2222554ea6343cd5253ce73e86ba0590.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Gerunds & Infinitives Unit 9 Grammar Forms & Functions 3
Gerunds & Infinitives Unit 9 Grammar Forms & Functions 3
 Gerunds as Subjects & Objects Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. This is an A. Painting my favorite subject. incomplete sentence. Correct. “Painting” is the B. Painting is my subject (gerund – verb + favorite subject. ing). Correct. Single gerund A. Scuba diving subjects take a singular takes a lot of money. verb. Incorrect. Single gerund B. Scuba diving take subjects take a singular a lot of money. verb. Correct. Gerunds are A. He stopped singular, cycling. add “-s. ” so don’t Incorrect. stopped B. He Gerunds are singular, so don’t add “-s. ” cyclings. Click to go to next slide.
Gerunds as Subjects & Objects Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. This is an A. Painting my favorite subject. incomplete sentence. Correct. “Painting” is the B. Painting is my subject (gerund – verb + favorite subject. ing). Correct. Single gerund A. Scuba diving subjects take a singular takes a lot of money. verb. Incorrect. Single gerund B. Scuba diving take subjects take a singular a lot of money. verb. Correct. Gerunds are A. He stopped singular, cycling. add “-s. ” so don’t Incorrect. stopped B. He Gerunds are singular, so don’t add “-s. ” cyclings. Click to go to next slide.
 Gerunds as Subjects & Objects Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Two or more A. Winning and gerunds as subjects create losing are important a plural subject and take a lessons to learn. plural verb. Incorrect. Two or more B. Winning and gerunds as subjects create losing is important a plural subject and take a lessons to learn. plural verb. Incorrect. “Are running” is A. They is running in the present progressive the park. verb (not a gerund). Correct. “Are running” is B. They are running the present progressive in the park. verb (not a gerund). Correct. Need a verb in A. Let’s go surfing. front of the gerund object. Incorrect. Need a verb in B. Let’s surfing. front of the gerund object. Click to go to next slide.
Gerunds as Subjects & Objects Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Two or more A. Winning and gerunds as subjects create losing are important a plural subject and take a lessons to learn. plural verb. Incorrect. Two or more B. Winning and gerunds as subjects create losing is important a plural subject and take a lessons to learn. plural verb. Incorrect. “Are running” is A. They is running in the present progressive the park. verb (not a gerund). Correct. “Are running” is B. They are running the present progressive in the park. verb (not a gerund). Correct. Need a verb in A. Let’s go surfing. front of the gerund object. Incorrect. Need a verb in B. Let’s surfing. front of the gerund object. Click to go to next slide.
 Gerunds as objects of prepositions Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. You can A. She is interested have a gerund as the object in him. of a preposition. Both are correct. You can B. She is interested have a gerund as the object in seeing him. of a preposition. Incorrect. You can use a A. I amin a prepositional gerund good at learn phrase, but not a verb languages. (learn). Correct. You can use a B. I am good at gerund in a prepositional learning languages. phrase, but not a verb (learn). Incorrect. Present A. They looking progessive verbs (are forward to seeing us looking) require a “be” verb tomorrow. with it. Correct. The verb is simple B. They look forward present, which is fine, and to seeing us the gerund is in the tomorrow. prepositional phrase. Click to go to next slide.
Gerunds as objects of prepositions Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. You can A. She is interested have a gerund as the object in him. of a preposition. Both are correct. You can B. She is interested have a gerund as the object in seeing him. of a preposition. Incorrect. You can use a A. I amin a prepositional gerund good at learn phrase, but not a verb languages. (learn). Correct. You can use a B. I am good at gerund in a prepositional learning languages. phrase, but not a verb (learn). Incorrect. Present A. They looking progessive verbs (are forward to seeing us looking) require a “be” verb tomorrow. with it. Correct. The verb is simple B. They look forward present, which is fine, and to seeing us the gerund is in the tomorrow. prepositional phrase. Click to go to next slide.
 Gerunds after common expressions Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. After “can’t A. I can’t stand wait stand” I could have put the infinitive in line. but not “to wait, ” the verb “wait. ” Correct. Often use a gerund B. I can’t stand waiting in line. after “can’t stand. ” Correct. Need a gerund A. It’s not worth usually after the phrase “it’s worrying about it. not worth. ” Incorrect. Need a gerund B. It’s not worth usually after the phrase “it’s worry about it. not worth. ” Correct. Usually put a A. Ginger has gerund after learning difficulty the phrase “have difficulty. ” languages. Incorrect. Usually put a B. Ginger has gerund after the phrase difficulty learn “have difficulty. ” languages. Click to go to next slide.
Gerunds after common expressions Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. After “can’t A. I can’t stand wait stand” I could have put the infinitive in line. but not “to wait, ” the verb “wait. ” Correct. Often use a gerund B. I can’t stand waiting in line. after “can’t stand. ” Correct. Need a gerund A. It’s not worth usually after the phrase “it’s worrying about it. not worth. ” Incorrect. Need a gerund B. It’s not worth usually after the phrase “it’s worry about it. not worth. ” Correct. Usually put a A. Ginger has gerund after learning difficulty the phrase “have difficulty. ” languages. Incorrect. Usually put a B. Ginger has gerund after the phrase difficulty learn “have difficulty. ” languages. Click to go to next slide.
 Verbs followed by infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Need an infinitive A. We agreed to look (to look) after the verb, not after their kids. a verb (look). Incorrect. Need an infinitive B. We agreed look (to look) after the verb, not after their kids. a verb (look). C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. “Everybody” A. Everybody verb. “To takes a singular want to succeed” is the infinitive succeed. after the verb. Correct. “Everybody” takes B. a singular verb. “To Everybody wants succeed” is the infinitive to succeed. after the verb. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. Sometimes can A. They object after the have an asked her to verb and before the stay. infinitive “to stay. ” Incorrect. Sometimes can B. They asked her have an object after the verb and before the stay. infinitive “to stay. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
Verbs followed by infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Need an infinitive A. We agreed to look (to look) after the verb, not after their kids. a verb (look). Incorrect. Need an infinitive B. We agreed look (to look) after the verb, not after their kids. a verb (look). C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. “Everybody” A. Everybody verb. “To takes a singular want to succeed” is the infinitive succeed. after the verb. Correct. “Everybody” takes B. a singular verb. “To Everybody wants succeed” is the infinitive to succeed. after the verb. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. Sometimes can A. They object after the have an asked her to verb and before the stay. infinitive “to stay. ” Incorrect. Sometimes can B. They asked her have an object after the verb and before the stay. infinitive “to stay. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
 Verbs followed by gerunds or infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. Can use a A. gerund or infinitivesnow. It started to after some verbs. Both are correct. Can use a B. gerund or infinitive after It started snowing. some verbs. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. A. The class stopped Correct. Remember that an talking when the infinitive is “to” + base verb. teacher entered. B. The class stopped Incorrect. Remember that an infinitive iswhen base to talking “to” + the teacher enter. verb. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. Can use the A. I remembered go infinitive “to go” or the gerund “going, ” but not the to the post office. verb “go. ” Correct. Can use the B. I remembered to infinitive “to go” or the go to the post office. gerund “going, ” but not the verb “go. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
Verbs followed by gerunds or infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. Can use a A. gerund or infinitivesnow. It started to after some verbs. Both are correct. Can use a B. gerund or infinitive after It started snowing. some verbs. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. A. The class stopped Correct. Remember that an talking when the infinitive is “to” + base verb. teacher entered. B. The class stopped Incorrect. Remember that an infinitive iswhen base to talking “to” + the teacher enter. verb. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. Can use the A. I remembered go infinitive “to go” or the gerund “going, ” but not the to the post office. verb “go. ” Correct. Can use the B. I remembered to infinitive “to go” or the go to the post office. gerund “going, ” but not the verb “go. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
 Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Adjective Infinitive He was pleased to see me. We were disappointed to hear the news. **Infinitives can come after some adjectives. Usually the adjective describes a feeling or attitude. Noun/Indefinite Pronoun Infinitive Do you have anything to read? I have some letters to write. **Infinitives can come after nouns or indefinite pronouns like “everybody” or “anything. ” **Infinitives after a noun often mean an obligation or necessity. **Use “for” + noun/indefinite pronoun to show who the infinitive refers to.
Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Adjective Infinitive He was pleased to see me. We were disappointed to hear the news. **Infinitives can come after some adjectives. Usually the adjective describes a feeling or attitude. Noun/Indefinite Pronoun Infinitive Do you have anything to read? I have some letters to write. **Infinitives can come after nouns or indefinite pronouns like “everybody” or “anything. ” **Infinitives after a noun often mean an obligation or necessity. **Use “for” + noun/indefinite pronoun to show who the infinitive refers to.
 Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Need “for” in front A. I have some work for James“James. ” of the noun to do. B. I have Need “for” in Incorrect. some work front James to do. of the noun “James. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “To visit” is an A. I’m afraid to visit infinitive and infinitives often follow the word the dentist. “afraid. ” Incorrect. “Of visit” is not B. I’m afraid of have an infinitive. Could visit “afraid ofdentist. the visiting” since “visiting” is a gerund. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. This sentence is A. Mike willingly to an incomplete sentence. It stop for milk. doesn’t have any verb. Correct. “Willing” is the B. Mike is willing to adjective after the “be” verb and for often use stop we milk. infinitives after “willing. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Click on the correct sentence. Correct. Need “for” in front A. I have some work for James“James. ” of the noun to do. B. I have Need “for” in Incorrect. some work front James to do. of the noun “James. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “To visit” is an A. I’m afraid to visit infinitive and infinitives often follow the word the dentist. “afraid. ” Incorrect. “Of visit” is not B. I’m afraid of have an infinitive. Could visit “afraid ofdentist. the visiting” since “visiting” is a gerund. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. This sentence is A. Mike willingly to an incomplete sentence. It stop for milk. doesn’t have any verb. Correct. “Willing” is the B. Mike is willing to adjective after the “be” verb and for often use stop we milk. infinitives after “willing. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
 Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. This sentence is A. It timebecause it is incomplete to leave. missing a verb. Correct. The infinitive after the noun means that it is B. It’s time toleave now leave. necessary for me to or that I should leave now. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. We often use an A. She was determined after infinitive to study “determined. ” harder. Incorrect. I She was gerund B. can use the “studying, ” but the sentence is determined studying incomplete. “Studying harder” harder. would what? C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “To go” is the A. I want everyone infinitive after the indefinite to go to page 21. pronoun “everyone. ” Incorrect. Need an infinitive B. I want everyone go to“everyone. ” after page 21. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
Infinitives after Certain Adjectives, Nouns, & Indefinite Pronouns Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. This sentence is A. It timebecause it is incomplete to leave. missing a verb. Correct. The infinitive after the noun means that it is B. It’s time toleave now leave. necessary for me to or that I should leave now. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. We often use an A. She was determined after infinitive to study “determined. ” harder. Incorrect. I She was gerund B. can use the “studying, ” but the sentence is determined studying incomplete. “Studying harder” harder. would what? C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “To go” is the A. I want everyone infinitive after the indefinite to go to page 21. pronoun “everyone. ” Incorrect. Need an infinitive B. I want everyone go to“everyone. ” after page 21. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
 “Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Subject Verb Too + Adjective/ Adverb For + Object Infinitive It is too cold for the boys to go to the beach. He spoke too quickly for me to understand. **Use “too” for a negative meaning. **”Very” means to a great degree.
“Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Subject Verb Too + Adjective/ Adverb For + Object Infinitive It is too cold for the boys to go to the beach. He spoke too quickly for me to understand. **Use “too” for a negative meaning. **”Very” means to a great degree.
 “Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Which is the most Incorrect. sentence? negative. This sentence is mostly positive. A. I am very busy. Correct. “Too” means that I can’t help busy B. I am too you. to C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. We often use an A. My computer freezes too after infinitive much to get any work done. “determined. ” Incorrect. This sentence is B. My front of “get” missing “to” incomputer so it doesn’t have an infinitive. get freezes much too. ALSO, “too” should be in done. the any work front of adverb “much. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “Very much” A. She wanted very explains her strong desire much to play. Incorrect. wanted too B. She “Too” should be “very” in this sentence. much to play. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. help you. Click to go to next slide.
“Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Which is the most Incorrect. sentence? negative. This sentence is mostly positive. A. I am very busy. Correct. “Too” means that I can’t help busy B. I am too you. to C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. We often use an A. My computer freezes too after infinitive much to get any work done. “determined. ” Incorrect. This sentence is B. My front of “get” missing “to” incomputer so it doesn’t have an infinitive. get freezes much too. ALSO, “too” should be in done. the any work front of adverb “much. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “Very much” A. She wanted very explains her strong desire much to play. Incorrect. wanted too B. She “Too” should be “very” in this sentence. much to play. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. help you. Click to go to next slide.
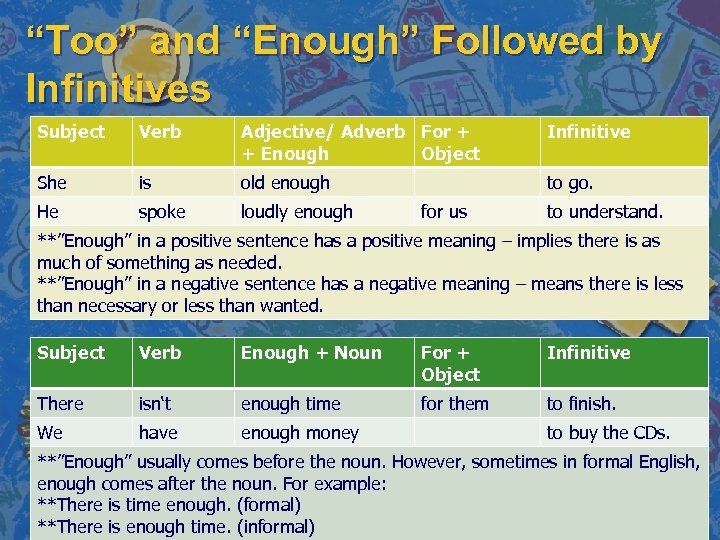 “Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Subject Verb Adjective/ Adverb For + + Enough Object Infinitive She is old enough to go. He spoke loudly enough for us to understand. **”Enough” in a positive sentence has a positive meaning – implies there is as much of something as needed. **”Enough” in a negative sentence has a negative meaning – means there is less than necessary or less than wanted. Subject Verb Enough + Noun For + Object Infinitive There isn‘t enough time for them to finish. We have enough money to buy the CDs. **”Enough” usually comes before the noun. However, sometimes in formal English, enough comes after the noun. For example: **There is time enough. (formal) **There is enough time. (informal)
“Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Subject Verb Adjective/ Adverb For + + Enough Object Infinitive She is old enough to go. He spoke loudly enough for us to understand. **”Enough” in a positive sentence has a positive meaning – implies there is as much of something as needed. **”Enough” in a negative sentence has a negative meaning – means there is less than necessary or less than wanted. Subject Verb Enough + Noun For + Object Infinitive There isn‘t enough time for them to finish. We have enough money to buy the CDs. **”Enough” usually comes before the noun. However, sometimes in formal English, enough comes after the noun. For example: **There is time enough. (formal) **There is enough time. (informal)
 “Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. The infinitive A. comes is old enough She after “enough” whichto drive. the comes after adjective “old. ” B. She “Enough” should be Incorrect. is enough old after the adjective “old. ” to drive. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. This sentence is A. Lincoln gets missing the “to” in front of enough time play each day. “play. ” Correct. “Enough” gets in B. Lincoln comes front of the noun “time” and is enough time to play followed by the infinitive “to each day. play. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “Enough” is after A. This coffee is not the adjective “warm” and is warm enough to followed by the infinitive “to drink. ” Incorrect. coffee is not B. This “Enough” should be after the adjective enough warm to “warm. ” drink. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
“Too” and “Enough” Followed by Infinitives Click on the correct sentence. Incorrect. The infinitive A. comes is old enough She after “enough” whichto drive. the comes after adjective “old. ” B. She “Enough” should be Incorrect. is enough old after the adjective “old. ” to drive. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Incorrect. This sentence is A. Lincoln gets missing the “to” in front of enough time play each day. “play. ” Correct. “Enough” gets in B. Lincoln comes front of the noun “time” and is enough time to play followed by the infinitive “to each day. play. ” C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Correct. “Enough” is after A. This coffee is not the adjective “warm” and is warm enough to followed by the infinitive “to drink. ” Incorrect. coffee is not B. This “Enough” should be after the adjective enough warm to “warm. ” drink. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Click to go to next slide.
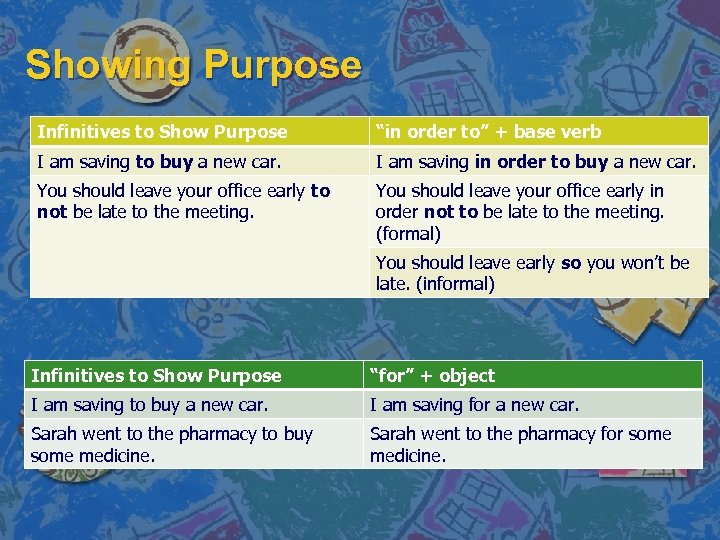 Showing Purpose Infinitives to Show Purpose “in order to” + base verb I am saving to buy a new car. I am saving in order to buy a new car. You should leave your office early to not be late to the meeting. You should leave your office early in order not to be late to the meeting. (formal) You should leave early so you won’t be late. (informal) Infinitives to Show Purpose “for” + object I am saving to buy a new car. I am saving for a new car. Sarah went to the pharmacy to buy some medicine. Sarah went to the pharmacy for some medicine.
Showing Purpose Infinitives to Show Purpose “in order to” + base verb I am saving to buy a new car. I am saving in order to buy a new car. You should leave your office early to not be late to the meeting. You should leave your office early in order not to be late to the meeting. (formal) You should leave early so you won’t be late. (informal) Infinitives to Show Purpose “for” + object I am saving to buy a new car. I am saving for a new car. Sarah went to the pharmacy to buy some medicine. Sarah went to the pharmacy for some medicine.
 Showing Purpose Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. Infinitives A. I drank a lot of can show purpose and “in coffee in order to” + base verb can stay awake. show purpose. Both are correct. Infinitives B. I drank a lot of can show purpose and “in coffee to stay verb can order to” + base awake. show purpose. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. A. Correct. The base verb Lincoln must take his vitamins in order “get” comes after “in order not to get sick. not to. ” B. Lincoln must take Incorrect. This sentence is his vitamins, so he missing “to” in front of will not “get. ” to get sick. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Both are correct. “For” A. Henry went to Los shows the purpose of his Angeles for dinner. trip to Los Angeles. B. Henry went“To buy” Both are correct. to Los shows the purpose of his Angeles to buy trip to Los Angeles. dinner. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. Click to end show.
Showing Purpose Click on the correct sentence. Both are correct. Infinitives A. I drank a lot of can show purpose and “in coffee in order to” + base verb can stay awake. show purpose. Both are correct. Infinitives B. I drank a lot of can show purpose and “in coffee to stay verb can order to” + base awake. show purpose. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. A. Correct. The base verb Lincoln must take his vitamins in order “get” comes after “in order not to get sick. not to. ” B. Lincoln must take Incorrect. This sentence is his vitamins, so he missing “to” in front of will not “get. ” to get sick. C. Both are Incorrect. Try correct. again. Both are correct. “For” A. Henry went to Los shows the purpose of his Angeles for dinner. trip to Los Angeles. B. Henry went“To buy” Both are correct. to Los shows the purpose of his Angeles to buy trip to Los Angeles. dinner. C. Both See Correct. are other answers. correct. Click to end show.


