b92ee64a26921d81913f78e8a10e46e9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

GERMANY – B. Müller What is PPP? Planning + Building + Financing + Operation (+ Post-contract life) = PPP-Sectors: PPP – construction, PPP – infrastructure
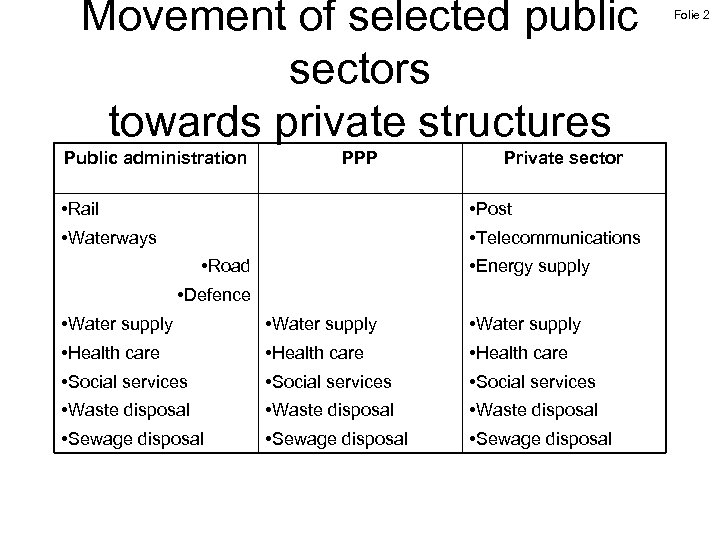
Movement of selected public sectors towards private structures Public administration PPP Private sector • Rail • Post • Waterways • Telecommunications • Road • Energy supply • Defence • Water supply • Health care • Social services • Waste disposal • Sewage disposal Folie 2
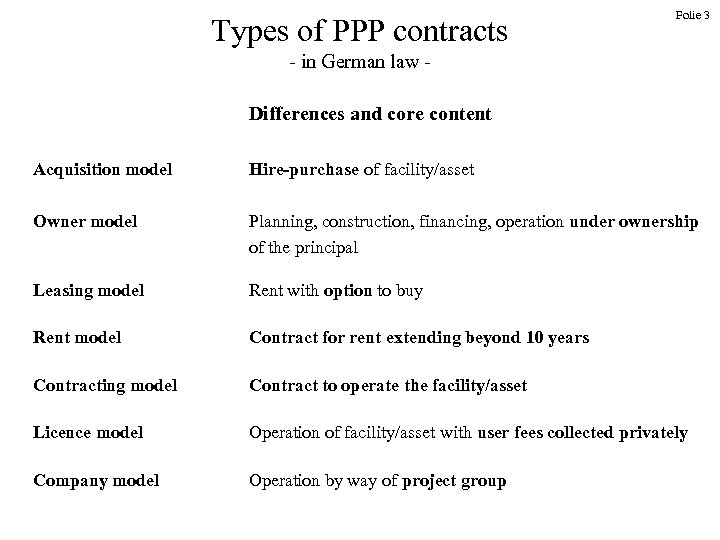
Types of PPP contracts Folie 3 - in German law Differences and core content Acquisition model Hire-purchase of facility/asset Owner model Planning, construction, financing, operation under ownership of the principal Leasing model Rent with option to buy Rent model Contract for rent extending beyond 10 years Contracting model Contract to operate the facility/asset Licence model Operation of facility/asset with user fees collected privately Company model Operation by way of project group
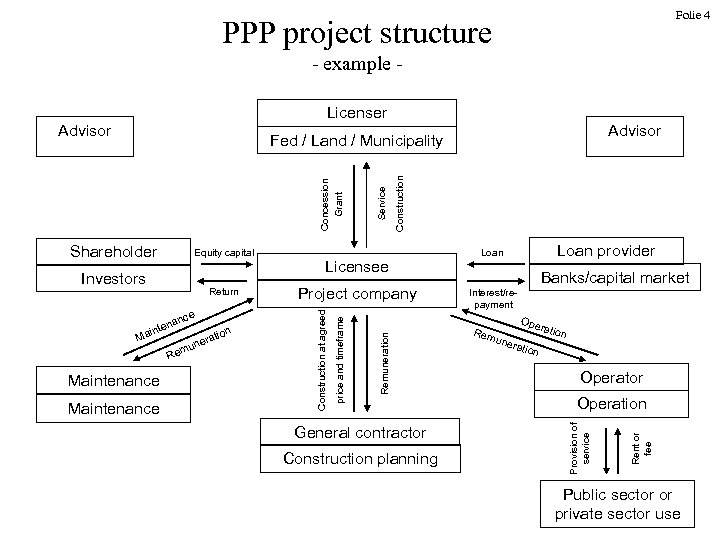
Folie 4 PPP project structure - example Licenser Advisor na inte nce Ma Re ne mu Maintenance on rati Construction Project company General contractor Construction planning Loan provider Loan Banks/capital market Interest/repayment Ope Rem ratio une ratio n n Operator Operation Provision of service Return Licensee Remuneration Investors price and timeframe Equity capital Construction at agreed Shareholder Service Concession Grant Fed / Land / Municipality Rent or fee Advisor Public sector or private sector use

Folie 5 History of PPP at EU level 07 May 2003 Commission publishes “Internal market strategy – priorities 2003 – 2006”, which highlights the need to clarify legal issues relating to PPP. The publication of a green paper on PPP is announced. 21 May 2003 Commission publishes Green Paper on services of general interest. This paper entails a substantial review of the Commission's service policy and asks whether a general legal framework should be created at Community level for services of general interest. The Commission plans top publish a green paper on public procurements and on PPP in the second half of the year. 30 Apr 2004 Commission adopts Green Paper 30 Apr 2004 Forwarded to the Council 30 Apr 2004 Forwarded to the European Parliament (EP) 27 Oct 2004 Opinion by the European Economic and Social Committee 17 Nov 2004 Opinion by the Committee of the Regions End 2005 Commission announces resolution on further PPP legislation for the end of 2006 26 Oct 2006 Resolution by EP

History of PPP at federal level in Germany Apr 2001 Federal Chancellor sets up “Kanzler-AG” Jun 2002 Federal Chancellor announces PPP competence centre Jul 2002 Steering committee (SC): “PPP in public construction works” Feb 2003 PPP federal study commissioned Jul 2003 Bundestag adopts motion for PPP resolution Dec 2003 Agreement by federal states ministers responsible for building Dec 2003 SC: Recommendations for framework conditions Nov 2004 Members’ initiative “PPPs Acceleration Act” Dec 2004 Agreement by federal state ministers responsible for finance (FMK) Jul 2004 PPP Task Force set up May 2005 Creation of federal PPP competence network Sep 2005 PPPs Acceleration Act comes into force Sep 2006 FMK decision: Standard guidelines on examining profitability Source: PPP Task Force, Federal Ministry for Transport, Building and Urban Affairs Folie 6
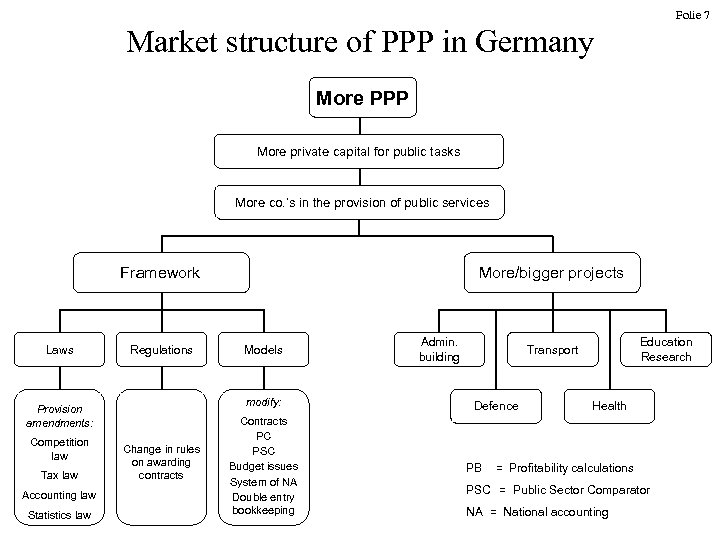
Folie 7 Market structure of PPP in Germany More PPP More private capital for public tasks More co. ’s in the provision of public services Framework Laws Regulations Tax law Accounting law Statistics law Models modify: Provision amendments: Competition law More/bigger projects Change in rules on awarding contracts Contracts PC PSC Budget issues System of NA Double entry bookkeeping Admin. building Education Research Transport Defence Health PB = Profitability calculations PSC = Public Sector Comparator NA = National accounting
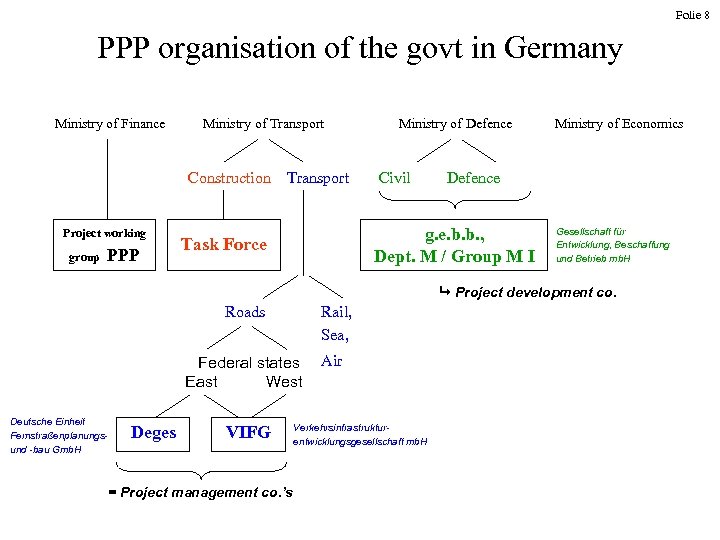
Folie 8 PPP organisation of the govt in Germany Ministry of Finance Ministry of Transport Construction Project working group PPP Transport Ministry of Defence Civil Defence g. e. b. b. , Dept. M / Group M I Task Force Ministry of Economics Gesellschaft für Entwicklung, Beschaffung und Betrieb mb. H Project development co. Roads Federal states East West Deutsche Einheit Fernstraßenplanungsund -bau Gmb. H Deges Rail, Sea, Air VIFG = Project management co. ’s Verkehrsinfrastrukturentwicklungsgesellschaft mb. H
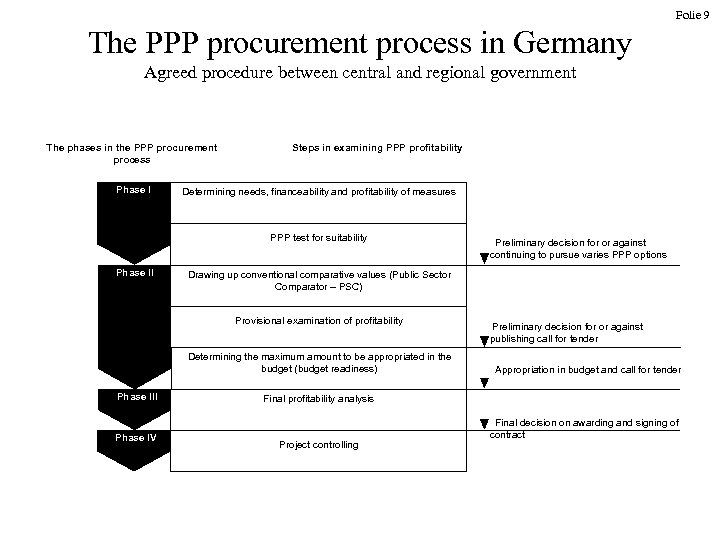
Folie 9 The PPP procurement process in Germany Agreed procedure between central and regional government The phases in the PPP procurement process Phase I Steps in examining PPP profitability Determining needs, financeability and profitability of measures PPP test for suitability Phase II Drawing up conventional comparative values (Public Sector Comparator – PSC) Provisional examination of profitability Determining the maximum amount to be appropriated in the budget (budget readiness) Phase III Phase IV Preliminary decision for or against continuing to pursue varies PPP options Preliminary decision for or against publishing call for tender Appropriation in budget and call for tender Final profitability analysis Project controlling Final decision on awarding and signing of contract
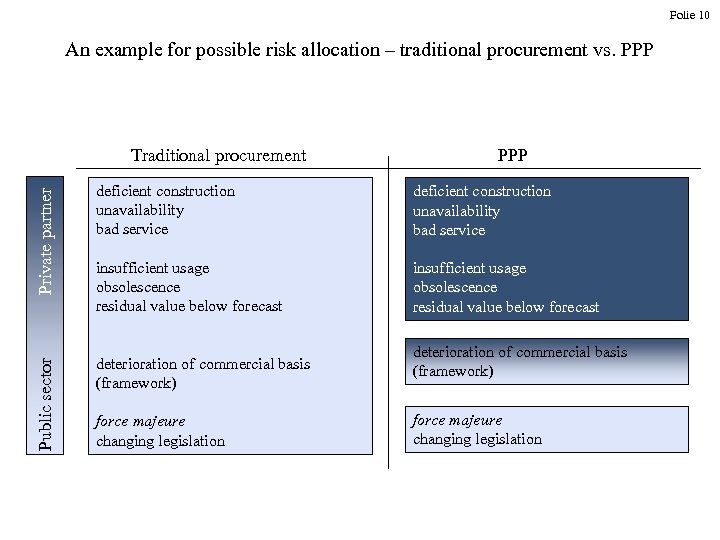
Folie 10 An example for possible risk allocation – traditional procurement vs. PPP Private partner PPP deficient construction unavailability bad service insufficient usage obsolescence residual value below forecast Public sector Traditional procurement deterioration of commercial basis (framework) force majeure changing legislation
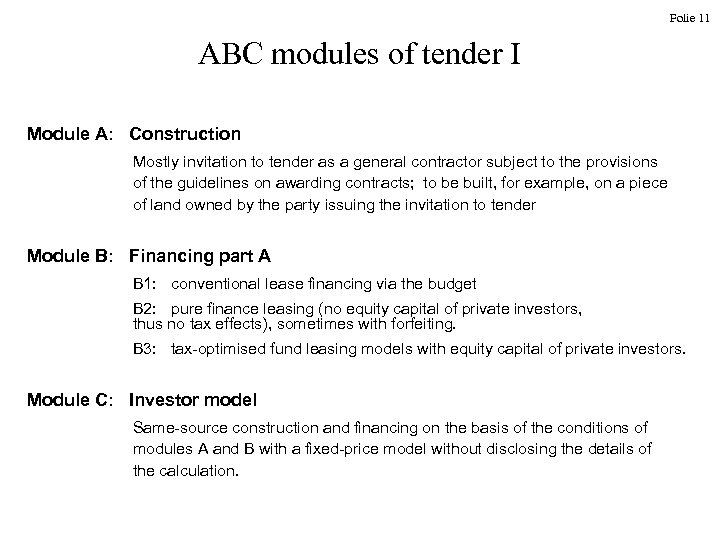
Folie 11 ABC modules of tender I Module A: Construction Mostly invitation to tender as a general contractor subject to the provisions of the guidelines on awarding contracts; to be built, for example, on a piece of land owned by the party issuing the invitation to tender Module B: Financing part A B 1: conventional lease financing via the budget B 2: pure finance leasing (no equity capital of private investors, thus no tax effects), sometimes with forfeiting. B 3: tax-optimised fund leasing models with equity capital of private investors. Module C: Investor model Same-source construction and financing on the basis of the conditions of modules A and B with a fixed-price model without disclosing the details of the calculation.
Folie 12 ABC modules of tender II In addition to parts A, B und C, additional tenders can be invited in suitable cases: Module D: Similar to Module C, but using functional description of construction and with the bidder’s own planning, possibly also on a piece of land owned by the party inviting tender. Module E: Offers to buy, hire-purchase of simply rent suitable objects which have already been built or which are in the process of being built.
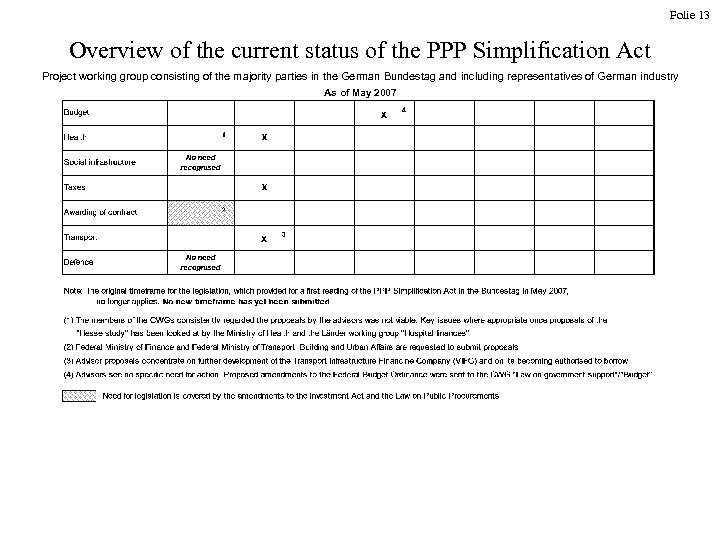
Folie 13 Overview of the current status of the PPP Simplification Act Project working group consisting of the majority parties in the German Bundestag and including representatives of German industry As of May 2007
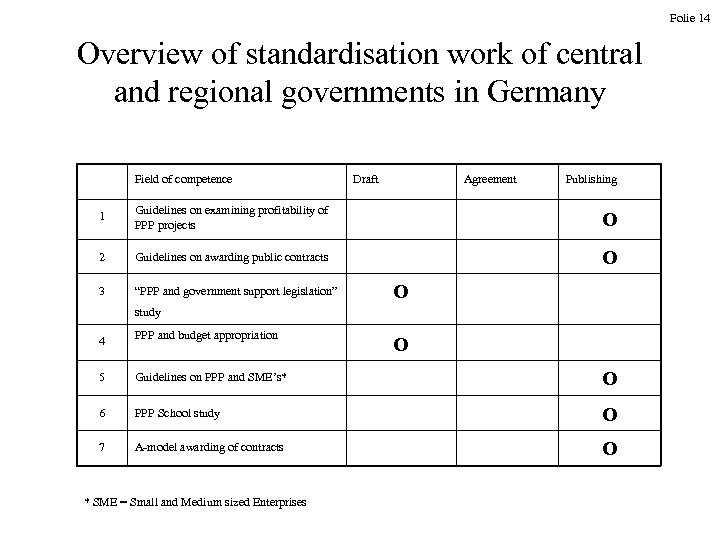
Folie 14 Overview of standardisation work of central and regional governments in Germany Field of competence Draft Agreement Publishing 1 Guidelines on examining profitability of PPP projects O 2 Guidelines on awarding public contracts O 3 “PPP and government support legislation” O study 4 PPP and budget appropriation 5 Guidelines on PPP and SME’s* O 6 PPP School study O 7 A-model awarding of contracts O * SME = Small and Medium sized Enterprises O
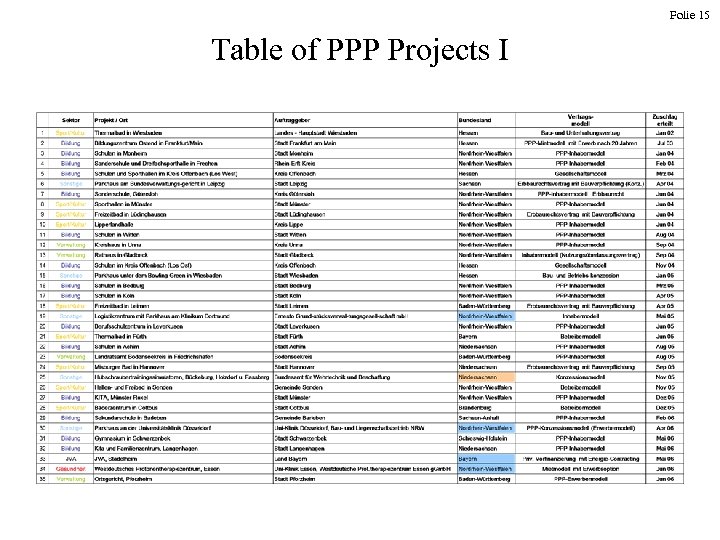
Folie 15 Table of PPP Projects I
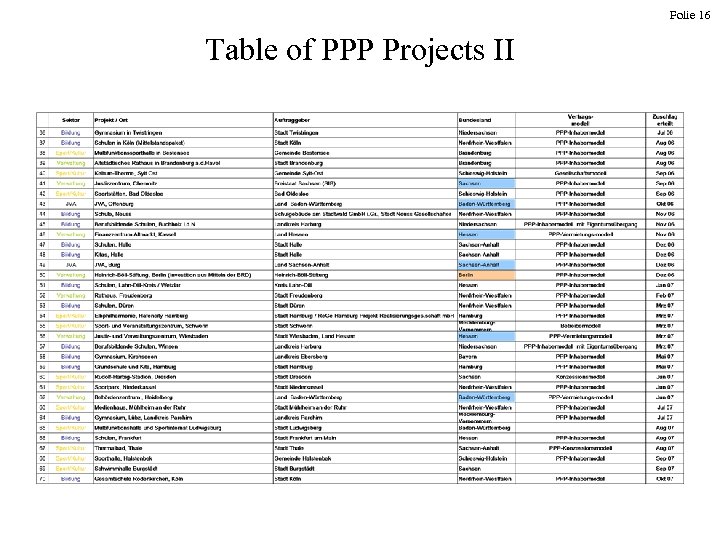
Folie 16 Table of PPP Projects II
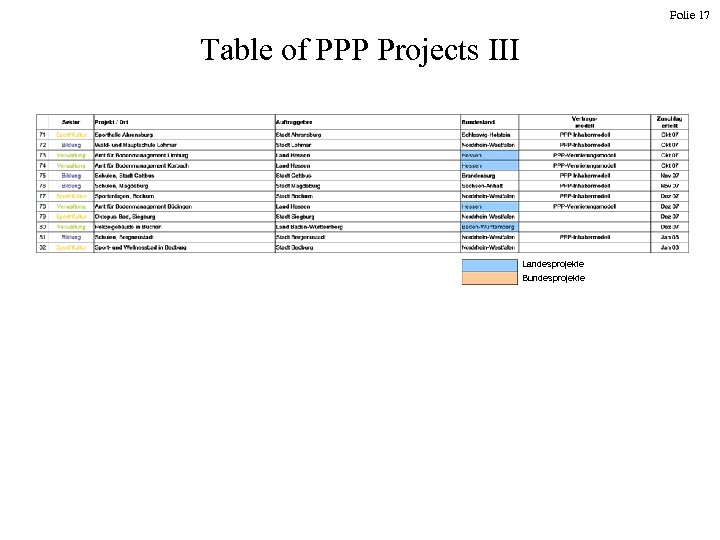
Folie 17 Table of PPP Projects III Landesprojekte Bundesprojekte
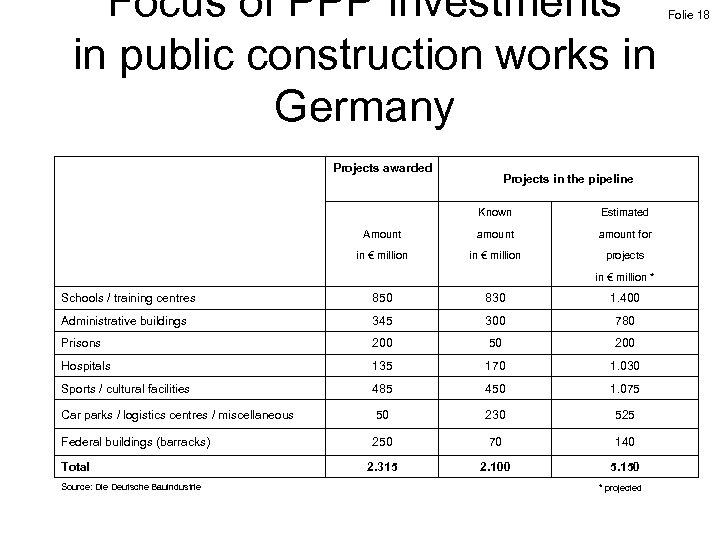
Focus of PPP investments in public construction works in Germany Folie 18 Projects awarded Projects in the pipeline Known Estimated Amount amount for in € million projects in € million * Schools / training centres 850 830 1. 400 Administrative buildings 345 300 780 Prisons 200 50 200 Hospitals 135 170 1. 030 Sports / cultural facilities 485 450 1. 075 Car parks / logistics centres / miscellaneous 50 230 525 Federal buildings (barracks) 250 70 140 2. 315 2. 100 5. 150 Total Source: Die Deutsche Bauindustrie * projected
Folie 19

Folie 20 Plans for the foundation of a company called Partnerschaften Deutschland

Folie 23 What Partnerschaften Deutschland represents Partnerschaften Deutschland is conceived as a broadly positioned quality service provider offering comprehensive consulting services on PPP matters for the public sector – with a focus on the early stages. What Partnerschaften Deutschland offers: – Objectivity, independence and credibility – Cost savings (optimisation of processes, standardisation, know-how) – Speed (especially easy to engage its services) But: Public authorities can continue to procure consulting services on the open market
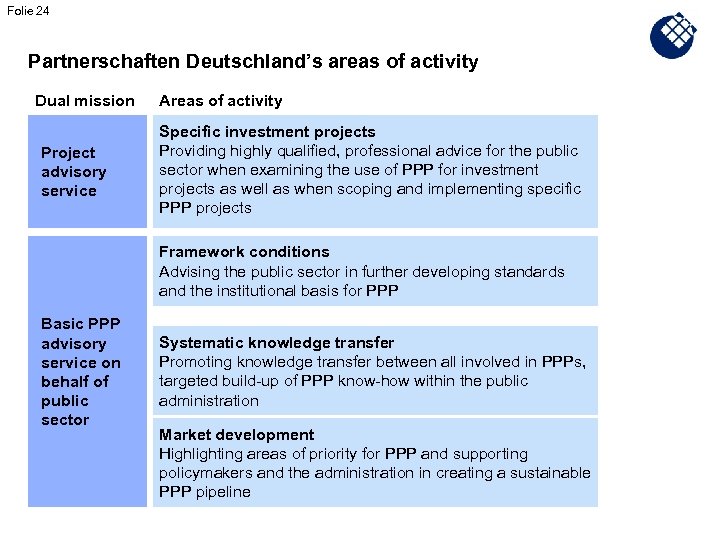
Folie 24 Partnerschaften Deutschland’s areas of activity Dual mission Project advisory service Areas of activity Specific investment projects Providing highly qualified, professional advice for the public sector when examining the use of PPP for investment projects as well as when scoping and implementing specific PPP projects Framework conditions Advising the public sector in further developing standards and the institutional basis for PPP Basic PPP advisory service on behalf of public sector Systematic knowledge transfer Promoting knowledge transfer between all involved in PPPs, targeted build-up of PPP know-how within the public administration Market development Highlighting areas of priority for PPP and supporting policymakers and the administration in creating a sustainable PPP pipeline
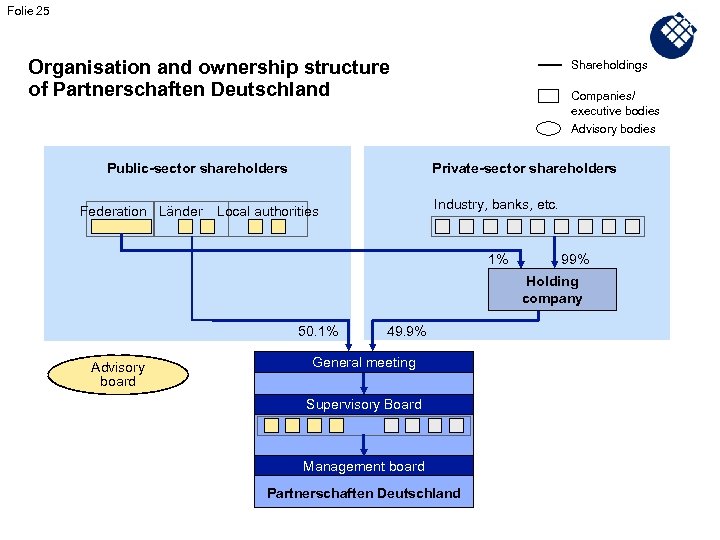
Folie 25 Organisation and ownership structure of Partnerschaften Deutschland Shareholdings Companies/ executive bodies Advisory bodies Public-sector shareholders Federation Länder Private-sector shareholders Industry, banks, etc. Local authorities 1% 99% Holding company 50. 1% Advisory board 49. 9% General meeting Supervisory Board Management board Partnerschaften Deutschland

Folie 26 Avoiding the adviser/tenderer problem and conflicts of interest n Avoiding the adviser/tenderer conflict and direct holdings through the interposition of the holding company and avoiding overlap between representatives of private shareholders and bodies or employees of Partnerschaften Deutschland n Delegation of staff from the private shareholders of the holding company are excluded from Partnerschaften Deutschland for project work n As the holding company is not dedicated to a specific purposes and is not dominated by one company (or industry) either, steps have been taken to ensure that the operative activities of Partnerschaften Deutschland cannot be influenced by the particular interests of its shareholders
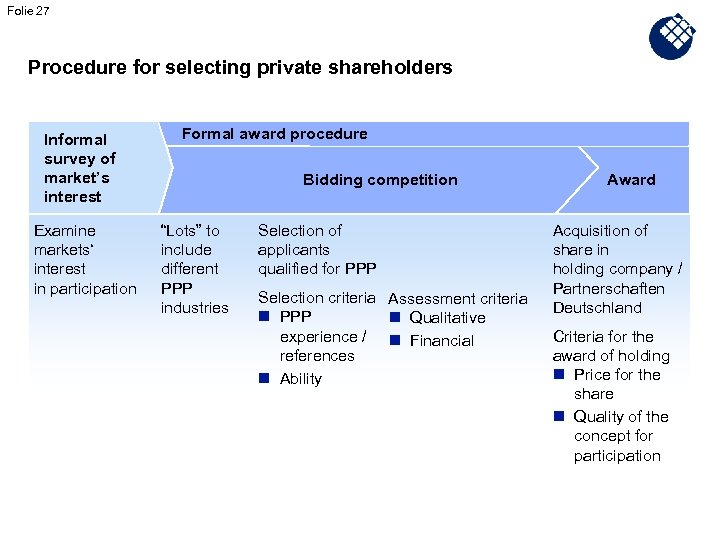
Folie 27 Procedure for selecting private shareholders Informal survey of market’s interest Examine markets‘ interest in participation Formal award procedure Bidding competition “Lots” to include different PPP industries Selection of applicants qualified for PPP Selection criteria Assessment criteria n PPP n Qualitative experience / n Financial references n Ability Award Acquisition of share in holding company / Partnerschaften Deutschland Criteria for the award of holding n Price for the share n Quality of the concept for participation
b92ee64a26921d81913f78e8a10e46e9.ppt