7094d1f36e23ff6bd00770bf3978ffe9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 George Washington Foreign & Domestic Disputes during the first Administration
George Washington Foreign & Domestic Disputes during the first Administration
 Initial Issues for the General • Sets up the Executive Branch into departments – Forms the first cabinet • Congress sets up the Federal Court System • Financial Program for the country – Debt – Tariffs and excise taxes – National Bank • Controversy over “necessary and proper” clause that Federalists use to justify creation of the bank
Initial Issues for the General • Sets up the Executive Branch into departments – Forms the first cabinet • Congress sets up the Federal Court System • Financial Program for the country – Debt – Tariffs and excise taxes – National Bank • Controversy over “necessary and proper” clause that Federalists use to justify creation of the bank
 Foreign Affairs The French Revolution – Jacobin’s Take over in France – Declare War on British. • U. S. alliance with France still in place, but had been with the French monarchy • Most Americans supported the idea of a French republic, but many dismayed by the mob violence of the Reign of Terror • Thomas Jefferson argues for U. S. support of the revolutionaries – Especially since Britain had been seizing American ships bound for France • What’s a president to do?
Foreign Affairs The French Revolution – Jacobin’s Take over in France – Declare War on British. • U. S. alliance with France still in place, but had been with the French monarchy • Most Americans supported the idea of a French republic, but many dismayed by the mob violence of the Reign of Terror • Thomas Jefferson argues for U. S. support of the revolutionaries – Especially since Britain had been seizing American ships bound for France • What’s a president to do?
 Neutrality Proclamation of Neutrality (April 22, 1793) • Washington doesn’t believe the country is strong enough to get involved in European conflicts. • French Ambassador “Citizen” Edmund Genet appeals directly to American people. – Washington outraged, requests French gov’t remove him, even Jefferson agrees. • House of Reps. Split (TJ, Mad. France/ Feds. & Hamilton Britain.
Neutrality Proclamation of Neutrality (April 22, 1793) • Washington doesn’t believe the country is strong enough to get involved in European conflicts. • French Ambassador “Citizen” Edmund Genet appeals directly to American people. – Washington outraged, requests French gov’t remove him, even Jefferson agrees. • House of Reps. Split (TJ, Mad. France/ Feds. & Hamilton Britain.
 Treaties The Jay Treaty (1795) – “Sell Out” • Chief Justice John Jay goes to Britain to try and stop seizing of U. S. ships, impressing sailors • Jay gone for a year, comes back with treaty – British agree to evacuate western frontier ports – No agreement on seizure of ships • Extremely unpopular, angers France supporters, only narrowly approved by Senate • But, NEUTRALITY preserved
Treaties The Jay Treaty (1795) – “Sell Out” • Chief Justice John Jay goes to Britain to try and stop seizing of U. S. ships, impressing sailors • Jay gone for a year, comes back with treaty – British agree to evacuate western frontier ports – No agreement on seizure of ships • Extremely unpopular, angers France supporters, only narrowly approved by Senate • But, NEUTRALITY preserved
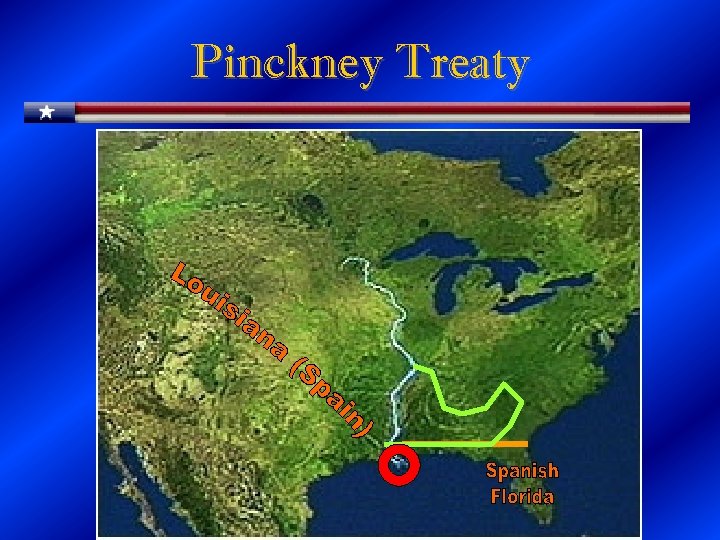
 The Pinckney Treaty • Spain sees Jay Treaty as sign that U. S. might be getting closer to its foe, Britain • Ambassador Pinckney negotiates treaty opening lower Mississippi and New Orleans to U. S. trade – U. S. no longer has to pay duties to Spain for transferring cargo into New Orleans. – U. S. can now use the Mississippi. • Spain gives up all of the land east of the Mississippi.
The Pinckney Treaty • Spain sees Jay Treaty as sign that U. S. might be getting closer to its foe, Britain • Ambassador Pinckney negotiates treaty opening lower Mississippi and New Orleans to U. S. trade – U. S. no longer has to pay duties to Spain for transferring cargo into New Orleans. – U. S. can now use the Mississippi. • Spain gives up all of the land east of the Mississippi.
 Pinckney Treaty
Pinckney Treaty
 Domestic Concerns Native Americans • American settlers moving farther west, encroaching on Indian lands. • British had been supplying some of the tribes with arms to attack new settlers. • 1790– Gen. Josiah Harmon attacks the Miami Indians. – Fought in Ohio & won by Little Turtle & NA • 1791 – Gen Arthur St. Clair Defeats Little Turtle & NA • 1792 – Gen Anthony Wayne & US Soldiers Try to expel NA – Little Turtle tries to negotiate but NA’s Refuse! • 1794 --Battle of Fallen Timbers – U. S. Army led by General Anthony Wayne defeats Shawnee, Wyandot, Delaware and others in Ohio • 1795 --Treaty of Greenville – Tribal chiefs surrender claims to Ohio
Domestic Concerns Native Americans • American settlers moving farther west, encroaching on Indian lands. • British had been supplying some of the tribes with arms to attack new settlers. • 1790– Gen. Josiah Harmon attacks the Miami Indians. – Fought in Ohio & won by Little Turtle & NA • 1791 – Gen Arthur St. Clair Defeats Little Turtle & NA • 1792 – Gen Anthony Wayne & US Soldiers Try to expel NA – Little Turtle tries to negotiate but NA’s Refuse! • 1794 --Battle of Fallen Timbers – U. S. Army led by General Anthony Wayne defeats Shawnee, Wyandot, Delaware and others in Ohio • 1795 --Treaty of Greenville – Tribal chiefs surrender claims to Ohio
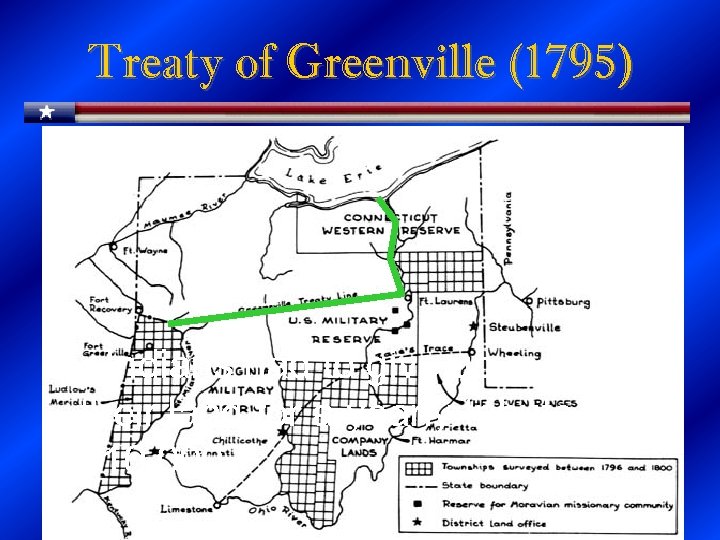 Treaty of Greenville (1795) • Indians had to give up most of their land for a yearly tribute of $10, 000
Treaty of Greenville (1795) • Indians had to give up most of their land for a yearly tribute of $10, 000
 The Whiskey Rebellion • Farmers in western Pennsylvania refuse to pay the federal tax on whiskey – couldn’t afford to pay the tax on whiskey they made from their excess corn • Defended their “liberties”, defied the federal government by attacking revenue collectors HUGE test for Washington Was the new federal government strong enough to deal with a rebellion against its own laws?
The Whiskey Rebellion • Farmers in western Pennsylvania refuse to pay the federal tax on whiskey – couldn’t afford to pay the tax on whiskey they made from their excess corn • Defended their “liberties”, defied the federal government by attacking revenue collectors HUGE test for Washington Was the new federal government strong enough to deal with a rebellion against its own laws?
 The Whiskey Rebellion • Washington responds to the crisis by federalizing 15, 000 state militia – Placed under the command of Alexander Hamilton, with GW at his side • Show of force is successful: Rebellion collapses without any bloodshed on either side Many Americans applaud Washington, say its better than the helpless gov’t during Shays’ Rebellion Westerners resent Washington, say action was unwarranted force against common people Thomas Jefferson emerges as the champion of the western farmer
The Whiskey Rebellion • Washington responds to the crisis by federalizing 15, 000 state militia – Placed under the command of Alexander Hamilton, with GW at his side • Show of force is successful: Rebellion collapses without any bloodshed on either side Many Americans applaud Washington, say its better than the helpless gov’t during Shays’ Rebellion Westerners resent Washington, say action was unwarranted force against common people Thomas Jefferson emerges as the champion of the western farmer
 Western Lands • The 13 states surrendered their western land claims to the federal government • Congress encourages the rapid settlement of land by passing the Public Land Act in 1796 – Orderly sale at reasonable prices • During Washington administration, three new states added: – Vermont (1791) – Kentucky(1792) – Tennessee (1796)
Western Lands • The 13 states surrendered their western land claims to the federal government • Congress encourages the rapid settlement of land by passing the Public Land Act in 1796 – Orderly sale at reasonable prices • During Washington administration, three new states added: – Vermont (1791) – Kentucky(1792) – Tennessee (1796)
 Washington’s Farewell In his farewell address, Washington warns Americans NOT to: • get involved in Europe • make “permanent alliances” • form political parties • put their section before the good of the country • But, parties had already been forming, and sectional interests continue to be a key feature of American politics • Wasington sets precedent of only serving two terms, even though there is no constitutional limit
Washington’s Farewell In his farewell address, Washington warns Americans NOT to: • get involved in Europe • make “permanent alliances” • form political parties • put their section before the good of the country • But, parties had already been forming, and sectional interests continue to be a key feature of American politics • Wasington sets precedent of only serving two terms, even though there is no constitutional limit


