 Geopolitical Energy Hotspots ‘Geopolitics’ is the study of the ways in which political decisions and processes affect the way resources and space are used. It is the combination of geography, economics and politics.
Geopolitical Energy Hotspots ‘Geopolitics’ is the study of the ways in which political decisions and processes affect the way resources and space are used. It is the combination of geography, economics and politics.
 The importance of the Middle East • Energy insecurity and the global reliance on fossil fuels are causing energy conflicts • The Middle East is a key world OIL SUPPLIER • As demand rises and supply peaks- the region will increase in importance • 71% of the world’s estimated 1000 billion barrels are in Middle East • By 2025 with no new discoveries, that proportion will increase to 83% • All major global economies depend hugely on Middle Eastern Oil. • The Middle East currently supplies 76% of Japan’s oil 26% of Western Europe’s and 21% of USA’s
The importance of the Middle East • Energy insecurity and the global reliance on fossil fuels are causing energy conflicts • The Middle East is a key world OIL SUPPLIER • As demand rises and supply peaks- the region will increase in importance • 71% of the world’s estimated 1000 billion barrels are in Middle East • By 2025 with no new discoveries, that proportion will increase to 83% • All major global economies depend hugely on Middle Eastern Oil. • The Middle East currently supplies 76% of Japan’s oil 26% of Western Europe’s and 21% of USA’s
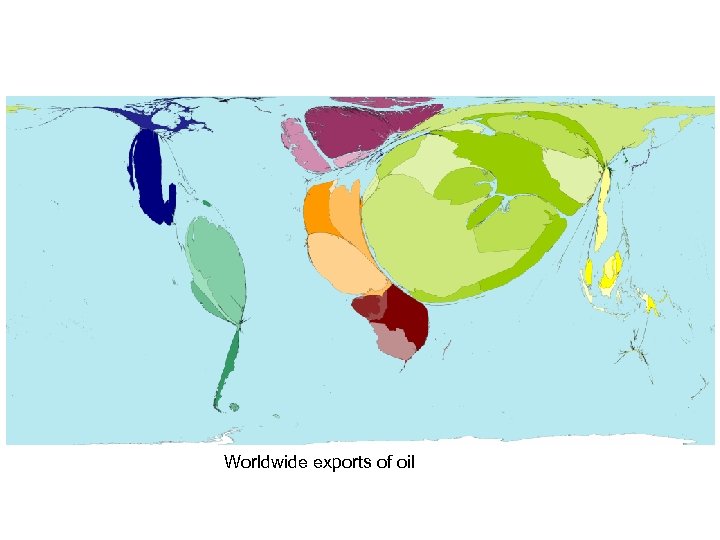 Worldwide exports of oil
Worldwide exports of oil
 Historical background • Early exploitations of Middle Eastern oil was coordinated by western companies, who at first paid little or no royalties to oil countries governments • Even the national borders were decided by Western civil servants after WW 1 (using rulers, maps and red pens!) • As a result, the West has been seen as arrogantresentment continues with major events today in Iran and Afghanistan. ( Eg: -Recent events linked the role of the BBC, UK govt. and the recent elections in Iran)
Historical background • Early exploitations of Middle Eastern oil was coordinated by western companies, who at first paid little or no royalties to oil countries governments • Even the national borders were decided by Western civil servants after WW 1 (using rulers, maps and red pens!) • As a result, the West has been seen as arrogantresentment continues with major events today in Iran and Afghanistan. ( Eg: -Recent events linked the role of the BBC, UK govt. and the recent elections in Iran)
 Current energy security issues in Middle East • Iran’s nuclear threat • Iran ongoing conflict with the USA • Terror threat of radicals in Saudi Arabia (attacks on oil supplies) • Fallout from Israel/ Palestine conflict after Second World War- Gaza strip issues • Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan • Tension between Pakistan and India over Kashmir- further unrest
Current energy security issues in Middle East • Iran’s nuclear threat • Iran ongoing conflict with the USA • Terror threat of radicals in Saudi Arabia (attacks on oil supplies) • Fallout from Israel/ Palestine conflict after Second World War- Gaza strip issues • Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan • Tension between Pakistan and India over Kashmir- further unrest
 Abqaiq : case study • World’s largest oil processing plant • Produces 6. 8 million oil barrels a day • 75% of Saudi’s total output • Hub of 12, 000 miles of oil and gas fields and pipelines- all vulnerable to direct attacks • A successful terror attack could halt production for up to a year • There’s nowhere that could produce that level of oil- thus world's would suffer mass oil supply problem
Abqaiq : case study • World’s largest oil processing plant • Produces 6. 8 million oil barrels a day • 75% of Saudi’s total output • Hub of 12, 000 miles of oil and gas fields and pipelines- all vulnerable to direct attacks • A successful terror attack could halt production for up to a year • There’s nowhere that could produce that level of oil- thus world's would suffer mass oil supply problem
 • 24 February 06 it was attacked by terrorists • 2 vehicles carrying explosives tried to smash their way through into plant compound • 2 hour gun battle ensued, during which explosives went off • 2 terrorists and 2 guards were killed • Plant however was undamaged… • Luckily…. • So what does the future hold? Watch this space!
• 24 February 06 it was attacked by terrorists • 2 vehicles carrying explosives tried to smash their way through into plant compound • 2 hour gun battle ensued, during which explosives went off • 2 terrorists and 2 guards were killed • Plant however was undamaged… • Luckily…. • So what does the future hold? Watch this space!
 • Read pg 40 -45 Oxford
• Read pg 40 -45 Oxford
 Task • ‘Energy pathways can be complex, and they face risk and disruption as a result of both physical and human causes’. Produce a report, using a range of case studies that support this statement. You should try and include information from a variety of locations.
Task • ‘Energy pathways can be complex, and they face risk and disruption as a result of both physical and human causes’. Produce a report, using a range of case studies that support this statement. You should try and include information from a variety of locations.