 GERMANIC LANGUAGES
GERMANIC LANGUAGES
 CONTENTS Classification of Germanic languages Origin and development of Germanic languages Germanic tribes and their dialects Alphabets and written records
CONTENTS Classification of Germanic languages Origin and development of Germanic languages Germanic tribes and their dialects Alphabets and written records
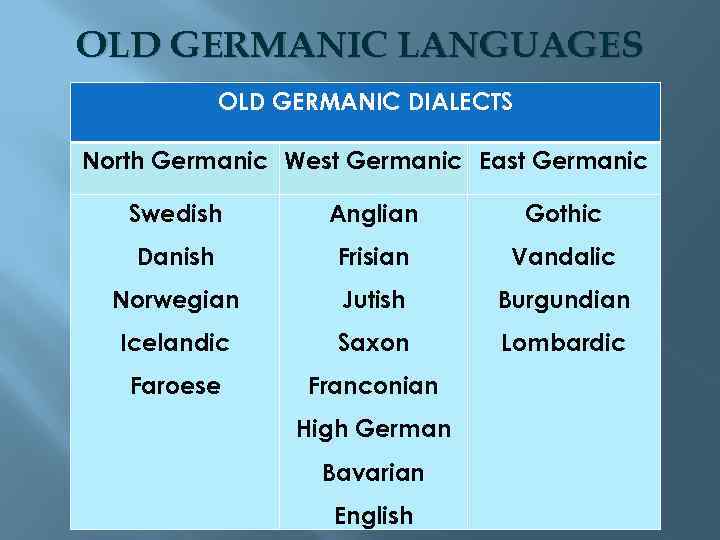 OLD GERMANIC LANGUAGES OLD GERMANIC DIALECTS North Germanic West Germanic East Germanic Swedish Anglian Gothic Danish Frisian Vandalic Norwegian Jutish Burgundian Icelandic Saxon Lombardic Faroese Franconian High German Bavarian English
OLD GERMANIC LANGUAGES OLD GERMANIC DIALECTS North Germanic West Germanic East Germanic Swedish Anglian Gothic Danish Frisian Vandalic Norwegian Jutish Burgundian Icelandic Saxon Lombardic Faroese Franconian High German Bavarian English
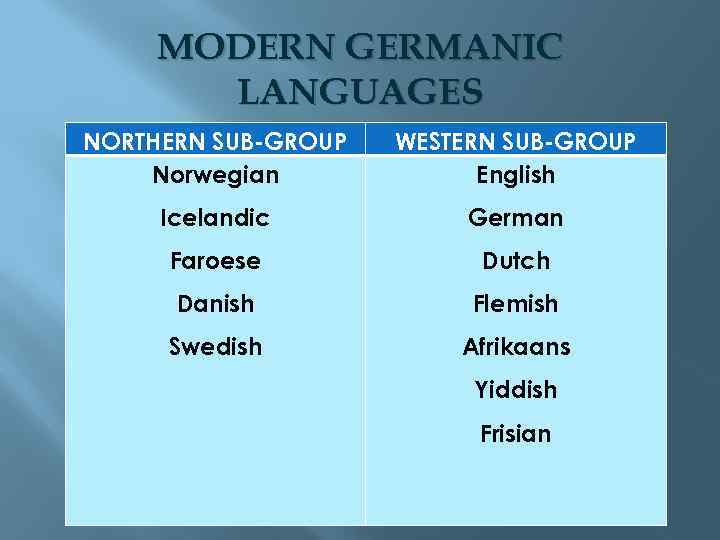 MODERN GERMANIC LANGUAGES NORTHERN SUB-GROUP Norwegian WESTERN SUB-GROUP English Icelandic German Faroese Dutch Danish Flemish Swedish Afrikaans Yiddish Frisian
MODERN GERMANIC LANGUAGES NORTHERN SUB-GROUP Norwegian WESTERN SUB-GROUP English Icelandic German Faroese Dutch Danish Flemish Swedish Afrikaans Yiddish Frisian
 ORIGIN AND DEVELOPMENT OF GERMANIC LANGUAGES The common language - Proto-Germanic or Common, Primitive, Proto-Teutonic. It split from related Indo-European languages between the 15 th and 10 th centuries BC.
ORIGIN AND DEVELOPMENT OF GERMANIC LANGUAGES The common language - Proto-Germanic or Common, Primitive, Proto-Teutonic. It split from related Indo-European languages between the 15 th and 10 th centuries BC.
 GERMANIC TRIBES 1. Vindili ( Modern East Germany) 2. Ingveones (Modern West Germany, North Sea, Holland) 3. Istævones (Modern West Germany, the Rhine) 4. Herminones (Modern South Germany) 5. Pevkins and Bastarns (Modern Rumania) 6. Hilleviones (Modern North Germany, Scandinavia)
GERMANIC TRIBES 1. Vindili ( Modern East Germany) 2. Ingveones (Modern West Germany, North Sea, Holland) 3. Istævones (Modern West Germany, the Rhine) 4. Herminones (Modern South Germany) 5. Pevkins and Bastarns (Modern Rumania) 6. Hilleviones (Modern North Germany, Scandinavia)
 EAST GERMANIC TRIBES Vandals Burgundians The Goths The Western group – Visigoth (visigotae) The Eastern group – Ostrogoth (ostrogotae)
EAST GERMANIC TRIBES Vandals Burgundians The Goths The Western group – Visigoth (visigotae) The Eastern group – Ostrogoth (ostrogotae)
 NORTH GERMANIC TRIBES The Teutons (the southern coast of the Scandinavian peninsular and Nothern Denmark) Common parent language - Old Norse or Old Scandinavian. Gave birth to Sweden, Denmark and Norway.
NORTH GERMANIC TRIBES The Teutons (the southern coast of the Scandinavian peninsular and Nothern Denmark) Common parent language - Old Norse or Old Scandinavian. Gave birth to Sweden, Denmark and Norway.
 WEST GERMANIC TRIBES Franconians or Franks ( Istaevones ) Angles, Frisians, Jutes and Saxons High Germans Low Germans Alemans, Bavarians
WEST GERMANIC TRIBES Franconians or Franks ( Istaevones ) Angles, Frisians, Jutes and Saxons High Germans Low Germans Alemans, Bavarians
 ALPHABETS Runic Gothic Latin
ALPHABETS Runic Gothic Latin
 WRITTEN RECORDS Runic inscriptions – from 200 -450 year Silver codex (Codex Argenteus) – 4 th c.
WRITTEN RECORDS Runic inscriptions – from 200 -450 year Silver codex (Codex Argenteus) – 4 th c.