08b5f312d73793530d8953c25e5b2129.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

GILDED AGE POLITICS Unit VB AP United States History

Third Party System (1860 -1896) ► Politics § Spoils system dominated the early period § Electorate ► Strong loyalty and intense interest § Regional campaigning ► Economics § Laissez-faire policies § “Business ran politics and politics was a branch of business. ”

Third Party System (1860 -1896) ► Democrats ► Republicans § Coalition ► White Southerners, Catholics, Lutherans, Jews, Immigrants ► States’ rights; laissez-faire § Bourbon Democrats ► Pro-business Democrats § Laissez-faire § Against protectionism ► Supported civil service reforms § Redeemer Democrats ► Southern Democrats return after Compromise of 1877 ► Business, upper-class, northern WASPs, reformers, blacks, scalawags, carpetbaggers ► Pro-business; tariffs; protectionism § Stalwarts ► Preserve spoils system and machine politics § Half-Breeds ► Pursued civil service reform § Mugwumps ► Independents corrupt GOP discouraged with

Third Party System (1860 -1896) ► Minor Parties § Greenback Party ►Wanted to continue paper currency policies § Prohibition Party ►Pursued policies to outlaw alcohol § Populist Party ►Discontent among farmers led to populism ►Bimetallism and progressive policies

Rutherford B. Hayes (R) (1877 -1881) ► Removed federal troops from the South § Attempted to pursue racial equality ► Great Railroad Strike of 1877 § Ordered federal troops to settle labor strikers ► Civil service reform § Promoted meritocracy in federal government
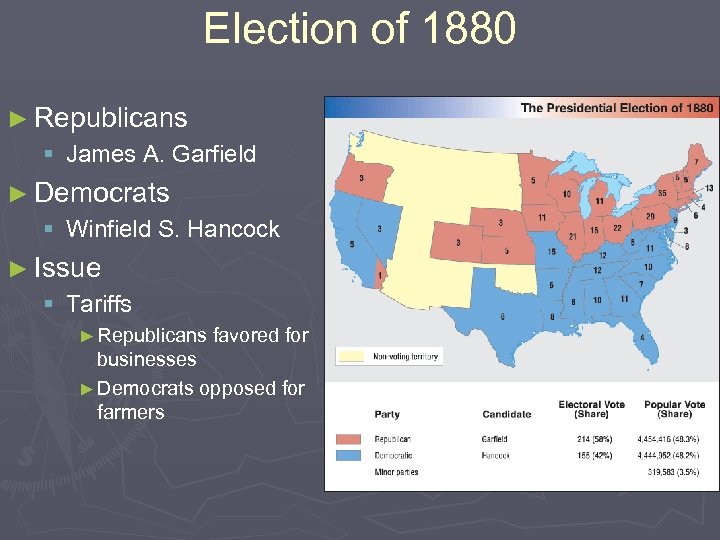
Election of 1880 ► Republicans § James A. Garfield ► Democrats § Winfield S. Hancock ► Issue § Tariffs ► Republicans favored for businesses ► Democrats opposed for farmers

James A. Garfield (R) (1881) ► Challenged political machines, spoils system, and senatorial courtesy ► Assassination § July 2, 1881 § Charles J. Guiteau ► “a disgruntled office-seeker” ► Death § September 19, 1881 ► Chester A. Arthur assumes presidency

Civil Service Reform ► Patronage/Spoils System dominated political appointments since Jackson ► Corruption during Grant administration called for reform § Stalwarts ► Supported machine politics and spoils system ► Roscoe Conkling § Half-breeds ► Pursued civil service reform ► James G. Blaine ► Garfield’s assassination ► Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act (1883) § United States Civil Service Commission § Federal employees based on expertise, civil service exams § Prohibited federal employees and campaign contributions

Chester A. Arthur (R) (1881 -1885) ► Assumed office after Garfield’s assassination ► Signed the Pendleton Act § Despite being a Stalwart ► Signed the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 ► United States Navy § Pursued modernization and expansion of U. S. fleet
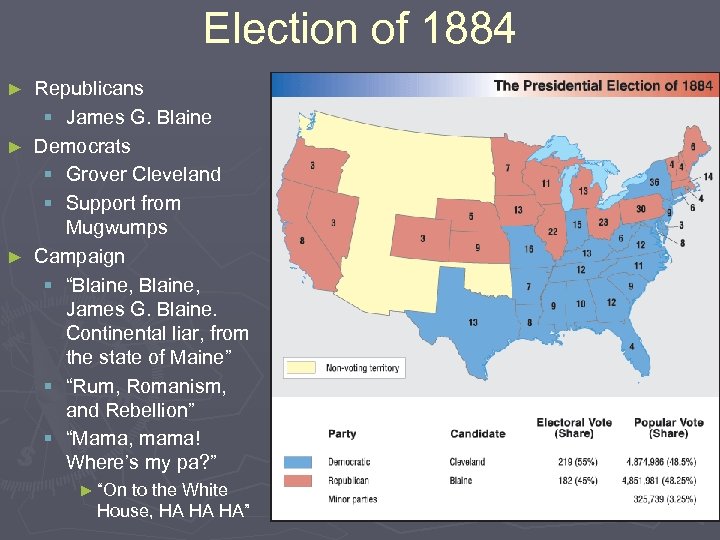
Election of 1884 Republicans § James G. Blaine ► Democrats § Grover Cleveland § Support from Mugwumps ► Campaign § “Blaine, James G. Blaine. Continental liar, from the state of Maine” § “Rum, Romanism, and Rebellion” § “Mama, mama! Where’s my pa? ” ► ► “On to the White House, HA HA HA”


Grover Cleveland (D) (1885 -1889) ► Considered presidency as a watchdog office - caretaker president § Vetoed twice as many as predecessors combined Haymarket Riot (1886) ► Signed Interstate Commerce Act (1887) ► § Established Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) ► First ► regulatory agency Opposed Civil War veteran pensions § Grand Army of the Republic (GAR) advocacy ► Pursued tariff reform
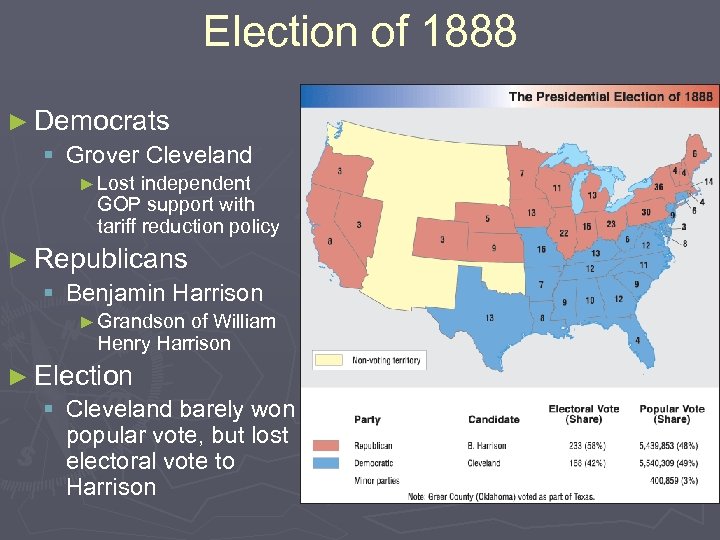
Election of 1888 ► Democrats § Grover Cleveland ► Lost independent GOP support with tariff reduction policy ► Republicans § Benjamin Harrison ► Grandson of William Henry Harrison ► Election § Cleveland barely won popular vote, but lost electoral vote to Harrison

Benjamin Harrison (R) (1889 -1893) ► Signed Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) ► Billion Dollar Congress § Federal budget over $1 B § Dependent Pensions Act (1890) ► Sherman Silver Purchase Act (1890) ► Mc. Kinley Tariff (1890) ► Homestead Strike (1892)

“What a funny little government”


The Populist Movement ► Origin and Evolution of Populist Party § Granger Movement -> § Farmers Alliance -> § Populist Movement -> § People’s Party/Populist Party ► Concentrations and bases in West and ► Omaha Platform (July 4, 1892) § Coinage of silver § Direct election of Senators § Graduated income tax § State laws through referendums/initiatives § Government ownership of infrastructure § 8 -hour workday § Abolition of national banks § Civil service reform South

Bimetallism ► For Silver § Overproduction led to decreased prices therefore a call for increase in money supply § Silver coinage would cause inflation lessening farmer and consumer debt to banks § Free Silver ► For Gold § Sound money § Banks and businesses preferred gold standard § Stable economy and prevents inflation ► Sherman Silver Purchase Act (1890) § U. S. Treasury ordered to buy 4. 5 million oz of silver monthly § Treasury notes could be turned in for silver or gold ► Most took gold depleting U. S. gold reserves

Mc. Kinley Tariff (1890) ► Protective tariff § Raised duties to 48. 4%, highest peacetime rate ever ► Support § Republicans § Manufacturers/Industrialists § Wage Earners ► Opponents § Democrats § Farmers § Inflation
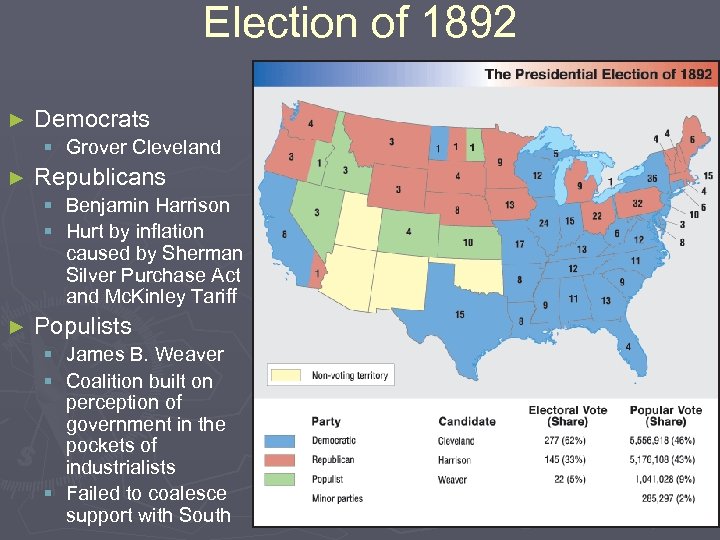
Election of 1892 ► Democrats § Grover Cleveland ► Republicans § Benjamin Harrison § Hurt by inflation caused by Sherman Silver Purchase Act and Mc. Kinley Tariff ► Populists § James B. Weaver § Coalition built on perception of government in the pockets of industrialists § Failed to coalesce support with South

Grover Cleveland (D) (1893 -1897) ► Panic of 1893 ► Wilson-Gorman Tariff (1894) § Eliminated Mc. Kinley Tariff and reduced rates ► Monetary Debate § Supported gold standard and repeal of Sherman Silver Purchase Act ► Pullman Strike (1894) § Deployed federal troops to settle the strike § Threatened postal mail delivery

Panic of 1893 ► Causes § Overexpansion § Railroad speculation ► Pennsylvania and Reading Railroad bankruptcy § Silver prices decreased ► ► Cleveland had Sherman Silver Purchase Act repealed Impact § Unemployment to 18. 4% § 16, 000 businesses and 500 banks bankrupt/failed § Pullman Strike (July 1894) § Coxey’s Army (1894) March on Washington by unemployed workers and farmers $500 million for jobs ► Dispersed by federal troops ► § J. P. Morgan and the Treasury ► Cleveland U. S. borrowed $65 million in gold

William Jennings Bryan (D) ► Panic of 1893 hurt Democrats ► “The Great Commoner” § Appealed to farmers, working class, middle class ► Amazing and passionate orator ► Became lightning rod for Populists/Silverites ► “Cross of Gold” Speech § Support of bimetallism § Earned him Democratic presidential nomination

Cross of Gold Speech ► “If they dare to come out in the open field and defend the gold standard as a good thing, we shall fight them to the uttermost, having behind us the producing masses of the nation and the world. Having behind us the commercial interests and the laboring interests and all the toiling masses, we shall answer their demands for a gold standard by saying to them, you shall not press down upon the brow of labor this crown of thorns. You shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold. ”
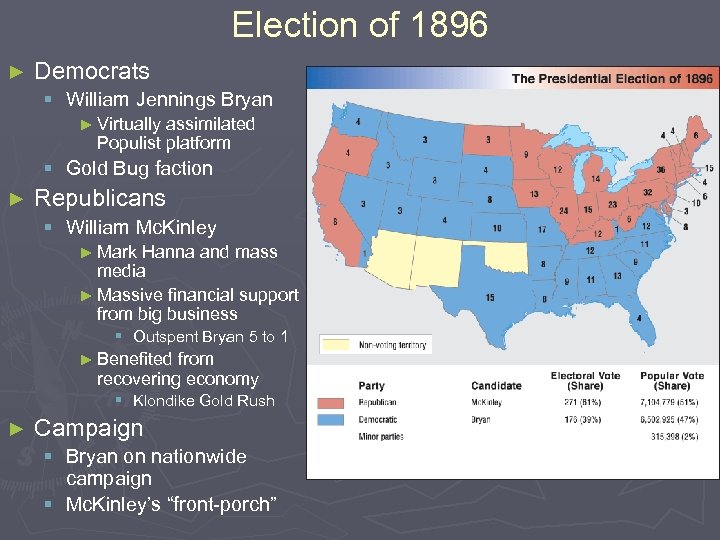
Election of 1896 ► Democrats § William Jennings Bryan ► Virtually assimilated Populist platform § Gold Bug faction ► Republicans § William Mc. Kinley ► Mark Hanna and mass media ► Massive financial support from big business § Outspent Bryan 5 to 1 ► Benefited from recovering economy § Klondike Gold Rush ► Campaign § Bryan on nationwide campaign § Mc. Kinley’s “front-porch”

1896 - Realignment Election ► Coalitions § Republicans ► Will dominate national government for next 35 years ► Business, professionals, skilled workers, middle class, commercial farmers ► Northeast, Upper Midwest, Pacific § Democrats ► Farmers, immigrants, unskilled labor ► South, Midwest ► Campaign § Finance § Contested States § Stump speech
08b5f312d73793530d8953c25e5b2129.ppt