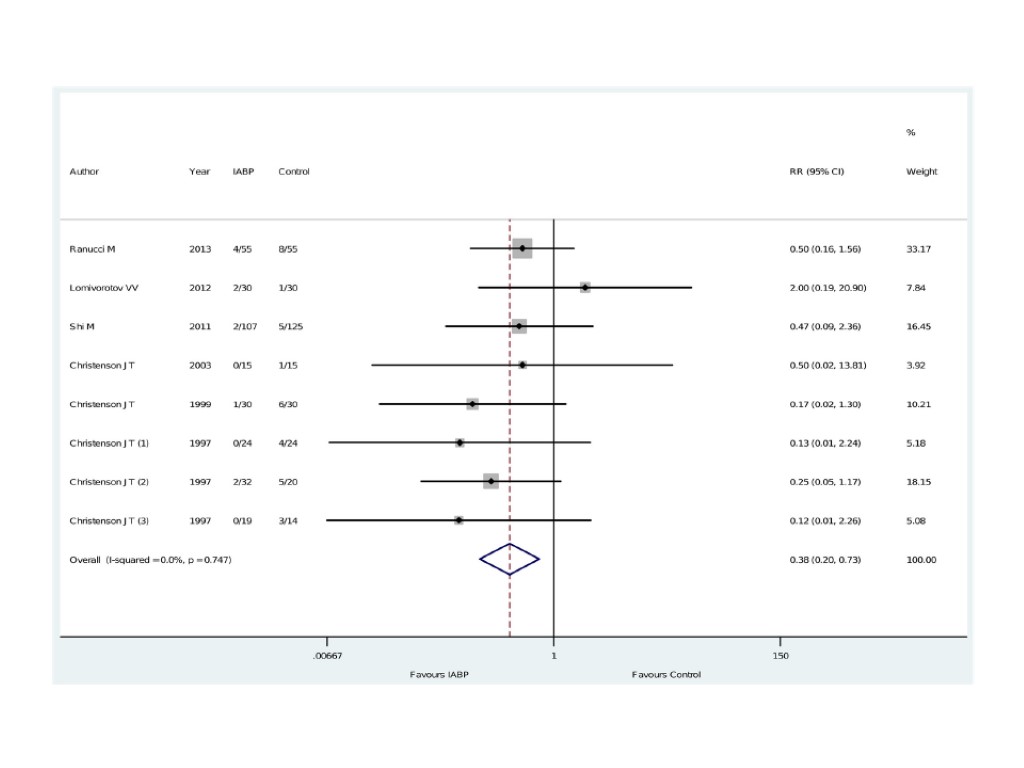
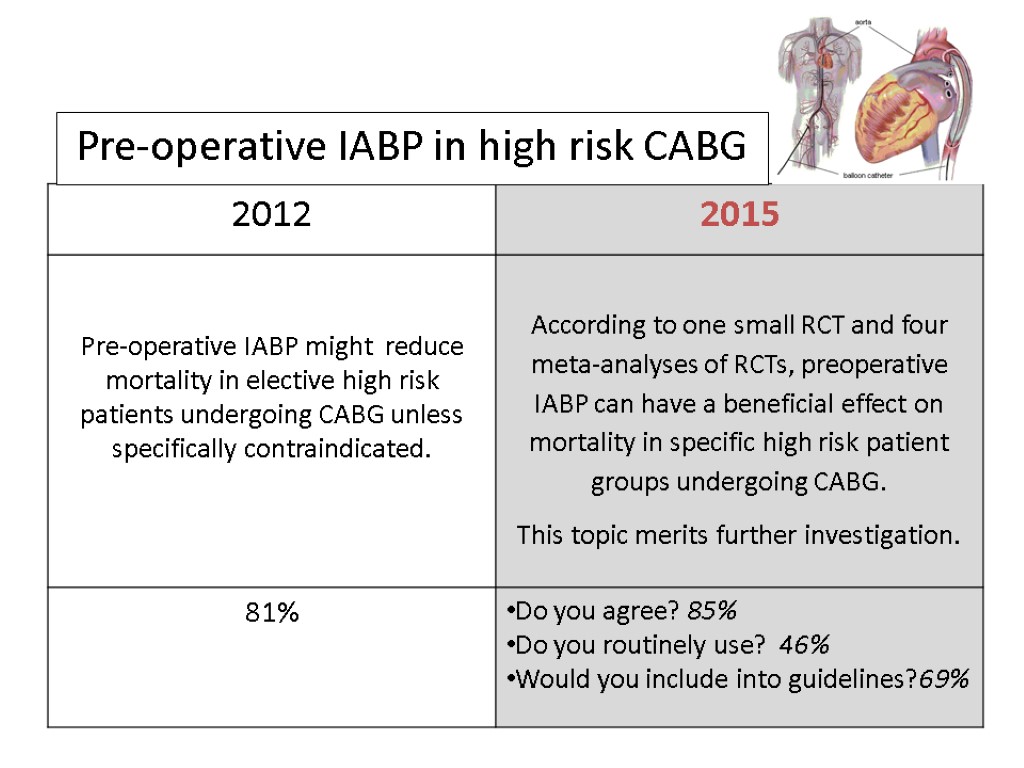
 Pre-operative IABP (IntraAortic Balloon Pump) in high risk CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting)
Pre-operative IABP (IntraAortic Balloon Pump) in high risk CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting)
 2008 The pooled odds ratio (OR) for hospital mortality in patients treated with preoperative IABP was 0.41 (95% CI, 0.21–0.82, p = 0.01). The number needed to treat was 17. The pooled OR for hospital mortality from randomized trials was 0.18 (95% CI, 0.06–0.57, p = 0.003) and from cohort studies was 0.54 (95% CI, 0.24–1.2, p = 0.13). There were three hospital deaths in the intervention arm and 18 in the non-intervention arm (odds ratio (OR) 0.16; 95% confidence intervals (CI): 0.06 to 0.4; P<0.0001).
2008 The pooled odds ratio (OR) for hospital mortality in patients treated with preoperative IABP was 0.41 (95% CI, 0.21–0.82, p = 0.01). The number needed to treat was 17. The pooled OR for hospital mortality from randomized trials was 0.18 (95% CI, 0.06–0.57, p = 0.003) and from cohort studies was 0.54 (95% CI, 0.24–1.2, p = 0.13). There were three hospital deaths in the intervention arm and 18 in the non-intervention arm (odds ratio (OR) 0.16; 95% confidence intervals (CI): 0.06 to 0.4; P<0.0001).





 Pre-operative IABP in high risk CABG
Pre-operative IABP in high risk CABG
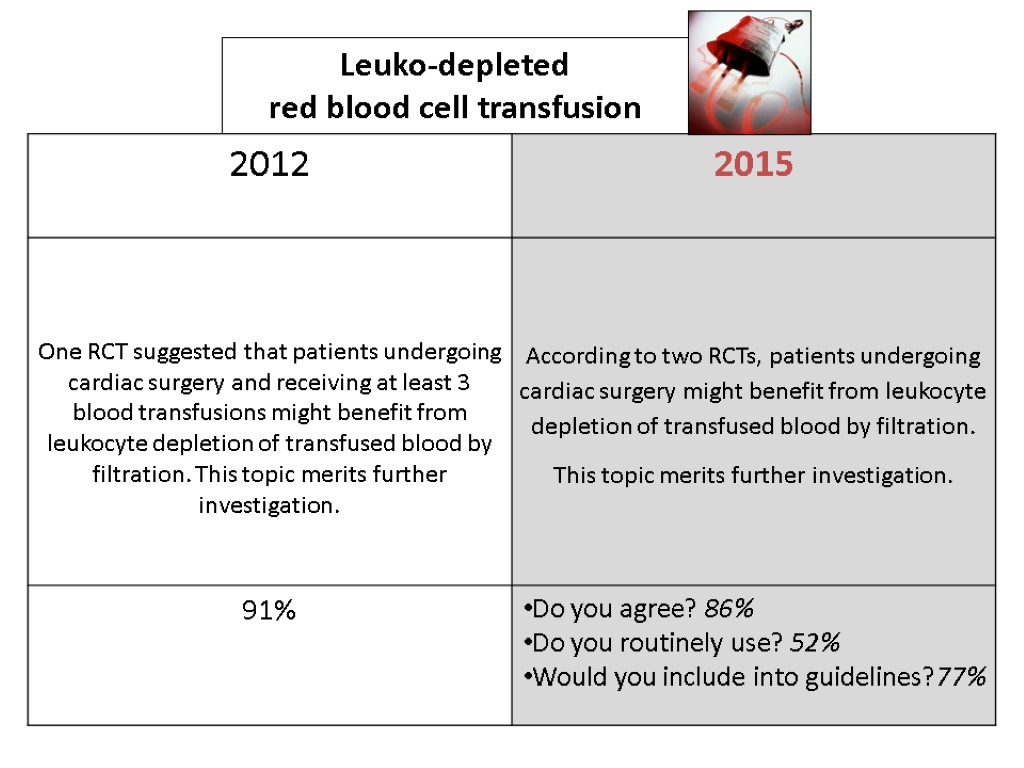
 Leuko-depleted red blood cell transfusion
Leuko-depleted red blood cell transfusion
 Inserisci leucodepletion
Inserisci leucodepletion

 Leuko-depleted red blood cell transfusion
Leuko-depleted red blood cell transfusion
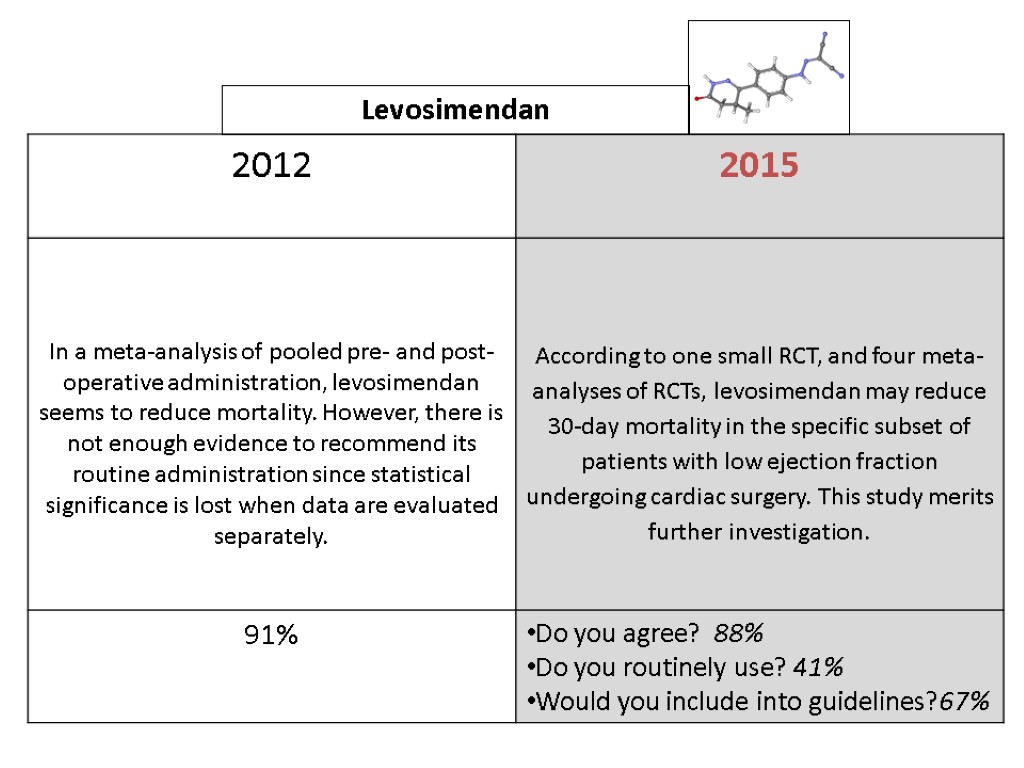
 Levosimendan
Levosimendan
![>February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%] >February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%]](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_85.jpg) February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%] in the levosimendan group v 26/205 [12.7%] in the control arm, odds ratio 0.35 [0.18-0.71], p for effect 0.003, p for heterogeneity 0.22, I2 27.4% with 440 patients included)
February, 2010 Levosimendan was associated with a significant reduction in postoperative mortality (11/235 [4.7%] in the levosimendan group v 26/205 [12.7%] in the control arm, odds ratio 0.35 [0.18-0.71], p for effect 0.003, p for heterogeneity 0.22, I2 27.4% with 440 patients included)




 Levosimendan
Levosimendan


 A special thanks to: HSR – LEVO (CHEETAH) Moscow Clinical Regional Research Institute (Valery Likhvantsev – Moscow) Scientific Research Institute for Complex Issues of Cardiovascular Disease (Evgeny Grigoryev – Kemerovo) Federal Center for Cardiac Surgery (Vadim Pasyuga – Astrakhan) Research Institute of Circulation Pathology (Vladimir Lomivorotov – Novosibirsk)
A special thanks to: HSR – LEVO (CHEETAH) Moscow Clinical Regional Research Institute (Valery Likhvantsev – Moscow) Scientific Research Institute for Complex Issues of Cardiovascular Disease (Evgeny Grigoryev – Kemerovo) Federal Center for Cardiac Surgery (Vadim Pasyuga – Astrakhan) Research Institute of Circulation Pathology (Vladimir Lomivorotov – Novosibirsk)
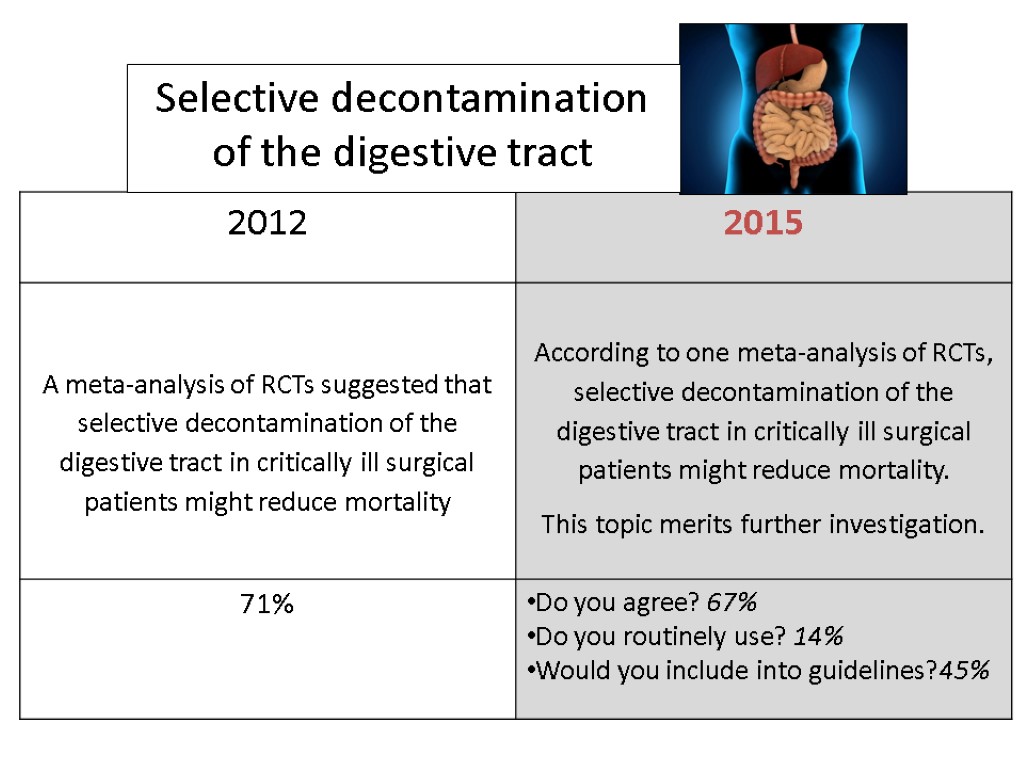
 Selective decontamination of the digestive tract
Selective decontamination of the digestive tract
 Mortality was significantly reduced with the use of selective decontamination of the digestive tract in critically ill surgical patients (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.52-0.93), while no such effect was demonstrated in critically ill medical patients (OR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.71-1.18). Arch Surg. 1999; 134: 170-176
Mortality was significantly reduced with the use of selective decontamination of the digestive tract in critically ill surgical patients (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.52-0.93), while no such effect was demonstrated in critically ill medical patients (OR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.71-1.18). Arch Surg. 1999; 134: 170-176
 Selective decontamination of the digestive tract
Selective decontamination of the digestive tract
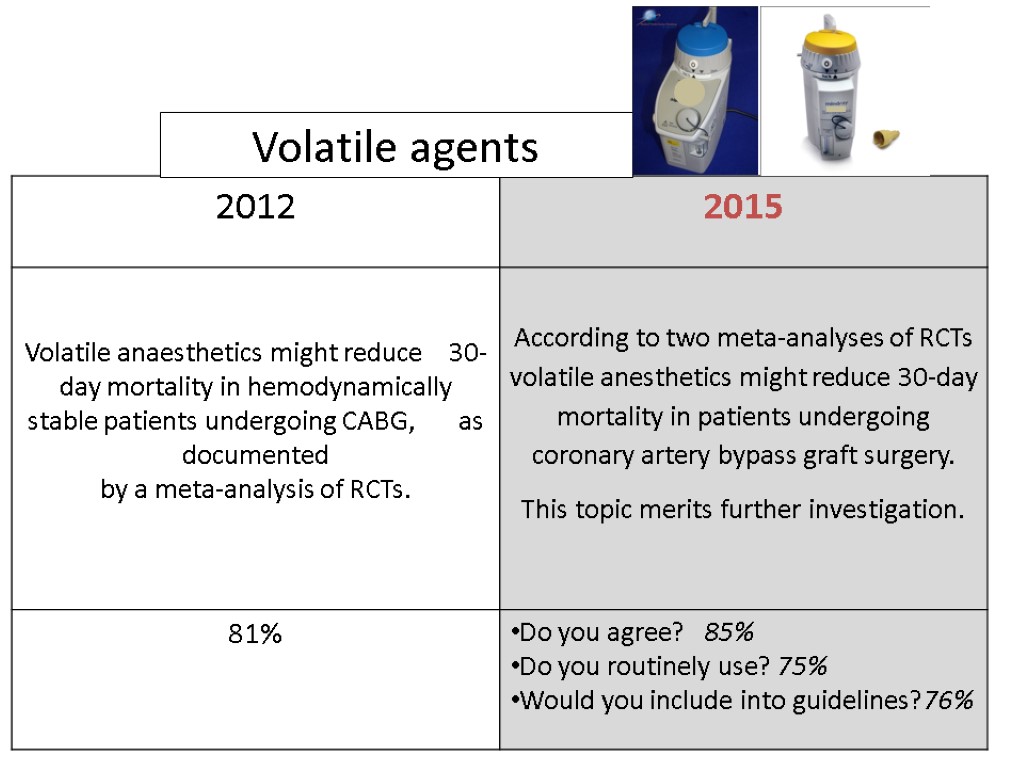
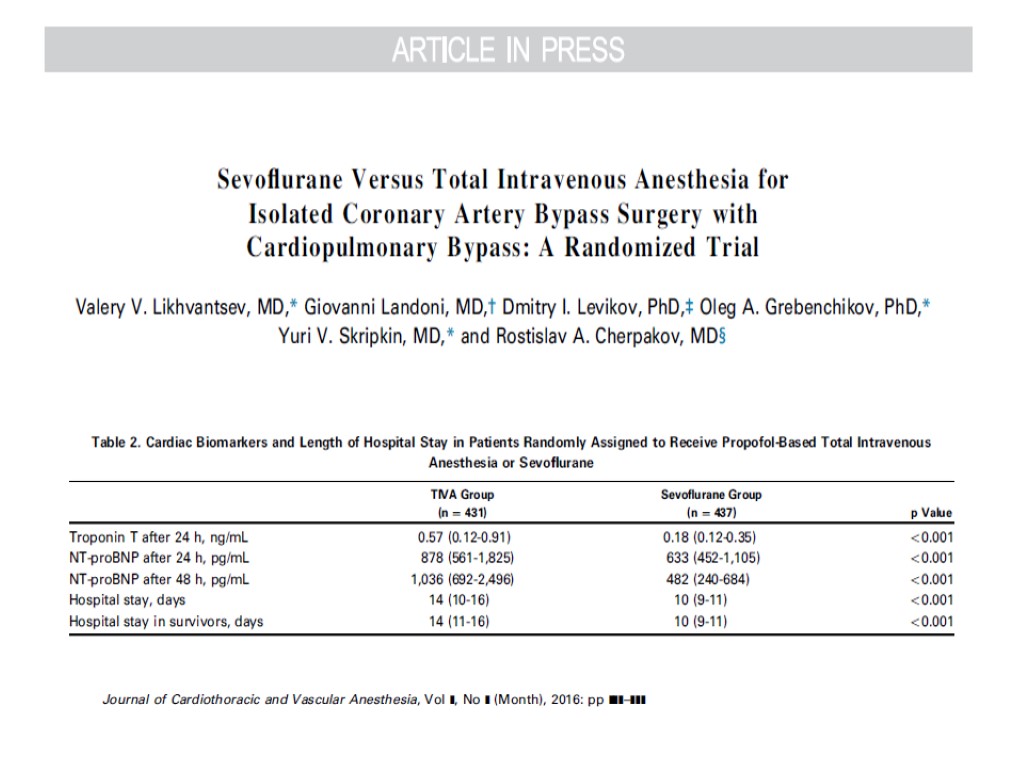
 Volatile agents
Volatile agents
![>Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the >Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_98.jpg) Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the volatile anesthetics group v 45/874 [5.1%] in the control arm, odds ratio [OR] 0.51 [0.32-0.84], p for effect 0.008, and p for heterogeneity 0.77) and mortality (4/977 [0.4%] v 14/872 [1.6%], OR 0.31 [0.12-0.80], p for effect 0.02, and p for heterogeneity 0.88) Volume 21, Issue 4, August 2007, Pages 502–511
Volatile anesthetics were associated with significant reductions of myocardial infarctions (24/979 [2.4%] in the volatile anesthetics group v 45/874 [5.1%] in the control arm, odds ratio [OR] 0.51 [0.32-0.84], p for effect 0.008, and p for heterogeneity 0.77) and mortality (4/977 [0.4%] v 14/872 [1.6%], OR 0.31 [0.12-0.80], p for effect 0.02, and p for heterogeneity 0.88) Volume 21, Issue 4, August 2007, Pages 502–511
 99
99
 Mortality 25/1,994=1.3% v 43/1,648=2.6% NNT=74 OR: 0.51(0.33-0.81) P=0.004
Mortality 25/1,994=1.3% v 43/1,648=2.6% NNT=74 OR: 0.51(0.33-0.81) P=0.004
 Volatile agents
Volatile agents



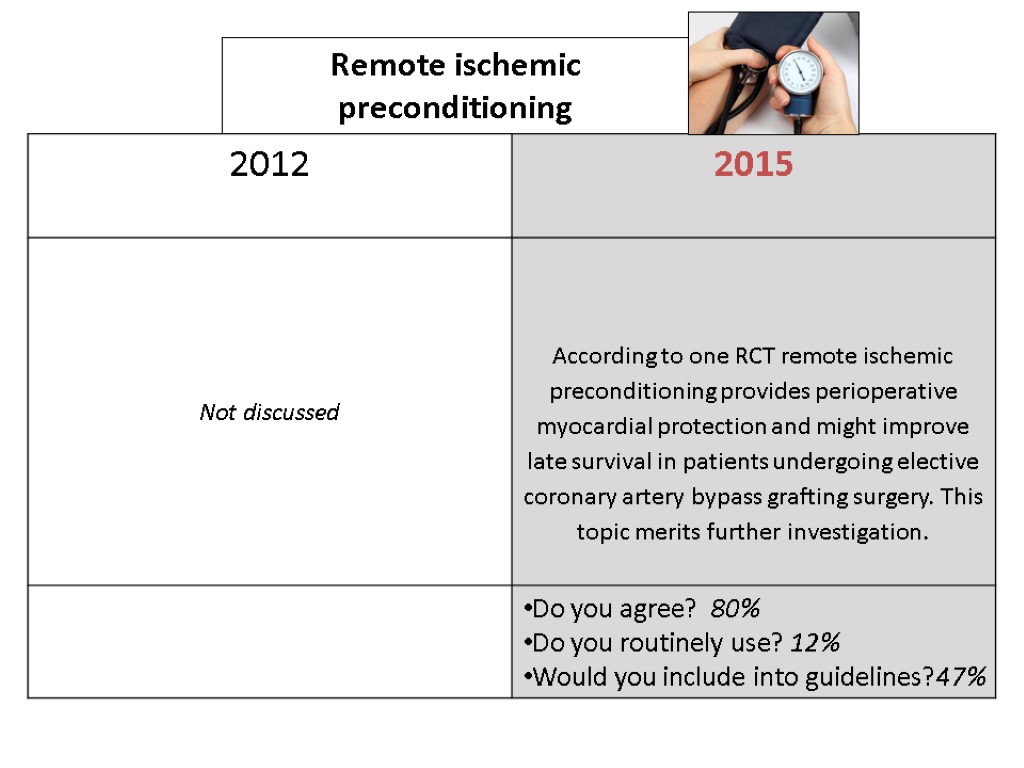
 Remote ischemic preconditioning
Remote ischemic preconditioning


 Remote ischemic preconditioning
Remote ischemic preconditioning
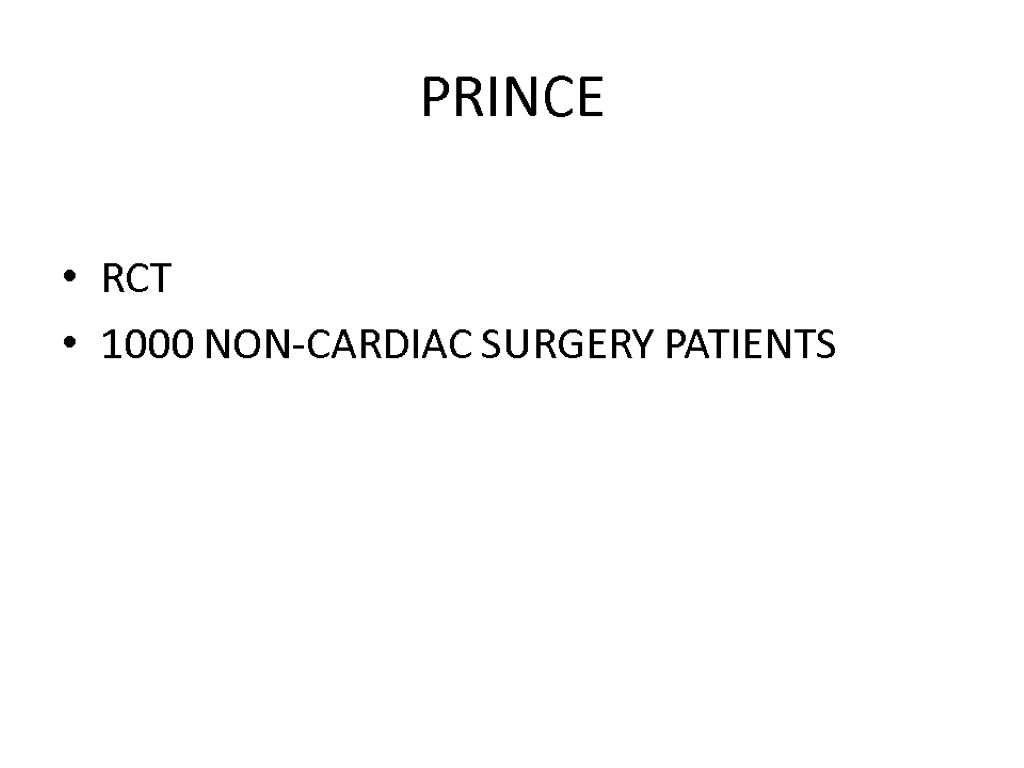
 PRINCE RCT 1000 NON-CARDIAC SURGERY PATIENTS
PRINCE RCT 1000 NON-CARDIAC SURGERY PATIENTS
 MECC (Minimal Extra Corporeal Circulation) in cardiac surgery
MECC (Minimal Extra Corporeal Circulation) in cardiac surgery

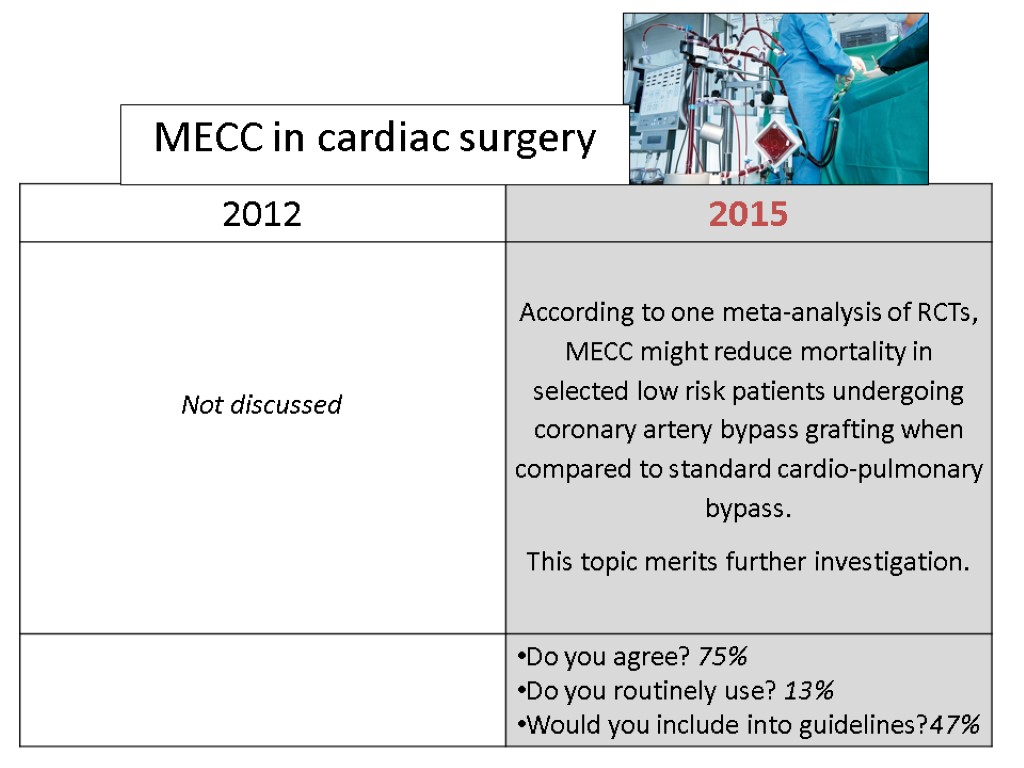
 MECC in cardiac surgery
MECC in cardiac surgery
 Interventions increasing postoperative mortality
Interventions increasing postoperative mortality
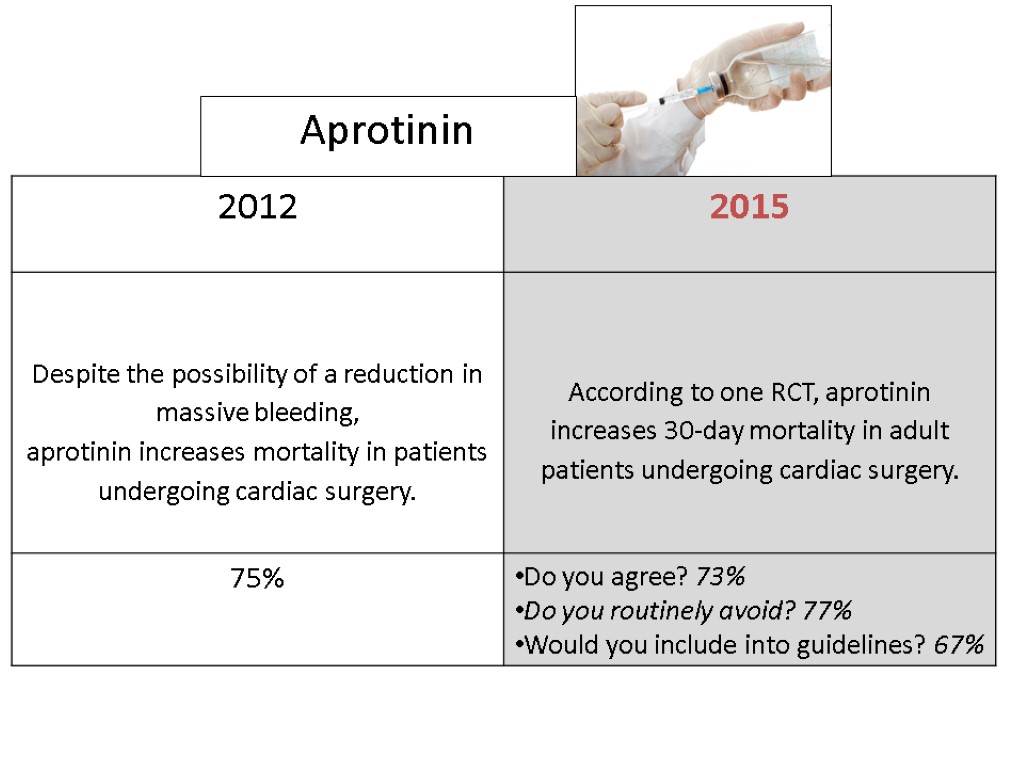
 Aprotinin
Aprotinin
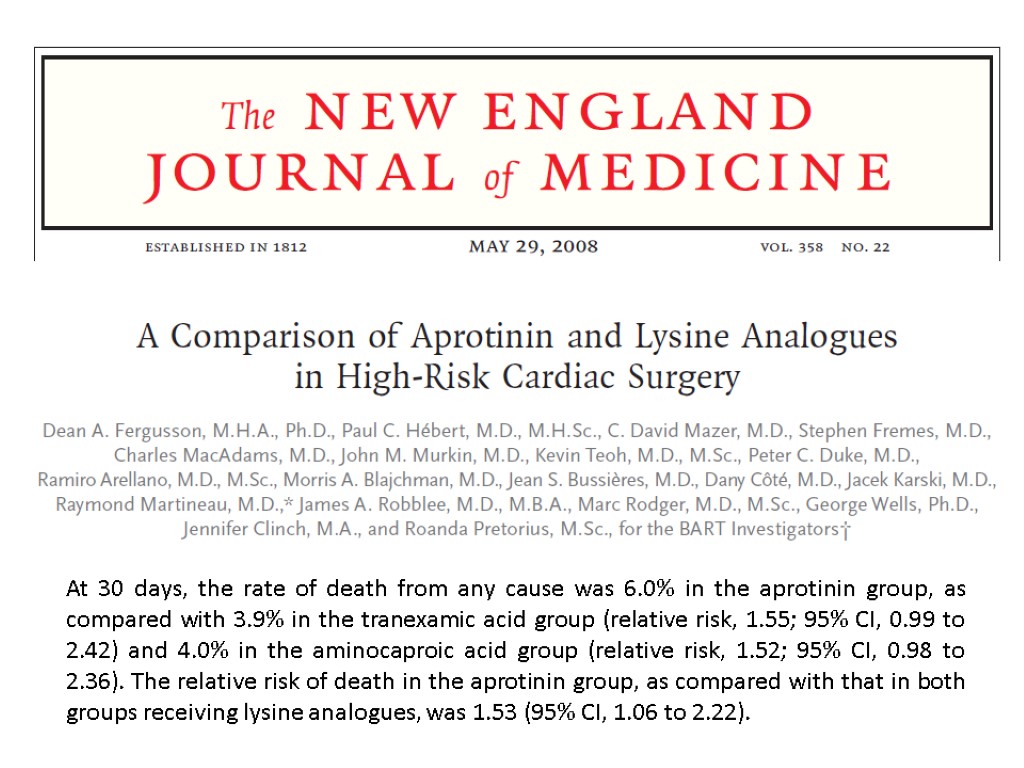
 At 30 days, the rate of death from any cause was 6.0% in the aprotinin group, as compared with 3.9% in the tranexamic acid group (relative risk, 1.55; 95% CI, 0.99 to 2.42) and 4.0% in the aminocaproic acid group (relative risk, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.98 to 2.36). The relative risk of death in the aprotinin group, as compared with that in both groups receiving lysine analogues, was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.06 to 2.22).
At 30 days, the rate of death from any cause was 6.0% in the aprotinin group, as compared with 3.9% in the tranexamic acid group (relative risk, 1.55; 95% CI, 0.99 to 2.42) and 4.0% in the aminocaproic acid group (relative risk, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.98 to 2.36). The relative risk of death in the aprotinin group, as compared with that in both groups receiving lysine analogues, was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.06 to 2.22).
 Aprotinin
Aprotinin
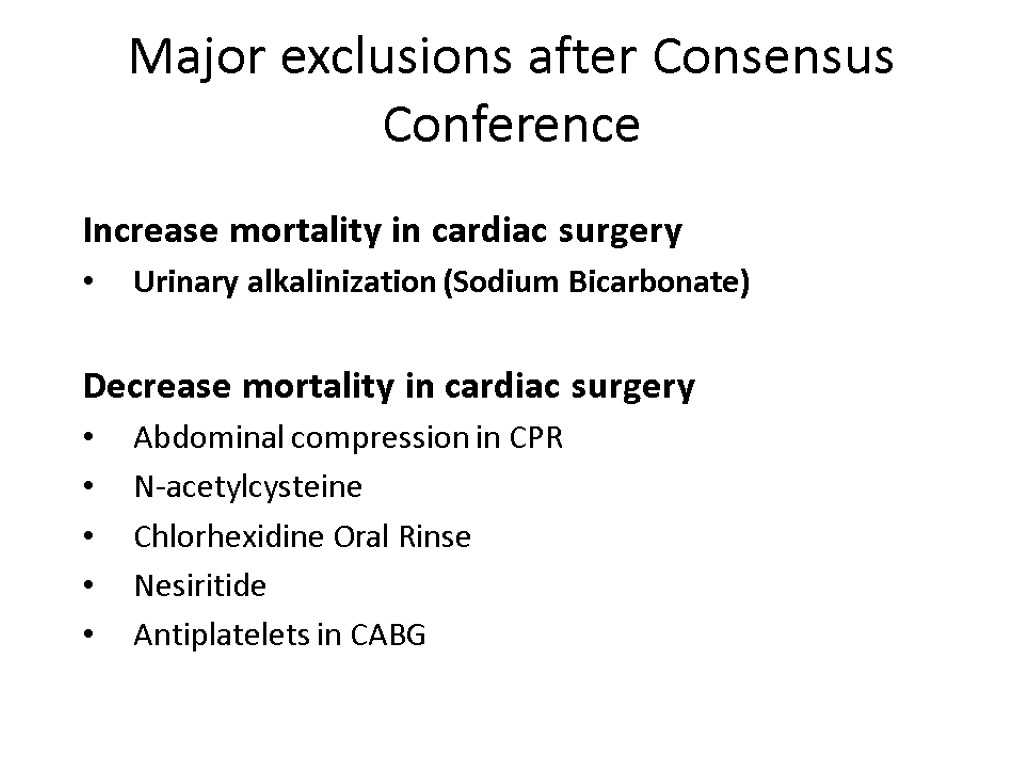
 Major exclusions after Consensus Conference Increase mortality in cardiac surgery Urinary alkalinization (Sodium Bicarbonate) Decrease mortality in cardiac surgery Abdominal compression in CPR N-acetylcysteine Chlorhexidine Oral Rinse Nesiritide Antiplatelets in CABG
Major exclusions after Consensus Conference Increase mortality in cardiac surgery Urinary alkalinization (Sodium Bicarbonate) Decrease mortality in cardiac surgery Abdominal compression in CPR N-acetylcysteine Chlorhexidine Oral Rinse Nesiritide Antiplatelets in CABG
 118
118
 NIV (non-invasive ventilation) in general wards. MET (medical emergency team). There are no hierarchies in the activation of emergency team. ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery), a multimodal perioperative care pathway designed to achieve early recovery for patients undergoing major surgery www.erassociety.org Several international and national multicenter randomized controlled trials (mRCT) are ongoing in the perioperative setting International consensus conferences were hold on a yearly basis starting from 2010 focusing on mortality reduction High volume Hospital. We perform approximately 30,000 interventions per year with highly specialized surgeons Sepsis management. A dedicated team of physicians and nurses regularly meets and updates internal guidelines on the management of septic patients. ICU (Intensive Care Unit) is readily available for patients with a complicated intraoperative course. The only patients that routinely go to the ICU are those undergoing thoracoabdominal aneurismectomy surgery, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery and pneumonectomy and those with an ASA≥4. A ECMO (ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation). An ECMO team is always available Acute Pain Service (APS). There is a 24/7 anesthesiologist dedicated team Teaching university hospital for medicine and nursing. Safety operating room check-lists have been implemented several years ago and are routinely applied Simulation and refresher courses are continuously performed on most of the above topics either in Italian, for Hospital personnel or in English, for visitors http://www.hsr.it/.
NIV (non-invasive ventilation) in general wards. MET (medical emergency team). There are no hierarchies in the activation of emergency team. ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery), a multimodal perioperative care pathway designed to achieve early recovery for patients undergoing major surgery www.erassociety.org Several international and national multicenter randomized controlled trials (mRCT) are ongoing in the perioperative setting International consensus conferences were hold on a yearly basis starting from 2010 focusing on mortality reduction High volume Hospital. We perform approximately 30,000 interventions per year with highly specialized surgeons Sepsis management. A dedicated team of physicians and nurses regularly meets and updates internal guidelines on the management of septic patients. ICU (Intensive Care Unit) is readily available for patients with a complicated intraoperative course. The only patients that routinely go to the ICU are those undergoing thoracoabdominal aneurismectomy surgery, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery and pneumonectomy and those with an ASA≥4. A ECMO (ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation). An ECMO team is always available Acute Pain Service (APS). There is a 24/7 anesthesiologist dedicated team Teaching university hospital for medicine and nursing. Safety operating room check-lists have been implemented several years ago and are routinely applied Simulation and refresher courses are continuously performed on most of the above topics either in Italian, for Hospital personnel or in English, for visitors http://www.hsr.it/.
 A) Ability to recognize early and manage complications. B) Patients at risk are monitored by telemetric devices in general wards. C) Staff adequate in number and competency. D) Debriefing E) Specialized anesthesiologists. The hospital provides a full range of ultra-specialized anesthesia services including general, loco-regional, neuro, cardiac, obstetrical and specialized ambulatory surgery. F) Modern and technologically advanced operatory rooms. G) Anesthesiologist as perioperative leader. H) Presence of dedicated anesthesia nurse. I) Patients follow perioperative standardized clinical pathways
A) Ability to recognize early and manage complications. B) Patients at risk are monitored by telemetric devices in general wards. C) Staff adequate in number and competency. D) Debriefing E) Specialized anesthesiologists. The hospital provides a full range of ultra-specialized anesthesia services including general, loco-regional, neuro, cardiac, obstetrical and specialized ambulatory surgery. F) Modern and technologically advanced operatory rooms. G) Anesthesiologist as perioperative leader. H) Presence of dedicated anesthesia nurse. I) Patients follow perioperative standardized clinical pathways
 www.democracybasedmedicine.org NON-CARDIAC SURGERY CARDIAC SURGERY Liberal transfusion Non Invasive Ventilation Statins Tranexamic acid Hemodynamic optimization Neuraxial anesthesia Beta blockers Insulin Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Leuco-depleted RBC transfusion Levosimendan Selective decontamination of the digestive tract Volatile anesthetics Remote ischemic preconditioning MECC Aprotinin
www.democracybasedmedicine.org NON-CARDIAC SURGERY CARDIAC SURGERY Liberal transfusion Non Invasive Ventilation Statins Tranexamic acid Hemodynamic optimization Neuraxial anesthesia Beta blockers Insulin Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Leuco-depleted RBC transfusion Levosimendan Selective decontamination of the digestive tract Volatile anesthetics Remote ischemic preconditioning MECC Aprotinin
 NEOTON
NEOTON

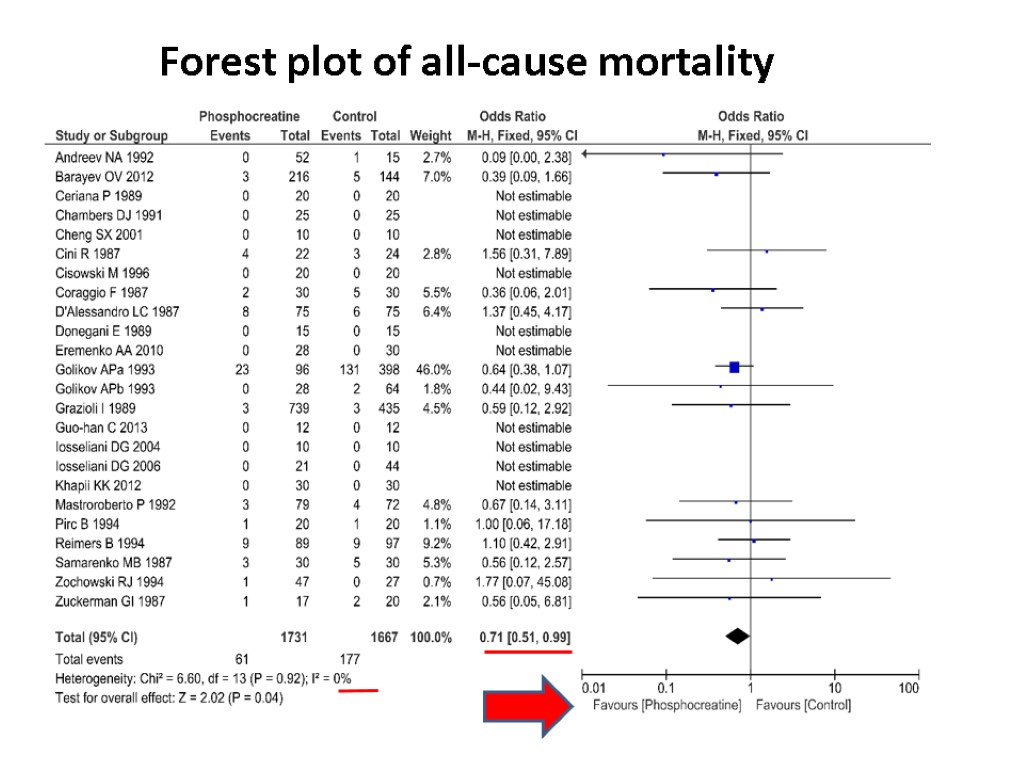
 Forest plot of all-cause mortality
Forest plot of all-cause mortality
![>All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients >All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients](https://present5.com/customparser/12536230_438059541 --- 1_landoni_1_mortality_reduction_moscow_2016.ppt/slide_125.jpg) All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.51-0.99, P=0.04, I2=0% 3,398 patients and 23 trials included
All-cause mortality Phosphocreatine versus placebo or standard treatment 61/1731 [3.5%] vs. 177/1667 [10.6%] patients OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.51-0.99, P=0.04, I2=0% 3,398 patients and 23 trials included
 PubMed/Medline, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Central Register, Google Scholar phosphocreatine, phosphorylcreatine, creatine phosphate, neoton, randomised, controlled trial Keywords Search up to November 1, 2015
PubMed/Medline, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Central Register, Google Scholar phosphocreatine, phosphorylcreatine, creatine phosphate, neoton, randomised, controlled trial Keywords Search up to November 1, 2015
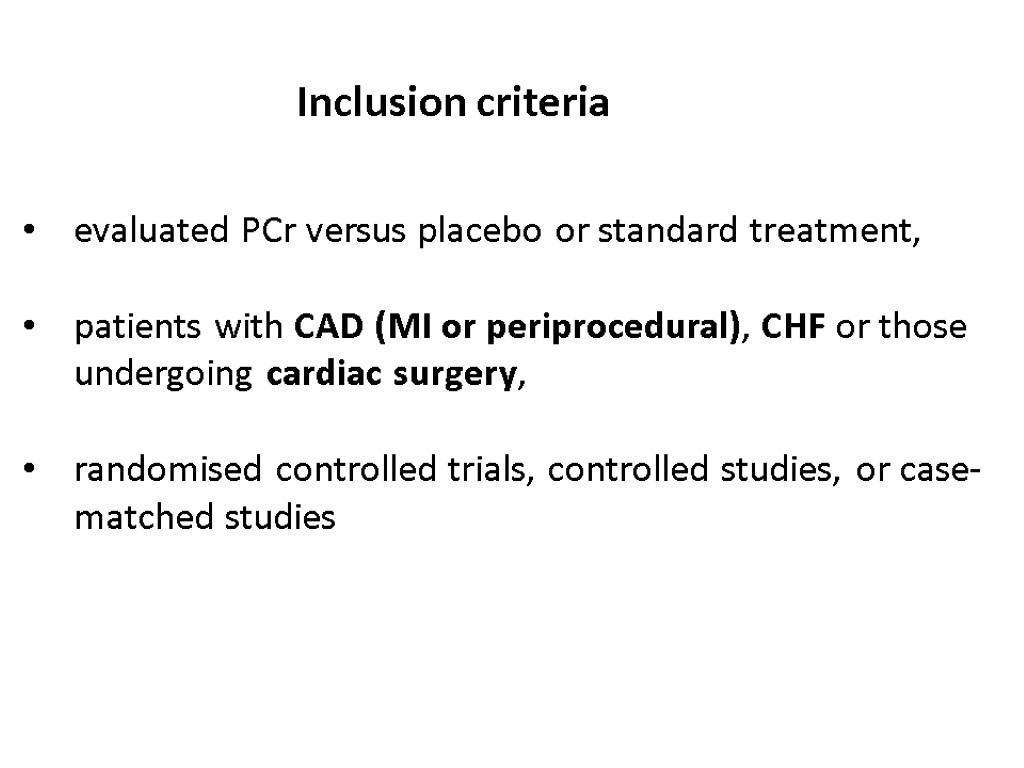
 Inclusion criteria evaluated PCr versus placebo or standard treatment, patients with CAD (MI or periprocedural), CHF or those undergoing cardiac surgery, randomised controlled trials, controlled studies, or case-matched studies
Inclusion criteria evaluated PCr versus placebo or standard treatment, patients with CAD (MI or periprocedural), CHF or those undergoing cardiac surgery, randomised controlled trials, controlled studies, or case-matched studies
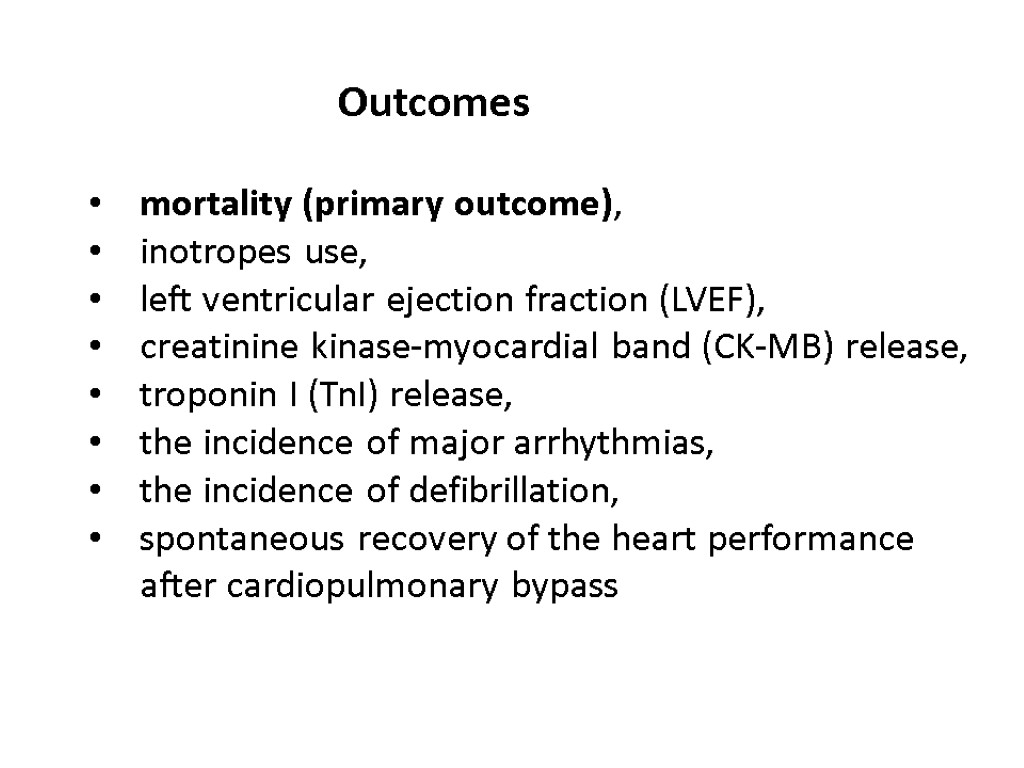
 mortality (primary outcome), inotropes use, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), creatinine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB) release, troponin I (TnI) release, the incidence of major arrhythmias, the incidence of defibrillation, spontaneous recovery of the heart performance after cardiopulmonary bypass Outcomes
mortality (primary outcome), inotropes use, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), creatinine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB) release, troponin I (TnI) release, the incidence of major arrhythmias, the incidence of defibrillation, spontaneous recovery of the heart performance after cardiopulmonary bypass Outcomes
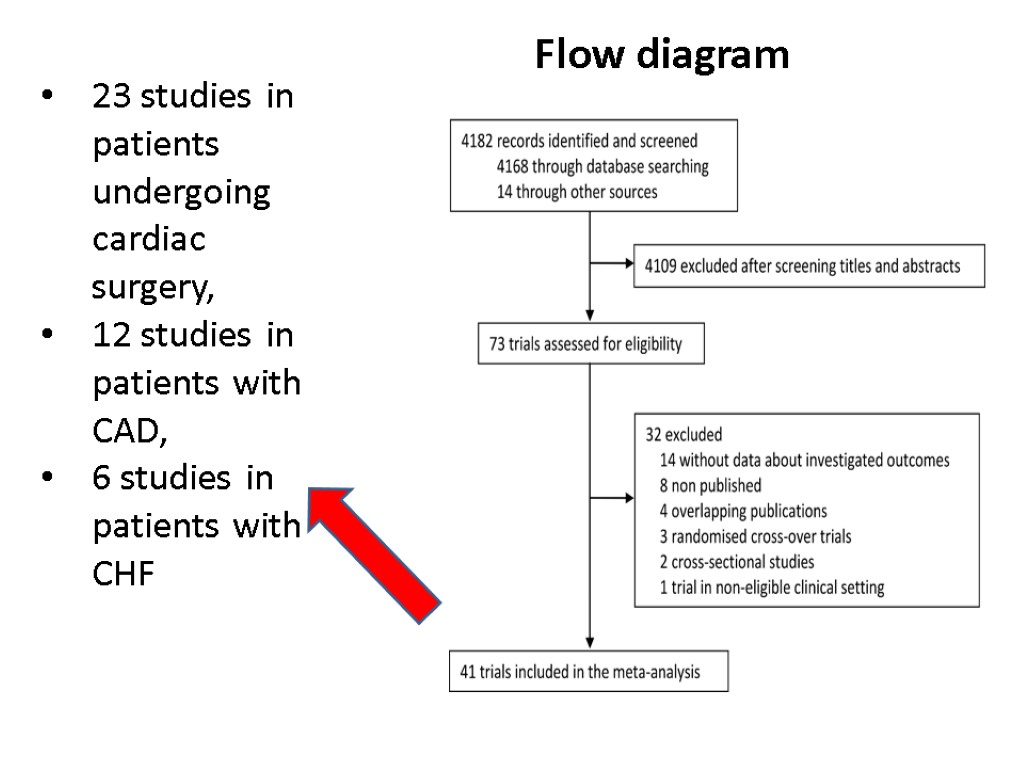
 Flow diagram 23 studies in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, 12 studies in patients with CAD, 6 studies in patients with CHF
Flow diagram 23 studies in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, 12 studies in patients with CAD, 6 studies in patients with CHF
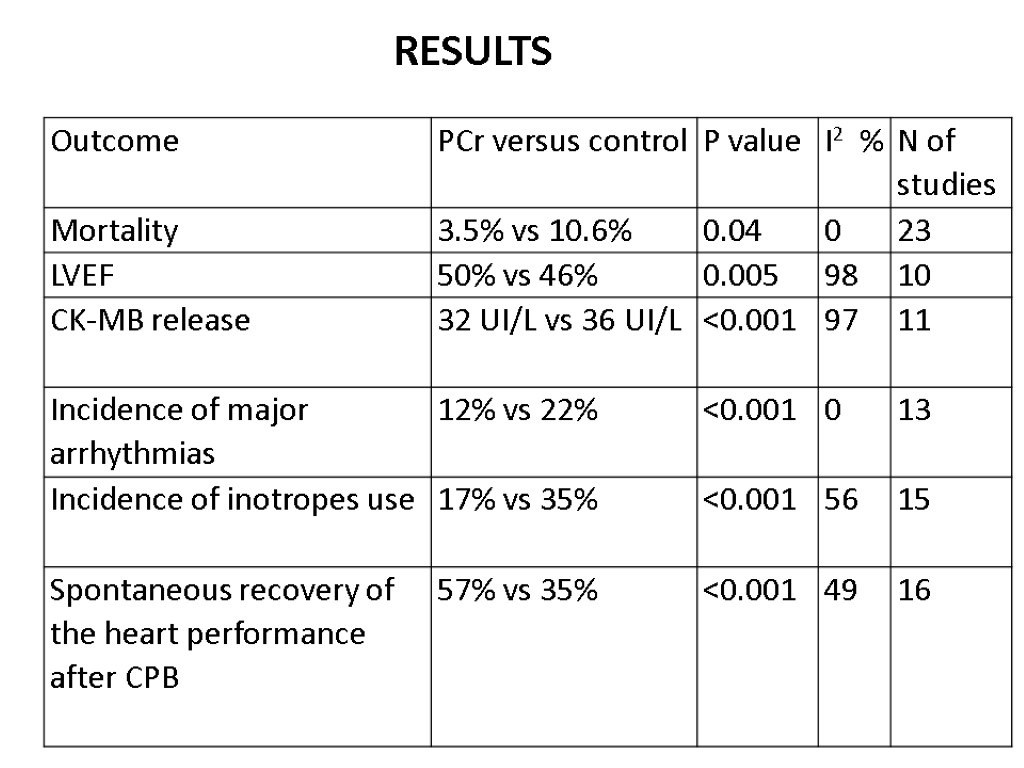
 RESULTS
RESULTS
 Phosphocreatine dosage Intravenously on average 4 g OR Added to plegia solution to provide concentration=10 mmol/L (2.5 g / L)
Phosphocreatine dosage Intravenously on average 4 g OR Added to plegia solution to provide concentration=10 mmol/L (2.5 g / L)
 Phosphocreatine is like
Phosphocreatine is like
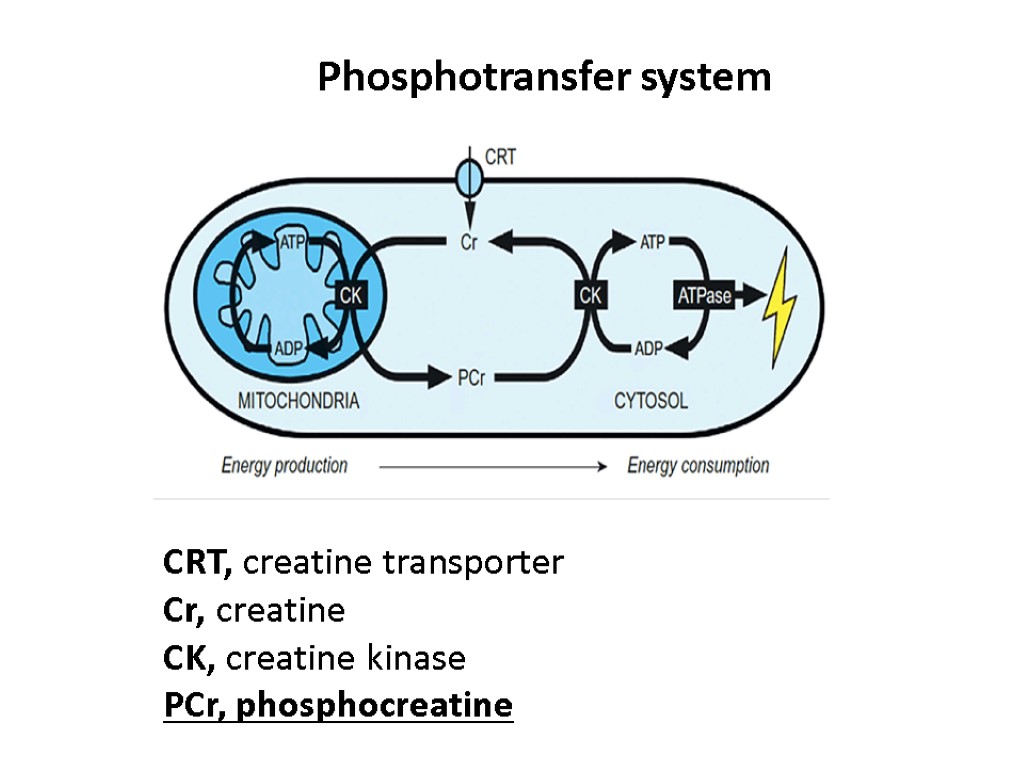
 Phosphotransfer system CRT, creatine transporter Cr, creatine CK, creatine kinase PCr, phosphocreatine
Phosphotransfer system CRT, creatine transporter Cr, creatine CK, creatine kinase PCr, phosphocreatine
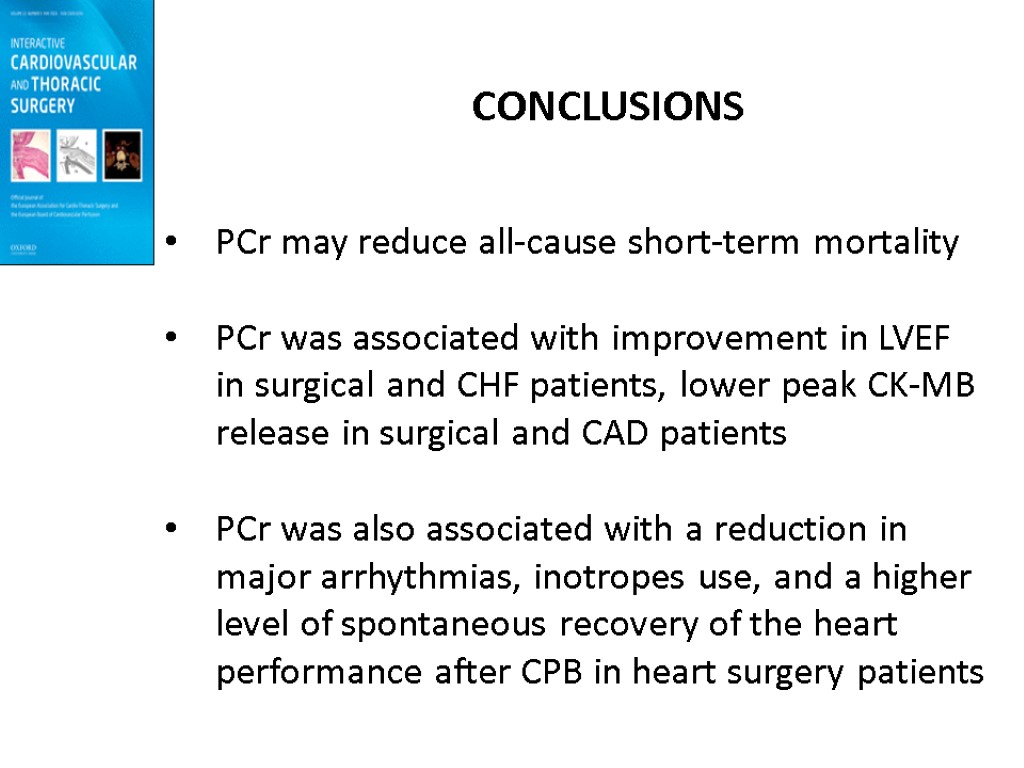
 CONCLUSIONS PCr may reduce all-cause short-term mortality PCr was associated with improvement in LVEF in surgical and CHF patients, lower peak CK-MB release in surgical and CAD patients PCr was also associated with a reduction in major arrhythmias, inotropes use, and a higher level of spontaneous recovery of the heart performance after CPB in heart surgery patients
CONCLUSIONS PCr may reduce all-cause short-term mortality PCr was associated with improvement in LVEF in surgical and CHF patients, lower peak CK-MB release in surgical and CAD patients PCr was also associated with a reduction in major arrhythmias, inotropes use, and a higher level of spontaneous recovery of the heart performance after CPB in heart surgery patients
 www.linkedin.com
www.linkedin.com
 Origin of Phosphocreatine
Origin of Phosphocreatine
 Phosphocreatine Pharmacological Research… Inventor: Ettore Strumia, MD Medical Pathology and Clinical Methodology, University of Turin, Italy Medical Director of Schiapparelli Pharmaceutics Early 80s
Phosphocreatine Pharmacological Research… Inventor: Ettore Strumia, MD Medical Pathology and Clinical Methodology, University of Turin, Italy Medical Director of Schiapparelli Pharmaceutics Early 80s
 Estonian Institute of Chemical Physics and Biophysics, research scientist 2007 until today Institute of Cybernetics, Academy of Sciences of Estonia, research, 1970-1971 Moscow University, department of Chemistry, junior research scientist, 1971-1972 Moscow Cardiocenter, senior research scientist, 1972-1981 Moscow Cardiocenter, head of the laboratory of Bioenergetics, 1981-1993 Prof. Valdur Saks Original Clinical Research… Early 80s
Estonian Institute of Chemical Physics and Biophysics, research scientist 2007 until today Institute of Cybernetics, Academy of Sciences of Estonia, research, 1970-1971 Moscow University, department of Chemistry, junior research scientist, 1971-1972 Moscow Cardiocenter, senior research scientist, 1972-1981 Moscow Cardiocenter, head of the laboratory of Bioenergetics, 1981-1993 Prof. Valdur Saks Original Clinical Research… Early 80s
 Dr. Khapiy K.K.
Dr. Khapiy K.K.
 Dr. Iosseliani D.G.
Dr. Iosseliani D.G.
 Dr. Ruda M.Y.
Dr. Ruda M.Y.
 Dr. Eremenko A.A.
Dr. Eremenko A.A.
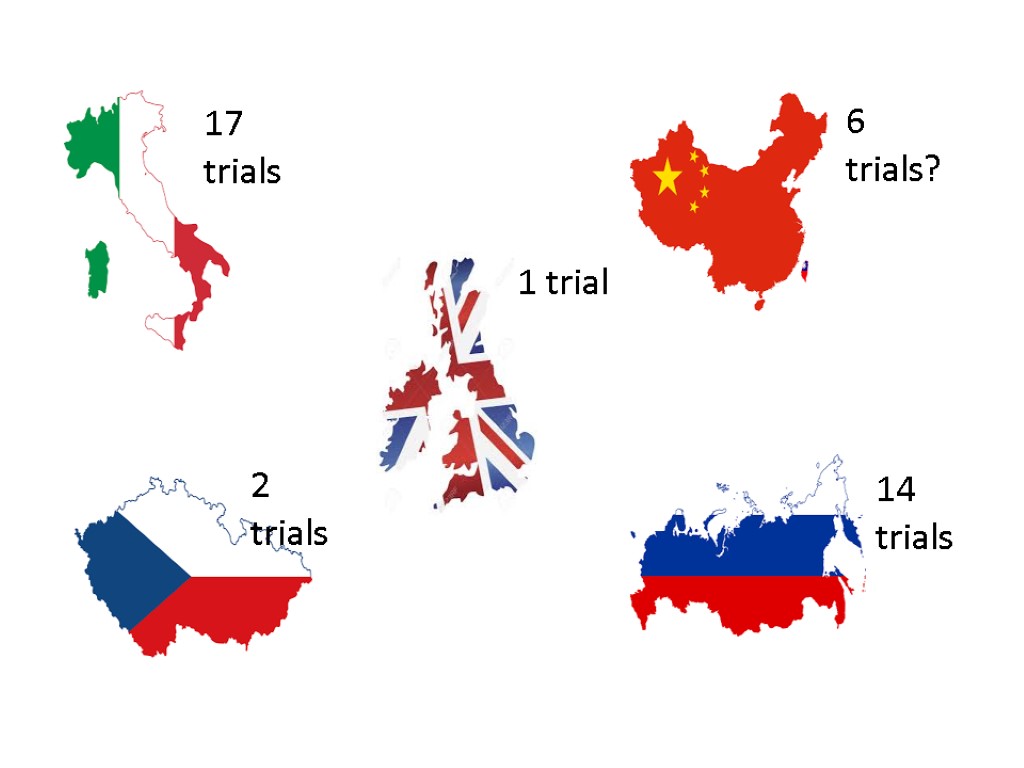
 17 trials 1 trial 6 trials? 2 trials 14 trials
17 trials 1 trial 6 trials? 2 trials 14 trials
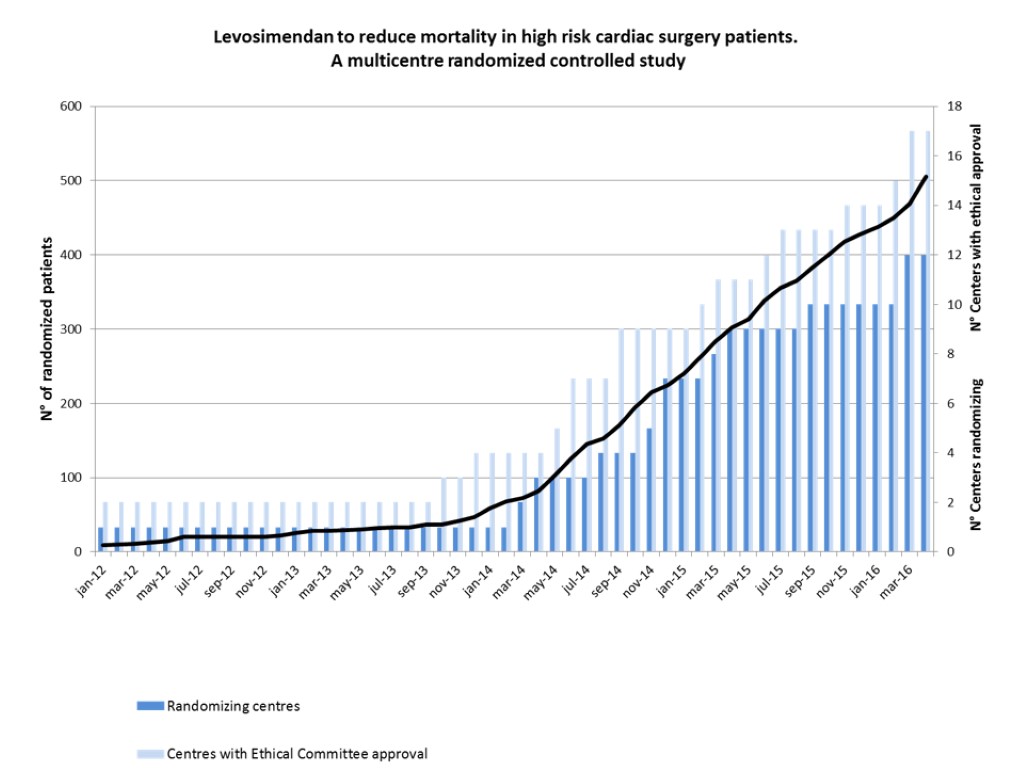
 Nearest Future PRISE trial Myocardial protection with Phosphocreatine in high-RIsk cardiac SurgEry patients: a single-center randomised double-blind placebo-controlled exploratory pilot clinical trial NCT02757443
Nearest Future PRISE trial Myocardial protection with Phosphocreatine in high-RIsk cardiac SurgEry patients: a single-center randomised double-blind placebo-controlled exploratory pilot clinical trial NCT02757443

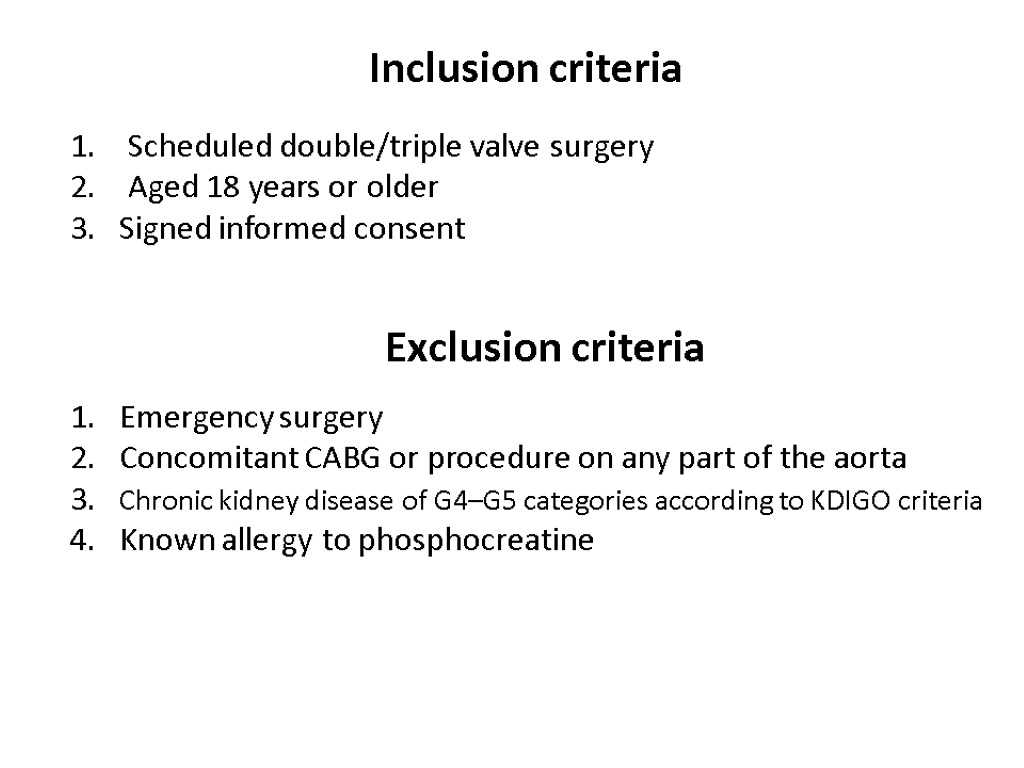
 Inclusion criteria Scheduled double/triple valve surgery Aged 18 years or older 3. Signed informed consent Exclusion criteria 1. Emergency surgery 2. Concomitant CABG or procedure on any part of the aorta 3. Chronic kidney disease of G4–G5 categories according to KDIGO criteria 4. Known allergy to phosphocreatine
Inclusion criteria Scheduled double/triple valve surgery Aged 18 years or older 3. Signed informed consent Exclusion criteria 1. Emergency surgery 2. Concomitant CABG or procedure on any part of the aorta 3. Chronic kidney disease of G4–G5 categories according to KDIGO criteria 4. Known allergy to phosphocreatine
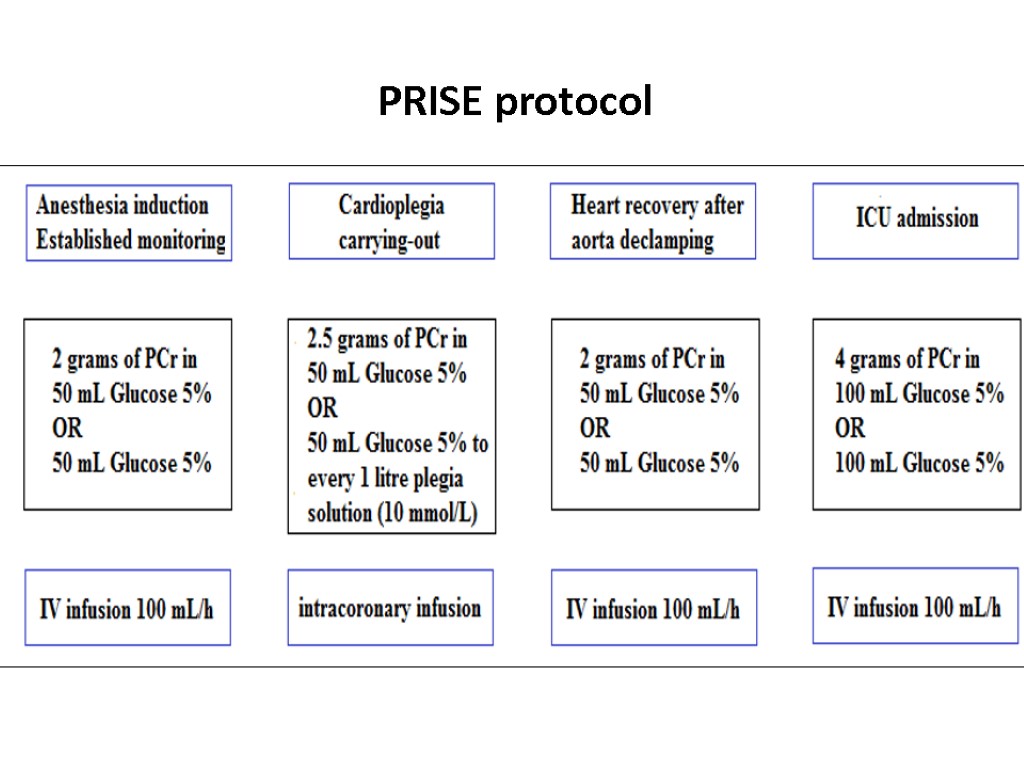
 PRISE protocol
PRISE protocol
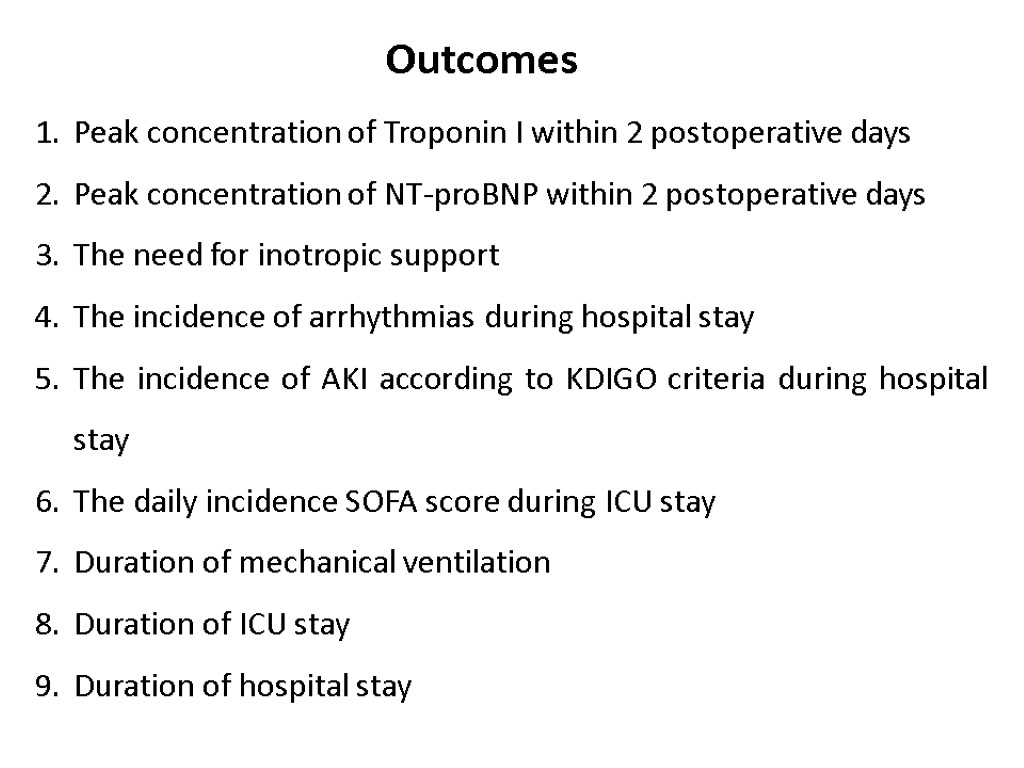
 Peak concentration of Troponin I within 2 postoperative days Peak concentration of NT-proBNP within 2 postoperative days The need for inotropic support The incidence of arrhythmias during hospital stay The incidence of AKI according to KDIGO criteria during hospital stay The daily incidence SOFA score during ICU stay Duration of mechanical ventilation Duration of ICU stay Duration of hospital stay Outcomes
Peak concentration of Troponin I within 2 postoperative days Peak concentration of NT-proBNP within 2 postoperative days The need for inotropic support The incidence of arrhythmias during hospital stay The incidence of AKI according to KDIGO criteria during hospital stay The daily incidence SOFA score during ICU stay Duration of mechanical ventilation Duration of ICU stay Duration of hospital stay Outcomes
 [email protected] To receive the power point of the presentation To receive the pdf of the cited manuscripts
[email protected] To receive the power point of the presentation To receive the pdf of the cited manuscripts
 TAKE HOME MESSAGE There are drugs/techniques/strategies that might reduce postoperative mortality. It is worth knowing them and studying them. [email protected] www.democracybasedmedicine.org
TAKE HOME MESSAGE There are drugs/techniques/strategies that might reduce postoperative mortality. It is worth knowing them and studying them. [email protected] www.democracybasedmedicine.org

