fccaf40c9099ade7382b8d07365d652e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77
 GILDED AGE INDUSTRIALISM Unit VA AP United States History
GILDED AGE INDUSTRIALISM Unit VA AP United States History
 American Industrial Expansion ► With the completion of Manifest Destiny throughout continental U. S. , the nation encompassed near-perfect elements for massive industrialization and economic expansion ► Economic Resources § Land ► Abundance and discovery of vast deposits of coal, iron ore, copper, timber, oil, gold, silver, agricultural § Labor ► Cheap wages, immigration, population growth § Capital ► Industrial capitalism and finance capitalism ► Federal subsidies and land sales ► Second Industrial Revolution and technological innovation § Entrepreneurial Ability ► Captains of Industry/Robber Barons
American Industrial Expansion ► With the completion of Manifest Destiny throughout continental U. S. , the nation encompassed near-perfect elements for massive industrialization and economic expansion ► Economic Resources § Land ► Abundance and discovery of vast deposits of coal, iron ore, copper, timber, oil, gold, silver, agricultural § Labor ► Cheap wages, immigration, population growth § Capital ► Industrial capitalism and finance capitalism ► Federal subsidies and land sales ► Second Industrial Revolution and technological innovation § Entrepreneurial Ability ► Captains of Industry/Robber Barons

 Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons ► Using four business entrepreneurs as case studies for American innovation, industrial growth, and expansion of capitalism. ► Cornelius Vanderbilt ► Andrew Carnegie ► John D. Rockefeller ► J. P. Morgan
Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons ► Using four business entrepreneurs as case studies for American innovation, industrial growth, and expansion of capitalism. ► Cornelius Vanderbilt ► Andrew Carnegie ► John D. Rockefeller ► J. P. Morgan
 Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: Cornelius Vanderbilt and Railroads Acquired his wealth in steamships and expanded into railroads in 1860 s ► Revamped northeast railroads through consolidation and standardization ► § New York Central Railroad § Regional railway system from New York to Chicago § Replaced and built lines with standard gauges ► Implementation of steel § Stronger to carry heavier loads § Safer due to no corrosion ► Vanderbilt University
Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: Cornelius Vanderbilt and Railroads Acquired his wealth in steamships and expanded into railroads in 1860 s ► Revamped northeast railroads through consolidation and standardization ► § New York Central Railroad § Regional railway system from New York to Chicago § Replaced and built lines with standard gauges ► Implementation of steel § Stronger to carry heavier loads § Safer due to no corrosion ► Vanderbilt University
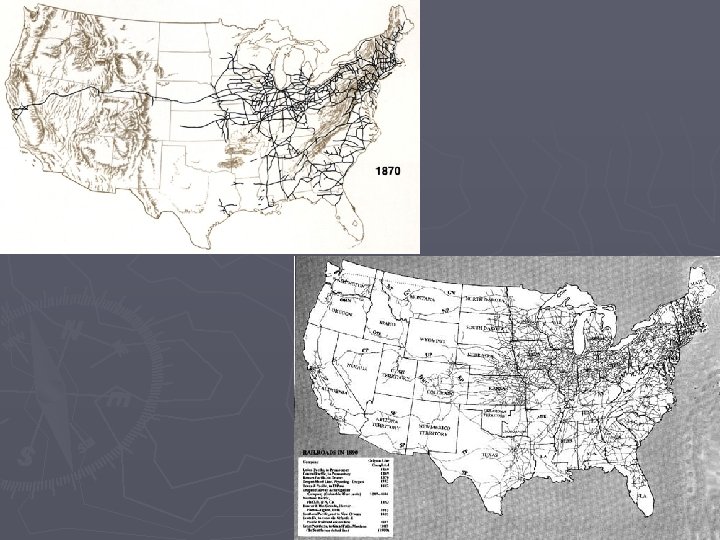
 Railroads Drive the Economy ► Growth and Influence § 35, 000 miles (1865) to 200, 000 miles (1900) § First Transcontinental Railroad (1869) ► Leland Stanford’s Union Pacific and Central Pacific meet at Promontory Summit, UT § Market connections, boomtowns, and jobs ► Federal Government Involvement § Pacific Railway Acts ► Land grants and government bonds to railroad companies ► Requirement of standardized gauges § By 1871, federal and state governments sold 300, 000 acres of land to railroads ► Innovation and Improvement § § Standardized gauges Westinghouse air brakes Steel Time zones
Railroads Drive the Economy ► Growth and Influence § 35, 000 miles (1865) to 200, 000 miles (1900) § First Transcontinental Railroad (1869) ► Leland Stanford’s Union Pacific and Central Pacific meet at Promontory Summit, UT § Market connections, boomtowns, and jobs ► Federal Government Involvement § Pacific Railway Acts ► Land grants and government bonds to railroad companies ► Requirement of standardized gauges § By 1871, federal and state governments sold 300, 000 acres of land to railroads ► Innovation and Improvement § § Standardized gauges Westinghouse air brakes Steel Time zones
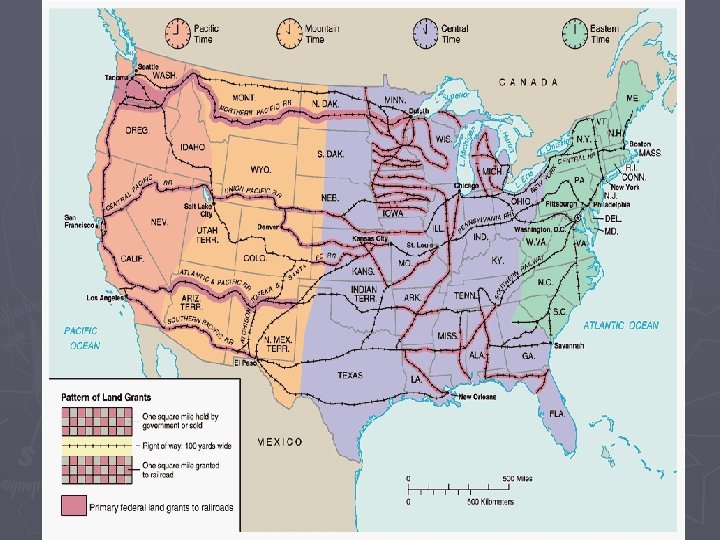
 The Business of Railroads ► Rate Wars § Competition among railroad companies was fierce and intense § Stronger companies lowered rates to drive out weaker companies Led to monopolies ► Increased rates dramatically ► ► Long haul and short haul rates § Price discrimination favored commercial farmers over small farmers ► Stock watering/watered stock § Inflated stocks led to higher consumer rates ► Pools § Competing lines fixed prices and divided business for max profits ► Grange Lines § Midwest farmers dependent on rail lines for shipping § High freight rates impoverished farmers
The Business of Railroads ► Rate Wars § Competition among railroad companies was fierce and intense § Stronger companies lowered rates to drive out weaker companies Led to monopolies ► Increased rates dramatically ► ► Long haul and short haul rates § Price discrimination favored commercial farmers over small farmers ► Stock watering/watered stock § Inflated stocks led to higher consumer rates ► Pools § Competing lines fixed prices and divided business for max profits ► Grange Lines § Midwest farmers dependent on rail lines for shipping § High freight rates impoverished farmers
 Commercial Farming ► Agriculture became commercialized on cash crops for national and international markets § Influx of Eastern capital and investment § From subsistence to market/stores § Pushed out local/small farmers ► Competition, deflated currency, and overproduction lowered prices while input costs increased ► “Middle Men” § Farmers lost massive share of profits to managers of their sales § Grain elevator and railroad companies charged expensive rents and transportation costs
Commercial Farming ► Agriculture became commercialized on cash crops for national and international markets § Influx of Eastern capital and investment § From subsistence to market/stores § Pushed out local/small farmers ► Competition, deflated currency, and overproduction lowered prices while input costs increased ► “Middle Men” § Farmers lost massive share of profits to managers of their sales § Grain elevator and railroad companies charged expensive rents and transportation costs
 The Farmers Organize ► Fueled by the Granger Movement § Granger laws ► Munn v. Illinois (1877) § States could regulate private companies if they served the public interest, I. e. grain elevators, railroads ► Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railway Co. v. Illinois (1886) § States could not regulate interstate commerce ► Interstate Commerce Act (1886) § Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) § Enforce fair railway rates, prohibit discriminatory practices by railroads ► National Alliance and the Ocala Platform (1890) § Unity against corporations and monopolies § Favored direct election of Senators, lower tariffs, graduated income tax, federal banking system § Evolves into People’s Party (Populists) and Omaha Platform (1892)
The Farmers Organize ► Fueled by the Granger Movement § Granger laws ► Munn v. Illinois (1877) § States could regulate private companies if they served the public interest, I. e. grain elevators, railroads ► Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railway Co. v. Illinois (1886) § States could not regulate interstate commerce ► Interstate Commerce Act (1886) § Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) § Enforce fair railway rates, prohibit discriminatory practices by railroads ► National Alliance and the Ocala Platform (1890) § Unity against corporations and monopolies § Favored direct election of Senators, lower tariffs, graduated income tax, federal banking system § Evolves into People’s Party (Populists) and Omaha Platform (1892)
 Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: Andrew Carnegie and Steel ► Managed Pennsylvania Railroad and invested in various industries ► Steel § Bessemer Process ► Vertical Integration ► Urbanization and Cities ► Labor Unions and Strikes
Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: Andrew Carnegie and Steel ► Managed Pennsylvania Railroad and invested in various industries ► Steel § Bessemer Process ► Vertical Integration ► Urbanization and Cities ► Labor Unions and Strikes
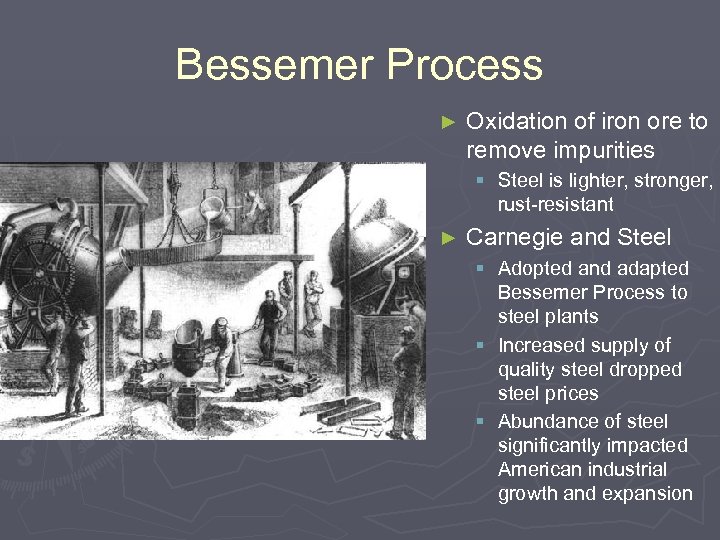 Bessemer Process ► Oxidation of iron ore to remove impurities § Steel is lighter, stronger, rust-resistant ► Carnegie and Steel § Adopted and adapted Bessemer Process to steel plants § Increased supply of quality steel dropped steel prices § Abundance of steel significantly impacted American industrial growth and expansion
Bessemer Process ► Oxidation of iron ore to remove impurities § Steel is lighter, stronger, rust-resistant ► Carnegie and Steel § Adopted and adapted Bessemer Process to steel plants § Increased supply of quality steel dropped steel prices § Abundance of steel significantly impacted American industrial growth and expansion
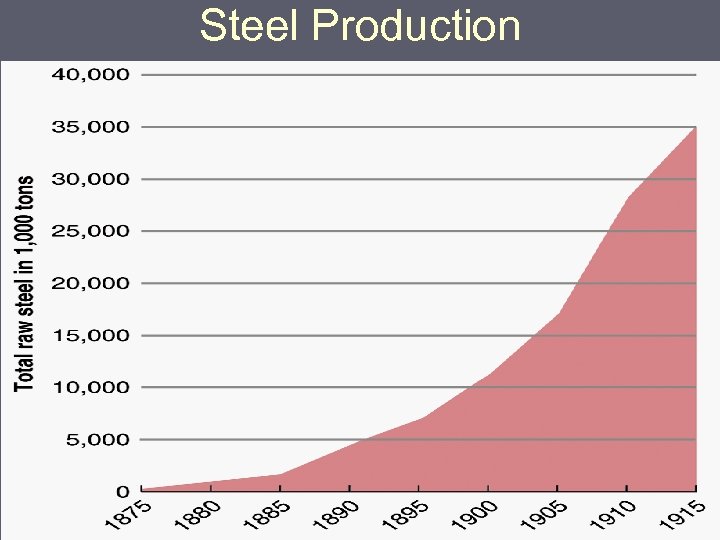 Steel Production
Steel Production
 Vertical Integration ► Carnegie acquired all aspects of steel production ► Limited competition, maximized profits, lowered prices
Vertical Integration ► Carnegie acquired all aspects of steel production ► Limited competition, maximized profits, lowered prices
 Steel and Cities ► Buildings § Skyscrapers ► Steel ► beams Infrastructure § Railroads § Bridges ► Brooklyn ► Bridge Urban Innovation § Mass Transit ► Elevated rails ► Subways § Elevators § Central steam-heating systems
Steel and Cities ► Buildings § Skyscrapers ► Steel ► beams Infrastructure § Railroads § Bridges ► Brooklyn ► Bridge Urban Innovation § Mass Transit ► Elevated rails ► Subways § Elevators § Central steam-heating systems
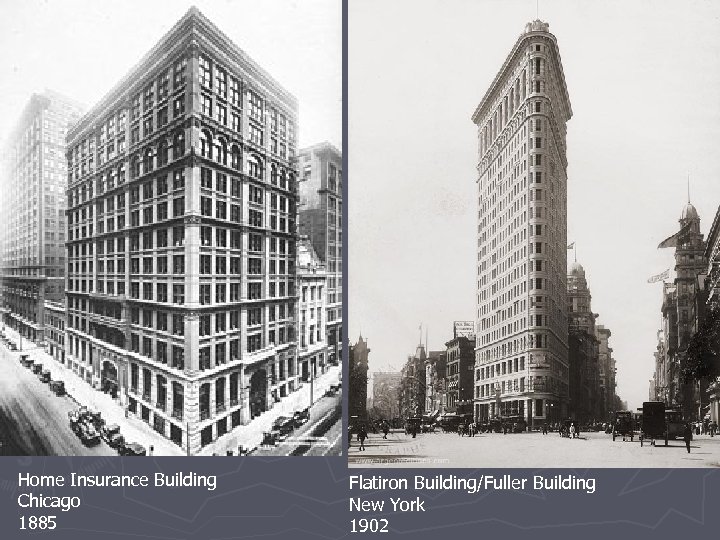 Home Insurance Building Chicago 1885 Flatiron Building/Fuller Building New York 1902
Home Insurance Building Chicago 1885 Flatiron Building/Fuller Building New York 1902
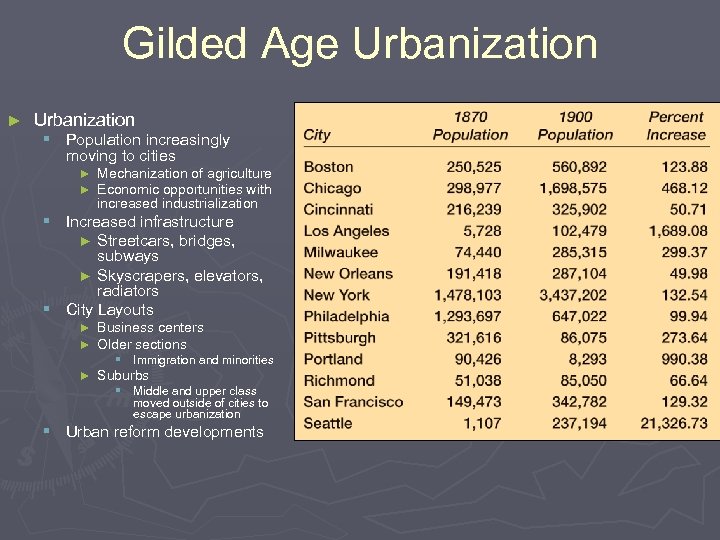 Gilded Age Urbanization ► Urbanization § Population increasingly moving to cities ► Mechanization of agriculture ► Economic opportunities with increased industrialization § Increased infrastructure ► Streetcars, bridges, subways ► Skyscrapers, elevators, radiators § City Layouts ► Business centers ► Older sections § Immigration and minorities ► Suburbs § Middle and upper class moved outside of cities to escape urbanization § Urban reform developments
Gilded Age Urbanization ► Urbanization § Population increasingly moving to cities ► Mechanization of agriculture ► Economic opportunities with increased industrialization § Increased infrastructure ► Streetcars, bridges, subways ► Skyscrapers, elevators, radiators § City Layouts ► Business centers ► Older sections § Immigration and minorities ► Suburbs § Middle and upper class moved outside of cities to escape urbanization § Urban reform developments
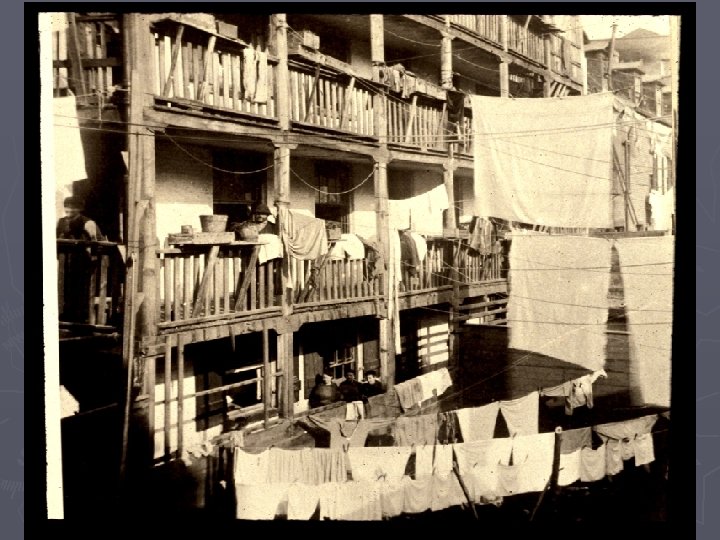
 Urban Problems ► Overcrowding § Tenement Living ► Pollution ► Crime ► Sanitation/Water Treatment ► Disease
Urban Problems ► Overcrowding § Tenement Living ► Pollution ► Crime ► Sanitation/Water Treatment ► Disease

 Urban and Social Reforms Municipal services ► Social Gospel ► § Apply Christian values toward social problems and issues § Josiah Strong, Walter Rauschenbusch, Richard T. Ely ► Settlement Houses § Jane Addams and Hull House § YMCA § Salvation Army ► Social Criticism § Jacob Riis - How the Other Half Lives (1889) § Henry George - Progress and Poverty (1879)
Urban and Social Reforms Municipal services ► Social Gospel ► § Apply Christian values toward social problems and issues § Josiah Strong, Walter Rauschenbusch, Richard T. Ely ► Settlement Houses § Jane Addams and Hull House § YMCA § Salvation Army ► Social Criticism § Jacob Riis - How the Other Half Lives (1889) § Henry George - Progress and Poverty (1879)
 Working Conditions Typical 12 hour days, 6 days a week ► Conditions ► § Poor ventilation and heavy equipment § In 1882, average of 675 workers killed each week § Injured = fired No benefits, such as vacation days, sick leave, health insurance, workers’ compensation, pensions ► Women ► § Earned half of what men earned in comparable or same jobs ► Child Labor § As young as 5 years old § 12 -14 hours for $. 27 ($6. 65)
Working Conditions Typical 12 hour days, 6 days a week ► Conditions ► § Poor ventilation and heavy equipment § In 1882, average of 675 workers killed each week § Injured = fired No benefits, such as vacation days, sick leave, health insurance, workers’ compensation, pensions ► Women ► § Earned half of what men earned in comparable or same jobs ► Child Labor § As young as 5 years old § 12 -14 hours for $. 27 ($6. 65)
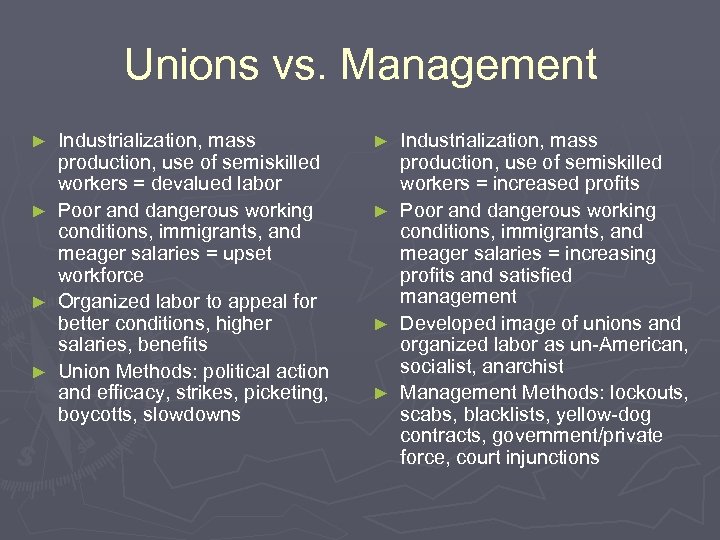 Unions vs. Management Industrialization, mass production, use of semiskilled workers = devalued labor ► Poor and dangerous working conditions, immigrants, and meager salaries = upset workforce ► Organized labor to appeal for better conditions, higher salaries, benefits ► Union Methods: political action and efficacy, strikes, picketing, boycotts, slowdowns ► Industrialization, mass production, use of semiskilled workers = increased profits ► Poor and dangerous working conditions, immigrants, and meager salaries = increasing profits and satisfied management ► Developed image of unions and organized labor as un-American, socialist, anarchist ► Management Methods: lockouts, scabs, blacklists, yellow-dog contracts, government/private force, court injunctions ►
Unions vs. Management Industrialization, mass production, use of semiskilled workers = devalued labor ► Poor and dangerous working conditions, immigrants, and meager salaries = upset workforce ► Organized labor to appeal for better conditions, higher salaries, benefits ► Union Methods: political action and efficacy, strikes, picketing, boycotts, slowdowns ► Industrialization, mass production, use of semiskilled workers = increased profits ► Poor and dangerous working conditions, immigrants, and meager salaries = increasing profits and satisfied management ► Developed image of unions and organized labor as un-American, socialist, anarchist ► Management Methods: lockouts, scabs, blacklists, yellow-dog contracts, government/private force, court injunctions ►
 National Labor Union (NLU) Founded in 1866 as the first national labor union ► Platform ► § 8 -hour workday § Monetary reform, cooperatives § Racial and gender equality ► Impact § 8 -hour workday for federal employees ► Decline § Panic of 1873 § Knights of Labor
National Labor Union (NLU) Founded in 1866 as the first national labor union ► Platform ► § 8 -hour workday § Monetary reform, cooperatives § Racial and gender equality ► Impact § 8 -hour workday for federal employees ► Decline § Panic of 1873 § Knights of Labor
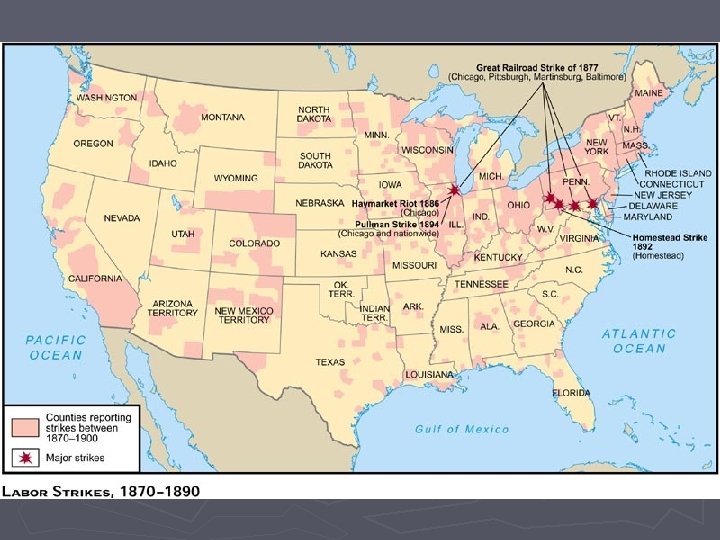
 Great Railroad Strike of 1877 ► ► July 14 -September 4, 1877 Causes § Panic of 1873 § Class conflict with wage cuts and unemployment ► Events § Strikers forced rail stoppages § Federal troops engaged strikers § Riots and massacres ► Impact § Would lead to better organization of workers and labor unions § Legislation to limit unions and preparations for potential conflicts
Great Railroad Strike of 1877 ► ► July 14 -September 4, 1877 Causes § Panic of 1873 § Class conflict with wage cuts and unemployment ► Events § Strikers forced rail stoppages § Federal troops engaged strikers § Riots and massacres ► Impact § Would lead to better organization of workers and labor unions § Legislation to limit unions and preparations for potential conflicts
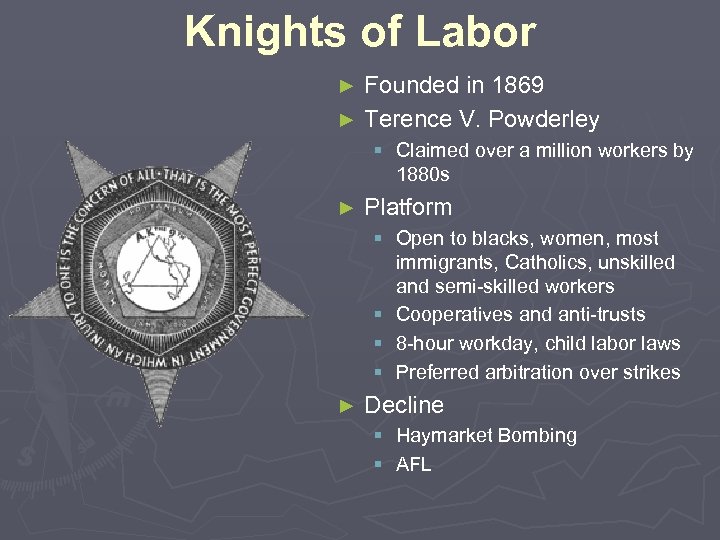 Knights of Labor Founded in 1869 ► Terence V. Powderley ► § Claimed over a million workers by 1880 s ► Platform § Open to blacks, women, most immigrants, Catholics, unskilled and semi-skilled workers § Cooperatives and anti-trusts § 8 -hour workday, child labor laws § Preferred arbitration over strikes ► Decline § Haymarket Bombing § AFL
Knights of Labor Founded in 1869 ► Terence V. Powderley ► § Claimed over a million workers by 1880 s ► Platform § Open to blacks, women, most immigrants, Catholics, unskilled and semi-skilled workers § Cooperatives and anti-trusts § 8 -hour workday, child labor laws § Preferred arbitration over strikes ► Decline § Haymarket Bombing § AFL
 Haymarket Riot of 1886 ► May Day (May 1 st) § Strike begins of harvesting workers ► May 3 rd § Police sent to protect strikers § Fight broke out and one person killed and several injured ► May 4 th Protest § Anarchists planned demonstration against police brutality § Police dispersed crowd of 2, 000 ► Bombing § A pipe bomb exploded and killed 7 police officers § Police fired into crowd killing 4 ► Trial § 8 innocent anarchists convicted of murder in a show trial § 4 hanged, 1 committed suicide, 3 pardoned by governor
Haymarket Riot of 1886 ► May Day (May 1 st) § Strike begins of harvesting workers ► May 3 rd § Police sent to protect strikers § Fight broke out and one person killed and several injured ► May 4 th Protest § Anarchists planned demonstration against police brutality § Police dispersed crowd of 2, 000 ► Bombing § A pipe bomb exploded and killed 7 police officers § Police fired into crowd killing 4 ► Trial § 8 innocent anarchists convicted of murder in a show trial § 4 hanged, 1 committed suicide, 3 pardoned by governor
 American Federation of Labor (AFL) Founded in 1886 as an organization of national craft unions of skilled workers ► Samuel Gompers ► “Bread and Butter” Unionism ► § Higher wages § Shorter working hours § Better working conditions ► Tactics § Used arbitration and strikes § Avoided political radicalism and extremism
American Federation of Labor (AFL) Founded in 1886 as an organization of national craft unions of skilled workers ► Samuel Gompers ► “Bread and Butter” Unionism ► § Higher wages § Shorter working hours § Better working conditions ► Tactics § Used arbitration and strikes § Avoided political radicalism and extremism
 Homestead Strike June 30 -July 6, 1892 ► Henry Frick ► § Manager of Carnegie Steel § Pursued wage cuts due to lower steel prices § Attempted to weaken steel workers union ► Events § Frick orders a lockout and hires scabs § Use of Pinkertons to disperse strikers § State militia broke the strike and took over the plant ► Impact § Weakened steel workers union § Tarnished Carnegie’s reputation
Homestead Strike June 30 -July 6, 1892 ► Henry Frick ► § Manager of Carnegie Steel § Pursued wage cuts due to lower steel prices § Attempted to weaken steel workers union ► Events § Frick orders a lockout and hires scabs § Use of Pinkertons to disperse strikers § State militia broke the strike and took over the plant ► Impact § Weakened steel workers union § Tarnished Carnegie’s reputation
 Pullman Strike (1894) ► Pullman Palace Car Company § Established “model town” for workers § In response to Panic of 1893, wages cut but not rents and town costs ► Eugene V. Debs § Led strike with American Railway Union ► Strike § Workers blocked transport of Pullman cars § Pullman Co. linked them to mail cars § President Grover Cleveland deployed federal troops and court injunctions to enforce postal service ► Opinion § Most Americans opposed the strike ► ► Included AFL and Samuel Gompers In Re Debs (1895) § Supreme Court ruled federal court injunctions to enforce interstate commerce constitutional
Pullman Strike (1894) ► Pullman Palace Car Company § Established “model town” for workers § In response to Panic of 1893, wages cut but not rents and town costs ► Eugene V. Debs § Led strike with American Railway Union ► Strike § Workers blocked transport of Pullman cars § Pullman Co. linked them to mail cars § President Grover Cleveland deployed federal troops and court injunctions to enforce postal service ► Opinion § Most Americans opposed the strike ► ► Included AFL and Samuel Gompers In Re Debs (1895) § Supreme Court ruled federal court injunctions to enforce interstate commerce constitutional
 Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: John D. Rockefeller and Oil ► Horizontal Integration ► Standard Oil § Trusts and monopolies ► Sherman Anti-trust Act (1890) ► Gilded Age Society ► Social Darwinism ► Gospel of Wealth
Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: John D. Rockefeller and Oil ► Horizontal Integration ► Standard Oil § Trusts and monopolies ► Sherman Anti-trust Act (1890) ► Gilded Age Society ► Social Darwinism ► Gospel of Wealth
 Standard Oil Rockefeller established Standard Oil in 1870 ► Uses for Oil ► § Kerosene lamps § Fuel for railroads Used vertical integration to control oil industry then horizontal integration to control oil market ► Eventually controlled 95% of oil refining ►
Standard Oil Rockefeller established Standard Oil in 1870 ► Uses for Oil ► § Kerosene lamps § Fuel for railroads Used vertical integration to control oil industry then horizontal integration to control oil market ► Eventually controlled 95% of oil refining ►
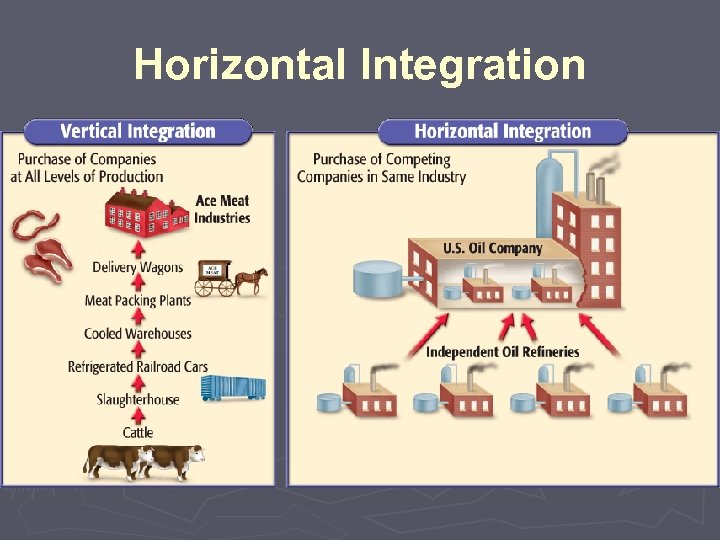 Horizontal Integration
Horizontal Integration

 Robber Barons and Trusts ► Tactics of Standard Oil § Lowered prices to drive out competitors § Threatened companies to sell to Standard Oil (buyouts) § Bribed railroads to buy Standard Oil fuel (rebates, kickbacks) § Bribed Congress members ► Standard Oil Trust § Stockholders’ shares traded for trust certificates § Board of Trustees controlled and administered companies as a whole § Shareholders earned dividends based on overall profits ► Monopolies § Controls prices § Limits competition § Pressure on other services to provide discounts and rebates
Robber Barons and Trusts ► Tactics of Standard Oil § Lowered prices to drive out competitors § Threatened companies to sell to Standard Oil (buyouts) § Bribed railroads to buy Standard Oil fuel (rebates, kickbacks) § Bribed Congress members ► Standard Oil Trust § Stockholders’ shares traded for trust certificates § Board of Trustees controlled and administered companies as a whole § Shareholders earned dividends based on overall profits ► Monopolies § Controls prices § Limits competition § Pressure on other services to provide discounts and rebates

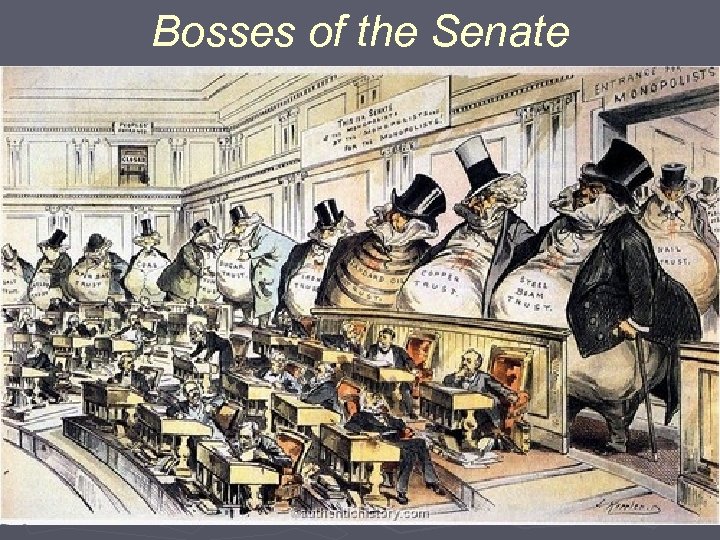 Bosses of the Senate
Bosses of the Senate
 Antitrust Movement ► Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) § Prohibits any “contract, combination, in the form of trust or otherwise, or conspiracy in restraint of trade or commerce” ► United States v. E. C. Knight Co. (1895) § Sugar refining monopoly tested Sherman Antitrust Act § Regulation applied to commerce and not manufacturing
Antitrust Movement ► Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) § Prohibits any “contract, combination, in the form of trust or otherwise, or conspiracy in restraint of trade or commerce” ► United States v. E. C. Knight Co. (1895) § Sugar refining monopoly tested Sherman Antitrust Act § Regulation applied to commerce and not manufacturing
 Scientific Management “Taylorism” ► Frederick W. Taylor ► Scientific management used to match labor with production demand ► Designed hierarchies ► Subdivisions of labor ► Time management ► Effects § Managerial class § Efficiency ► Increased factory production ► Lowered labor costs
Scientific Management “Taylorism” ► Frederick W. Taylor ► Scientific management used to match labor with production demand ► Designed hierarchies ► Subdivisions of labor ► Time management ► Effects § Managerial class § Efficiency ► Increased factory production ► Lowered labor costs
 Gilded Age Socioeconomics ► Socioeconomic gap extensively widened § By 1890 s, 10% of Americans controlled 90% of the nation’s wealth § Standard of living for upper class and middle class improved dramatically § Poor working class suffered in urban centers 2/3 of population were wage earners ► Expansion of middle class/white-collar workers ► § Due to growth of managers/administrators/expert s in businesses ► Iron law of wages § Supply and demand determined wages, not the consideration of workers’ welfare
Gilded Age Socioeconomics ► Socioeconomic gap extensively widened § By 1890 s, 10% of Americans controlled 90% of the nation’s wealth § Standard of living for upper class and middle class improved dramatically § Poor working class suffered in urban centers 2/3 of population were wage earners ► Expansion of middle class/white-collar workers ► § Due to growth of managers/administrators/expert s in businesses ► Iron law of wages § Supply and demand determined wages, not the consideration of workers’ welfare
 Gilded Age Women ► 20% of American women worked as wage earners § Most single women; 5% married § Low-income families required women in workplace ► Female-based Jobs § Typical home-associated industries: textiles, foods, domestic servants § New types of jobs: secretaries, bookkeepers, typists, communication operators § Women and feminized jobs considered low status and low salaries ► Gibson Girl § Iconic image of women as independent, stylish, and working § Led to women to seek new types of jobs
Gilded Age Women ► 20% of American women worked as wage earners § Most single women; 5% married § Low-income families required women in workplace ► Female-based Jobs § Typical home-associated industries: textiles, foods, domestic servants § New types of jobs: secretaries, bookkeepers, typists, communication operators § Women and feminized jobs considered low status and low salaries ► Gibson Girl § Iconic image of women as independent, stylish, and working § Led to women to seek new types of jobs
 Women’s Suffrage ► National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA) (1890) § Merger of NWSA and AWSA § Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony § Gave way to leadership of Carrie Chapman Catt ► Western States § Wyoming granted full suffrage in 1869
Women’s Suffrage ► National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA) (1890) § Merger of NWSA and AWSA § Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony § Gave way to leadership of Carrie Chapman Catt ► Western States § Wyoming granted full suffrage in 1869
 Gilded Age Families ► Stronger nuclear families ► Birth rates and family size rates decreased § Children as economic liability in urban areas ► Divorce rates increased § 1 in 12 by 1900
Gilded Age Families ► Stronger nuclear families ► Birth rates and family size rates decreased § Children as economic liability in urban areas ► Divorce rates increased § 1 in 12 by 1900
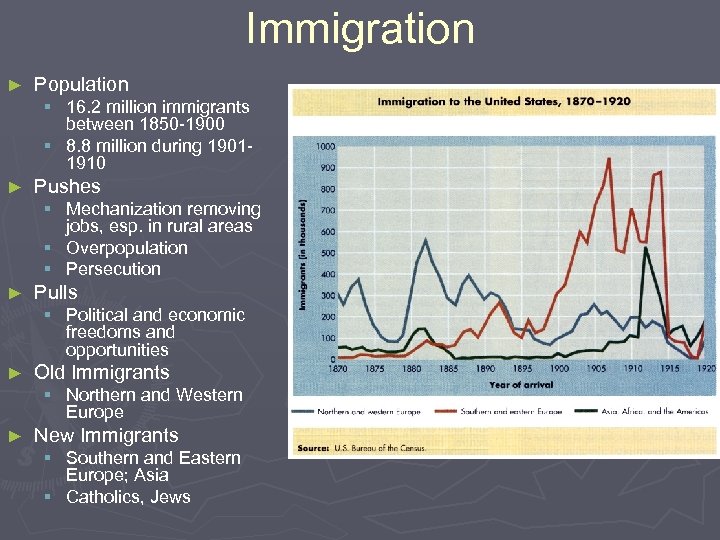 Immigration ► Population § 16. 2 million immigrants between 1850 -1900 § 8. 8 million during 19011910 ► Pushes § Mechanization removing jobs, esp. in rural areas § Overpopulation § Persecution ► Pulls § Political and economic freedoms and opportunities ► Old Immigrants § Northern and Western Europe ► New Immigrants § Southern and Eastern Europe; Asia § Catholics, Jews
Immigration ► Population § 16. 2 million immigrants between 1850 -1900 § 8. 8 million during 19011910 ► Pushes § Mechanization removing jobs, esp. in rural areas § Overpopulation § Persecution ► Pulls § Political and economic freedoms and opportunities ► Old Immigrants § Northern and Western Europe ► New Immigrants § Southern and Eastern Europe; Asia § Catholics, Jews

 Immigrant Issues ► Sociopolitical Enemies § Nativists § Josiah Strong - Our Country ► Legislation § Page Act of 1875 ► Forbade forced labor Asians, prostitutes, convicts § Immigration Acts of 1882, 1891 ► $0. 50 tax ► Forbid convicts, lunatics, idiots, diseased, disabled § Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) ► Chinese immigration ban for 10 years ► Chinese prevented from becoming citizens § United States v. Wong Kim Ark (1898) ► All people born in U. S. are citizens ► Political Machines § Employment, housing, social services for votes ► Ethnic Neighborhoods § Little Italy § Chinatown
Immigrant Issues ► Sociopolitical Enemies § Nativists § Josiah Strong - Our Country ► Legislation § Page Act of 1875 ► Forbade forced labor Asians, prostitutes, convicts § Immigration Acts of 1882, 1891 ► $0. 50 tax ► Forbid convicts, lunatics, idiots, diseased, disabled § Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) ► Chinese immigration ban for 10 years ► Chinese prevented from becoming citizens § United States v. Wong Kim Ark (1898) ► All people born in U. S. are citizens ► Political Machines § Employment, housing, social services for votes ► Ethnic Neighborhoods § Little Italy § Chinatown
 Ellis Island “…Give me your tired, your poor, Your huddled masses yearning to breathe free, The wretched refuse of your teeming shore…” Emma Lazarus - The New Colossus, 1883
Ellis Island “…Give me your tired, your poor, Your huddled masses yearning to breathe free, The wretched refuse of your teeming shore…” Emma Lazarus - The New Colossus, 1883
 Laissez-Faire and Social Darwinism ► Laissez-Faire Economics § Economy driven by the “invisible hand” of market forces (supply and demand) § Government should refrain from regulation or interference ► Social Darwinism § Herbert Spencer ► “Survival of the fittest” ► Wealth a result of hard work and brilliance ► Poor and unfortunate were lazy § William Graham Sumner ► Absolute freedom to struggle, succeed, or fail ► State intervention is futile ► Gospel of Wealth § Andrew Carnegie § Guardians of the nation’s wealth § “All revenue generated beyond your own needs should be used for the good of the community. ”
Laissez-Faire and Social Darwinism ► Laissez-Faire Economics § Economy driven by the “invisible hand” of market forces (supply and demand) § Government should refrain from regulation or interference ► Social Darwinism § Herbert Spencer ► “Survival of the fittest” ► Wealth a result of hard work and brilliance ► Poor and unfortunate were lazy § William Graham Sumner ► Absolute freedom to struggle, succeed, or fail ► State intervention is futile ► Gospel of Wealth § Andrew Carnegie § Guardians of the nation’s wealth § “All revenue generated beyond your own needs should be used for the good of the community. ”
 Horatio Alger Myth ► “Rags to riches” stories § Young American men, through hard work and virtue, will succeed § Also used a supporting wealthy philanthropic character ► Seemingly propaganda of the American Dream under free enterprise and capitalism
Horatio Alger Myth ► “Rags to riches” stories § Young American men, through hard work and virtue, will succeed § Also used a supporting wealthy philanthropic character ► Seemingly propaganda of the American Dream under free enterprise and capitalism
 Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: J. P. Morgan and Electricity ► Banking and Financing ► Science and Innovation ► Corporations ► Consumerism ► American Culture
Captains of Industry OR Robber Barons: J. P. Morgan and Electricity ► Banking and Financing ► Science and Innovation ► Corporations ► Consumerism ► American Culture
 Morganization ► J. P. Morgan and Co. § Financial capital and investment § Directly and indirectly pursued inventions and innovations ► Mergers and Consolidations § Railroad industry ► Interlocking directorates § Corporate board of directors sitting on boards of multiple corporations
Morganization ► J. P. Morgan and Co. § Financial capital and investment § Directly and indirectly pursued inventions and innovations ► Mergers and Consolidations § Railroad industry ► Interlocking directorates § Corporate board of directors sitting on boards of multiple corporations
 Electricity ► Thomas Edison § The Wizard of Menlo Park § Incandescent light bulb ► Safer than kerosene lamps ► New York City § Direct current (DC) ► Edison developed system of power stations ► Nicola Tesla § Alternate current (AC) ► Transfer farther of electricity faster and
Electricity ► Thomas Edison § The Wizard of Menlo Park § Incandescent light bulb ► Safer than kerosene lamps ► New York City § Direct current (DC) ► Edison developed system of power stations ► Nicola Tesla § Alternate current (AC) ► Transfer farther of electricity faster and
 Gilded Age Innovation ► ► ► Sewing Machine (1855) § Isaac Singer Transatlantic cable (1866) § Cyrus Field Dynamite (1866) § Alfred Nobel Typewriter (1867) § Christopher Scholes Air brakes (1868) § George Westinghouse Mail-order catalog (1872) § A. M. Ward Blue jeans (1873) § Levi Strauss Barbed wire (1873) § Joseph Glidden Telephone (1876) § Alexander Graham Bell* Phonograph (1877) § Thomas Edison Light bulb (1879) § Thomas Edison* Cash register (1879) § James Ritty ► ► ► Universal stock ticker (1885) § Thomas Edison Transformer (1885) § Nikola Tesla Gasoline automobile (1885) § Karl F. Benz Skyscraper (1885) § William Le Baron Jenney Film roll and Kodak camera (1889) § George Eastman* Motion picture camera (1891) § Thomas Edison* Radio (1895) § Guglielmo Marconi Subway (U. S. ) (1895) X-ray (1895) § Wilhelm C. Rontgen Powered flight (1903) § George and Wilbur Wright Alkaline battery (1906) § Thomas Edison Model T (1908) § Henry Ford
Gilded Age Innovation ► ► ► Sewing Machine (1855) § Isaac Singer Transatlantic cable (1866) § Cyrus Field Dynamite (1866) § Alfred Nobel Typewriter (1867) § Christopher Scholes Air brakes (1868) § George Westinghouse Mail-order catalog (1872) § A. M. Ward Blue jeans (1873) § Levi Strauss Barbed wire (1873) § Joseph Glidden Telephone (1876) § Alexander Graham Bell* Phonograph (1877) § Thomas Edison Light bulb (1879) § Thomas Edison* Cash register (1879) § James Ritty ► ► ► Universal stock ticker (1885) § Thomas Edison Transformer (1885) § Nikola Tesla Gasoline automobile (1885) § Karl F. Benz Skyscraper (1885) § William Le Baron Jenney Film roll and Kodak camera (1889) § George Eastman* Motion picture camera (1891) § Thomas Edison* Radio (1895) § Guglielmo Marconi Subway (U. S. ) (1895) X-ray (1895) § Wilhelm C. Rontgen Powered flight (1903) § George and Wilbur Wright Alkaline battery (1906) § Thomas Edison Model T (1908) § Henry Ford
 Monumental Innovation ► Charles Alderton § Experimented with various syrups and flavorings ► Robert Lazenby § Developed Dr. Pepper by 1885 § Patented and incorporated by 1891 ► St. Louis World’s Fair and Exposition (1904) § Introduces Dr. Pepper to the world § Along with hot dogs, hamburgers, and ice cream cones
Monumental Innovation ► Charles Alderton § Experimented with various syrups and flavorings ► Robert Lazenby § Developed Dr. Pepper by 1885 § Patented and incorporated by 1891 ► St. Louis World’s Fair and Exposition (1904) § Introduces Dr. Pepper to the world § Along with hot dogs, hamburgers, and ice cream cones
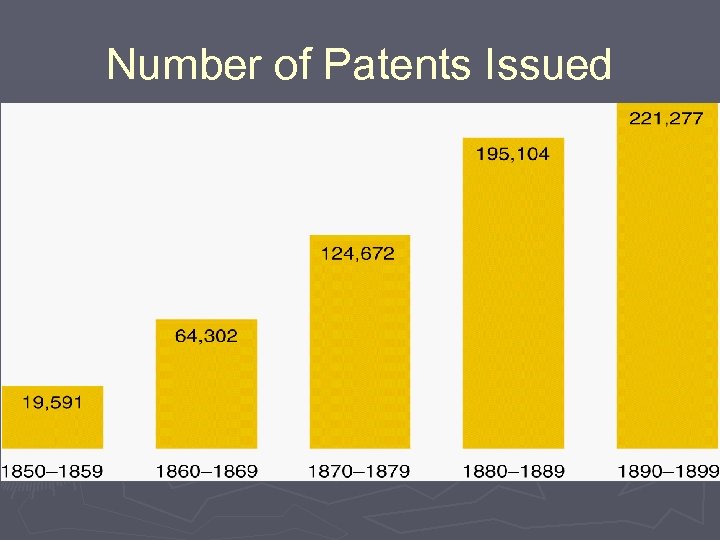 Number of Patents Issued
Number of Patents Issued
 Corporations ► American Telephone and Telegraph Co. (1885) § J. P. Morgan Co. financed merger of Bell and communication companies ► General Electric (1892) § J. P. Morgan merged Edison General Electric and Thomas-Houston Electric Company ► U. S. Steel (1901) § J. P. Morgan bought Carnegie Steel and merged with other steel companies § Becomes first billion dollar company in world
Corporations ► American Telephone and Telegraph Co. (1885) § J. P. Morgan Co. financed merger of Bell and communication companies ► General Electric (1892) § J. P. Morgan merged Edison General Electric and Thomas-Houston Electric Company ► U. S. Steel (1901) § J. P. Morgan bought Carnegie Steel and merged with other steel companies § Becomes first billion dollar company in world
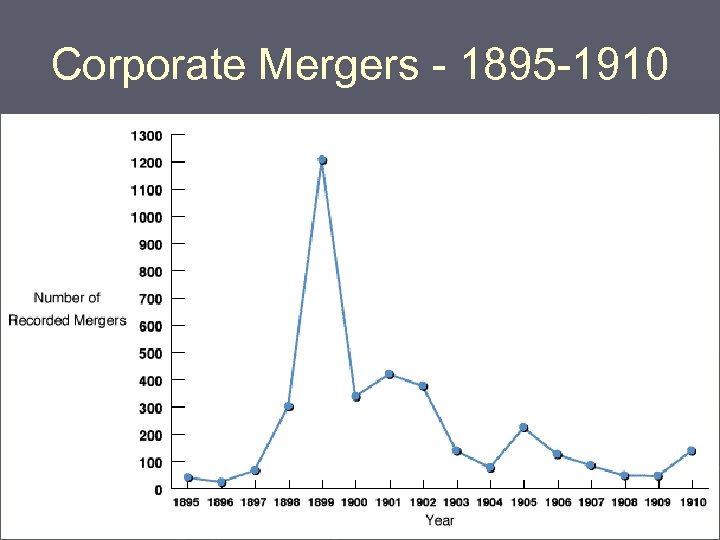 Corporate Mergers - 1895 -1910
Corporate Mergers - 1895 -1910
 Consumerism ► Wide variety of mass produced goods led to new marketing and sales ► Brand names and logos ► Department stores § R. H. Macy’s ► Chain stores § Woolworth’s ► Grocery stores ► Mail order catalogs § Montgomery Ward § Sears, Roebuck, Co.
Consumerism ► Wide variety of mass produced goods led to new marketing and sales ► Brand names and logos ► Department stores § R. H. Macy’s ► Chain stores § Woolworth’s ► Grocery stores ► Mail order catalogs § Montgomery Ward § Sears, Roebuck, Co.

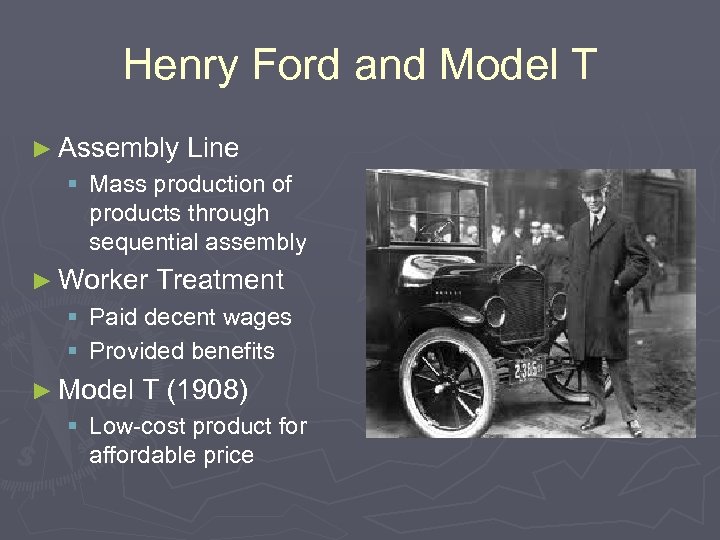 Henry Ford and Model T ► Assembly Line § Mass production of products through sequential assembly ► Worker Treatment § Paid decent wages § Provided benefits ► Model T (1908) § Low-cost product for affordable price
Henry Ford and Model T ► Assembly Line § Mass production of products through sequential assembly ► Worker Treatment § Paid decent wages § Provided benefits ► Model T (1908) § Low-cost product for affordable price
 Gilded Age Religion ► American Christians focused values toward consequences of industrialization and urbanization § Social Gospel ► Increases § Catholics, Jews ► New Christian Sects § Christian Science ► Spiritual life over material § Pentecostals ► Baptism tongues in spirit; speaking in § Salvation Army § Jehovah’s Witnesses ► Millenialist
Gilded Age Religion ► American Christians focused values toward consequences of industrialization and urbanization § Social Gospel ► Increases § Catholics, Jews ► New Christian Sects § Christian Science ► Spiritual life over material § Pentecostals ► Baptism tongues in spirit; speaking in § Salvation Army § Jehovah’s Witnesses ► Millenialist
 Temperance and Reform Alcohol and vices blamed for urban problems ► Regulating Morality ► § Comstock Law (1873) ► Temperance Organizations § National Prohibition Party (1869) § Women’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) (1874) ► Frances E. Willard § Antisaloon League (1893) § Carrie Nation ► “Hatchetations” ► Reform Groups § Planned parenthood § Humane societies § Anti-prostitution
Temperance and Reform Alcohol and vices blamed for urban problems ► Regulating Morality ► § Comstock Law (1873) ► Temperance Organizations § National Prohibition Party (1869) § Women’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) (1874) ► Frances E. Willard § Antisaloon League (1893) § Carrie Nation ► “Hatchetations” ► Reform Groups § Planned parenthood § Humane societies § Anti-prostitution
 Gilded Age Academics ► Educational Reforms § Compulsory Education ► Most states required 8 -14 year olds to attend schools § Kindergartens § Public Education ► Dramatic increase in high schools and adult education ► Comprehensive education ► Led to 90% literacy rate § Colleges and Universities ► Increased through federal legislation and philanthropy ► Science § Darwin and Natural Selection (Evolution) § Technological Innovation ► Social Sciences § Scientific method applied to behavioral sciences § Development of psychology, sociology, political science ► William James’s Principles of Psychology
Gilded Age Academics ► Educational Reforms § Compulsory Education ► Most states required 8 -14 year olds to attend schools § Kindergartens § Public Education ► Dramatic increase in high schools and adult education ► Comprehensive education ► Led to 90% literacy rate § Colleges and Universities ► Increased through federal legislation and philanthropy ► Science § Darwin and Natural Selection (Evolution) § Technological Innovation ► Social Sciences § Scientific method applied to behavioral sciences § Development of psychology, sociology, political science ► William James’s Principles of Psychology
 Gilded Age Entertainment and Leisure ► Causes § Urbanization, less working hours, advertisements ► Vaudevilles § Popularized with family-friendly subjects and material Saloons ► Amusement Parks ► § Coney Island ► Circus § P. T. Barnum ► Sports § Spectator ► Baseball, boxing, football, basketball § Amateur ► Golf, tennis
Gilded Age Entertainment and Leisure ► Causes § Urbanization, less working hours, advertisements ► Vaudevilles § Popularized with family-friendly subjects and material Saloons ► Amusement Parks ► § Coney Island ► Circus § P. T. Barnum ► Sports § Spectator ► Baseball, boxing, football, basketball § Amateur ► Golf, tennis
 Realism and Naturalism ► Realism § Objective reality § Depict accurate and true characters and settings § Absent of emotional embellishment ► Naturalism § Depiction of objects in natural settings § Time and place accuracy Brooklyn Bridge at Night Edward Willis Redfield 1909
Realism and Naturalism ► Realism § Objective reality § Depict accurate and true characters and settings § Absent of emotional embellishment ► Naturalism § Depiction of objects in natural settings § Time and place accuracy Brooklyn Bridge at Night Edward Willis Redfield 1909
 Gilded Age Art ► Ashcan School § Depiction of New York City urban life § George Bellows ► James M. Whistler ► Winslow Homer ► Mary Cassatt Both Members of This Club George Bellows 1909
Gilded Age Art ► Ashcan School § Depiction of New York City urban life § George Bellows ► James M. Whistler ► Winslow Homer ► Mary Cassatt Both Members of This Club George Bellows 1909
 Winslow Homer’s Breezing Up
Winslow Homer’s Breezing Up
 George Bellow’s New York
George Bellow’s New York
 James Whistler’s Arrangement in Grey and Black No. 1 (Whistler’s Mother) (1871)
James Whistler’s Arrangement in Grey and Black No. 1 (Whistler’s Mother) (1871)
 Mary Cassat’s The Child’s Bath (1893)
Mary Cassat’s The Child’s Bath (1893)
 Gilded Age Architecture ► Victorian Influence § Henry Hobson Richardson ► Louis Sullivan § “Father of Skyscrapers” § “form follows function” ► Frank Lloyd Wright § “organic architecture” ► Foursquare Homes
Gilded Age Architecture ► Victorian Influence § Henry Hobson Richardson ► Louis Sullivan § “Father of Skyscrapers” § “form follows function” ► Frank Lloyd Wright § “organic architecture” ► Foursquare Homes
 Richardson’s Trinity Church
Richardson’s Trinity Church
 Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater
Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater
 Foursquare Home
Foursquare Home
 Gilded Age Press and Literature ► Press § Joseph Pulitzer’s New York World & William Randolph Hearst ► Sensationalism and scandals § Magazines ► Editorial style based on investigative journalism ► Forum ► Non-Fiction § Toward facts, investigations, American expansion § Helen Hunt Jackson’s A Century of Dishonor (1881) § Alfred Thayer Mahan’s The Influence of Sea Power on History (1890) § Josiah Strong’s Our Country ► Literature § Authors focused on character development and realism over plot § Lewis Wallace ► Ben-Hur: A Tale of Christ § Mark Twain ► The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn ► The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today § Stephen Crane ► The Red Badge of Courage § Jack London ► The Call of the Wild; White Fang
Gilded Age Press and Literature ► Press § Joseph Pulitzer’s New York World & William Randolph Hearst ► Sensationalism and scandals § Magazines ► Editorial style based on investigative journalism ► Forum ► Non-Fiction § Toward facts, investigations, American expansion § Helen Hunt Jackson’s A Century of Dishonor (1881) § Alfred Thayer Mahan’s The Influence of Sea Power on History (1890) § Josiah Strong’s Our Country ► Literature § Authors focused on character development and realism over plot § Lewis Wallace ► Ben-Hur: A Tale of Christ § Mark Twain ► The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn ► The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today § Stephen Crane ► The Red Badge of Courage § Jack London ► The Call of the Wild; White Fang
 Gilded Age Music ► Mainstream Music § John Philip Sousa – The March King ► The Washington Post ► Stars and Stripes Forever ► Semper Fidelis § Screamers – Circus Marches ► Entry of the ► Circus Bee ► Gladiators Popular Music § Ragtime ► Originated from black communities combining African syncopation and classical music ► Scott Joplin § Maple Leaf Rag § The Entertainer § The Blues ► Originated c. 1890 from Deep South based on ballads among slaves ► Lyrics mostly soulful and melancholy
Gilded Age Music ► Mainstream Music § John Philip Sousa – The March King ► The Washington Post ► Stars and Stripes Forever ► Semper Fidelis § Screamers – Circus Marches ► Entry of the ► Circus Bee ► Gladiators Popular Music § Ragtime ► Originated from black communities combining African syncopation and classical music ► Scott Joplin § Maple Leaf Rag § The Entertainer § The Blues ► Originated c. 1890 from Deep South based on ballads among slaves ► Lyrics mostly soulful and melancholy


